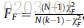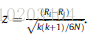本文主要是介绍一种可扩展的同时进化实例和特征选择方法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
#引用
##Latex
@article{GARCIAPEDRAJAS2013150,
title = “A scalable approach to simultaneous evolutionary instance and feature selection”,
journal = “Information Sciences”,
volume = “228”,
pages = “150 - 174”,
year = “2013”,
issn = “0020-0255”,
doi = “https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2012.10.006”,
url = “http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025512006718”,
author = “Nicol’{a}s Garc’{\i}a-Pedrajas and Aida de Haro-Garc’{\i}a and Javier P’{e}rez-Rodr’{\i}guez”,
keywords = “Simultaneous instance and feature selection, Instance selection, Feature selection, Instance-based learning, Very large problems”
}
##Normal
Nicolás García-Pedrajas, Aida de Haro-García, Javier Pérez-Rodríguez,
A scalable approach to simultaneous evolutionary instance and feature selection,
Information Sciences,
Volume 228,
2013,
Pages 150-174,
ISSN 0020-0255,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2012.10.006.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025512006718)
Keywords: Simultaneous instance and feature selection; Instance selection; Feature selection; Instance-based learning; Very large problems
#摘要
enormous amount of information
bioinformatics, security and intrusion detection and text mining
data reduction — removing
-
missing
-
redundant
-
information-poor data and/or
-
erroneous data
from the dataset to obtain a tractable problem size -
feature selection
-
feature-value discretization
-
instance selection
the divide-and-conquer principle + bookkeeping
in linear time
#主要内容
Instance selection:choosing a subset of the total available data to achieve the original purpose of the datamining application as though all the data were being used
- prototype selection(k-Nearest Neighbors)
- obtaining the training set for a learning algorithm(classification trees or neural networks)
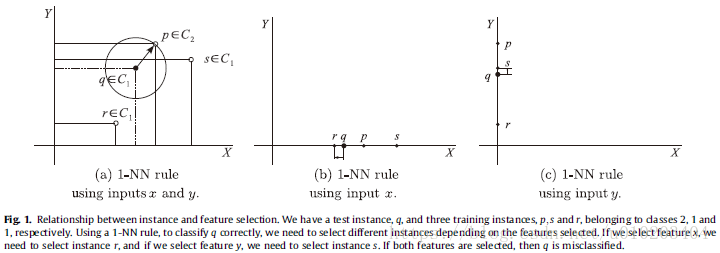
‘‘the isolation of the smallest set of instances that enable us to predict the class of a query instance with the same (or higher) accuracy than the original set’’
The objectives of feature selection:
- To avoid over-fitting and to improve model performance
- To provide faster and more cost-effective models
- To gain a deeper insight into the underlying processes that generated the data
simultaneous instance and feature selection
scalable simultaneous instance and feature selection method (SSIFSM)
#相关工作
three fundamental approaches for scaling up learning methods:
- designing fast algorithms
- partitioning the data
- using a relational representation
The stratification strategy
分层策略
splits the training data into disjoint strata with equal class distribution
#算法
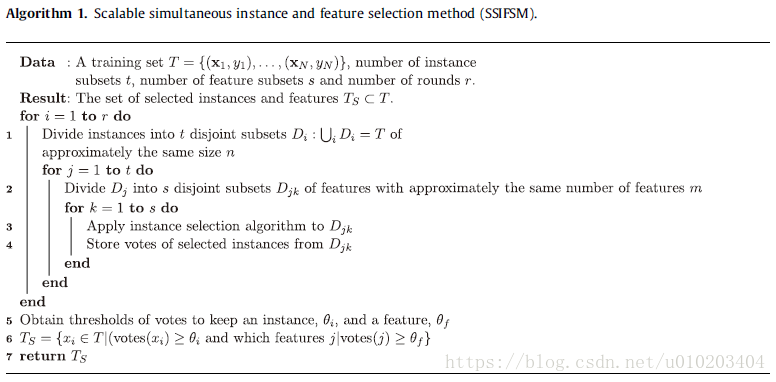
Scalable simultaneous instance and feature selection method (SSIFSM)
K K K classes and N N N training instances with M M M features
T = { ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , … , ( x N , y N ) } T = \left\{ \left(x_1, y_1 \right), \left(x_2, y_2 \right), \ldots, \left(x_N, y_N \right) \right\} T={(x1,y1),(x2,y2),…,(xN,yN)}
Y = { 1 , … , K } Y = \left\{ 1, \ldots, K \right\} Y={1,…,K}
simultaneous instance and feature selection
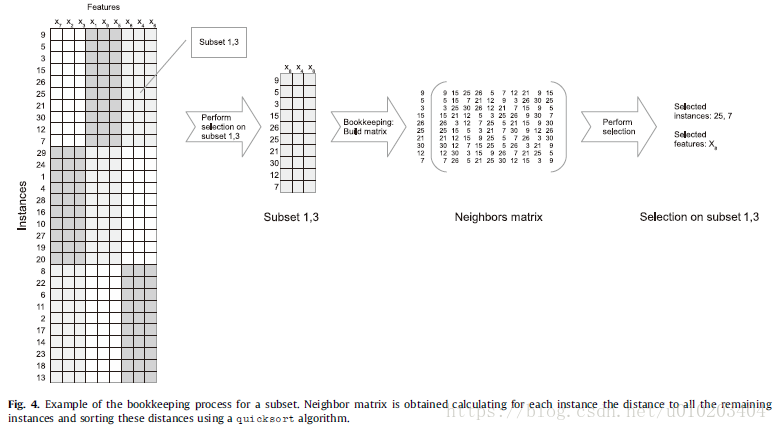
Bookkeeping
an evolutionary algorithm
a CHC algorithm —
Cross-generational elitist selection, Heterogeneous recombination and Cataclysmic mutation
- To obtain the next generation for a population of size P P P, the parents and the offspring are put together and the P P P best individuals are selected.
