本文主要是介绍OpenCV pyramid lk(Lucas Kanade)光流算法自己的一些注释,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
参考如下:
代码注释的一个参考文章 https://blog.csdn.net/findgeneralgirl/article/details/107919541
原理参考文章
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41368247/article/details/82562165
https://blog.csdn.net/sgfmby1994/article/details/68489944
这两篇文章都是先写了光流的基本原理公式,再写LK光流的一些公式,最后写Pyramid LK的公式原理,
照理来说,光流,LK光流和Pyramid LK光流三者应该是承上启下的关系,后面的在前面基础上做修改,但是实际看起来,这三个的公式是不太关联的,
一个算法唱三出戏,每出戏都不一样,
看到一半再去对代码,发现是完全对不起来的,直到看到最后的Pyramid LK,公式才和代码对得起来了。
这个函数可以看到基本函数调用流程,1是建图像金字塔,2是求梯度,3是LKTrackerInvoker 核心代码在这里
void SparsePyrLKOpticalFlowImpl::calc( InputArray _prevImg, InputArray _nextImg,
InputArray _prevPts, InputOutputArray _nextPts,
OutputArray _status, OutputArray _err)
{
...
if (levels1 < 0)
maxLevel = buildOpticalFlowPyramid(_prevImg, prevPyr, winSize, maxLevel, false);
if (levels2 < 0)
maxLevel = buildOpticalFlowPyramid(_nextImg, nextPyr, winSize, maxLevel, false);
if( (criteria.type & TermCriteria::COUNT) == 0 )
criteria.maxCount = 30;
else
criteria.maxCount = std::min(std::max(criteria.maxCount, 0), 100);
if( (criteria.type & TermCriteria::EPS) == 0 )
criteria.epsilon = 0.01;
else
criteria.epsilon = std::min(std::max(criteria.epsilon, 0.), 10.);
criteria.epsilon *= criteria.epsilon;
// dI/dx ~ Ix, dI/dy ~ Iy
Mat derivIBuf;
if(lvlStep1 == 1)
derivIBuf.create(prevPyr[0].rows + winSize.height*2, prevPyr[0].cols + winSize.width*2, CV_MAKETYPE(derivDepth, prevPyr[0].channels() * 2));
for( level = maxLevel; level >= 0; level-- )
{
Mat derivI;
if(lvlStep1 == 1)
{
Size imgSize = prevPyr[level * lvlStep1].size();
Mat _derivI( imgSize.height + winSize.height*2,
imgSize.width + winSize.width*2, derivIBuf.type(), derivIBuf.ptr() );
derivI = _derivI(Rect(winSize.width, winSize.height, imgSize.width, imgSize.height));
calcSharrDeriv(prevPyr[level * lvlStep1], derivI); //求微分
copyMakeBorder(derivI, _derivI, winSize.height, winSize.height, winSize.width, winSize.width, BORDER_CONSTANT|BORDER_ISOLATED);
}
else
derivI = prevPyr[level * lvlStep1 + 1];
CV_Assert(prevPyr[level * lvlStep1].size() == nextPyr[level * lvlStep2].size());
CV_Assert(prevPyr[level * lvlStep1].type() == nextPyr[level * lvlStep2].type());
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
typedef tegra::LKTrackerInvoker<cv::detail::LKTrackerInvoker> LKTrackerInvoker;
#else
typedef cv::detail::LKTrackerInvoker LKTrackerInvoker;
#endif
parallel_for_(Range(0, npoints), LKTrackerInvoker(prevPyr[level * lvlStep1], derivI,
nextPyr[level * lvlStep2], prevPts, nextPts,
status, err,
winSize, criteria, level, maxLevel,
flags, (float)minEigThreshold));
}
}
} // namespace
} // namespace cv
static void calcSharrDeriv(const cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst)
{
using namespace cv;
using cv::detail::deriv_type;
int rows = src.rows, cols = src.cols, cn = src.channels(), colsn = cols*cn, depth = src.depth();
