本文主要是介绍Theano-Deep Learning Tutorials 笔记:Recurrent Neural Networks with Word Embeddings,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
教程地址:http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/rnnslu.html
相关论文:Grégoire Mesnil, Xiaodong He, Li Deng and Yoshua Bengio - Investigation of Recurrent Neural Network Architectures and Learning Methods for Spoken Language Understanding
Grégoire Mesnil, Yann Dauphin, Kaisheng Yao, Yoshua Bengio, Li Deng, Dilek Hakkani-Tur, Xiaodong He, Larry Heck, Gokhan Tur, Dong Yu and Geoffrey Zweig - Using Recurrent Neural Networks for Slot Filling in Spoken Language Understanding
Task
The Slot-Filling (Spoken Language Understanding)是给句子中每个word分配标签,是一个分类问题。
Dataset
数据集是DARPA的一个小型数据集:ATIS (Airline Travel Information System),下面例子使用了Inside Outside Beginning (IOB) representation。
| Input (words) | show | flights | from | Boston | to | New | York | today |
| Output (labels) | O | O | O | B-dept | O | B-arr | I-arr | B-date |
数据集中训练集句子4978个,word 56590个;测试集句子893,word 9198个;平均句长 15;The number of classes (different slots) is 128 including the O label (NULL).
As Microsoft Research people,把训练集中只出现一次的word标记为<UNK>,用这个标记去代表测试集中没见过的word;As Ronan Collobert and colleagues,把数字序列换成 DIGIT,如1984 变成 DIGITDIGITDIGITDIGIT。
把训练集分80%为训练集,20%为验证集。当F1 score为95%时,小数据集对性能的影响会大于0.6%。详见Microsoft Research people。
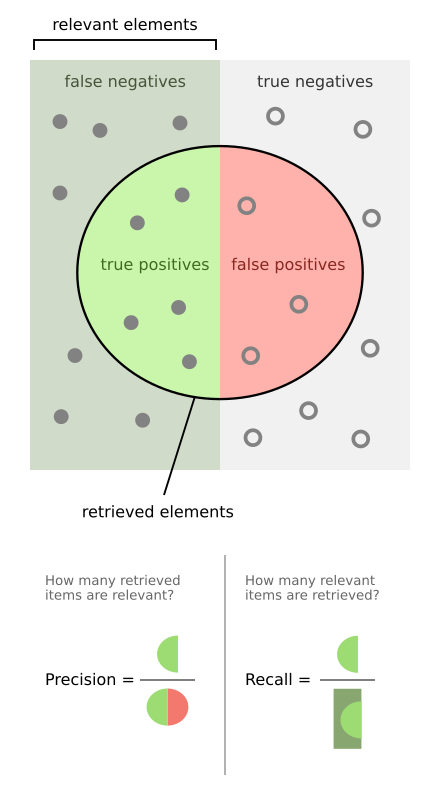
下面有3个实验评价指标:Precision,Recall,F1 score;
前两个看下图很好理解,在模式识别领域,一般都指定recall为多少情况下,比较precision的好坏。F1 score是根据Precision和Recall计算的。
教程使用conlleval PERL script(是一个计算上述指标的脚本代码)来评价性能。
Recurrent Neural Network Model
Raw input encoding
每个word对应一个token。在ATIS字典中,每个token对应一个index。每个句子都是一个index(int32)的数组。每个set(训练集,测试集,验证集)是 list of arrays of indexes(list是python的list)。python字典用来把 indexes 映射到 words 。
>>> sentence
array([383, 189, 13, 193, 208, 307, 195, 502, 260, 539,
7, 60, 72, 8, 350, 384], dtype=int32)
>>> map(lambda x: index2word[x], sentence)
['please', 'find', 'a', 'flight', 'from', 'miami', 'florida',
'to', 'las', 'vegas', '<UNK>', 'arriving', 'before', 'DIGIT', "o'clock", 'pm']
map(function, iterable, ...) 第一个参数为函数,第二个参数为输入。
就是对 iterable 中每个元素都运行 function 函数,最后返回 list(list中为每个元素的函数运行结果)。
>>> def add100(x):
... return x+100
...
