本文主要是介绍C++:二叉搜索树模拟实现(KV模型),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
C++:二叉搜索树模拟实现(KV模型)
- 前言
- 模拟实现KV模型
- 1. 节点封装
- 2、前置工作(默认构造、拷贝构造、赋值重载、析构函数等)
- 2. 数据插入(递归和非递归版本)
- 3、数据删除(递归和非递归版本)
- 3.1 查找待删除节点位置
- 3.2 删除数据及相关节点调整
- 3.3 完整代码以及递归和非递归版本
- 四、查找数据
- 五、中序遍历
- 六、所有代码
前言
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,他对数据有严格的要求,具体表现在以下几个方面:
- 如果一个根节点的左子树不为空,则左子树中所有节点的值都必须小于根节点的值;如果它的右子树不为空,则右子树中所有节点的值都必须大于根节点的值。
- 它的左右子树也都必须是一个二叉搜索树,也都必须满足第一条。
- 二叉搜索树中的每个节点都是唯一的,不允许重复!!!
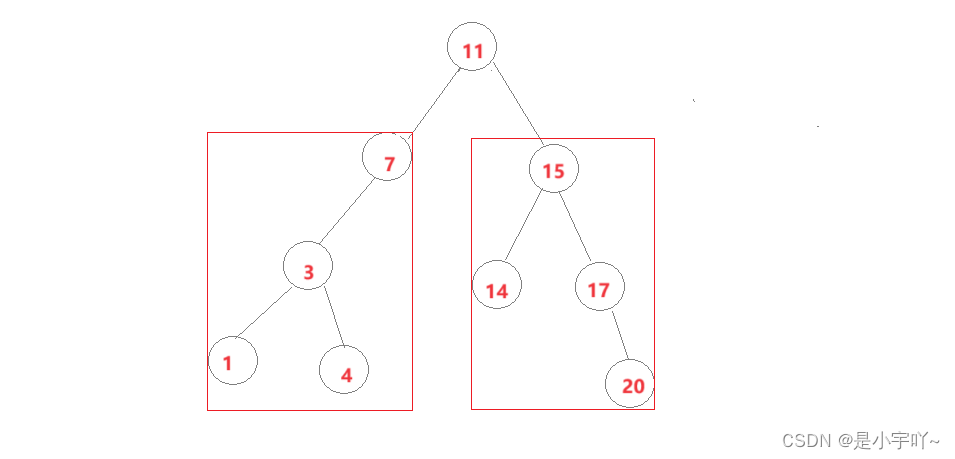
二叉搜索树的实际应用主要分为K模型和KV模型。
- K模型:即Key作为关键码,二叉搜索树中只存储Key一个数据。而关键码则是待搜索的值。比如:我们经常通过软件查找是否存在某个单词,是否拼写正确。
- KV模型:存储的数据中,每个Key对应一个Value,即键值对<Key, Value>。 我们经常通过Key去查找对应的Val.比如:我们通过英文来查找对应的中文,就是一个最常见的KV场景。
模拟实现KV模型
1. 节点封装
由于是KV模型,我们需要存储Key和Value俩个值。同时二叉搜索树也是二叉树,我们需要它的左右节点。因此节点疯转如下:
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{K _key;V _value;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//默认构造函数, 用于后续new创建节点BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value):_key(key), _value(value), _right(nullptr), _left(nullptr){}
};
2、前置工作(默认构造、拷贝构造、赋值重载、析构函数等)
接下来是KV模型封装的框架,以及默认构造、拷贝构造、赋值重载、析构函数。比较简单,就直接给出代码了哈。
template<class K, class V>class BSTree{typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;//节点重命名public://默认构造BSTree():_root(nullptr){}//拷贝构造BSTree(BSTree<K, V>& t){_root = Copy(t._root);}//赋值重载BSTree<K, V>& operator=(BSTree<K, V> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}//析构函数~BSTree(){Destory(_root);}private:Node* _root = nullptr;};
}
2. 数据插入(递归和非递归版本)
首先我们需要查找数据待插入的位置(为了保证插入数据后整体依然是一颗二叉搜索树).。同时查找插入位置时,只有key是有严格要求的,Value只是附带。
即:如果根节点为空,即是待插入数据位置;否则开始查找,如果待插入数据大于根节点往右子树节点走;如果待插入数据小于根节点往左子树节点走。不断循环,直到查找到空节点时,即为数据待插入的位置;如果查找到的大小和待插入数据值相等则返回false(确保二叉搜索树中的每个节点唯一)
【非递归版本】:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{if (_root == nullptr)//根节点为空{_root = new Node(key, value);return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;//后续插入数据链接时,需要和父节点相连while (cur){if (cur->_key > key)//待插入数据小于当前节点,往左子树查找{parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if(cur->_key < key)//待插入数据大于当前节点,往右子树查找{parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else//待插入数据等于当前节点,不允许插入{return false;}}//链接Node* newNode = new Node(key, value); //链接时,我们无法确定插入节点时在父节点的左边还是右边,需要进一步比较if (parent->_key > key)parent->_left = newNode;elseparent->_right = newNode;return true;