CV_Assert(depth == CV_8U);
dst.create(rows, cols, CV_MAKETYPE(DataType<deriv_type>::depth, cn*2));
int x, y, delta = (int)alignSize((cols + 2)*cn, 16);
AutoBuffer<deriv_type> _tempBuf(delta*2 + 64);
deriv_type *trow0 = alignPtr(_tempBuf + cn, 16), *trow1 = alignPtr(trow0 + delta, 16);
for( y = 0; y < rows; y++ )
{
//rows>1一般是成立的,也就是说不是第0行扩展一行,而是第1行,那就是BORDER_REFLECT_101类型的扩展,那梯度不是肯定是0了吗,确实是这样的,4个边梯度值都是0
const uchar* srow0 = src.ptr<uchar>(y > 0 ? y-1 : rows > 1 ? 1 : 0);
const uchar* srow1 = src.ptr<uchar>(y);
const uchar* srow2 = src.ptr<uchar>(y < rows-1 ? y+1 : rows > 1 ? rows-2 : 0);
deriv_type* drow = dst.ptr<deriv_type>(y);
// do vertical convolution
x = 0;
//t0:3 t1:-1
// 10 0
// 3 1
for( ; x < colsn; x++ )
{
int t0 = (srow0[x] + srow2[x])*3 + srow1[x]*10;
int t1 = srow2[x] - srow0[x];
trow0[x] = (deriv_type)t0; //这里t0,t1是同一列数据求,而不是间隔1列,3列求,是中间数据,
trow1[x] = (deriv_type)t1;
}
// make border
int x0 = (cols > 1 ? 1 : 0)*cn, x1 = (cols > 1 ? cols-2 : 0)*cn;
for( int k = 0; k < cn; k++ )
{
trow0[-cn + k] = trow0[x0 + k]; trow0[colsn + k] = trow0[x1 + k];
trow1[-cn + k] = trow1[x0 + k]; trow1[colsn + k] = trow1[x1 + k];
}
// do horizontal convolution, interleave the results and store them to dst
x = 0;
//求微分操作
//t0:-3 0 3 t1:-3 -10 -3
// -10 0 10 0 0 0
// -3 0 3 3 10 3
for( ; x < colsn; x++ )
{
deriv_type t0 = (deriv_type)(trow0[x+cn] - trow0[x-cn]); //这里两个都是trow0,也就是上面的t0,别看错
deriv_type t1 = (deriv_type)((trow1[x+cn] + trow1[x-cn])*3 + trow1[x]*10);
drow[x*2] = t0; drow[x*2+1] = t1;
}
}
}
void cv::detail::LKTrackerInvoker::operator()(const Range& range) const
{
CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION()
Point2f halfWin((winSize.width-1)*0.5f, (winSize.height-1)*0.5f);
const Mat& I = *prevImg;
const Mat& J = *nextImg;
const Mat& derivI = *prevDeriv;
int j, cn = I.channels(), cn2 = cn*2;
cv::AutoBuffer<deriv_type> _buf(winSize.area()*(cn + cn2));
int derivDepth = DataType<deriv_type>::depth;
Mat IWinBuf(winSize, CV_MAKETYPE(derivDepth, cn), (deriv_type*)_buf);
Mat derivIWinBuf(winSize, CV_MAKETYPE(derivDepth, cn2), (deriv_type*)_buf + winSize.area()*cn);
for( int ptidx = range.start; ptidx < range.end; ptidx++ )
{
Point2f prevPt = prevPts[ptidx]*(float)(1./(1 << level));
Point2f nextPt;
if( level == maxLevel )
{
if( flags & OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW )
nextPt = nextPts[ptidx]*(float)(1./(1 << level));
else
nextPt = prevPt;
}
else
nextPt = nextPts[ptidx]*2.f; //非最高层,nextPt的坐标是上一层的坐标*2,, 这里就是上一层的结果反馈到本层
nextPts[ptidx] = nextPt;
Point2i iprevPt, inextPt;
prevPt -= halfWin;
iprevPt.x = cvFloor(prevPt.x);
iprevPt.y = cvFloor(prevPt.y);
if( iprevPt.x < -winSize.width || iprevPt.x >= derivI.cols ||
iprevPt.y < -winSize.height || iprevPt.y >= derivI.rows )
{
if( level == 0 )
{
if( status )
status[ptidx] = false;
if( err )
err[ptidx] = 0;
}
continue;
}
float a = prevPt.x - iprevPt.x;
float b = prevPt.y - iprevPt.y;