>>> hh = [11,22,33]
>>> map(add100,hh)
[111, 122, 133]
本例子中 function为add100,iterable为hh。hh中每个元素都加了100,然后返回 list。
lambda x: index2word[x] 这句是一个单行函数,所以对应map参数中的function。用 lambda 可以省去定义函数的过程(一般的定义就是用def....),代码更简洁。
所以map(lambda x: index2word[x], sentence)功能就是对sentence中每个数,都调用 index2word[x] 找出其对应的word。
同样地,通过 index 得出 label:
>>> labels
array([126, 126, 126, 126, 126, 48, 50, 126, 78, 123, 81, 126, 15,
14, 89, 89], dtype=int32)
>>> map(lambda x: index2label[x], labels)
['O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'O', 'B-fromloc.city_name', 'B-fromloc.state_name',
'O', 'B-toloc.city_name', 'I-toloc.city_name', 'B-toloc.state_name',
'O', 'B-arrive_time.time_relative', 'B-arrive_time.time',
'I-arrive_time.time', 'I-arrive_time.time']
Context window
context window 就是根据指定的 window size (1,3,5...)把句子中的每个word及其前后(1,3,5...个)word提取出来。
返回结果为 list of list of indexes。
def contextwin(l, win):
'''
win :: int corresponding to the size of the window
given a list of indexes composing a sentence
l :: array containing the word indexes
it will return a list of list of indexes corresponding
to context windows surrounding each word in the sentence
'''
assert (win % 2) == 1
assert win >= 1
l = list(l)
lpadded = win // 2 * [-1] + l + win // 2 * [-1]
out = [lpadded[i:(i + win)] for i in range(len(l))]
assert len(out) == len(l)
return out
index -1 是word在句子开头结尾时,出现前面或后面没有word 这种情况就填上 -1。
看下面这个例子就很清楚: 其中0,1,2,3,4 为word的index。
>>> x
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=int32)
>>> contextwin(x, 3)
[[-1, 0, 1],
[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 2, 3, 4],
[ 3, 4,-1]]
>>> contextwin(x, 7)
[[-1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3],
[-1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,-1],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,-1,-1],
[ 1, 2, 3, 4,-1,-1,-1]]
上面这个matrix中,每行表示一个 word 的context window。
Word embeddings
现在我们得到了contex windows,是一个 indexes 的矩阵,每个元素是一个index,对应一个 word(通过index2word可以得出word)。
现在需要把 index 转换成 embeddings (对应每个 word 的实数向量)。
import theano, numpy
from theano import tensor as T
# nv :: size of our vocabulary
# de :: dimension of the embedding space
# cs :: context window size
nv, de, cs = 1000, 50, 5
embeddings = theano.shared(0.2 * numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, \
(nv+1, de)).astype(theano.config.floatX)) # add one for PADDING at the end
idxs = T.imatrix() # as many columns as words in the context window and as many lines as words in the sentence
x = self.emb[idxs].reshape((idxs.shape[0], de*cs))
x为一个矩阵,大小为(句子中单词数,de 乘以 cs)。
例子: 句子中单词数为 5,de 为 50 ,cs 为 7,所以结果矩阵大小为(5,50*7)
>>> sample
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=int32)
>>> csample = contextwin(sample, 7)
[[-1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3],
[-1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,-1],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,-1,-1],
[ 1, 2, 3, 4,-1,-1,-1]]
>>> f = theano.function(inputs=[idxs], outputs=x)
>>> f(csample)
array([[-0.08088442, 0.08458307, 0.05064092, ..., 0.06876887,
-0.06648078, -0.15192257],
[-0.08088442, 0.08458307, 0.05064092, ..., 0.11192625,
0.08745284, 0.04381778],
[-0.08088442, 0.08458307, 0.05064092, ..., -0.00937143,
0.10804889, 0.1247109 ],
[ 0.11038255, -0.10563177, -0.18760249, ..., -0.00937143,
0.10804889, 0.1247109 ],
[ 0.18738101, 0.14727569, -0.069544 , ..., -0.00937143,
0.10804889, 0.1247109 ]], dtype=float32)
>>> f(csample).shape
(5, 350)
这个matrix 是 context window word embeddings 序列。
每行为一个向量,对应句子中一个 word,现在很容易应用RNN了。
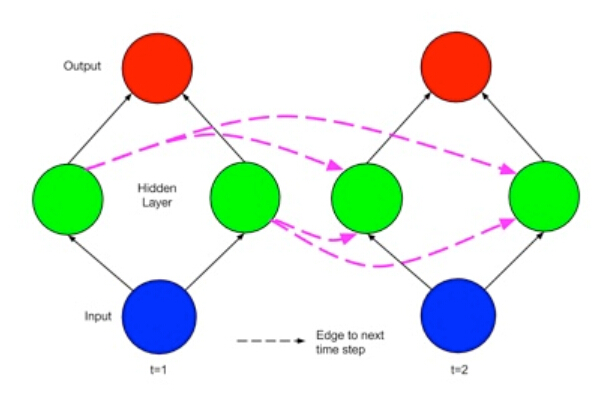
Elman recurrent neural network
(Elman) recurrent neural network (E-RNN)把当前时刻(time t)的输入以及前一时刻(time t-1)的隐藏层状态作为输入。
上节中的矩阵,每行就代表一个时刻 time t。第0行对应 t=0,第一行对应 t=1......。
E-RNN中需要学习的参数如下:
- the word embeddings (real-valued matrix)
- the initial hidden state (real-value vector)
- two matrices for the linear projection of the input
tand the previous hidden layer statet-1(神经网络中的权重W) - (optional) bias. Recommendation: don’t use it.
