本文主要是介绍【二叉树层序遍历】【队列】Leetcode 102 107 199 637 429 515 116 117 104 111,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
【二叉树层序遍历】【队列】Leetcode 102 107 199 637 429 515 116 117
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历解法 用队列实现
- 107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II解法
- 199. 二叉树的右视图 解法
- 637. 二叉树的层平均值 解法
- 429. N叉树的层序遍历
- 515. 在每个树行中找最大值
- 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度
- 111. 二叉树的最小深度
---------------🎈🎈102. 二叉树的层序遍历 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈199. 二叉树的右视图 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈637. 二叉树的层平均值 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈429. N叉树的层序遍历 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈515. 在每个树行中找最大值 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈104. 二叉树的最大深度 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
---------------🎈🎈111. 二叉树的最小深度 题目链接🎈🎈-------------------
102. 二叉树的层序遍历解法 用队列实现


时间复杂度O(N)
空间复杂度O(N)
import com.sun.source.tree.Tree;/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();if(root == null) return result;Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){List<Integer> tempres = new ArrayList<>();int size = myqueue.size(); // 获取当前层的节点数for(int i = 0; i< size; i++){TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();tempres.add(temp.val);if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}}result.add(tempres);}return result;}
}
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II解法
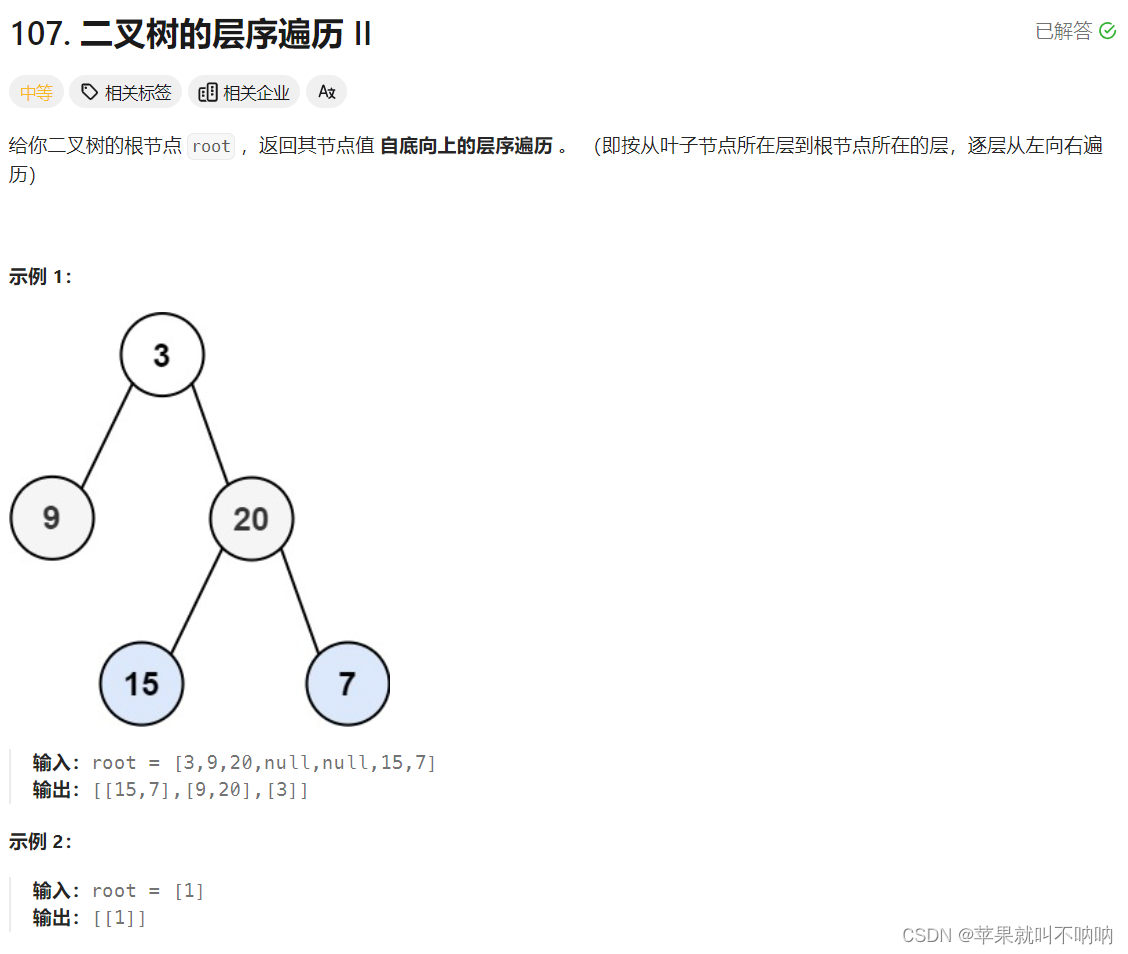
在基础的层序遍历的基础上增加一个Collections.reverse()翻转输出即可
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root==null) return result;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){List<Integer> resulttemp = new ArrayList<>();int size = myqueue.size(); for(int i = 0; i< size; i++){TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();resulttemp.add(temp.val);if(temp.left != null) {myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null) {myqueue.add(temp.right);}}result.add(resulttemp);}Collections.reverse(result);return result;}
}
199. 二叉树的右视图 解法
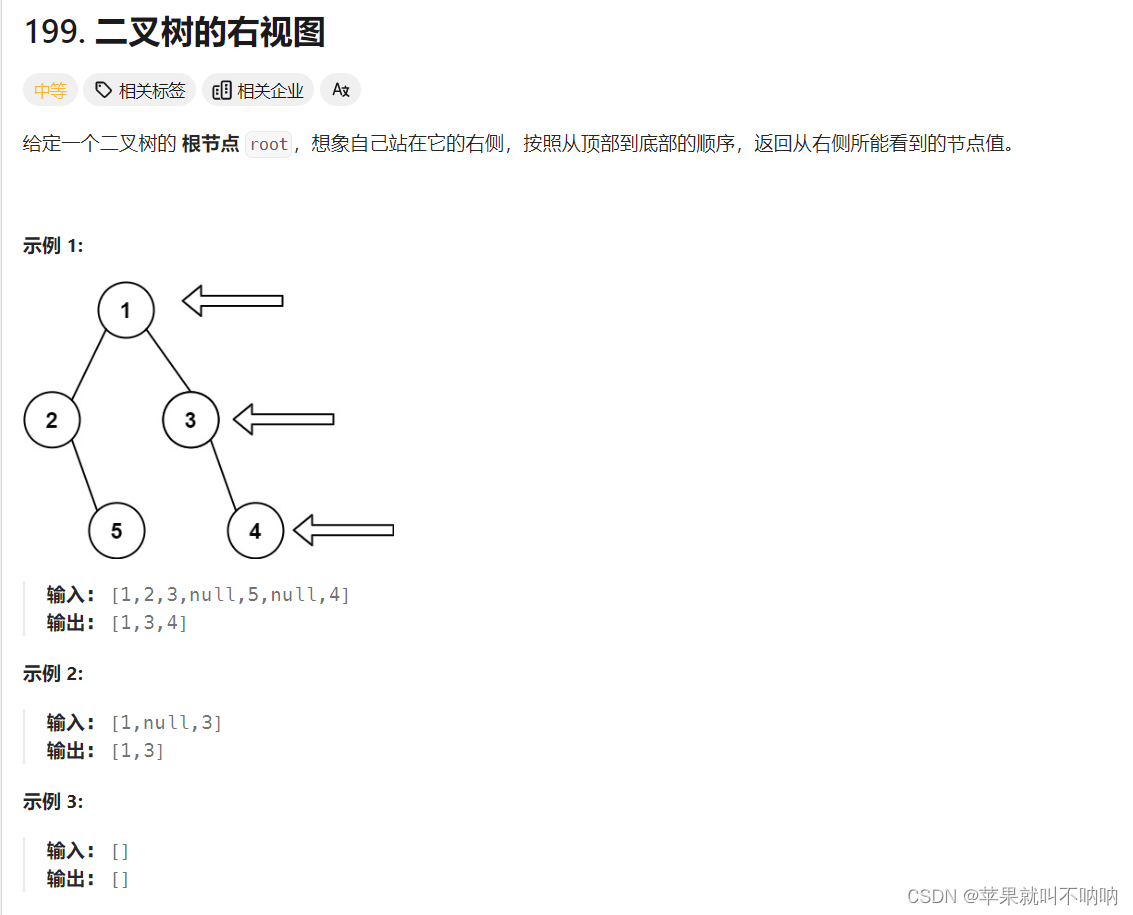
