本文主要是介绍【大数据面试知识点】Spark的DAGScheduler,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Spark数据本地化是在哪个阶段计算首选位置的?
先看一下DAGScheduler的注释,可以看到DAGScheduler除了Stage和Task的划分外,还做了缓存的跟踪和首选运行位置的计算。
DAGScheduler注释:
The high-level scheduling layer that implements stage-oriented scheduling. It computes a DAG of stages for each job, keeps track of which RDDs and stage outputs are materialized, and finds a minimal schedule to run the job. It then submits stages as TaskSets to an underlying TaskScheduler implementation that runs them on the cluster. A TaskSet contains fully independent tasks that can run right away based on the data that's already on the cluster (e.g. map output files from previous stages), though it may fail if this data becomes unavailable.
Spark stages are created by breaking the RDD graph at shuffle boundaries. RDD operations with "narrow" dependencies, like map() and filter(), are pipelined together into one set of tasks in each stage, but operations with shuffle dependencies require multiple stages (one to write a set of map output files, and another to read those files after a barrier). In the end, every stage will have only shuffle dependencies on other stages, and may compute multiple operations inside it. The actual pipelining of these operations happens in the RDD.compute() functions of various RDDs
In addition to coming up with a DAG of stages, the DAGScheduler also determines the preferred locations to run each task on, based on the current cache status, and passes these to the low-level TaskScheduler. Furthermore, it handles failures due to shuffle output files being lost, in which case old stages may need to be resubmitted. Failures *within* a stage that are not caused by shuffle file loss are handled by the TaskScheduler, which will retry each task a small number of times before cancelling the whole stage.
When looking through this code, there are several key concepts:
- Jobs (represented by ActiveJob) are the top-level work items submitted to the scheduler. For example, when the user calls an action, like count(), a job will be submitted through submitJob. Each Job may require the execution of multiple stages to build intermediate data.
- Stages (Stage) are sets of tasks that compute intermediate results in jobs, where each task computes the same function on partitions of the same RDD. Stages are separated at shuffle boundaries, which introduce a barrier (where we must wait for the previous stage to finish to fetch outputs). There are two types of stages: ResultStage, for the final stage that executes an action, and ShuffleMapStage, which writes map output files for a shuffle. Stages are often shared across multiple jobs, if these jobs reuse the same RDDs.
- Tasks are individual units of work, each sent to one machine.
- Cache tracking: the DAGScheduler figures out which RDDs are cached to avoid recomputing them and likewise remembers which shuffle map stages have already produced output files to avoid redoing the map side of a shuffle.
- Preferred locations: the DAGScheduler also computes where to run each task in a stage based on the preferred locations of its underlying RDDs, or the location of cached or shuffle data.
- Cleanup: all data structures are cleared when the running jobs that depend on them finish, to prevent memory leaks in a long-running application.
To recover from failures, the same stage might need to run multiple times, which are called "attempts". If the TaskScheduler reports that a task failed because a map output file from a previous stage was lost, the DAGScheduler resubmits that lost stage. This is detected through a CompletionEvent with FetchFailed, or an ExecutorLost event. The DAGScheduler will wait a small amount of time to see whether other nodes or tasks fail, then resubmit TaskSets for any lost stage(s) that compute the missing tasks. As part of this process, we might also have to create Stage objects for old (finished) stages where we previously cleaned up the Stage object. Since tasks from the old attempt of a stage could still be running, care must be taken to map any events received in the correct Stage object.
Here's a checklist to use when making or reviewing changes to this class:
- All data structures should be cleared when the jobs involving them end to avoid indefinite accumulation of state in long-running programs.
- When adding a new data structure, update DAGSchedulerSuite.assertDataStructuresEmpty to include the new structure. This will help to catch memory leaks.