- To avoid premature convergence, only different individuals separated by a threshold Hamming distance—in our implementation, the length of the chromosome divided by four—are allowed to mate.
- During crossover, two parents exchange exactly half of their nonmatching bits. This operator is referred to as Half Uniform Crossover (HUX).
- Mutation is not used during the regular evolution. To avoid premature convergence or stagnation of the search, the population is reinitialized when the individuals are not diverse. In such a case, only the best individual is retained in the new population.
a c c ( x ) acc(x) acc(x) — the accuracy — 1-NN classifier
r e d ( x ) red(x) red(x) — the reduction — KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 3: 1 ̲ - \frac{N'}{N}…
α \alpha α — a weighting parameter — 0.5 0.5 0.5
the instance and feature selection
record the number of times that each instance and feature has been selected to be kept
— the number of votes (its similarity to the combination of classifiers in an ensemble by voting)
— repeated for r r r rounds
all the instances of a certain subset belong to the same class — ignored
the combination of the different rounds
the philosophy of ensembles of classifiers
several weak learners are combined to form a strong classifier — several weak (in the sense that they are applied to subsets of the training data) instance and feature selection procedures are combined to produce a strong and fast selection method
bagging or boosting
number of votes — KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 8: [ 0, r ̲\cdot s ] (an instance)
an instance is in s s s subsets in every round.
Each feature is in t t t subsets each round.
KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 8: [ 0, r ̲\cdot t ] (an feature)
threshold
majority voting — at least half (depends heavily on the problem)
automatically
θ i \theta_i θi — threshold for instance
θ f \theta_f θf — threshold for feature
T ( θ i , θ f ) T \left( \theta_i, \theta_f \right) T(θi,θf) — the subset of the training set
1-NN classifier
all the possible values
β \beta β — close to 1 1 1 — 0.75 0.75 0.75
r e d ( x ) = 1 − ( s i + s f ) N + M red \left( x \right) = 1 - \dfrac{ \left( s_i + s_f \right) }{ N + M } red(x)=1−N+M(si+sf)
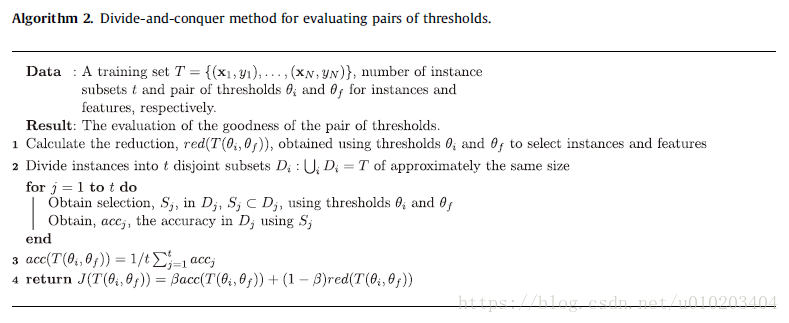
evaluate all possible pairs of instance and feature thresholds — KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 5: [ r ̲\cdot s ] \tim… — O ( N 2 M ) O(N^2M) O(N2M)
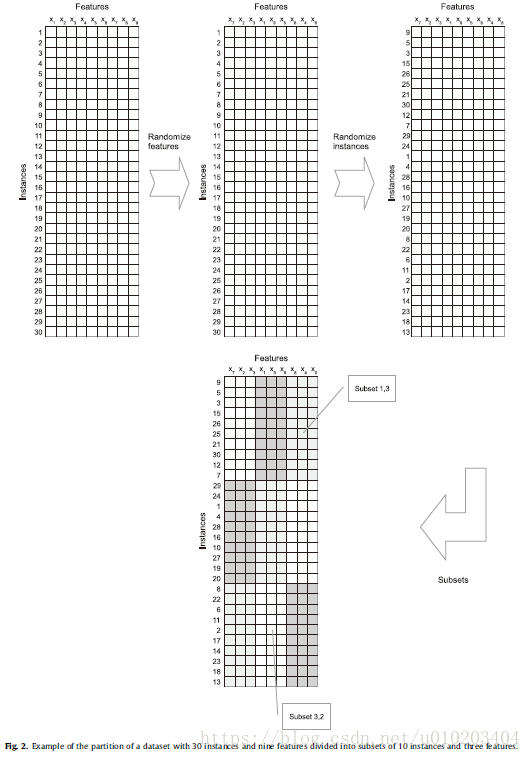
a divide-and-conquer method
the same partition philosophy
training set is divided into random disjoint subsets and the accuracy is estimated separately in each subset using the average evaluation of all the subsets for the fitness of each pair of thresholds
The scalability of the method is assured by the following features:
- Application of the method to small datasets. Due to the small size of the subsets in which the selection process is applied, the selection process will always be fast, regardless of the complexity of the instance and feature selection method used in the subsets.