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return result;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();if(temp.left!=null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right!= null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}if(i == size-1){result.add(temp.val);}}}return result;}
}
637. 二叉树的层平均值 解法
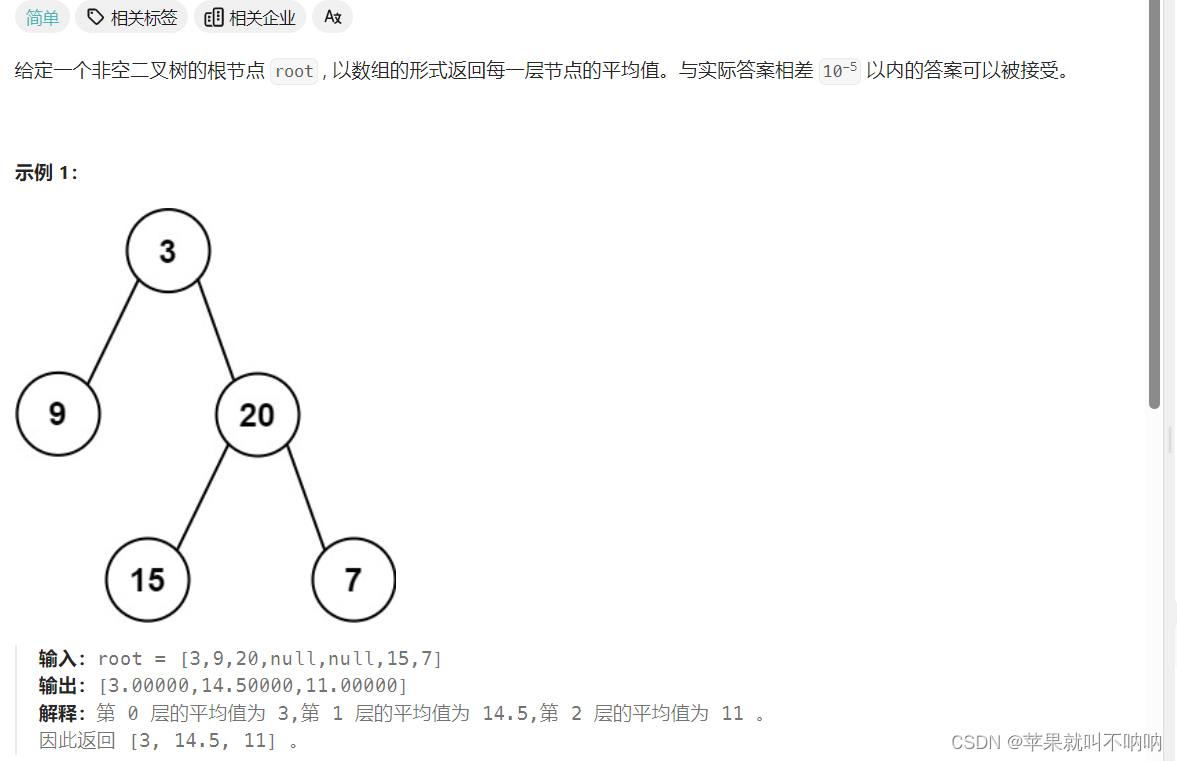
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {List<Double> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return result;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size(); //得到size:当前层节点数double sum = 0;for(int i = 0; i<size; i++){ //弹出并得到size个节点的平均值,并将下一层的节点加入到队列TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();sum += temp.val;if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}}result.add(sum/size);}return result;}
}
429. N叉树的层序遍历

/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {public int val;public List<Node> children;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {val = _val;children = _children;}
};