DAGScheduler的运行时机
DAGScheduler运行时机:Driver端初始化SparkContext时。DAGScheduler是在整个Spark Application的入口即 SparkContext中声明并实例化的。在实例化DAGScheduler之前,巳经实例化了SchedulerBackend和底层调度器 TaskScheduler。
如果是SQL任务的话,SparkSQL通过Catalyst(Spark SQL的核心是Catalyst优化器)将SQL先翻译成逻辑计划再翻译成物理计划,再转换成RDD的操作。之后运行时再通过DAGScheduler做RDD任务的划分和调度。
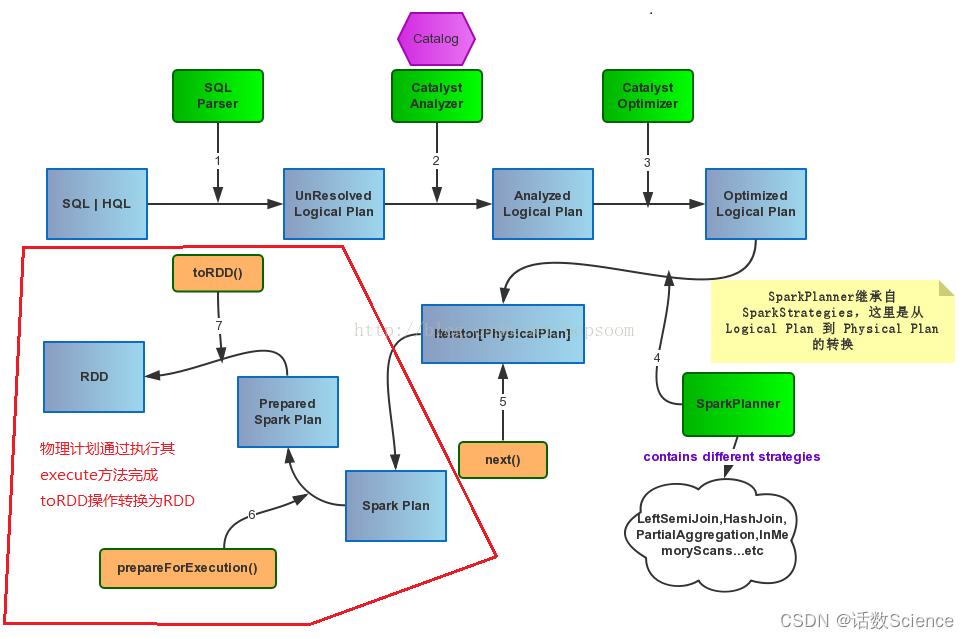
DAGScheduler如何划分Stage的?
用户提交的计算任务是一个由RDD依赖构成的DAG,Spark会把RDD的依赖以shuffle依赖为边界划分成多个Stage,这些Stage之间也相互依赖,形成了Stage的DAG。然后,DAGScheduler会按依赖关系顺序执行这些Stage。
要是把RDD依赖构成的DAG看成是逻辑执行计划(logic plan),那么,可以把Stage看成物理执行计划,为了更好的理解这个概念,我们来看一个例子。
下面的代码用来对README.md文件中包含整数值的单词进行计数,并打印RDD之间的依赖关系(Lineage):
scala> val counts = sc.textFile("README.md").flatMap(x=>x.split("\\W+")).filter(_.matches(".*\\d.*")).map(x=>(x,1)).reduceByKey(_+_)// 调用一个action函数,用来触发任务的提交和执行scala> counts.collect()// 打印RDD的依赖关系(Lineage)scala> counts.toDebugStringres7: String =(2) ShuffledRDD[17] at reduceByKey at <console>:24 []+-(2) MapPartitionsRDD[16] at map at <console>:24 []| MapPartitionsRDD[15] at filter at <console>:24 []| MapPartitionsRDD[14] at flatMap at <console>:24 []| README.md MapPartitionsRDD[13] at textFile at <console>:24 []| README.md HadoopRDD[12] at textFile at <console>:24 []DAGScheduler会根据Shuffle划分前后两个Stage:即StageShuffleMapStage和ResultStage
ShuffleMapStage
先看下ShuffleMapStage的注释,核心就是再讲ShuffleMapStage是做ShuffleWrite的Stage,Stage中是算子的pipline。
ShuffleMapStages are intermediate stages in the execution DAG that produce data for a shuffle.
They occur right before each shuffle operation, and might contain multiple pipelined operations before that (e.g. map and filter). When executed, they save map output files that can later be fetched by reduce tasks. The `shuffleDep` field describes the shuffle each stage is part of, and variables like `outputLocs` and `numAvailableOutputs` track how many map outputs are ready.
