本文主要是介绍CGAL5.4.1 边塌陷算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
1、使用曲面网格的示例
2、使用默认多面体的示例
3、使用丰富多面体的示例
主要对1、使用曲面网格的示例 进行深度研究
CGAL编译与安装CGAL安装到验证到深入_cgal测试代码-CSDN博客
参考资料CGAL 5.4.5 - Triangulated Surface Mesh Simplification: User Manual
meshlab下载打开off文件MeshLab
1、使用曲面网格的示例
下面的例子说明了如何简化曲面网格。未指定的代价策略默认为 Lindstrom-Turk。
预览源文件 cube-meshed.off

stop_ratio 0.1代表只有之前10%的边量
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/edge_collapse.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/Policies/Edge_collapse/Count_ratio_stop_predicate.h>
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> Kernel;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point_3;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point_3> Surface_mesh;
namespace SMS = CGAL::Surface_mesh_simplification;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Surface_mesh surface_mesh;const std::string filename =CGAL::data_file_path(R"(C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\cube-meshed.off)");std::ifstream is(filename);if (!is || !(is >> surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Failed to read input mesh: " << filename << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}if (!CGAL::is_triangle_mesh(surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Input geometry is not triangulated." << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();// In this example, the simplification stops when the number of undirected edges// drops below 10% of the initial countdouble stop_ratio = 0.1;SMS::Count_ratio_stop_predicate<Surface_mesh> stop(stop_ratio);int r = SMS::edge_collapse(surface_mesh, stop);std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();std::cout << "\nFinished!