- Only small datasets must be kept in memory. This allows the application of instance and feature selection when datasets do not fit into memory.
- Bookkeeping is applied in the evolution for every subset.
##Complexity of our methodology
linear in the number of instances, N, of the dataset
The process of random partition — O ( N M ) O(NM) O(NM)
a subset of fixed size, n n n
the complexity of the CHC selection algorithm
K K K — the number of operations required by the selection algorithm to perform its task in a dataset of size n n n
N N N instances and M M M features
his selection process once for each subset, N n M m \frac{N}{n} \frac{M}{m} nNmM times
O ( ( N n M m ) K ) O \left( \left( \frac{N}{n} \frac{M}{m} \right) K \right) O((nNmM)K)
r r r rounds
O ( r ( N n M m ) K ) O \left( r \left( \frac{N}{n} \frac{M}{m} \right) K \right) O(r(nNmM)K)
linear
easy parallel implementation
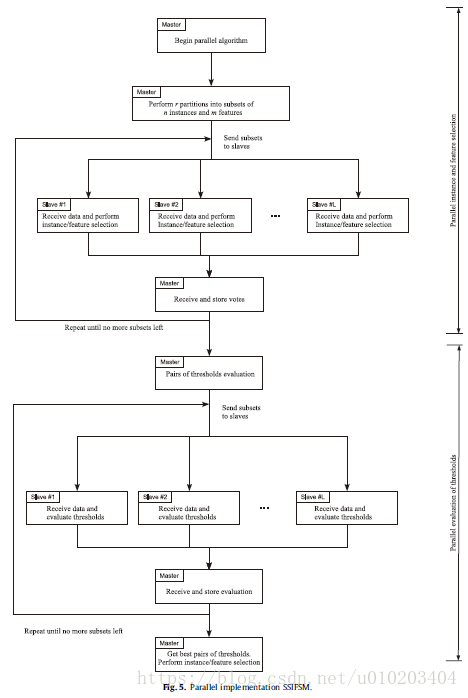
##Parallel implementation
the master/slave architecture
master — the partition of the dataset and sends the subsets to each slave
slave — performs the selection algorithm + returns the selected instances and features to the master
master — stores the votes for each kept instance and feature
communication between different tasks
occurs only twice:
- Before each slave initiates its selection process, it must receive the subset of data to perform that process. This amount of information is always small because the method is based on each slave taking care of only a small part of the whole dataset. Furthermore, if the slaves can access the disk, they can read the necessary data directly from it.
- Once the selection process is finished, the slaves send the selection performed to the master. This selection consists of a list of the selected instances and features, which is a small sequence of integers.
the best value for the votes threshold:
- Before each slave initiates the evaluation of a certain pair of thresholds, it must receive the subset of data to perform that task. This amount of information is always small because the method is based on each slave taking care of only a small part of the whole dataset.
- Once the evaluation process is finished, the slaves send the evaluation performed to the master. The evaluation is the error obtained when the corresponding pair of thresholds is used, which is a real number.