const int W_BITS = 14, W_BITS1 = 14;
const float FLT_SCALE = 1.f/(1 << 20);
int iw00 = cvRound((1.f - a)*(1.f - b)*(1 << W_BITS));
int iw01 = cvRound(a*(1.f - b)*(1 << W_BITS));
int iw10 = cvRound((1.f - a)*b*(1 << W_BITS));
int iw11 = (1 << W_BITS) - iw00 - iw01 - iw10;
int dstep = (int)(derivI.step/derivI.elemSize1());
int stepI = (int)(I.step/I.elemSize1());
int stepJ = (int)(J.step/J.elemSize1());
acctype iA11 = 0, iA12 = 0, iA22 = 0;
float A11, A12, A22;
// extract the patch from the first image, compute covariation matrix of derivatives
int x, y;
for( y = 0; y < winSize.height; y++ )
{
const uchar* src = I.ptr() + (y + iprevPt.y)*stepI + iprevPt.x*cn;
const deriv_type* dsrc = derivI.ptr<deriv_type>() + (y + iprevPt.y)*dstep + iprevPt.x*cn2;
deriv_type* Iptr = IWinBuf.ptr<deriv_type>(y);
deriv_type* dIptr = derivIWinBuf.ptr<deriv_type>(y);
x = 0;
for( ; x < winSize.width*cn; x++, dsrc += 2, dIptr += 2 )
{
//这里的Ix,Iy在坐标是小数时是通过整数点的值插值得到的,
int ival = CV_DESCALE(src[x]*iw00 + src[x+cn]*iw01 +
src[x+stepI]*iw10 + src[x+stepI+cn]*iw11, W_BITS1-5);
int ixval = CV_DESCALE(dsrc[0]*iw00 + dsrc[cn2]*iw01 +
dsrc[dstep]*iw10 + dsrc[dstep+cn2]*iw11, W_BITS1);
int iyval = CV_DESCALE(dsrc[1]*iw00 + dsrc[cn2+1]*iw01 + dsrc[dstep+1]*iw10 +
dsrc[dstep+cn2+1]*iw11, W_BITS1);
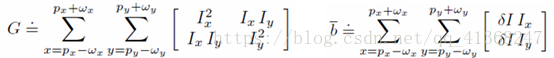
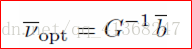
//这里就和上面公式对得起来了,上面是公式推导的最后一步,就是求G和b,然后光流vopt就是G的逆乘b,前面公式的推导,可以看一下,理解一下,稍微能看懂,或者假装可以看懂吧,
Iptr[x] = (short)ival;
dIptr[0] = (short)ixval; //Ix
dIptr[1] = (short)iyval; // Iy
//这里一看就知道是iA11是公式里的Ix2窗口每个点的累加, iA22对应Iy2,iA12对应 Ix*Iy
iA11 += (itemtype)(ixval*ixval);
iA12 += (itemtype)(ixval*iyval);
iA22 += (itemtype)(iyval*iyval);
}
}
A11 = iA11*FLT_SCALE;
A12 = iA12*FLT_SCALE;
A22 = iA22*FLT_SCALE;
_ __
G = | A11 A12 |
|_ A12 A22 _|
下面是科普
普通的2x2矩阵
_ _
A = | a11 a12 |
|_ a21 a22 _|
行列式det(A)或|A|为对角相乘相减a11*a22-a21*a12
A的逆A-1
A-1 = (1/|A| ) A*
方阵可逆的充分必要条件是行列式detA = |A|不等于0,
A*是伴随矩阵,定义行列式|A|的各个元素的代数余子式Aij所构成的矩阵,称为矩阵A的伴随矩阵
2x2矩阵的伴随矩阵
_ _
A* = | a22 -a12 |
|_ -a21 a11 _|
A可逆还有一种充分必要条件是特征值不等于0, 特征值,英文名字叫eigen,
2x2矩阵求特征值
Ax = λx => (A-λE)x=0 或(λE-A)x=0
_ _
| λ-a11 -a12 |
|_ -a21 λ-a22 _|
x有解上面|λE-A|=0
(λ-a11)*(λ-a22)-a12*a21=0,求λ变成一元二次方程

float D = A11*A22 - A12*A12; //一看就知道是行列式了
minEig 按上面推导得到的特征值
float minEig = (A22 + A11 - std::sqrt((A11-A22)*(A11-A22) + 4.f*A12*A12))/(2*winSize.width*winSize.height);
if( err && (flags & OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS) != 0 )
err[ptidx] = (float)minEig;
if( minEig < minEigThreshold || D < FLT_EPSILON ) 特征值小于某个数,就认为特征值为0,方阵不可逆
{
if( level == 0 && status )
status[ptidx] = false;
continue;
}
D = 1.f/D;
nextPt -= halfWin;
Point2f prevDelta;
for( j = 0; j < criteria.maxCount; j++ )
{
inextPt.x = cvFloor(nextPt.x);
inextPt.y = cvFloor(nextPt.y);
if( inextPt.x < -winSize.width || inextPt.x >= J.cols ||
inextPt.y < -winSize.height || inextPt.y >= J.rows )
{
