本文主要是介绍torchaudio - Python wave 读取音频数据对比,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
torchaudio - Python wave 读取音频数据对比
1. torchaudio: an audio library for PyTorch
https://github.com/pytorch/audio
Data manipulation and transformation for audio signal processing, powered by PyTorch.
torchaudio: an audio library for PyTorch
https://github.com/pytorch/audio
The following is the corresponding torchaudio versions and supported Python versions.
torch | torchaudio | python |
|---|---|---|
master / nightly | master / nightly | >=3.6 |
1.5.0 | 0.5.0 | >=3.5 |
1.4.0 | 0.4.0 | ==2.7, >=3.5, <=3.8 |
2. torchaudio.load(filepath, out=None, normalization=True, channels_first=True, num_frames=0, offset=0, signalinfo=None, encodinginfo=None, filetype=None)
https://pytorch.org/audio/
Loads an audio file from disk into a tensor.
将音频文件从磁盘加载到张量中。
2.1 Parameters
filepath (str or pathlib.Path) – Path to audio file. - 音频文件的路径。
out (torch.Tensor, optional) – An output tensor to use instead of creating one. (Default: None) - 使用输出张量 out 而不是创建一个张量。
normalization (bool, number, or callable, optional) – If boolean True, then output is divided by 1 << 31 (assumes signed 32-bit audio), and normalizes to [-1, 1]. If number, then output is divided by that number. If callable, then the output is passed as a parameter to the given function, then the output is divided by the result. (Default: True)
channels_first (bool) – Set channels first or length first in result. (Default: True) - 返回结果中第一维度是 channels or length。
num_frames (int, optional) – Number of frames to load. 0 to load everything after the offset. (Default: 0) - 要加载的帧数。
offset (int, optional) – Number of frames from the start of the file to begin data loading. (Default: 0) - 从文件开始到开始数据加载的帧数。
signalinfo (sox_signalinfo_t, optional) – A sox_signalinfo_t type, which could be helpful if the audio type cannot be automatically determined. (Default: None) - sox_signalinfo_t 类型,如果不能自动确定音频类型,这可能会有所帮助。
encodinginfo (sox_encodinginfo_t, optional) – A sox_encodinginfo_t type, which could be set if the audio type cannot be automatically determined. (Default: None) - sox_encodinginfo_t 类型,如果不能自动确定音频类型,则可以设置。
filetype (str, optional) – A filetype or extension to be set if sox cannot determine it automatically. (Default: None) - 如果 sox 无法自动确定要设置的文件类型或扩展名。
2.2 Returns
An output tensor of size [C x L] or [L x C] where L is the number of audio frames and C is the number of channels. An integer which is the sample rate of the audio (as listed in the metadata of the file)
2.3 Return type
Tuple[torch.Tensor, int]
2.4 Example
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# yongqiang chengfrom __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_functionimport torchaudio# WAV file
audio_file = "/mnt/f/yongqiang_work/ding.wav"data, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file)
print("data.size() =", data.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data_normalized, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=True)
print("data_normalized.size() =", data_normalized.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/envs/pt-1.4_py-3.6/bin/python /home/yongqiang/pytorch_work/end2end-asr-pytorch-example/yongqiang.py
data.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100
data_normalized.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100Process finished with exit code 0
2.5 data, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=False)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# yongqiang chengfrom __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_functionimport torchaudio# WAV file
audio_file = "/mnt/f/yongqiang_work/ding.wav"data, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=False)
print("data.size() =", data.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data = data.numpy()data_normalized, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=True)
print("data_normalized.size() =", data_normalized.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data_normalized = data_normalized.numpy()/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/envs/pt-1.4_py-3.6/bin/python /home/yongqiang/pytorch_work/end2end-asr-pytorch-example/yongqiang.py
data.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100
data_normalized.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100Process finished with exit code 0



2.6 data_normalized, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=True)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# yongqiang chengfrom __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_functionimport torchaudio# WAV file
audio_file = "/mnt/f/yongqiang_work/ding.wav"data, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=False)
print("data.size() =", data.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data = data.numpy()data_normalized, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=True)
print("data_normalized.size() =", data_normalized.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data_normalized = data_normalized.numpy()print("yongqiang cheng")/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/envs/pt-1.4_py-3.6/bin/python /home/yongqiang/pytorch_work/end2end-asr-pytorch-example/yongqiang.py
data.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100
data_normalized.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100
yongqiang chengProcess finished with exit code 0