#试验
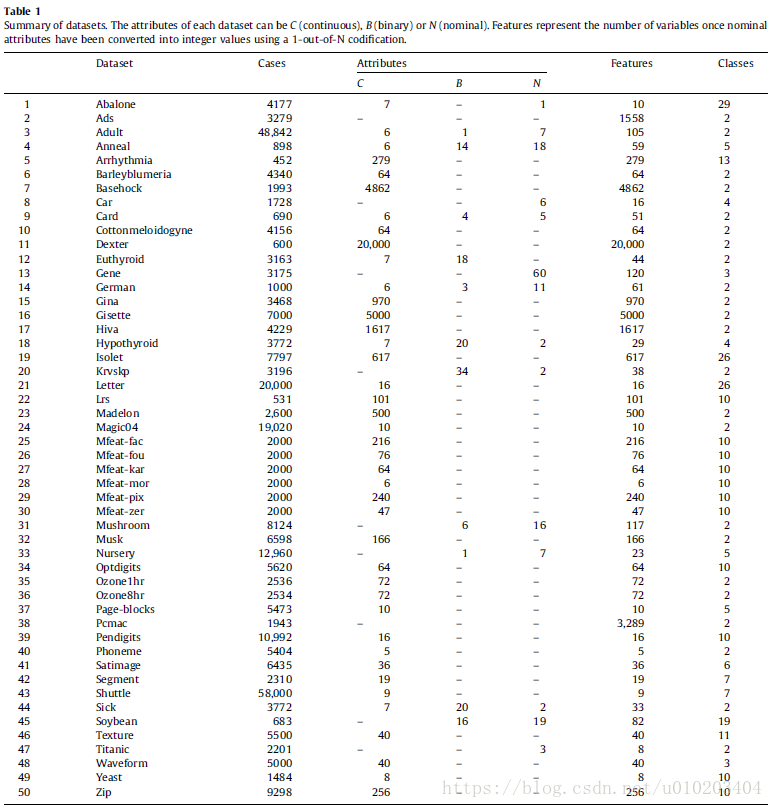
50 problems
the UCI Machine Learning Repository
the reduction and accuracy
a 10-fold cross-validation method
a 1-nearest neighbor (1-NN) classifier
from small to medium sizes
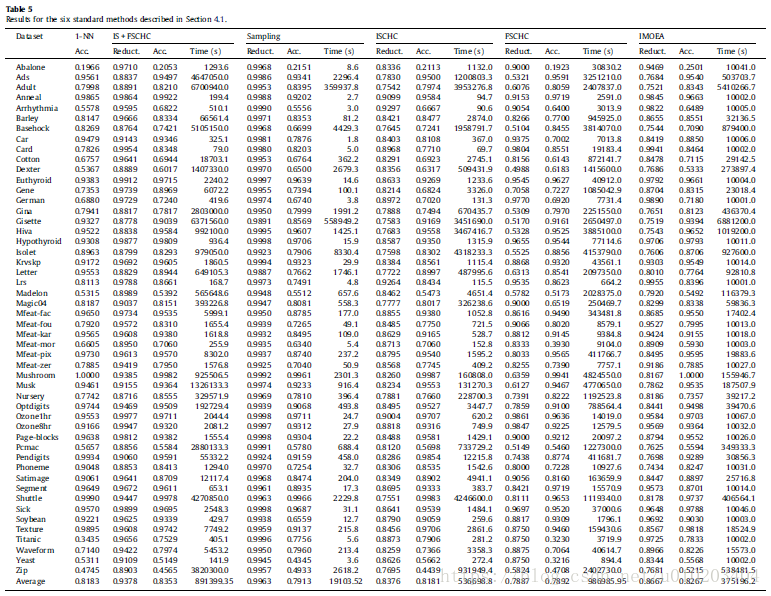
##Algorithms for the comparison
- Nearest neighbor error using all instances and features is chosen as a baseline measure (1-NN). Any method of performing selection of features or instances must at least match the performance of the 1-NN algorithm or improve its accuracy if possible.
- As stated, Cano et al. [10] performed a comprehensive comparison of the performances of different evolutionary algorithms for instance selection. They compared a generational genetic algorithm, a steady-state genetic algorithm, a CHC genetic algorithm and a population-based incremental learning algorithm. Among these methods, CHC achieved the best overall performance (ISCHC). Therefore, we have included the CHC algorithm in our comparison. [10] J.R. Cano, F. Herrera, M. Lozano, Using evolutionary algorithms as instance selection for data reduction in KDD: an experimental study, IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation 7 (2003) 561–575.
- Feature selection using a genetic algorithm (FSCHC). Following the same idea used for instance selection, we used a CHC algorithm for feature selection with the same characteristics of the algorithm used for instance selection.
- Instance and feature selection using a genetic algorithm (IS + FSCHC). Combining the two previous methods, we also used a CHC algorithm that simultaneously evolved the instances and features.
- Intelligent Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm (IMOEA) [13] method. This method is a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm, which considers both instance and feature selection. The algorithm has two objectives, maximization of training accuracy and minimization of the number of instances and features selected. The multi-objective algorithm used is based on Pareto dominance because the approach is common in multi-objective algorithms [65]. The fitness of each individual is the difference between the individuals it dominates and the individuals that dominate it. The algorithm also includes a new crossover operator called intelligent crossover, which incorporates the systematic reasoning ability of orthogonal experimental design [43] to estimate the contribution of each gene to the fitness of the individuals.
- The major aim of our method is scalability. However, if scalability can be achieved with a simple random sampling method, it may be argued that our method is superfluous. Thus, our last method for comparison is a CHC algorithm for instance and feature selection, which uses a random sampling of instances (SAMPLING). The method is applied using a random 10% of all the instances in the dataset.