\n" << r << " edges removed.\n" << surface_mesh.number_of_edges() << " final edges.\n";std::cout << "Time elapsed: " << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time - start_time).count() << "ms" << std::endl;CGAL::IO::write_polygon_mesh(R"(C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\out.off)", surface_mesh, CGAL::parameters::stream_precision(17));return EXIT_SUCCESS;
} 

2、使用默认多面体的示例
下面的示例展示了使用默认顶点、半边和面简化多面体_3 的过程。未指定的代价策略默认为 Lindstrom-Turk。
C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\small_cube.off 1000 C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\small_cube_out.off#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
// Simplification function
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/edge_collapse.h>
// Stop-condition policy
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/Policies/Edge_collapse/Count_stop_predicate.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> Kernel;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<Kernel> Surface_mesh;
namespace SMS = CGAL::Surface_mesh_simplification;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Surface_mesh surface_mesh;const std::string filename = (argc > 1) ? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("meshes/small_cube.off");std::ifstream is(filename);if (!is || !(is >> surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Failed to read input mesh: " << filename << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}if (!CGAL::is_triangle_mesh(surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Input geometry is not triangulated." << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}// This is a stop predicate (defines when the algorithm terminates).// In this example, the simplification stops when the number of undirected edges// left in the surface mesh drops below the specified number (1000)const std::size_t edge_count_treshold = (argc > 2) ? std::stoi(argv[2]) : 1000;SMS::Count_stop_predicate<Surface_mesh> stop(edge_count_treshold);// This the actual call to the simplification algorithm.// The surface mesh and stop conditions are mandatory arguments.// The index maps are needed because the vertices and edges// of this surface mesh lack an "id()" field.std::cout << "Collapsing edges of Polyhedron: " << filename << ", aiming for " << edge_count_treshold << " final edges..." << std::endl;int r = SMS::edge_collapse(surface_mesh, stop,CGAL::parameters::vertex_index_map(get(CGAL::vertex_external_index, surface_mesh)).halfedge_index_map(get(CGAL::halfedge_external_index, surface_mesh)));std::cout << "\nFinished!\n" << r << " edges removed.\n"<< (surface_mesh.size_of_halfedges() / 2) << " final edges.\n";std::ofstream os(argc > 3 ? argv[3] : "out.off");os.precision(17);os << surface_mesh;return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
点和面一样
3、 使用丰富多面体的示例
下面的示例等同于上一个示例,但使用的是丰富多面体,其半边支持 id 字段,用于存储算法所需的边索引。
C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\small_cube.off 0.1 C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\small_cube_out.off#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
// Extended polyhedron items which include an id() field