*/class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<Node> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return result;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();List<Integer> restemp = new ArrayList<>();for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){Node temp = myqueue.poll();restemp.add(temp.val); // 将值temp.val加入restempfor(Node node:temp.children){ // 遍历temp.chirdren 即为遍历每一个temp的子节点,如果不为null就加入到列表中if(node != null){myqueue.add(node);}}}result.add(restemp);}return result;}
}
515. 在每个树行中找最大值
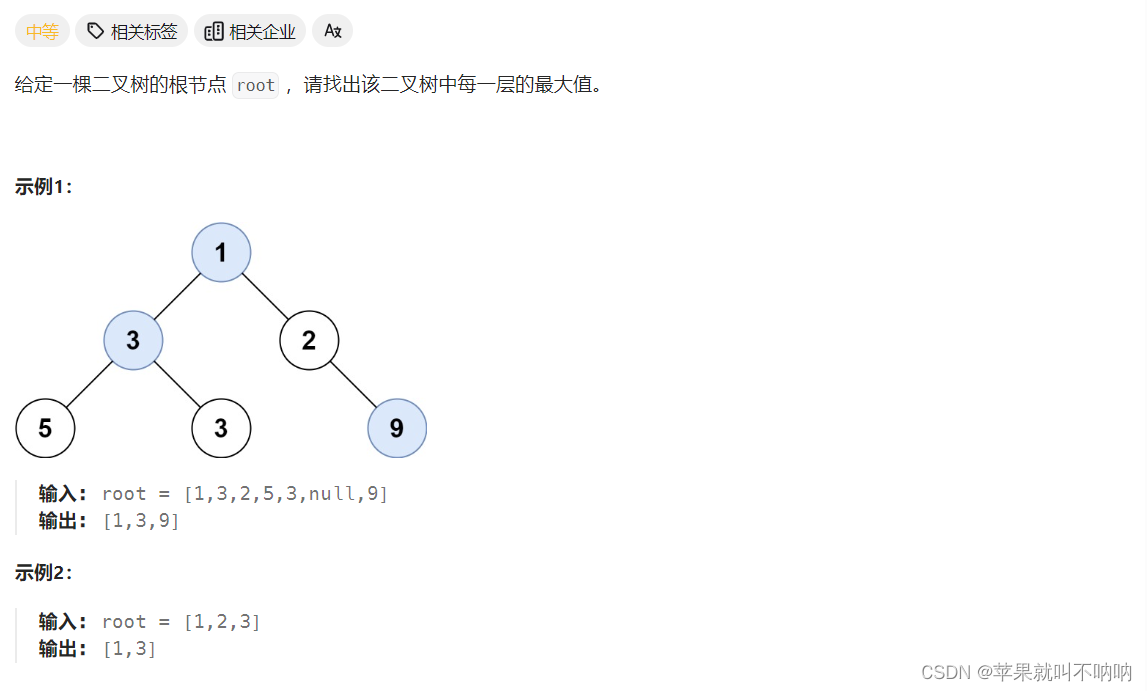
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return result;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();int max = (int)Math.pow(-2, 31);for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}if(max < temp.val){max = temp.val;}}result.add(max);}return result;}
}
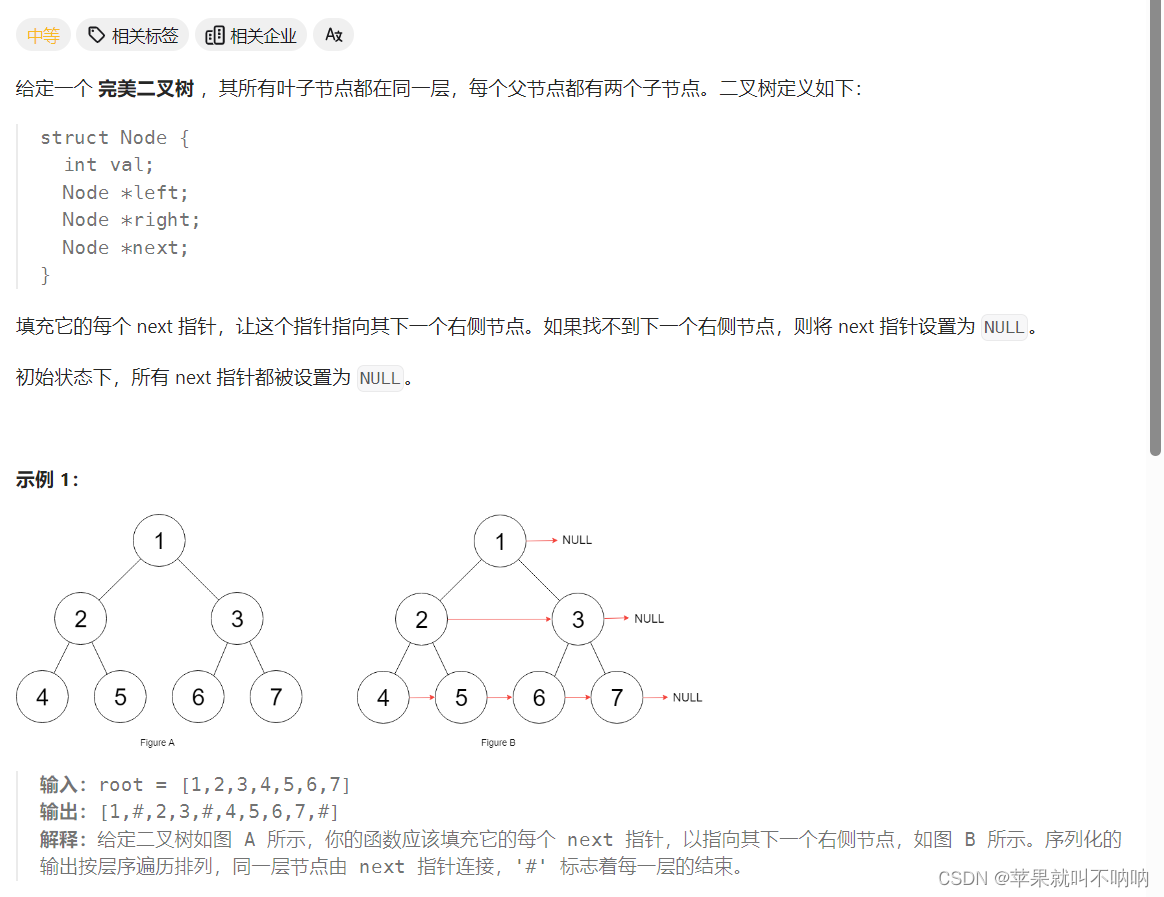
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {public int val;public Node left;public Node right;public Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {val = _val;left = _left;right = _right;next = _next;}
};
