本文主要是介绍##单机版Python##社团划分——有向图的Label Propagation算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在博文社区划分——Label Propagation中,介绍了Label Propagation社区划分算法的基本原理,基本的Label Propagation算法是针对无向图的社区划分算法。
一、基本Label Propagation算法原理
对于网络中的每一个节点,在初始阶段,Label Propagation算法对每一个节点一个唯一的标签,在每一个迭代的过程中,每一个节点根据与其相连的节点所属的标签改变自己的标签,更改的原则是选择与其相连的节点中所属标签最多的社区标签为自己的社区标签,这便是标签传播的含义。随着社区标签的不断传播,最终紧密连接的节点将有共同的标签。
其中,标签的异步更新方式如下:
Cx(t)=f(Cxi1(t),⋯,Cxim(t),Cxi(m+1)(t−1),⋯ , Cxik(t−1))
Label Propagation算法的过程如下:
- 对网络中的每一节点初始化其所属社区标签,如对于节点x,初始化其社区标签为Cx(0)=x;
- 设置代数t;
- 对于网络中的节点设置其遍历顺序和节点的集合X;
- 对于每一个节点x∈X,令Cx(t)=f(Cxi1(t),⋯,Cxim(t),Cxi(m+1)(t−1),⋯,Cxik(t−1));
- 判断是否可以迭代结束,如果否,则设置t=t+1,重新遍历。
二、有向图的Label Propagation算法
1、有向图
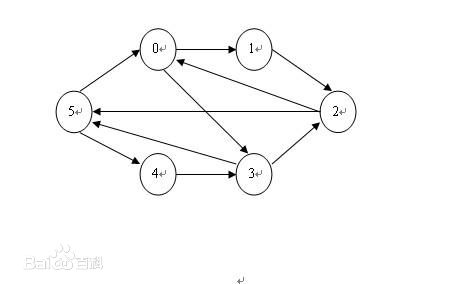
有向图是指图中的边是带有方向的图。对于有向图,每两个节点之间的边的条数是两条,分别为流出的边和流入的边,其流出边的总数为出度,流入边的总数为入度,如下图的有向图:
(图片来自百度百科)
对于节点5,其出度为2,入度也为2。对于更多的有向图的知识,可参阅相关图论的书。
2、对于Label Propagation算法的修正
要使得Label Propagation算法能够求解有向图的社区划分,问题即变为如何将有向图转换成无向图。即如何定义有向图中两个节点之间的边的权重。对于这个问题,设计了如下的公式:
其中wi,j表示的是节点j对于节点i的权重,λi,j表示的是节点i到节点j的权重,λj,i表示的是节点j到节点i的权重。通过参数α和参数β可以调节不同的权重比例。
通过如上的办法将有向图的Label Propagation算法转换成无向图的Label Propagation算法进行求解。
三、实验
对于如下的数据:
0 2 1
2 0 2
0 3 2
3 0 1
0 4 3
4 0 1
0 5 2
5 0 1
1 2 3
2 1 1
1 4 5
4 1 2
1 7 1
7 1 4
2 4 2
4 2 2
2 5 9
5 2 7
2 6 1
6 2 4
3 7 1
7 3 5
4 10 1
10 4 4
5 7 1
7 5 2
5 11 1
11 5 2
6 7 3
7 6 7
6 11 5
11 6 2
8 9 1
9 8 6
8 10 4
10 8 2
8 11 2
11 8 1
8 14 5
14 8 3
8 15 8
15 8 5
9 12 2
12 9 1
9 14 1
14 9 2
10 11 10
11 10 1
10 12 2
12 10 3
10 13 9
13 10 8
10 14 8
14 10 7
11 13 1
13 11 4程序源码如下:
#####################################
# Author:zhaozhiyong
# Date:20160602
# Fun:Label Propagation
#####################################
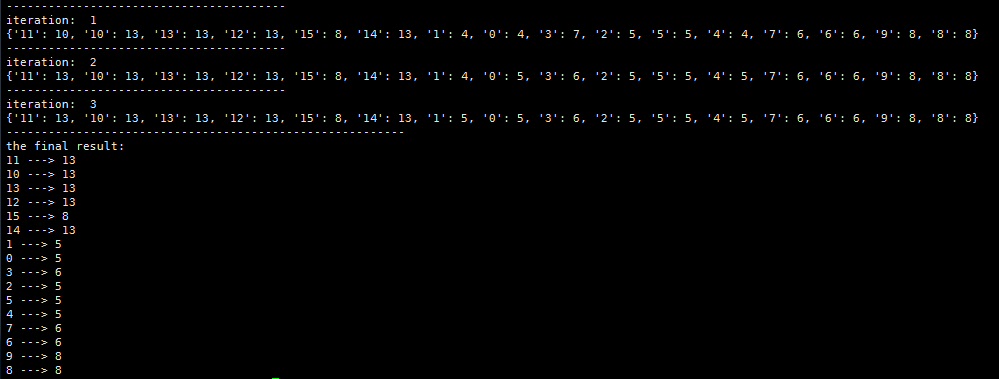
import stringdef loadData(filePath):f = open(filePath)vector_dict = {}edge_dict_out = {}#outedge_dict_in = {}#infor line in f.readlines():lines = line.strip().split("\t")if lines[0] not in vector_dict:vector_dict[lines[0]] = string.atoi(lines[0])if lines[1] not in vector_dict:vector_dict[lines[1]] = string.atoi(lines[1])if lines[0] not in edge_dict_out:edge_list = []if len(lines) == 3:edge_list.append(lines[1] + ":" + lines[2])edge_dict_out[lines[0]] = edge_listelse:edge_list = edge_dict_out[lines[0]]if len(lines) == 3:edge_list.append(lines[1] + ":" + lines[2])edge_dict_out[lines[0]] = edge_listif lines[1] not in edge_dict_in:edge_list = []if len(lines) == 3:edge_list.append(lines[0] + ":" + lines[2])edge_dict_in[lines[1]] = edge_listelse:edge_list = edge_dict_in[lines[1]]if len(lines) == 3:edge_list.append(lines[0] + ":" + lines[2])edge_dict_in[lines[1]] = edge_listf.close()return vector_dict, edge_dict_out, edge_dict_indef get_max_community_label(vector_dict, adjacency_node_list):label_dict = {}# generate the label_dictfor node in adjacency_node_list:node_id_weight = node.strip().split(":")node_id = node_id_weight[0]node_weight = float(node_id_weight[1])if vector_dict[node_id] not in label_dict:label_dict[vector_dict[node_id]] = node_weightelse:label_dict[vector_dict[node_id]] += node_weight# find the max labelsort_list = sorted(label_dict.items(), key = lambda d: d[1], reverse=True)return sort_list[0][0]def check(vector_dict, edge_dict):#for every nodefor node in vector_dict.keys():adjacency_node_list = edge_dict[node]node_label = vector_dict[node]#suject to label_check = {}for ad_node in adjacency_node_list:node_id_weight = ad_node.strip().split(":")node_id = node_id_weight[0]node_weight = node_id_weight[1]if vector_dict[node_id] not in label_check:label_check[vector_dict[node_id]] = float(node_weight)else:label_check[vector_dict[node_id]] += float(node_weight)#print label_checksort_list = sorted(label_check.items(), key = lambda d: d[1], reverse=True)if node_label == sort_list[0][0]:continueelse:return 0return 1 def label_propagation(vector_dict, edge_dict_out, edge_dict_in):#rebuild edge_dictedge_dict = {}for node in vector_dict.iterkeys():out_list = edge_dict_out[node]in_list = edge_dict_in[node]#print "node:", node#print "out_list:", out_list#print "in_list:", in_list#print "------------------------------------------------"out_dict = {}for out_x in out_list:out_xs = out_x.strip().split(":")if out_xs[0] not in out_dict:out_dict[out_xs[0]] = float(out_xs[1])in_dict = {}for in_x in in_list:in_xs = in_x.strip().split(":")if in_xs[0] not in in_dict:in_dict[in_xs[0]] = float(in_xs[1])#print "out_dict:", out_dict#print "in_dict:", in_dictlast_list = []for x in out_dict.iterkeys():out_x = out_dict[x]in_x = 0.0if x in in_dict:in_x = in_dict.pop(x)result = out_x + 0.5 * in_xlast_list.append(x + ":" + str(result))if not in_dict:for x in in_dict.iterkeys():in_x = in_dict[x]result = 0.5 * in_xlast_list.append(x + ":" + str(result))#print "last_list:", last_listif node not in edge_dict:edge_dict[node] = last_list#initial, let every vector belongs to a communityt = 0#for every node in a random orderwhile True:if (check(vector_dict, edge_dict) == 0):t = t+1print "----------------------------------------"print "iteration: ", tfor node in vector_dict.keys():adjacency_node_list = edge_dict[node]vector_dict[node] = get_max_community_label(vector_dict, adjacency_node_list)print vector_dictelse:breakreturn vector_dictif __name__ == "__main__":vector_dict, edge_dict_out, edge_dict_in = loadData("./cd_data.txt")print vector_dictprint edge_dict_outprint edge_dict_in#print "original community: ", vector_dictvec_new = label_propagation(vector_dict, edge_dict_out, edge_dict_in)print "---------------------------------------------------------"print "the final result: "for key in vec_new.keys():print str(key) + " ---> " + str(vec_new[key])最终的结果:
程序和数据的github地址
这篇关于##单机版Python##社团划分——有向图的Label Propagation算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!