if( level == 0 && status )
status[ptidx] = false;
break;
}
a = nextPt.x - inextPt.x;
b = nextPt.y - inextPt.y;
iw00 = cvRound((1.f - a)*(1.f - b)*(1 << W_BITS));
iw01 = cvRound(a*(1.f - b)*(1 << W_BITS));
iw10 = cvRound((1.f - a)*b*(1 << W_BITS));
iw11 = (1 << W_BITS) - iw00 - iw01 - iw10;
acctype ib1 = 0, ib2 = 0;
float b1, b2;
for( y = 0; y < winSize.height; y++ )
{
const uchar* Jptr = J.ptr() + (y + inextPt.y)*stepJ + inextPt.x*cn;
const deriv_type* Iptr = IWinBuf.ptr<deriv_type>(y);
const deriv_type* dIptr = derivIWinBuf.ptr<deriv_type>(y);
x = 0;
for( ; x < winSize.width*cn; x++, dIptr += 2 )
{
int diff = CV_DESCALE(Jptr[x]*iw00 + Jptr[x+cn]*iw01 +
Jptr[x+stepJ]*iw10 + Jptr[x+stepJ+cn]*iw11,
W_BITS1-5) - Iptr[x];
//这里一看就知道ib1是上面公式里的dI * Ix窗口内各点累加, dI就是diff,prev和next图像同点的差值,
//ib2对应dI * Iy
ib1 += (itemtype)(diff*dIptr[0]);
ib2 += (itemtype)(diff*dIptr[1]);
}
}
b1 = ib1*FLT_SCALE;
b2 = ib2*FLT_SCALE;
_ _
G* = | A22 -A12 |
|_ -A12 A11 _|
_ _ _ _
| A22 -A12 | * | b1 | * D
|_ -A12 A11 _| |_ b2 _|
和下面delta结果好象符号是反的,没明白为什么
Point2f delta( (float)((A12*b2 - A22*b1) * D), //这个就是vopt=G-1b的公式了
(float)((A12*b1 - A11*b2) * D));
//delta = -delta;
nextPt += delta;
nextPts[ptidx] = nextPt + halfWin;
if( delta.ddot(delta) <= criteria.epsilon ) //当delta偏移值很小时,可跳出迭代,认为该delta就是最终的delta
break;
//这里最多迭代criteria.maxCount次,默认是30,我的理解是pyramid lk公式求出来之后就直接是结果了,没有提到还需要迭代,
//这里的迭代依据是什么,为什么每次迭代的步长为delta*0.5f, 理解不了
if( j > 0 && std::abs(delta.x + prevDelta.x) < 0.01 && //如果前后两次delta变化比较小,也可认为已经找到delta了
std::abs(delta.y + prevDelta.y) < 0.01 )
{
nextPts[ptidx] -= delta*0.5f;
break;
}
prevDelta = delta;
} //end of criteria.maxCount
CV_Assert(status != NULL);
if( status[ptidx] && err && level == 0 && (flags & OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS) == 0 )
{
Point2f nextPoint = nextPts[ptidx] - halfWin;
Point inextPoint;
inextPoint.x = cvFloor(nextPoint.x);
inextPoint.y = cvFloor(nextPoint.y);
if( inextPoint.x < -winSize.width || inextPoint.x >= J.cols ||
inextPoint.y < -winSize.height || inextPoint.y >= J.rows )
{
if( status )
status[ptidx] = false;
continue;
}
float aa = nextPoint.x - inextPoint.x;
float bb = nextPoint.y - inextPoint.y;
iw00 = cvRound((1.f - aa)*(1.f - bb)*(1 << W_BITS));
iw01 = cvRound(aa*(1.f - bb)*(1 << W_BITS));
iw10 = cvRound((1.f - aa)*bb*(1 << W_BITS));
iw11 = (1 << W_BITS) - iw00 - iw01 - iw10;
float errval = 0.f;
for( y = 0; y < winSize.height; y++ )
{
const uchar* Jptr = J.ptr() + (y + inextPoint.y)*stepJ + inextPoint.x*cn;
const deriv_type* Iptr = IWinBuf.ptr<deriv_type>(y);
for( x = 0; x < winSize.width*cn; x++ )
{
int diff = CV_DESCALE(Jptr[x]*iw00 + Jptr[x+cn]*iw01 +
Jptr[x+stepJ]*iw10 + Jptr[x+stepJ+cn]*iw11,
W_BITS1-5) - Iptr[x];
errval += std::abs((float)diff);
}
}
err[ptidx] = errval * 1.f/(32*winSize.width*cn*winSize.height);
}
}
}
这篇关于OpenCV pyramid lk(Lucas Kanade)光流算法自己的一些注释的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