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_items_with_id_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/edge_collapse.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/Policies/Edge_collapse/Count_ratio_stop_predicate.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> Kernel;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;
// Setup an enriched polyhedron type which stores an id() field in the items
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<Kernel, CGAL::Polyhedron_items_with_id_3> Surface_mesh;
typedef boost::graph_traits<Surface_mesh>::vertex_descriptor vertex_descriptor;
typedef boost::graph_traits<Surface_mesh>::halfedge_descriptor halfedge_descriptor;
namespace SMS = CGAL::Surface_mesh_simplification;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Surface_mesh surface_mesh;const std::string filename = (argc > 1) ? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("meshes/small_cube.off");std::ifstream is(filename);if (!is || !(is >> surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Failed to read input mesh: " << filename << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}if (!CGAL::is_triangle_mesh(surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Input geometry is not triangulated." << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}// The items in this polyhedron have an "id()" field// which the default index maps used in the algorithm// need to get the index of a vertex/edge.// However, the Polyhedron_3 class doesn't assign any value to// this id(), so we must do it here:int index = 0;for (halfedge_descriptor hd : halfedges(surface_mesh))hd->id() = index++;index = 0;for (vertex_descriptor vd : vertices(surface_mesh))vd->id() = index++;// In this example, the simplification stops when the number of undirected edges// drops below xx% of the initial countconst double ratio = (argc > 2) ? std::stod(argv[2]) : 0.1;SMS::Count_ratio_stop_predicate<Surface_mesh> stop(ratio);// The index maps are not explicitelty passed as in the previous// example because the surface mesh items have a proper id() field.// On the other hand, we pass here explicit cost and placement// function which differ from the default policies, ommited in// the previous example.std::cout << "Collapsing edges of mesh: " << filename << ", aiming for " << 100 * ratio << "% of the input edges..." << std::endl;int r = SMS::edge_collapse(surface_mesh, stop);std::cout << "\nFinished!\n" << r << " edges removed.\n"<< (surface_mesh.size_of_halfedges() / 2) << " final edges.\n";std::ofstream os((argc > 3) ? argv[3] : "out.off");os.precision(17);os << surface_mesh;return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
主要对1、使用曲面网格的示例 进行深度研究
曲面网格简化是指在尽可能保留整体形状、体积和边界的前提下,减少曲面网格中使用的面的数量。它与细分相反。
本文介绍的算法可以使用一种称为 "边缘折叠 "的方法,简化任何具有任意数量连接组件、有或无边界(边界或孔)和手柄(任意种属)的定向 2-manifold曲面。粗略地说,这种方法包括用一个顶点迭代替换一条边,每次折叠删除 2 个三角形。
边的折叠优先级由用户提供的成本函数决定,替换顶点的坐标由另一个用户提供的放置函数决定。当满足用户提供的停止谓词(如达到所需的边数)时,算法终止。
这里实现的算法是通用的,因为它不要求曲面网格是特定类型的,而要求它是可变曲面图(MutableFaceGraph)和半边列表图(HalfedgeListGraph)概念的模型。我们给出了 Surface_mesh、Polyhedron_3 和 OpenMesh 的示例。
计算折叠成本和顶点位置的具体方法称为成本策略。用户可以选择不同的策略,以策略和相关参数的形式传递给算法。
当前版本的软件包提供了一组实现三种策略的策略:默认的 Lindstrom-Turk 策略、Garland-Heckbert 策略,以及由边长成本和可选的中点放置(速度更快,但精度较低)组成的策略。
