本文主要是介绍树的非递归遍历(层序),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
层序是采用队列的方式来遍历的
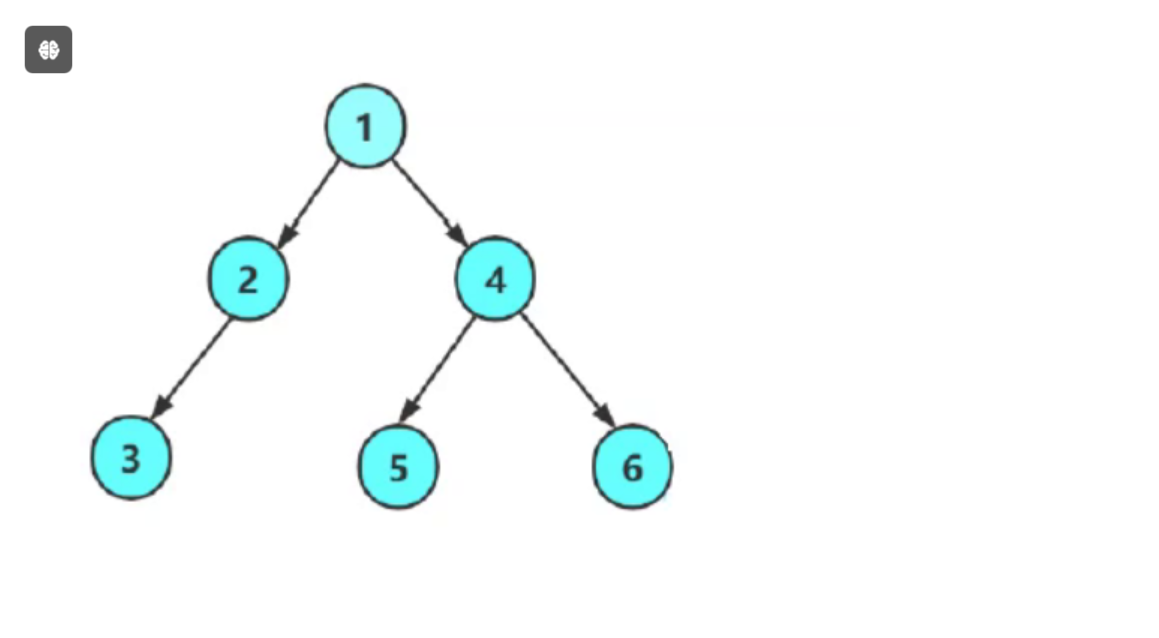
就比如说上面这颗树
他层序的就是:1 24 356
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Que q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%d ", front->val);if (front->left){QueuePush(&q, front->left);}if (front->right){QueuePush(&q, front->right);}}}
打印NULL ,这里front也会把NULL带进去
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Que q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front){printf("%d ", front->val);QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}else{printf("N ");}}}完整代码(栈和队列是复制前几篇的代码)
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int BinTreeType;
struct BinTreeNode
{struct BinTreeNode* left;struct BinTreeNode* right;BinTreeType val;};
typedef struct BinTreeNode BTNode;BTNode* BuyBTNode(BinTreeType val);
BTNode* CreateTree();
void PreOrder(BTNode* root);
void InOrder(BTNode* root);
void PostOrder(BTNode* root);
int TreeSize(BTNode* root);
int MaxDepth(BTNode* root);
int TreeLevel(BTNode* root, int k);
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, int x);
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include"BinTree.h"
typedef BTNode* QueueData;
struct QueueNode
{QueueData val;struct QueueNode* next;
};
typedef struct QueueNode QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* phead;QNode* ptail;int size;
}Que;
void QueueInit(Que* pq);//队列初始化
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);//队列销毁void QueuePush(Que* pq,QueueData x);//入队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq);//出队列QueueData QueueBack(Que* pq);
QueueData QueueFront(Que* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
int QueueSize(Que* pq);#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"BinTree.h"
BTNode* BuyBTNode(BinTreeType val)
{BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail!");exit(1);}newnode->val = val;newnode->left = NULL;newnode->right = NULL;return newnode;
}
BTNode* CreateTree()
{BTNode* n1 = BuyBTNode(1);BTNode* n2 = BuyBTNode(2);BTNode* n3 = BuyBTNode(3);BTNode* n4 = BuyBTNode(4);BTNode* n5 = BuyBTNode(5);BTNode* n6 = BuyBTNode(6);n1->left = n2;n1->right = n4;n2->left = n3;n2->right = NULL;n3->left = NULL;n3->right = NULL;n4->left = n5;n4->right = n6;n5->left = NULL;n5->right = NULL;n6->left = NULL;n6->right = NULL;return n1;
}
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return ;}printf("%d ", root->val);PreOrder(root->left);PreOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}InOrder(root->left);printf("%d ", root->val);InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}PostOrder(root->left);PostOrder(root->right);printf("%d ", root->val);
}
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}else{return TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right)+1;}}int MaxDepth(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}int leftDepth = MaxDepth(root->left);int rightDepth = MaxDepth(root->left);if (leftDepth > rightDepth){return leftDepth + 1;}else{return rightDepth + 1;}
}
int TreeLevel(BTNode* root, int k)
{assert(k > 0);if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (k == 1){return 1;}return TreeLevel(root->left, k - 1) + TreeLevel(root->right, k - 1);
}
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, int x)
{if (root == NULL){return NULL;}if (root->val == x){return root;}BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret1){return ret1;}return TreeFind(root->right, x); }
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){return 0;}if (BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) == NULL && BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right) == NULL){return 1; } return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"queue.h"
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->phead = NULL;pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{QNode* pcur = pq->phead;while (pcur){QNode* next = pcur->next;free(pcur);pcur = next;}pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueuePush(Que* pq,QueueData x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (Que*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(1);}newnode->val = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->ptail){pq->ptail->next = newnode;pq->ptail = newnode;}else{pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{assert(pq->phead != NULL);if (pq->phead->next == NULL){free(pq->phead);pq->phead =pq->ptail= NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->phead->next;free(pq->phead); pq->phead = next;}pq->size--;
}QueueData QueueFront(Que* pq)
{assert(pq!=NULL);assert(pq->phead != NULL);return pq->phead->val;
}
QueueData QueueBack(Que* pq)
{assert(pq!=NULL);assert(pq->ptail != NULL);return pq->ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{return pq->phead == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"BinTree.h"
#include"queue.h"
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Que q;QueueInit(&q);if (root){QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front){printf("%d ", front->val);QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}else{printf("N ");}}}
int main()
{BTNode* root= CreateTree();//PreOrder(root);printf("\n");LevelOrder(root);}
这篇关于树的非递归遍历(层序)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