The source code used for all methods is in C and is licensed under the GNU General Public License.
in a cluster of 32 blades
Each blade is a biprocessor DELL Power Edge M600 with four cores per processor
256 cores
a 1 GB network
2.5 GHz
each blade has 16 GB of memory
##Statistical tests
Iman-Davenport test — based on the χ F 2 \chi^2_F χF2
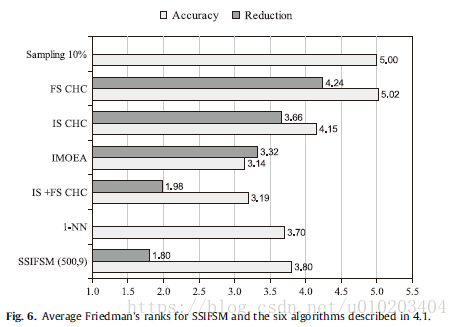
Friedman test — compares the average ranks of k k k algorithms — more powerful than the Friedman test
following a F F F distribution with KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 4: k -̲ 1 and KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 5: (k -̲ 1) (N - 1) degrees of freedom
pairwise comparisons — the Wilcoxon test — stronger
family-wise error
The test statistic for comparing the ith and jth classifier
z z z — used to find the corresponding probability from the table of normal distribution
The Bonferroni–Dunn test — Holm
Holm’s procedure — more powerful than Bonferroni–Dunn’s
##Evaluation measures
accuracy — the percentage of instances classified correctly
reduction — the percentage of total data removed during the evolution
class-imbalanced problems
- true positives (TPs)
- false positives (FPs)
- true negatives (TNs)
- false negatives (FNs)