}
【递归版本】:
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{//由于我们查找位置需要从根节点开始查找,所以这里通过另一个函数来传递实现return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)
{if (root == nullptr){//注意上述我们形参都是引用,所以不用新增Parent节点root = new Node(key, value);return true;}if (root->_key > key)//待插入数据小于当前节点,往左子树查找return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);else if (root->_key < key)//待插入数据大于当前节点,往右子树查找return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);elsereturn false;
}
3、数据删除(递归和非递归版本)
3.1 查找待删除节点位置
删除数据,我们首先需要和插入数据一样,先查找到待删除节点。和插入类似就不多说了。
【查找待删除数据】:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{if (_root == nullptr)//为空即不存在待删除数据return false;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key)//待删除数据小于当前节点,往左子树查找{parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_key < key)//待删除数据大于当前节点,往右子树查找{parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{//当前位置即为待删除节点,装备删除数据 }}return false;//整棵树中不存在待删除数据
}
3.2 删除数据及相关节点调整
插找到待删除数据后,显然如果只是简单将该节点删除,有可能将不满足二叉搜索树的要求,那怎么办呢?
删除数据分为以下三种情况:
- 左子树为空
左子树为空主要分为以下情形:右子树为空,左子树不为空;左右子树均为空(省略)。
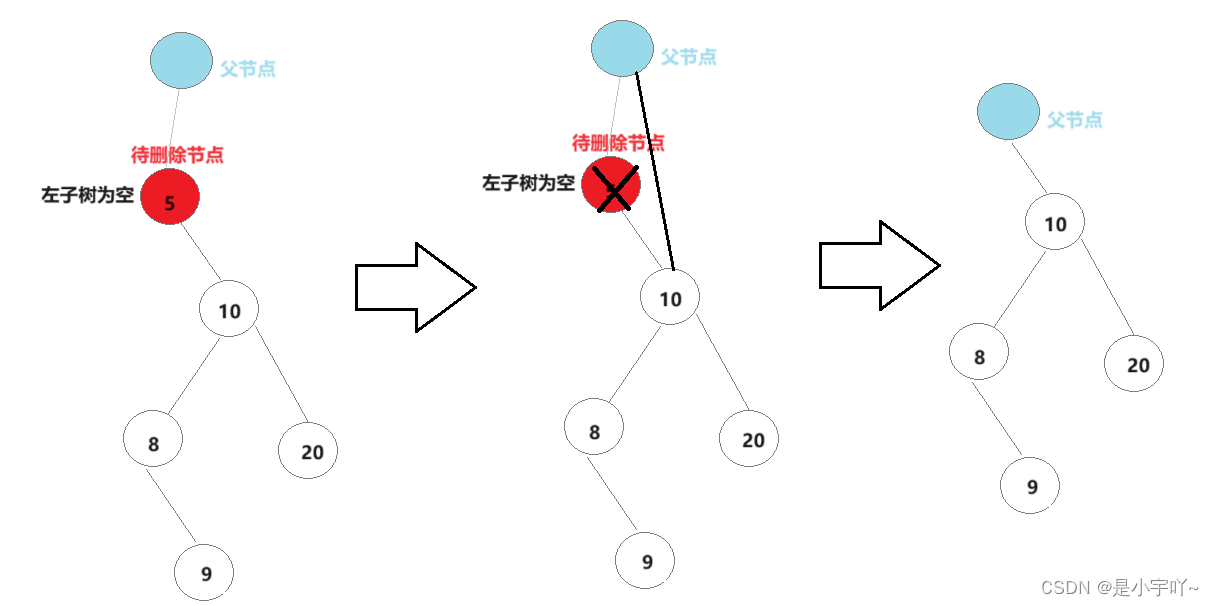
不管上述那种情况,我们发现只需将父节点的下一个节点指向待删除节点的右指针即可。但需要注意的是,如果待删除节点为根节点,它将没有父节点,需要单独处理。
【代码实现】:
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左子树为空
{if (parent == _root)//cur为根节点{_root = cur->_right;}else{if (parent->_key > cur->_key)//待删除节点在父节点左子树中{parent->_left = cur->_right;}else//待删除节点在父节点右子树中{parent->_right = cur->_right;}}delete cur;
}
- 右子树为空
右子树为空分为单纯右子树为空和左右子树均为空(省)。具体处理方式和左子树为空类似就不多说了。
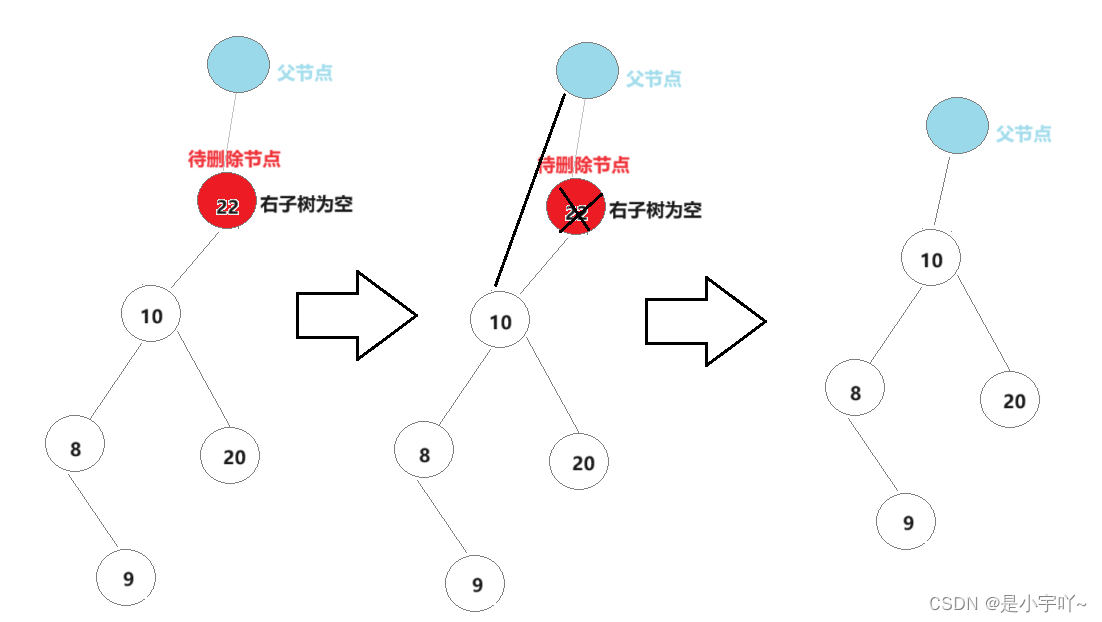
【代码实现】:
//左右子树均不为空,查找右子树最小元素进行交换后删除
if (parent == _root)//cur为根节点
{_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_key > cur->_key){parent->_left = cur->_left;}else{parent->_right = cur->_left;}}delete cur;
}
- 左右子树均不为空
这种情况我们可以查找左子树最大值或右子树最小值和待删除删除节点进行交换,交换后我们可以转化为上述两种子问题来删除数据。(接下来博主以交换右子树最小值为例)
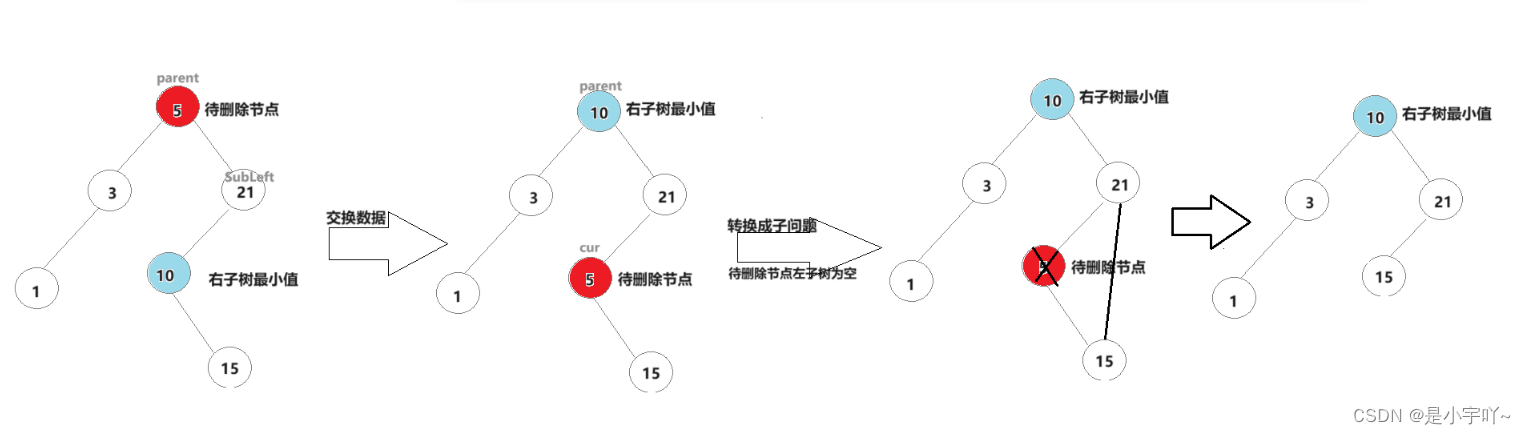
Node* subLeft = cur->_right;
Node* parent = cur;
while (subLeft->_left)
{parent = cur;subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
//交换
swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);
swap(cur->_value, subLeft->_value);
//删除
if (parent->_right = subLeft)
{parent->_right = subLeft->_right;