ShuffleMapStages can also be submitted independently as jobs with DAGScheduler.submitMapStage.
For such stages, the ActiveJobs that submitted them are tracked in `mapStageJobs`. Note that there can be multiple ActiveJobs trying to compute the same shuffle map stage.
ShuffleMapStages是在DAG执行过程中产生的Stage,用来为Shuffle产生数据。ShuffleMapStages发生在每个Shuffle操作之前,在Shuffle之前可能有多个窄转换操作,比如:map,filter,这些操作可以形成流水线(pipeline)。当执行ShuffleMapStages时,会产生Map的输出文件,这些文件会被随后的Reduce任务使用。
ShuffleMapStages也可以作为Jobs,通过DAGScheduler.submitMapStage函数单独进行提交。对于这样的Stages,会在变量mapStageJobs中跟踪提交它们的ActiveJobs。 要注意的是,可能有多个ActiveJob尝试计算相同的ShuffleMapStages。
它为一个shuffle过程产生map操作的输出文件。它也可能是自适应查询规划/自适应调度工作的最后阶段。
ResultStage
再看ResultStage的注释
ResultStages apply a function on some partitions of an RDD to compute the result of an action.
The ResultStage object captures the function to execute, `func`, which will be applied to each partition, and the set of partition IDs, `partitions`. Some stages may not run on all partitions of the RDD, for actions like first() and lookup().
ResultStage是Job的最后一个Stage,该Stage是基于执行action函数的rdd来创建的。该Stage用来计算一个action操作的结果。该类的声明如下:
private[spark] class ResultStage(id: Int,rdd: RDD[_],val func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,val partitions: Array[Int],parents: List[Stage], //依赖的父StagefirstJobId: Int,callSite: CallSite)extends Stage(id, rdd, partitions.length, parents, firstJobId, callSite) {为了计算action操作的结果,ResultStage会在目标RDD的一个或多个分区上使用函数:func。需要计算的分区id集合保存在成员变量:partitions中。但对于有些action操作,比如:first(),take()等,函数:func可能不会在所有分区上使用。
另外,在提交Job时,会先创建ResultStage。但在提交Stage时,会先递归找到该Stage依赖的父级Stage,并先提交父级Stage。如下图所示:

举个例子:
思考题
如下rdd运算,为什么最终只划分了3个Stage
scala> val rdd1 = sc.textFile("/root/tmp/a.txt",3).flatMap(x=>x.split(",")).map(x=>(x,1)).reduceByKey((a,b)=>a+b)