*/class Solution {public Node connect(Node root) {Queue<Node> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return root;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();Node head = myqueue.peek();for (int i = 0; i <size; i++) {Node temp = myqueue.poll();if(temp != head){head.next = temp;head = head.next;}if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);myqueue.add(temp.right);}}}return root;}
}
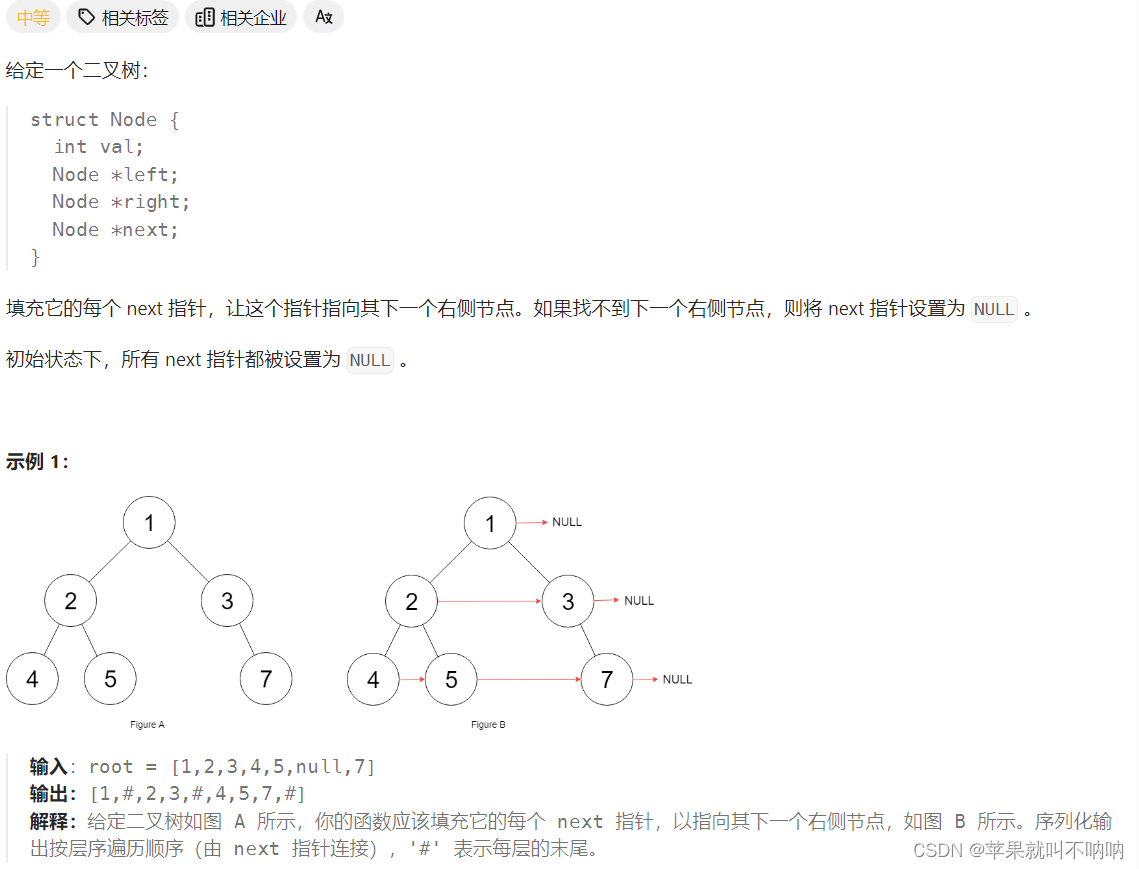
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {public int val;public Node left;public Node right;public Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int _val) {val = _val;}public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {val = _val;left = _left;right = _right;next = _next;}
};
*/class Solution {public Node connect(Node root) {Queue<Node> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return root;myqueue.add(root);while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();Node head = myqueue.peek();for(int i = 0; i <size; i++){Node temp = myqueue.poll();if(temp != head){head.next = temp;head = head.next;}if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}}} return root; }