文献[4]、[5]中介绍的策略的主要特点是,简化后的曲面网格在每一步都不会与原始曲面网格(或前一步的曲面网格)进行比较,因此无需保留额外的信息,如原始曲面网格或局部变化的历史记录。因此被称为无记忆简化。
与 Lindstrom-Turk 策略一样,[2] 中提出的 Garland-Heckbert 策略不将生成的网格与原始网格进行比较,也不依赖于局部变化的历史。相反,它通过为每个顶点分配四元矩阵来编码与原始网格的近似距离。
关键函数
/*
surface_mesh : 要简化的曲面网格
stop_predicate : 表示何时必须完成简化的策略
vertex_index_map(vimap):赋予每个顶点唯一整数索引的属性映射
edge_index_map(eimap):赋予每条边唯一整数索引的属性图
edge_is_constrained_map(ebmap):指定一条边是否为受约束边的属性图
get_cost(cf):计算折叠成本的函数对象
get_placement(pf):计算剩余顶点位置的函数对象
filter(filter):用于拒绝下一条折叠边的候选对象的函数对象
visitor(vis) : 跟踪简化过程的函数对象
*/
int r = edge_collapse(surface_mesh, stop_predicate、
CGAL::parameters::vertex_index_map(vimap)
.edge_index_map(eimap)
.edge_is_border_map(ebmap)
.get_cost(cf)
.get_placement(pf)
.filter(filter
.visitor(vis));
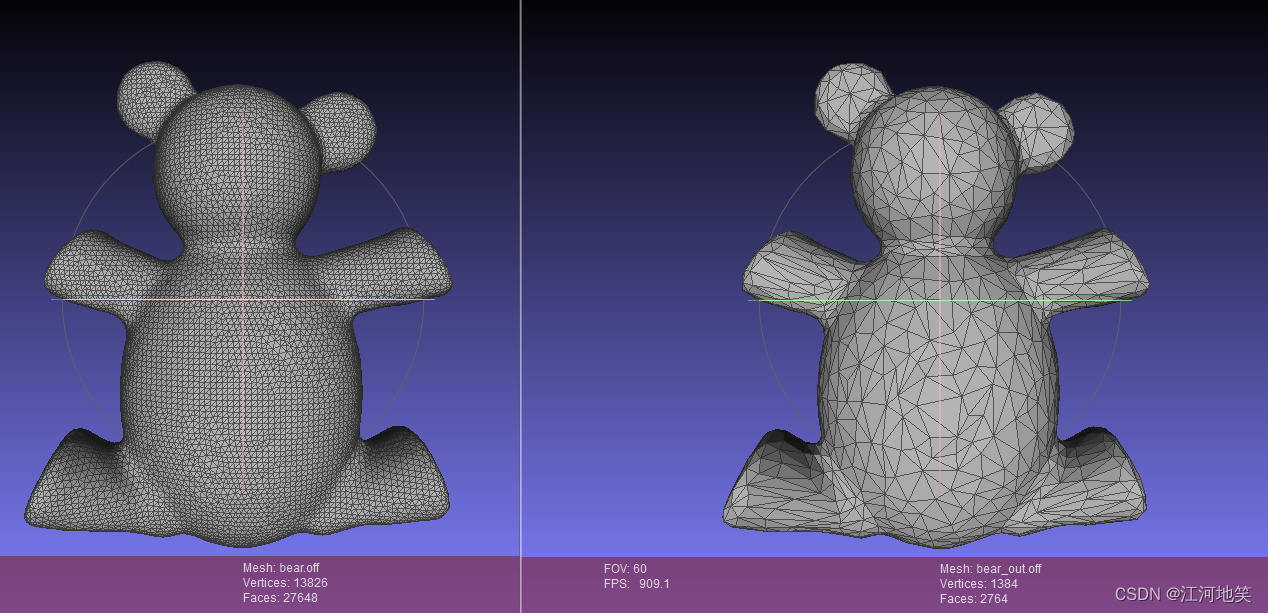
这里读取的数据是off文件,如果需要读取其他文件例如ply,obj则需要转换位Surface_mesh格式,先解析一下这个格式
Surface_mesh surface_mesh;const std::string filename = CGAL::data_file_path(R"(C:\chenqi\ThridParty\CGAL-5.4.3\data\meshes\bear.off)");std::ifstream is(filename);if (!is || !(is >> surface_mesh)){std::cerr << "Failed to read input mesh: " << filename << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}- 下载的obj网站:Borderlands角色扮演 | 免费3D模型 | 专业3D扫描方案 (artec3d.cn)
读取obj进行网格简化,已经测试,这份代码只可以处理网格,不可以处理带纹理的
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/OBJ.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/edge_collapse.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_simplification/Policies/Edge_collapse/Count_ratio_stop_predicate.h>
#include <fstream>typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> Kernel;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point> Surface_Mesh;