val rdd1: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Int)] = ShuffledRDD[4] at reduceByKey at <console>:1scala> val rdd2 = sc.textFile("/root/tmp/a.txt",3).flatMap(_.split(",")).map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_+_)
val rdd2: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Int)] = ShuffledRDD[9] at reduceByKey at <console>:1scala> val rdd3 = rdd1.join(rdd2)
val rdd3: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, (Int, Int))] = MapPartitionsRDD[12] at join at <console>:1scala> val rdd4 = rdd3.groupByKey()
val rdd4: org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD[(String, Iterable[(Int, Int)])] = MapPartitionsRDD[13] at groupByKey at <console>:1scala> rdd4.collect().foreach(println)
(c,Seq((2,2)))
(d,Seq((1,1)))
(a,Seq((2,2)))
(b,Seq((1,1)))scala> rdd4.toDebugString
val res8: String =
(3) MapPartitionsRDD[13] at groupByKey at <console>:1 []| MapPartitionsRDD[12] at join at <console>:1 []| MapPartitionsRDD[11] at join at <console>:1 []| CoGroupedRDD[10] at join at <console>:1 []| ShuffledRDD[4] at reduceByKey at <console>:1 []+-(3) MapPartitionsRDD[3] at map at <console>:1 []| MapPartitionsRDD[2] at flatMap at <console>:1 []| /root/tmp/a.txt MapPartitionsRDD[1] at textFile at <console>:1 []| /root/tmp/a.txt HadoopRDD[0] at textFile at <console>:1 []| ShuffledRDD[9] at reduceByKey at <console>:1 []+-(3) MapPartitionsRDD[8] at map at <console>:1 []| MapPartitionsRDD[7] at flatMap at <console>:1 []| /root/tmp/a.txt MapPartitionsRDD[6] at textFile at <console>:1 []| /root/t...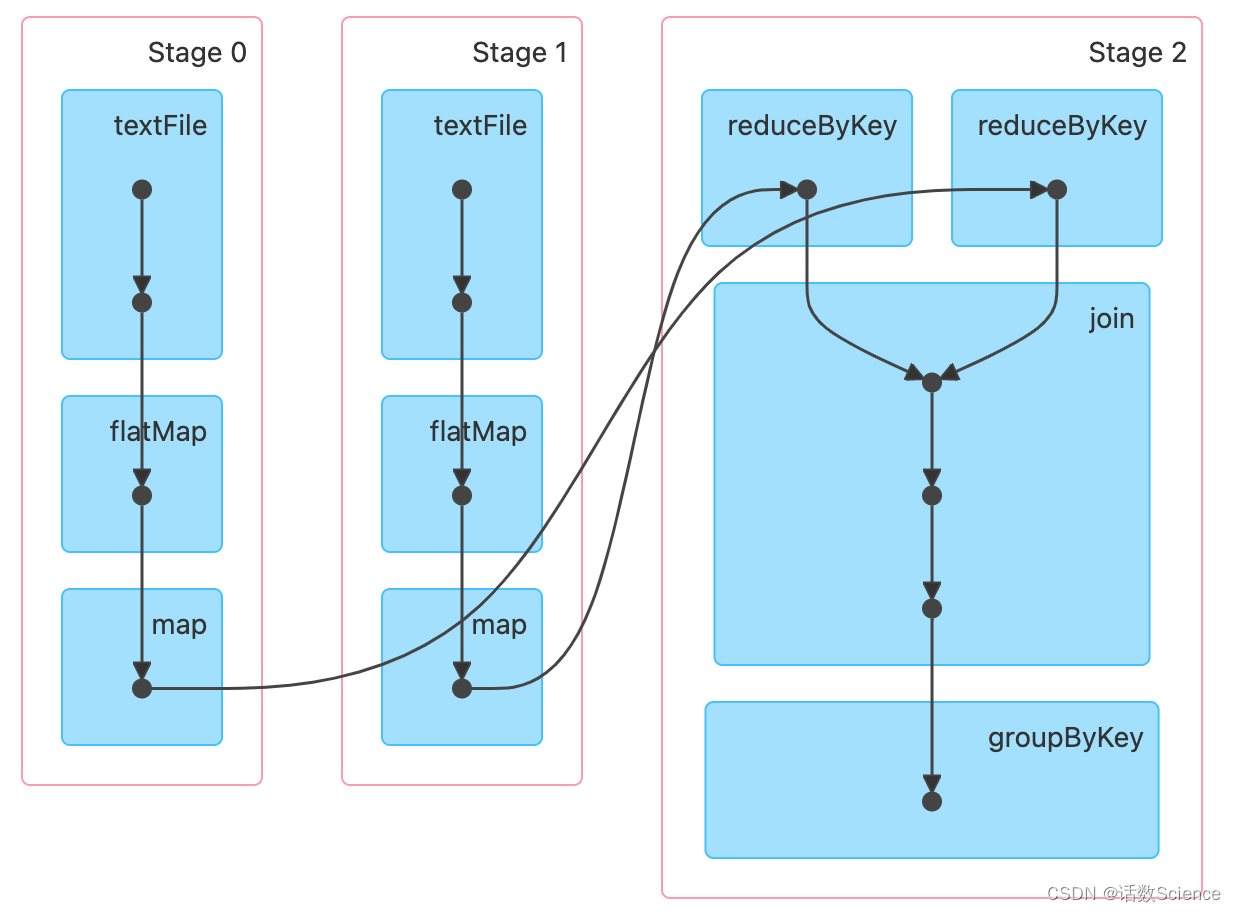
参考:DAGScheduler-Stage的划分与提交 - 知乎Spark SQL 源码分析之Physical Plan 到 RDD的具体实现_physicalplan到rdd的具体实现-CSDN博客
一文搞定Spark的DAG调度器(DAGScheduler)_spark dagscheduler-CSDN博客
这篇关于【大数据面试知识点】Spark的DAGScheduler的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