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度

/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {// 层序遍历Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return 0;myqueue.add(root);int result = 0;while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}}result +=1;}return result;}
}
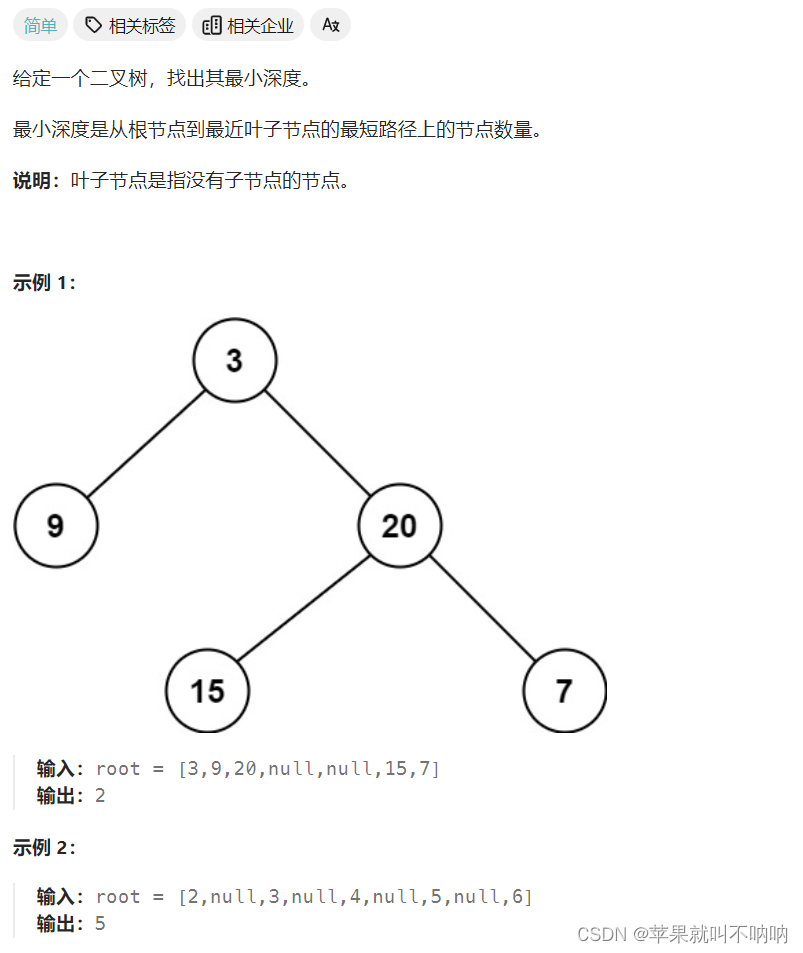
111. 二叉树的最小深度
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {// 层序遍历Queue<TreeNode> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();if(root == null) return 0;myqueue.add(root);int result = 0;while(!myqueue.isEmpty()){int size = myqueue.size();for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){TreeNode temp = myqueue.poll();if(temp.left != null){myqueue.add(temp.left);}if(temp.right != null){myqueue.add(temp.right);}if(temp.left == null && temp.right==null){return result+1;}}result +=1;}return result;}
}这篇关于【二叉树层序遍历】【队列】Leetcode 102 107 199 637 429 515 116 117 104 111的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