namespace SMS = CGAL::Surface_mesh_simplification;int main() {Surface_Mesh surface_mesh;std::string input_filename = R"(C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\OBJ\borderlands_cosplay-obj\out.obj)"; // Replace with your input OBJ file pathstd::string output_filename = R"(C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\OBJ\borderlands_cosplay-obj\out2.obj)"; // Replace with your desired output OBJ file path// Read the mesh from OBJ fileif (!CGAL::IO::read_polygon_mesh(input_filename, surface_mesh)) {std::cerr << "Failed to read input mesh: " << input_filename << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}// Perform edge collapse simplificationdouble stop_ratio = 0.5; // Adjust this ratio as neededSMS::Count_ratio_stop_predicate<Surface_Mesh> stop(stop_ratio);SMS::edge_collapse(surface_mesh, stop);// Write the simplified mesh to OBJ fileif (!CGAL::IO::write_polygon_mesh(output_filename, surface_mesh)) {std::cerr << "Failed to write output mesh: " << output_filename << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;}return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
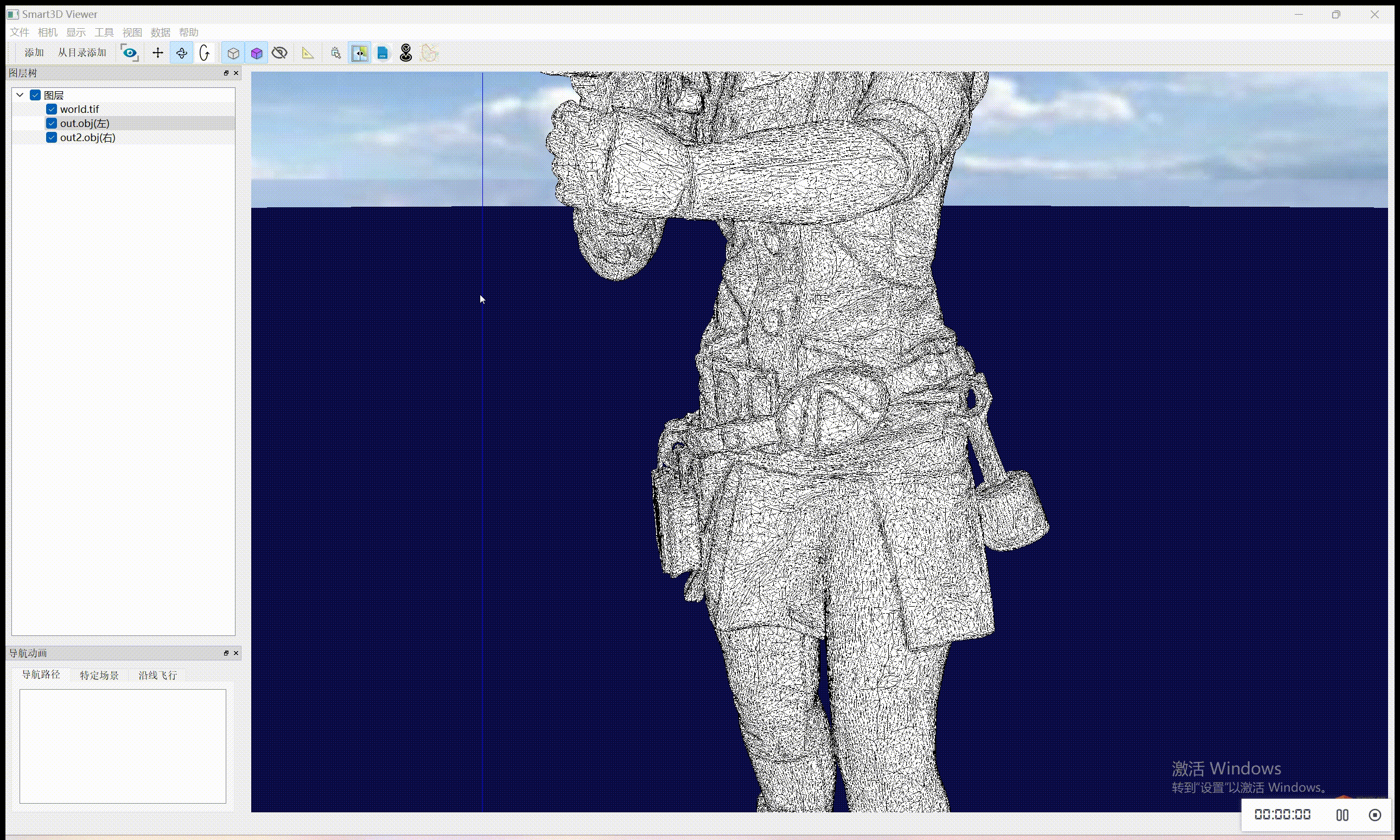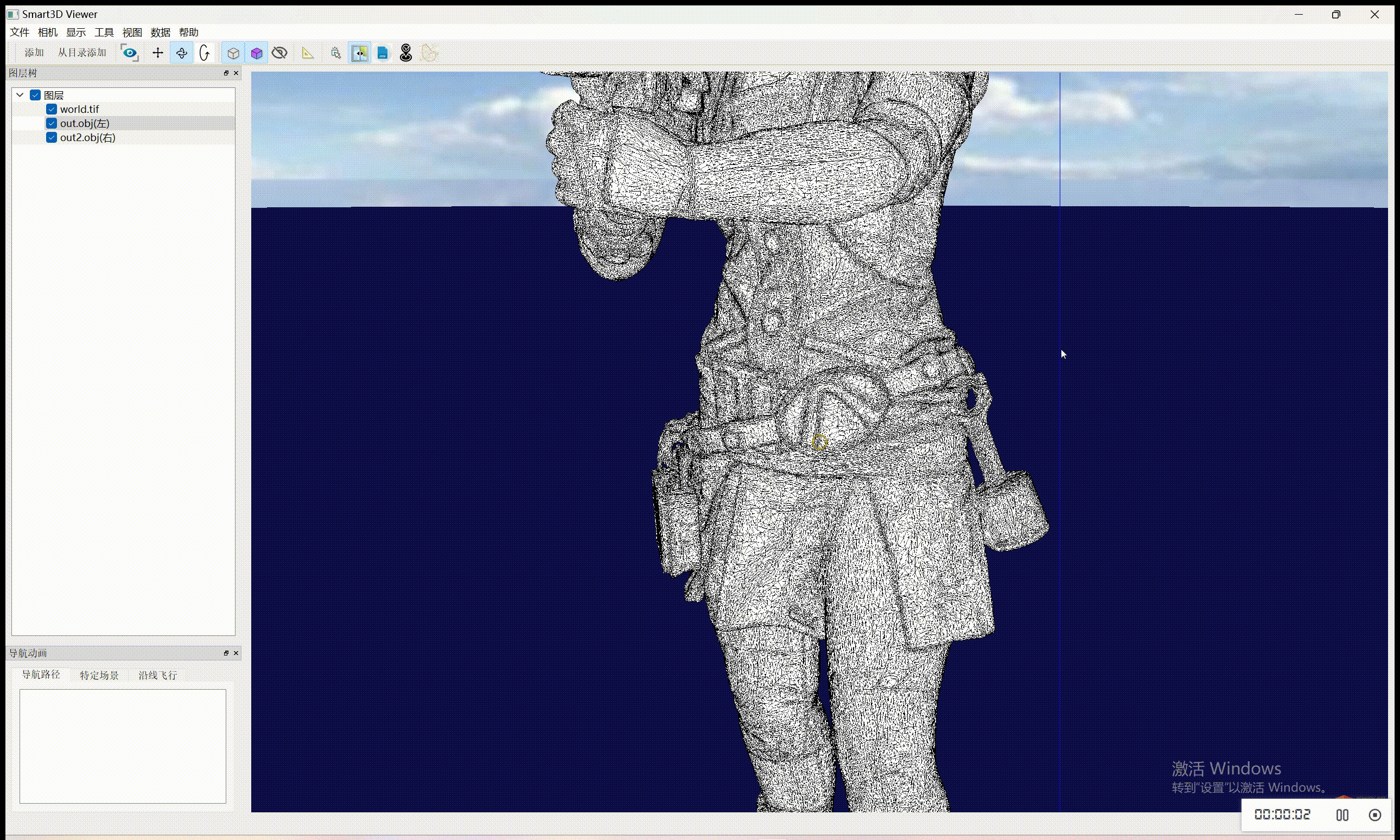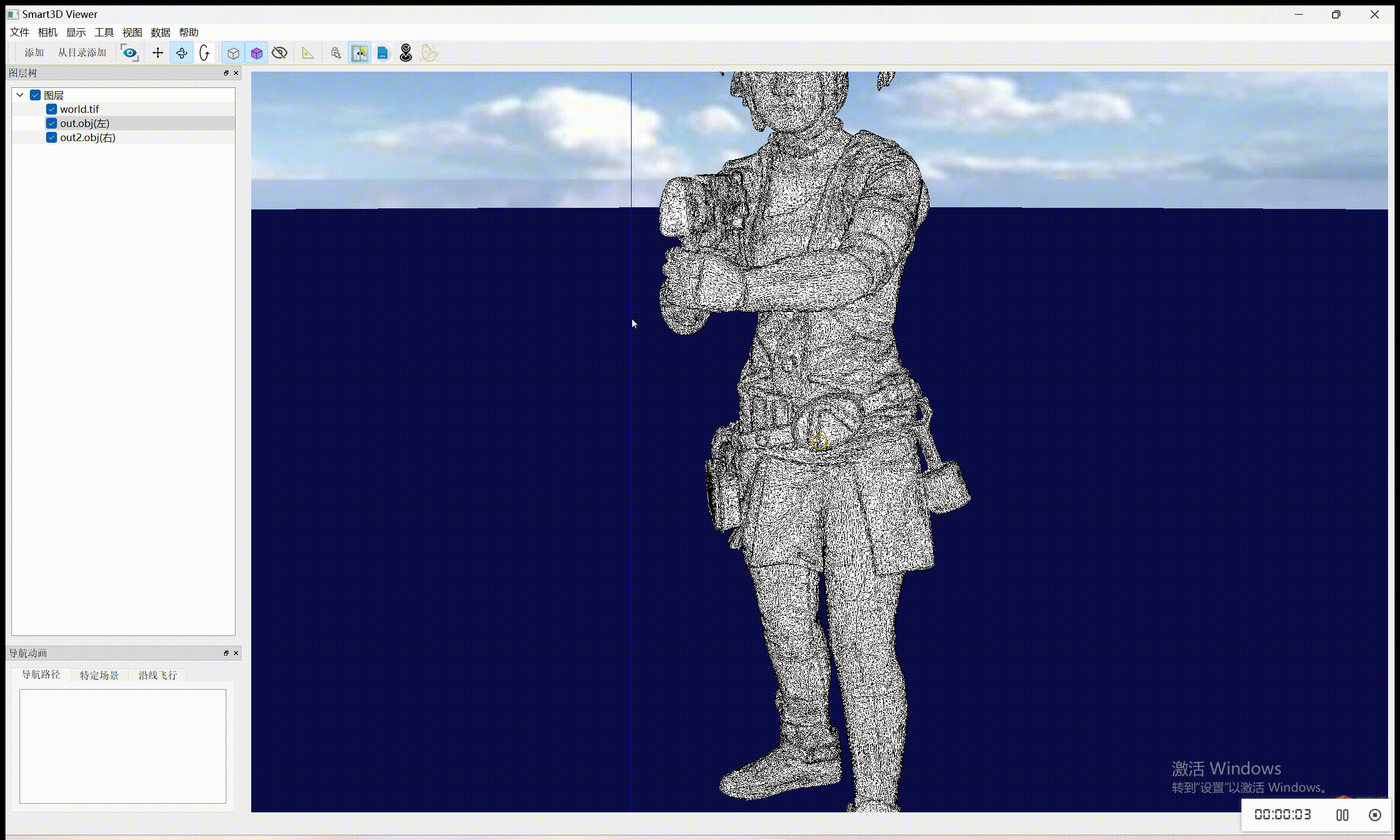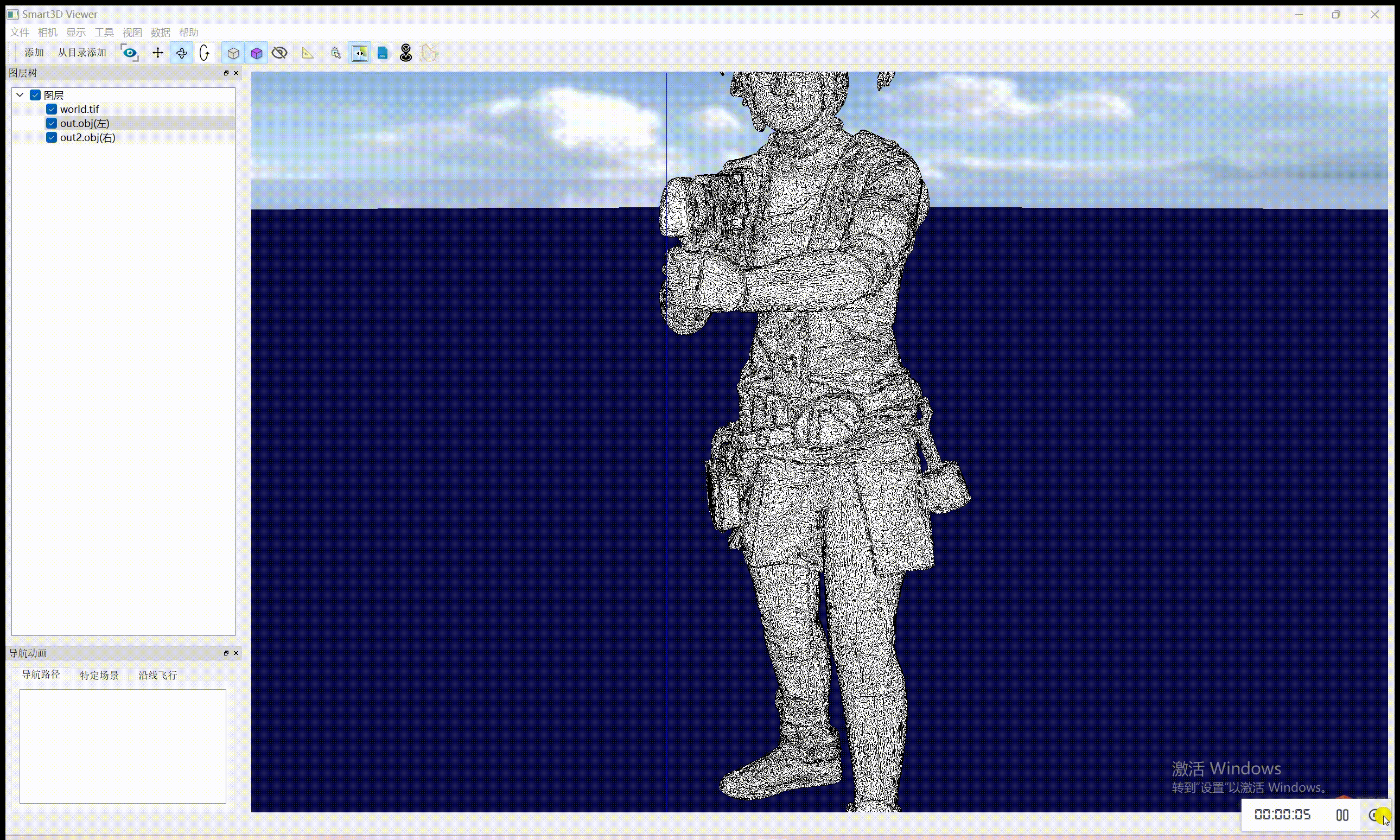
至于实现纹理贴图自动更新,需要自己额外实现塌陷策略、停止的标准。目前代码是已经有一部分了,还需要完善,后续会更新。
在简化前记录纹理坐标:在开始网格简化之前,记录下每个顶点的纹理坐标。
自定义边缘坍塌操作:实现一个自定义的边缘坍塌策略,在边缘坍塌的同时更新相关顶点的纹理坐标。这可能涉及计算坍塌操作中涉及的顶点的新纹理坐标。
简化网格:使用自定义策略来简化网格。
输出简化后的网格和纹理坐标:在简化过程完成后,输出简化后的网格和更新后的纹理坐标到 OBJ 文件。
参考文章:网格简化 QEM 方法详解 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
这篇关于CGAL5.4.1 边塌陷算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









