本文主要是介绍【Python】TKinter在多线程时刷新GUI的一些碎碎念,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
注:本文不讲TKinter的基本操作,以及多线程的概念,操作
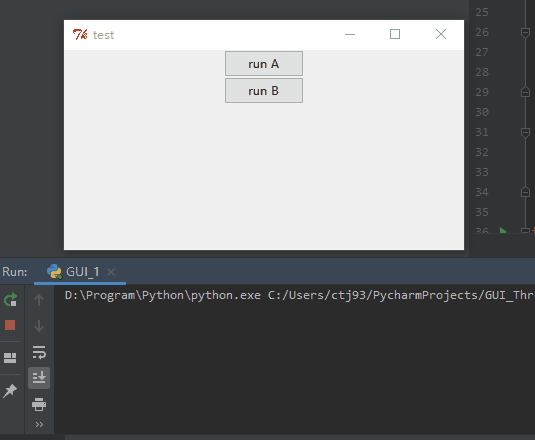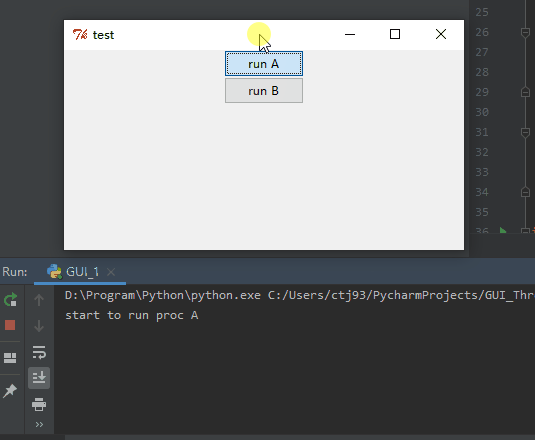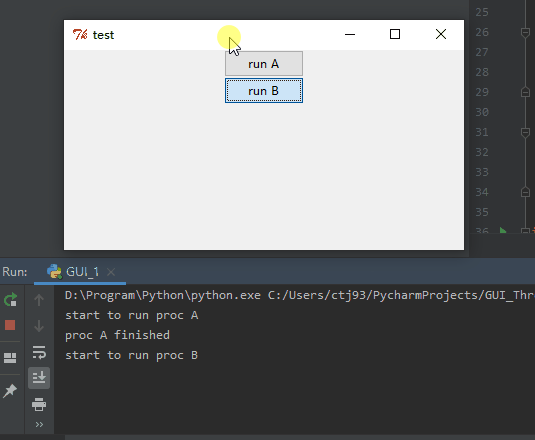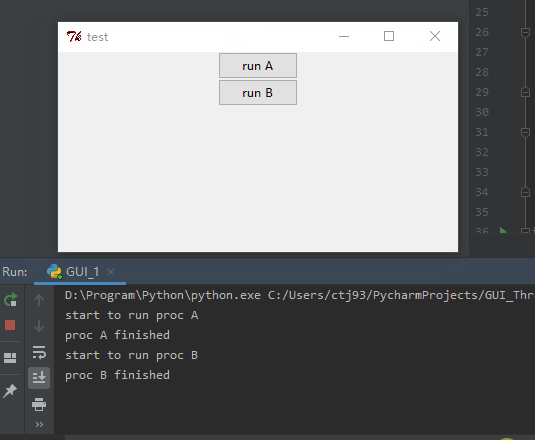
首先要讲的是一个TKinter使用时常常遇到的问题,因为TKinter自身刷新GUI是单线程的,用户在调用mainloop方法后,主线程会一直不停循环刷新GUI,但是如果用户给某个widget绑定了一个很耗时的方法A时,这个方法A也是在主线程里调用,于是这个耗时的方法A会阻塞住刷新GUI的主线程,表现就是整个GUI卡住了,只有等这个耗时的方法结束后,GUI才会对用户操作响应, 如下图Gif所示:
代码如下:
from Tkinter import *
from ttk import *
import timeclass GUI():def __init__(self, root):self.initGUI(root)def initGUI(self, root):root.title("test")root.geometry("400x200+700+500")root.resizable = Falseself.button_1 = Button(root, text="run A", width=10, command=self.A)self.button_1.pack(side="top")self.button_2 = Button(root, text="run B", width=10, command=self.B)self.button_2.pack(side="top")root.mainloop()def A(self):print "start to run proc A"time.sleep(3)print "proc A finished"def B(self):print "start to run proc B"time.sleep(3)print "proc B finished"if __name__ == "__main__":root = Tk()myGUI = GUI(root)很简单一段代码,GUI里只有两个button,分别绑定了两个耗时3秒的方法A和方法B,首先我点击了上面一个button调用方法A,在A运行期间,我又调用了方法B,可以看到在方法A运行期间,方法B并没有运行,而是等A运行完之后,才运行了方法B,而且在方法A运行过程中,整个GUI没有响应我对下面一个button的点击,而且GUI界面无法拖拽,只有两个方法结束后才拖拽起来。
最简单的解决上述问题的办法就是利用多线程,把两个耗时方法丢到两个子线程里运行,就可以避开主线程被阻塞的问题,所以对上面代码稍稍修改一下,如下所示:
from Tkinter import *
from ttk import *
import threading
import timeclass GUI():def __init__(self, root):self.initGUI(root)def initGUI(self, root):root.title("test")root.geometry("400x200+700+500")root.resizable = Falseself.button_1 = Button(root, text="run A", width=10, command=self.A)self.button_1.pack(side="top")self.button_2 = Button(root, text="run B", width=10, command=self.B)self.button_2.pack(side="top")root.mainloop()def __A(self):print "start to run proc A"time.sleep(3)print "proc A finished"def A(self):T = threading.Thread(target=self.__A)T.start()def __B(self):print "start to run proc B"time.sleep(3)print "proc B finished"def B(self):T = threading.Thread(target=self.__B)T.start()if __name__ == "__main__":root = Tk()myGUI = GUI(root)结果如下图:

可以看到,这次两个方法都可以正常运行, 而且GUI也不会卡住。
然而,事情并不会就这么简单结束了,实际应用中,我们的GUI不可能只有两个简单的Button,有时候,我们也有需要即时刷新GUI自身的情况,比如我们假设有这么一个简单的GUI程序,界面只有一个Button和一个Text,点击Button后,每隔一秒将当前时间打印到Text上,也就说,在这个程序里,我们需要动态修改widget。还是看下最简单的情况:

本来,一般理想情况下,用户点击了button之后,应该会立即能在Text里显示出当前时间,然而在这个例子里,我们可以看到,用户点击Button之后,隔了三秒,才将所有的输出一次显示出来,原因还是之前提到的, TKinter本身是单线程的,显示时间这个方法耗时3秒,会卡住主线程,主线程在这三秒内去执行显示时间的方法去了,GUI不会立即刷新,代码如下:
from Tkinter import *
from ttk import *
import threading
import time
import sysdef fmtTime(timeStamp):timeArray = time.localtime(timeStamp)dateTime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeArray)return dateTimeclass re_Text():def __init__(self, widget):self.widget = widgetdef write(self, content):self.widget.insert(INSERT, content)self.widget.see(END)class GUI():def __init__(self, root):self.initGUI(root)def initGUI(self, root):root.title("test")root.geometry("400x200+700+500")root.resizable = Falseself.button = Button(root, text="click", width=10, command=self.show)self.button.pack(side="top")self.scrollBar = Scrollbar(root)self.scrollBar.pack(side="right", fill="y")self.text = Text(root, height=10, width=45, yscrollcommand=self.scrollBar.set)self.text.pack(side="top", fill=BOTH, padx=10, pady=10)self.scrollBar.config(command=self.text.yview)sys.stdout = re_Text(self.text)root.mainloop()def show(self):i = 0while i < 3:print fmtTime(time.time())time.sleep(1)i += 1if __name__ == "__main__":root = Tk()myGUI = GUI(root)上面这段代码的GUI里只有一个button和一个Text,我将标准输出stdout重定向到了一个自定义的类里,这个类的write方法可以更改Text的内容,具体就不细说了,如果对重定向标准输出还不了解的,可以自行百度或者Google。
这个时候,如果对Tkinter不熟悉的同学肯定会想,我把上面代码里的show方法丢到子线程里去跑,不就可以解决这个问题了,那我们就先尝试一下,再改一改代码:
from Tkinter import *
from ttk import *
import threading
import time
import sysdef fmtTime(timeStamp):timeArray = time.localtime(timeStamp)dateTime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeArray)return dateTimeclass re_Text():def __init__(self, widget):self.widget = widgetdef write(self, content):self.widget.insert(INSERT, content)self.widget.see(END)class GUI():def __init__(self, root):self.initGUI(root)def initGUI(self, root):root.title("test")root.geometry("400x200+700+500")root.resizable = Falseself.button = Button(root, text="click", width=10, command=self.show)self.button.pack(side="top")self.scrollBar = Scrollbar(root)self.scrollBar.pack(side="right", fill="y")self.text = Text(root, height=10, width=45, yscrollcommand=self.scrollBar.set)self.text.pack(side="top", fill=BOTH, padx=10, pady=10)self.scrollBar.config(command=self.text.yview)sys.stdout = re_Text(self.text)root.mainloop()def __show(self):i = 0while i < 3:print fmtTime(time.time())time.sleep(1)i += 1def show(self):T = threading.Thread(target=self.__show, args=())T.start()if __name__ == "__main__":root = Tk()myGUI = GUI(root)运行结果如下:

难道成了?看起来这段代码确实完美满足了我们的要求,GUI没有阻塞。但是这里还是存在两个问题,(1):上述代码里,利用子线程去更新Text是不安全的,因为可能存在不同线程同时修改Text的情况,这样可能导致打印出来的内容直接混乱掉。(2):上述代码可能会直接报错,这个应该和TCL版本有关,我自己就遇到了在Windows下可以运行,但centos下会报错的情况。 而且另外题外话,在Google,Stackoverflow上基本都是不推荐子线程里更新GUI。
目前,比较好的解决GUI阻塞,而且不在子线程里更新GUI的办法,还是利用python自带的队列Queue,以及Tkinter下面的after方法。
首先说下Queue这个class,Queue是python自带的一个队列class,其应用遵循着先入先出的原则。利用Queue.put方法将元素推进Queue里,再利用Queue.get方法将元素取出,最先推进去的元素会被最先取出。看下面的例子:
import Queue
import timequeue = Queue.Queue()
for i in range(0, 4):time.sleep(0.5)element = "element %s"%iprint "put %s"%elementqueue.put(element)while not queue.empty():time.sleep(0.5)print "get %s"%queue.get()结果如下:

可以看到,element1-element4依次被推进Queue,然后get方法会将最先取出“最先放进去的”元素
然后讲下after方法,TKinter的TK类下有个after方法,其实大部分控件都有这个after方法, 这个方法是个定时方法,用途是GUI启动后定时执行一个方法,如果我们在被after调用的方法里再次调用这个after方法, 就可以实现一个循环效果,但这个循环不像while那样会阻塞住主线程。代码如下:
from Tkinter import *
from ttk import *class GUI():def __init__(self, root):self.initGUI(root)def loop(self):print "loop proc running"self.root.after(1000, self.loop)def initGUI(self, root):self.root = rootself.root.title("test")self.root.geometry("400x200+80+600")self.root.resizable = Falseself.root.after(1000, self.loop)self.root.mainloop()if __name__ == "__main__":root = Tk()myGUI = GUI(root)这段代码里,after办法调用了loop 方法,在loop里又再次调用了after方法执行自己。效果如下:

好了,知道了after方法和Queue,我们现在的思路是这样的:
(1):先把stdout映射到Queue去,所有需要print的内容全部给推到Queue里去。
(2):在GUI启动后,让after方法定时去将Queue里的内容取出来,写入Text里,如果after方法时间间隔足够短,看起来和即时刷新没什么区别。
这样一来,我们所有耗时的方法丢进子线程里执行,标准输出映射到了Queue,after方法定时从Queue里取出元素写入Text,Text由主线程更新,不会阻塞GUI的主线程,代码如下:
# coding=utf-8
from Tkinter import *
from ttk import *
import threading
import time
import sys
import Queuedef fmtTime(timeStamp):timeArray = time.localtime(timeStamp)dateTime = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", timeArray)return dateTime#自定义re_Text,用于将stdout映射到Queue
class re_Text():def __init__(self, queue):self.queue = queuedef write(self, content):self.queue.put(content)class GUI():def __init__(self, root):#new 一个Quue用于保存输出内容self.msg_queue = Queue.Queue()self.initGUI(root)#在show_msg方法里,从Queue取出元素,输出到Textdef show_msg(self):while not self.msg_queue.empty():content = self.msg_queue.get()self.text.insert(INSERT, content)self.text.see(END)#after方法再次调用show_msgself.root.after(100, self.show_msg)def initGUI(self, root):self.root = rootself.root.title("test")self.root.geometry("400x200+700+500")self.root.resizable = Falseself.button = Button(self.root, text="click", width=10, command=self.show)self.button.pack(side="top")self.scrollBar = Scrollbar(self.root)self.scrollBar.pack(side="right", fill="y")self.text = Text(self.root, height=10, width=45, yscrollcommand=self.scrollBar.set)self.text.pack(side="top", fill=BOTH, padx=10, pady=10)self.scrollBar.config(command=self.text.yview)#启动after方法self.root.after(100, self.show_msg)#将stdout映射到re_Textsys.stdout = re_Text(self.msg_queue)root.mainloop()def __show(self):i = 0while i < 3:print fmtTime(time.time())time.sleep(1)i += 1def show(self):T = threading.Thread(target=self.__show, args=())T.start()if __name__ == "__main__":root = Tk()myGUI = GUI(root)结果如下,还是一样,不会有任何阻塞主线程的情况:

值得一提的是,上述代码里重新映射stdout的写法不够pythonic,正确姿势应该是继承Queue类型,再重载write方法,比较好的写法是这样:
class re_Text(Queue.Queue):def __init__(self):Queue.Queue.__init__(self)def write(self, content):self.put(content)然后直接new一个re_Text,不需要Queue的实例去初始化,将stdout映射过去就行。
完事了,写完了,有什么错误或者建议请指正,阿里嘎多
这篇关于【Python】TKinter在多线程时刷新GUI的一些碎碎念的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