}
else
{parent->_left = subLeft->_right;
}
delete subLeft;
3.3 完整代码以及递归和非递归版本
递归思路和非递归差球不多,就不一一分析了,下面直接给出两种实现方式代码。
【非递归版本】:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{if (_root == nullptr)return false;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{//装备删除数据if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左子树为空{if (parent == _root)//cur为根节点{_root = cur->_right;}else{if (parent->_key > cur->_key){parent->_left = cur->_right;}else{parent->_right = cur->_right;}}delete cur;}else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右子树为空{if (parent == _root)//cur为根节点{_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_key > cur->_key){parent->_left = cur->_left;}else{parent->_right = cur->_left;}}delete cur;}else{//左右子树均不为空,查找右子树最小元素进行交换后删除Node* subLeft = cur->_right;Node* parent = cur;while (subLeft->_left){parent = cur;subLeft = subLeft->_left;}//交换swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);swap(cur->_value, subLeft->_value);//删除if (parent->_right = subLeft){parent->_right = subLeft->_right;}else{parent->_left = subLeft->_right;}delete subLeft;}return true;}}return false;
}
【递归版本】:
//删除:递归版本
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{return _EraseR(_root, key);//同理,由于需要根节点,在通过一层函数来实现
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{if (root == nullptr)//非找到return false;if (root->_key > key)//转化成递归子问题,在左子树中删除keyreturn _EraseR(root->_left, key);else if (root->_key < key)//转化成递归子问题,在右子树中删除keyreturn _EraseR(root->_right, key);else{//删除数据if (root->_left == nullptr){Node* del = root;root = root->_right;delete del;return true;}else if (_root->_right == nullptr){Node* del = root;root = root->_left;delete del;return true;}else{Node* subLeft = root->_right;while (subLeft->_left){subLeft = subLeft->_left;}//交换swap(root->_key, subLeft->_key);swap(root->_value, subLeft->_value);return _EraseR(root->_right, key); }}
}
四、查找数据
【递归版本】:
//查找:递归版本
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{return _FindR(_root, key);
}
Node* _FindR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;if (root->_key > key)return _FindR(root->_left, key);else if (root->_key < key)return _FindR(root->_right, key);elsereturn root;
}
【非递归版本】:
//查找:非递归版本
Node* Find(const K& key)
{Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key)cur = cur->_left;else if (cur->_key < key)cur = cur->_right;else{//找到了return cur;}}return nullptr;
}
五、中序遍历
//中序遍历
void Inorder()
{_Inorder(_root);cout << endl;
}void _Inorder(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr)return;_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << "->" << root->_value << " " << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);
}
六、所有代码
gitee:所有代码及测试代码
namespace KeyValue
{template<class K, class V>struct BSTreeNode{K _key;V _value;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//默认构造函数BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value):_key(key), _value(value), _right(nullptr), _left(nullptr){}};template<class K, class V>class BSTree{typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;public:
////默认构造BSTree():_root(nullptr){}//拷贝构造BSTree(BSTree<K, V>& t){_root = Copy(t._root);}//赋值重载BSTree<K, V>& operator=(BSTree<K, V> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}//析构函数~BSTree(){Destory(_root);}
////插入, 非递归版本bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(key, value);return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if(cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}//链接Node* newNode = new Node(key, value); if (parent->_key > key)parent->_left = newNode;elseparent->_right = newNode;return true;}// 插入: 递归遍布bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value){return _InsertR(_root, key, value);}
///查找:非递归版本Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key)cur = cur->_left;else if (cur->_key < key)cur = cur->_right;else{//找到了return cur;}}return nullptr;}//查找:递归版本Node* FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}
///删除:非递归版本bool Erase(const K& key){if (_root == nullptr)return false;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{//装备删除数据if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左子树为空{if (parent == _root)//cur为根节点{_root = cur->_right;}else{if (parent->_key > cur->_key){parent->_left = cur->_right;}else{parent->_right = cur->_right;}}delete cur;}else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右子树为空{if (parent == _root)//cur为根节点{_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_key > cur->_key){parent->_left = cur->_left;}else{parent->_right = cur->_left;}}delete cur;}else{//左右子树均不为空,查找右子树最小元素进行交换后删除Node* subLeft = cur->_right;Node* parent = cur;while (subLeft->_left){parent = cur;subLeft = subLeft->_left;}//交换swap(cur->_key, subLeft->_key);swap(cur->_value, subLeft->_value);//删除if (parent->_right = subLeft){parent->_right = subLeft->_right;}else{parent->_left = subLeft->_right;}delete subLeft;}return true;}}return false;}//删除:递归版本bool EraseR(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root, key);}
///中序遍历void Inorder(){_Inorder(_root);cout << endl;}void _Inorder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_Inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << "->" << root->_value << " " << endl;_Inorder(root->_right);}private:Node* Copy(Node*& root){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_key, root->_value);newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left);newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right);return newRoot;}void Destory(Node*& root){if (root == nullptr)return;Destory(root->_right);Destory(root->_left);delete root;root = nullptr;}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return false;if (root->_key > key)return _EraseR(root->_left, key);else if (root->_key < key)return _EraseR(root->_right, key);else{//删除数据if (root->_left == nullptr){Node* del = root;root = root->_right;delete del;return true;}else if (_root->_right == nullptr){Node* del = root;root = root->_left;delete del;return true;}else{Node* subLeft = root->_right;while (subLeft->_left){subLeft = subLeft->_left;}//交换swap(root->_key, subLeft->_key);swap(root->_value, subLeft->_value);return _EraseR(root->_right, key); }}}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value){if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key, value);return true;}if (root->_key > key)return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);else if (root->_key < key)return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);elsereturn false;}Node* _FindR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;if (root->_key > key)return _FindR(root->_left, key);else if (root->_key < key)return _FindR(root->_right, key);elsereturn root;}Node* _root = nullptr;};
}
这篇关于C++:二叉搜索树模拟实现(KV模型)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