有
- the sensitivity (Sn) — S n = T P T P + F N Sn = \frac{TP}{TP+FN} Sn=TP+FNTP
- the specificity (Sp) — S p = T N T N + F P Sp = \frac{TN}{TN+FP} Sp=TN+FPTN
- the G - mean measure — G − m e a n = S p ⋅ S n G-mean = \sqrt{Sp \cdot Sn} G−mean=Sp⋅Sn
the reduction — 1 − n N m M 1 - \frac{n}{N} \frac{m}{M} 1−NnMm
##实验结果
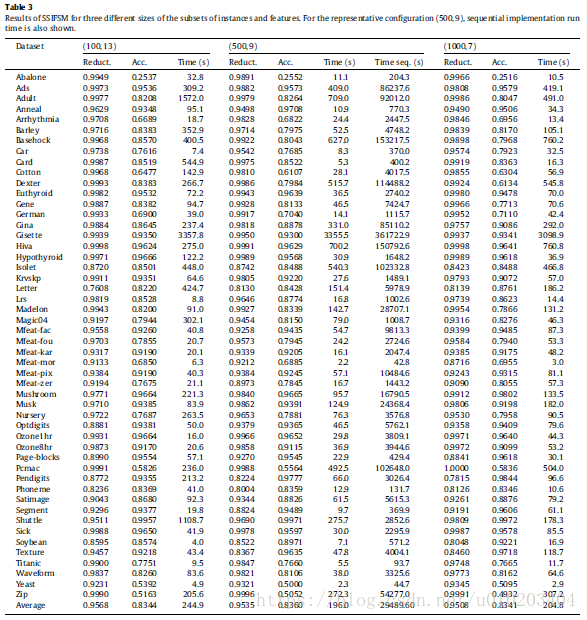
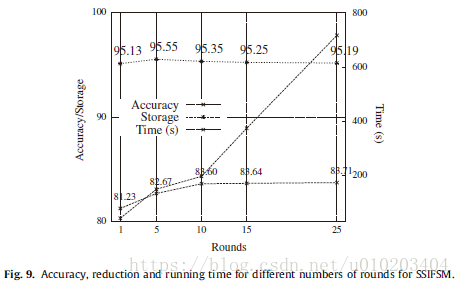
regarding the size of the subsets used
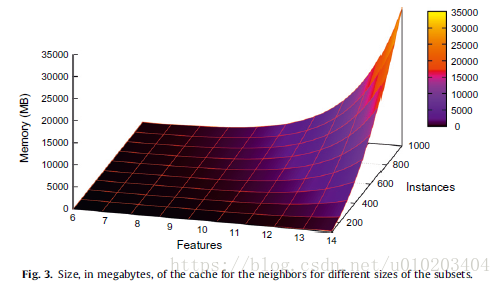
- 1000 instances and seven features — (1000,7)
- 500 instances and nine features — (500,9)
- 100 instances and 13 features — (100,13)
cache — 300–400 MB
memory thrashing
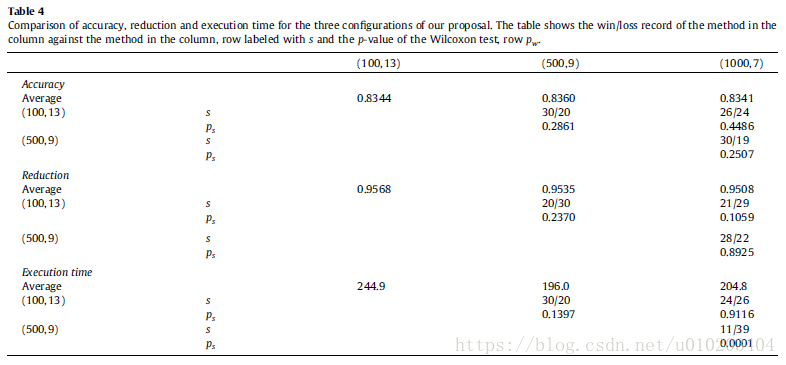
no significant differences among the three configurations for both accuracy and reduction
execution time — remarkable differences
The Iman–Davenport test with a p-value of 0.0000 for both accuracy and reduction — significant differences
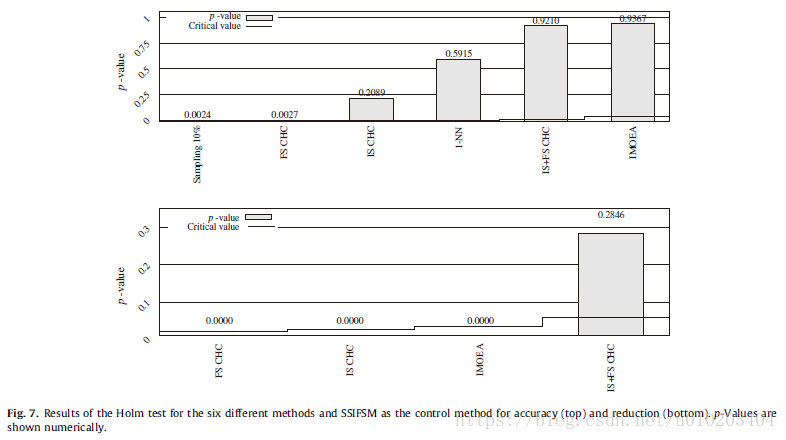
Holm’s procedure —
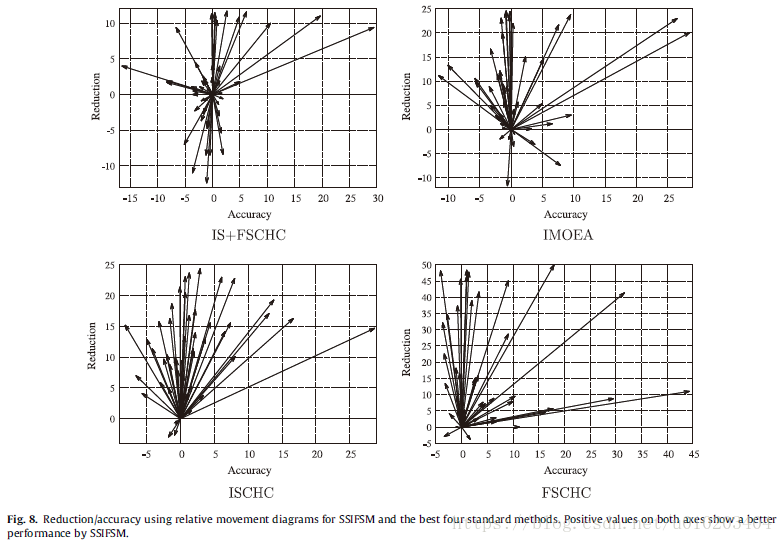
the κ \kappa κ-error relative movement diagrams —
— the reduction difference — instead of the κ \kappa κ difference value
These diagrams use an arrow to represent the results of two methods applied to the same dataset.