- softmax classification layer on top
超参数如下:
- dimension of the word embedding(de,50)
- size of the vocabulary
- number of hidden units
- number of classes
- random seed + way to initialize the model
class RNNSLU(object): ''' elman neural net model ''' def __init__(self, nh, nc, ne, de, cs): ''' nh :: dimension of the hidden layer nc :: number of classes ne :: number of word embeddings in the vocabulary de :: dimension of the word embeddings cs :: word window context size ''' # parameters of the model self.emb = theano.shared(name='embeddings', value=0.2 * numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, (ne+1, de)) # add one for padding at the end .astype(theano.config.floatX)) self.wx = theano.shared(name='wx', value=0.2 * numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, (de * cs, nh)) .astype(theano.config.floatX)) self.wh = theano.shared(name='wh', value=0.2 * numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, (nh, nh)) .astype(theano.config.floatX)) self.w = theano.shared(name='w', value=0.2 * numpy.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, (nh, nc)) .astype(theano.config.floatX)) self.bh = theano.shared(name='bh', value=numpy.zeros(nh, dtype=theano.config.floatX)) self.b = theano.shared(name='b', value=numpy.zeros(nc, dtype=theano.config.floatX)) self.h0 = theano.shared(name='h0', value=numpy.zeros(nh, dtype=theano.config.floatX)) # bundle self.params = [self.emb, self.wx, self.wh, self.w, self.bh, self.b, self.h0]ne=nv (size of our vocabulary,1000)?
emb大小为(ne+1,de)每行对应vocabulary中一个word,表明如何把这个word转换成一个de维的向量。emb这个matrix也是需要在训练中学习的。
通过embedding matrix得出输入:
idxs = T.imatrix() x = self.emb[idxs].reshape((idxs.shape[0], de*cs)) y_sentence = T.ivector('y_sentence') # labels
用 scan (theano带的)来实现 递归:def recurrence(x_t, h_tm1): h_t = T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(x_t, self.wx) + T.dot(h_tm1, self.wh) + self.bh) s_t = T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(h_t, self.w) + self.b) return [h_t, s_t] [h, s], _ = theano.scan(fn=recurrence, sequences=x, outputs_info=[self.h0, None], n_steps=x.shape[0]) p_y_given_x_sentence = s[:, 0, :] y_pred = T.argmax(p_y_given_x_sentence, axis=1)
Theano自动计算梯度,最大化 log-likelihood:(这里和教程给的代码其实不一样,代码中损失函数,训练都是用的句子中最后一个词,这里给出的是整个句子,如 p_y_given_x_lastword = s[-1,0,:],-1表示取末尾)lr = T.scalar('lr') sentence_nll = -T.mean(T.log(p_y_given_x_sentence) [T.arange(x.shape[0]), y_sentence]) sentence_gradients = T.grad(sentence_nll, self.params) sentence_updates = OrderedDict((p, p - lr*g) for p, g in zip(self.params, sentence_gradients))分类,训练函数:
self.classify = theano.function(inputs=[idxs], outputs=y_pred) self.sentence_train = theano.function(inputs=[idxs, y_sentence, lr], outputs=sentence_nll, updates=sentence_updates)
为了保证 word embeddings(50维向量) 在单位球上,需在每次更新后归一化:self.normalize = theano.function(inputs=[], updates={self.emb: self.emb / T.sqrt((self.emb**2) .sum(axis=1)) .dimshuffle(0, 'x')})
Training
Updates
使用随机梯度下降,一个句子为一个minibatch,每一个句子更新一次参数。每次更新后,都要对 word embeddings 归一化。
Stopping Criterion
Early-stoppong,按给定数量的epochs训练,每次epoch后都在验证集上测试 F1 score,保留最佳模型。
Hyper-Parameter Selection
使用 KISS random search。
超参如下:
- learning rate : uniform([0.05,0.01])
- window size : random value from {3,...,19}
- number of hidden units : random value from {100,200}
- embedding dimension : random value from {50,100}
Word Embedding Nearest Neighbors
教程目的是用RNN做 word embedding,就是如何把 word 变成向量更好,通过训练,不断更新emb参数矩阵,最终得出结果。
通过 L2 (欧氏距离)距离 和 cosine 距离两种方式判断 word 间的相似度,两种方式结果一样,k近邻如下:
由于vocabulary只有500个words,所有效果一般。atlanta back ap80 but aircraft business a august actually cheap phoenix live ap57 if plane coach people september provide weekday denver lives ap up service first do january prices weekdays tacoma both connections a airplane fourth but june stop am columbus how tomorrow now seating thrift numbers december number early seattle me before amount stand tenth abbreviation november flight sfo minneapolis out earliest more that second if april there milwaukee pittsburgh other connect abbreviation on fifth up july serving jfk ontario plane thrift restrictions turboprop third serve jfk thank shortest montreal service coach mean mean twelfth database october ticket bwi philadelphia fare today interested amount sixth passengers may are lastest
这篇关于Theano-Deep Learning Tutorials 笔记:Recurrent Neural Networks with Word Embeddings的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!