a convenient way of summarizing the results
arrows pointing up-right
arrows pointing down-left
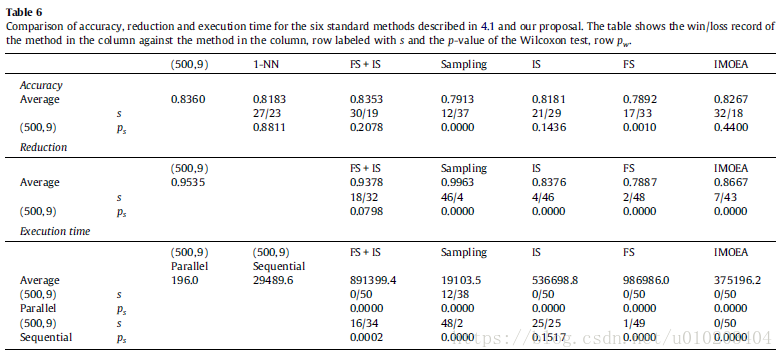
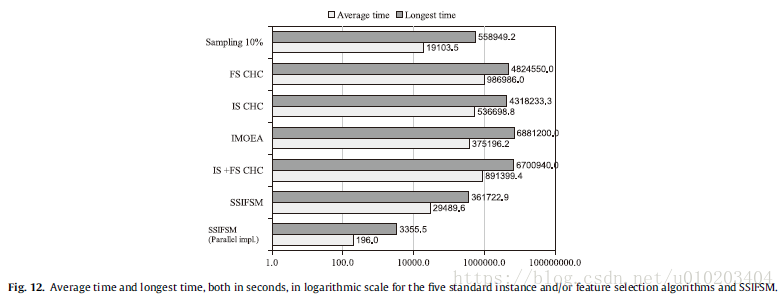
Regarding time — an approximately linear behavior
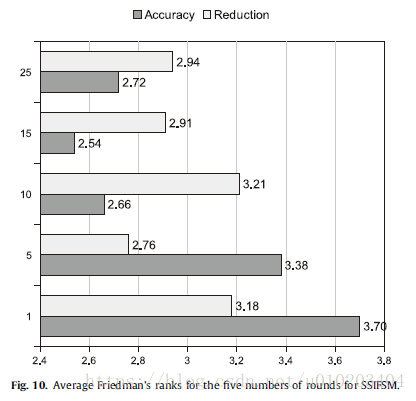
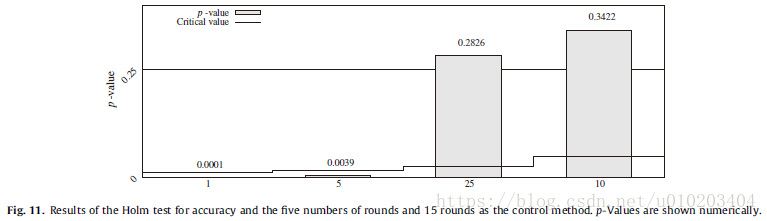
Holm test — (15 rounds)
###运行时间
the philosophy of divide-and-conquer
bookkeeping
the wall-clock time
significantly faster
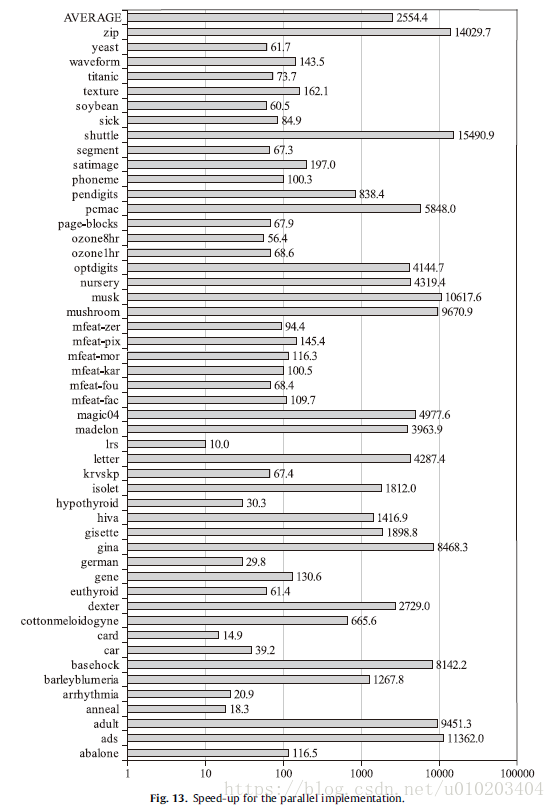
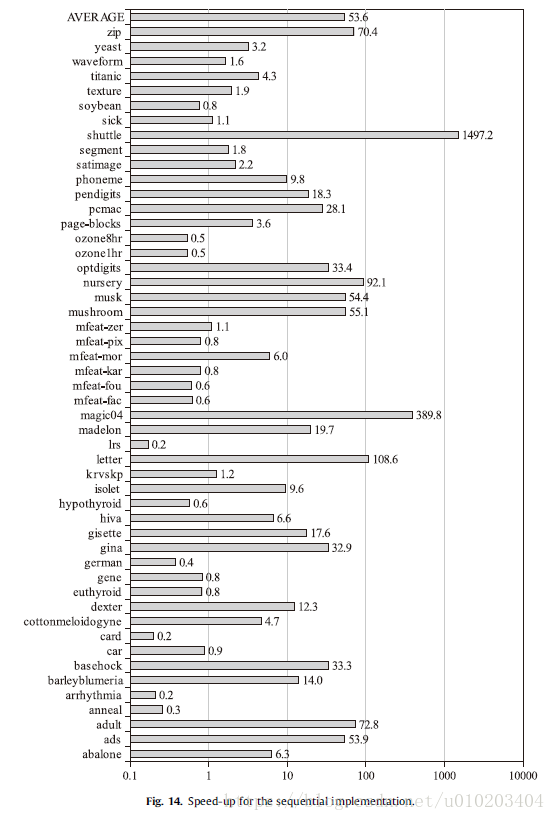
the speedup of SSIFSM with respect to the standard IS + FSCHC for the parallel and sequential implementations respectively —
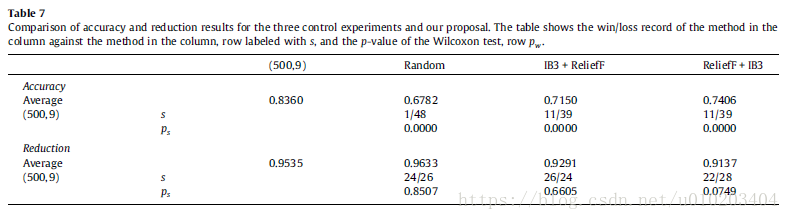
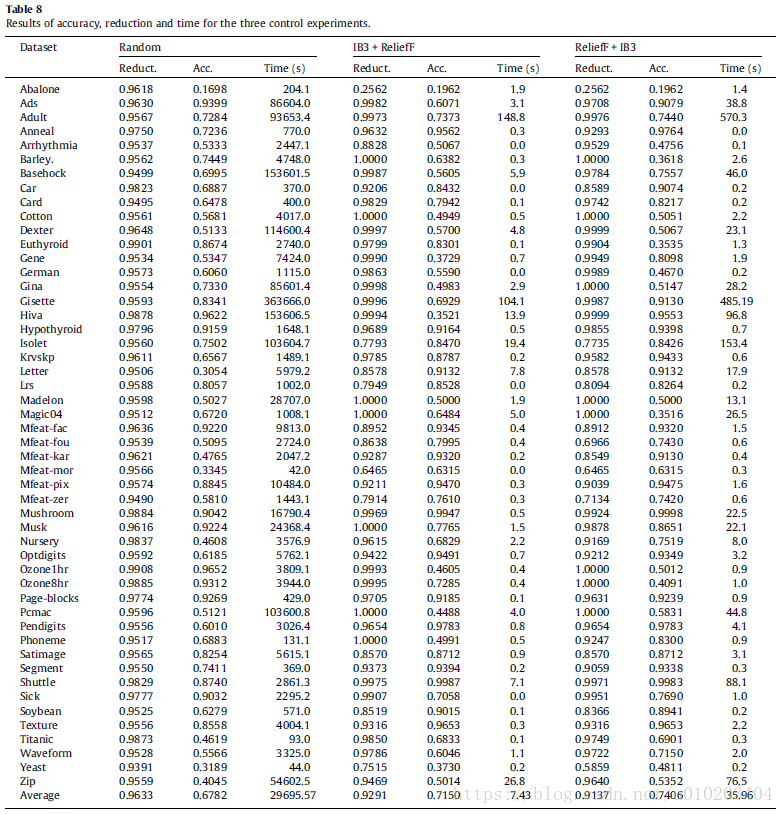
three control experiments —
- a random selection method — [ 5 % , 15 % ] [5\%,15\%] [5%,15%] and [ 15 % , 25 % ] [15\%,25\%] [15%,25%] (instance and features)
- IB3 [1] algorithm for instance selection and ReliefF [55] method for feature selection
- IB3 [1] algorithm for feature selection and ReliefF [55] method for instance selection
the performance in terms of reduction was similar
a very significant worsening of the accuracy
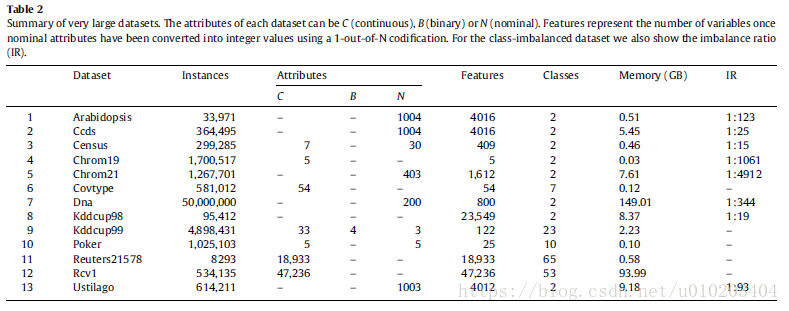
###Scalability to very large datasets
problems with many instances, many features and both many instances and features
the largest set containing 50 million instances and 800 features
a large imbalance ratio
G-mean
#结论
simultaneous instance and feature selection
a bookkeeping mechanism
a voting method
a CHC algorithm
class-imbalanced data
scaled up to problems of very large size
scalability:
- instance and feature selection is always performed over small datasets
- a bookkeeping approach
- only small subsets must be kept in memory
decision trees
support vector machines
这篇关于一种可扩展的同时进化实例和特征选择方法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!