3. Python wave 读取音频数据
Python wave 读取音频数据,针对 sample width in bytes = 2 bytes,short / short int 可以表示的的最大范围是 [-32768, 32767],注意查看读取的数据。Python wave 同 torchaudio.load() 读取音频数据表示范围有区别,注意对比。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# yongqiang chengfrom __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_functionimport wave
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# WAV file
audio_file = "/mnt/f/yongqiang_work/ding.wav"
object = wave.open(audio_file, "rb")# (nchannels, sampwidth, framerate, nframes, comptype, compname)
params = object.getparams()
nchannels, sampwidth, framerate, nframes, comptype, compname = params[:6]
print("nchannels =", nchannels)
print("sampwidth =", sampwidth)
print("framerate =", framerate)
print("nframes =", nframes)
print("comptype =", comptype)
print("compname =", compname)# Returns number of audio channels (1 for mono, 2 for stereo).
print("object.getnchannels() =", object.getnchannels())# Returns sample width in bytes.
print("object.getsampwidth() =", object.getsampwidth())# Returns sampling frequency.
print("object.getframerate() =", object.getframerate())# Returns number of audio frames.
print("object.getnframes() =", object.getnframes())# Returns compression type ('NONE' is the only supported type).
print("object.getcomptype() =", object.getcomptype())# Human-readable version of getcomptype(). Usually 'not compressed' parallels 'NONE'.
print("object.getcompname() =", object.getcompname())# Reads and returns at most n frames of audio, as a bytes object.
str_data = object.readframes(nframes)
# nframes = 17504, channels = 2, sampwidth = 2
# str_data (bytes: 70016) = nframes * channels * sampwidth = 17504 * 2 * 2 = 70016
num_bytes = len(str_data) # num_bytes = 70016
print("num_bytes =", num_bytes, "bytes")
object.close()wave_data = np.fromstring(str_data, dtype=np.short)
wave_data.shape = -1, 2
wave_data = wave_data.T
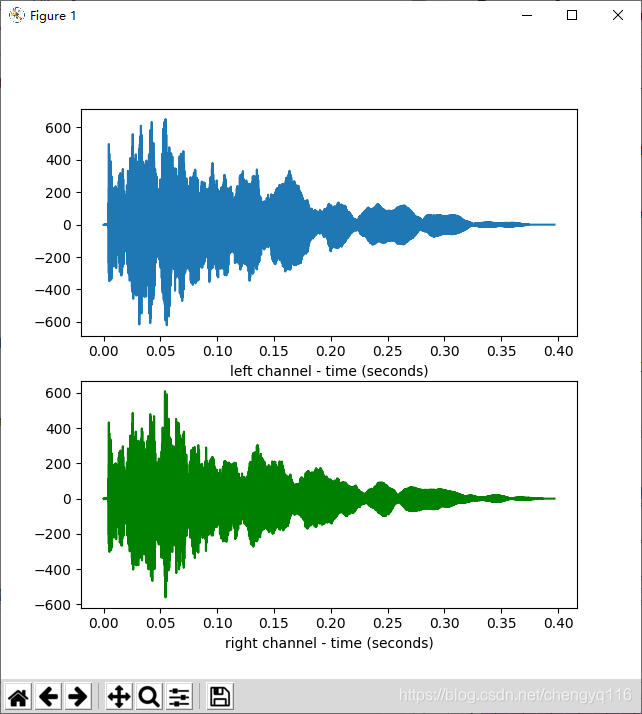
time = np.arange(0, nframes) * (1.0 / framerate)plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(time, wave_data[0])
plt.xlabel("left channel - time (seconds)")
plt.subplot(212)
plt.plot(time, wave_data[1], c="g")
plt.xlabel("right channel - time (seconds)")
plt.show()/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/envs/pt-1.4_py-3.6/bin/python /home/yongqiang/pytorch_work/end2end-asr-pytorch-example/yongqiang.py
nchannels = 2
sampwidth = 2
framerate = 44100
nframes = 17504
comptype = NONE
compname = not compressed
object.getnchannels() = 2
object.getsampwidth() = 2
object.getframerate() = 44100
object.getnframes() = 17504
object.getcomptype() = NONE
object.getcompname() = not compressed
num_bytes = 70016 bytesProcess finished with exit code 0
short / short int 可以表示的的最大范围是 [-32768, 32767]
2^15 = 32768



4. 数据对比
- torchaudio
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# yongqiang chengfrom __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_functionimport torchaudio# WAV file
audio_file = "/mnt/f/yongqiang_work/ding.wav"data, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=False)
print("data.size() =", data.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data = data.numpy()
print("data[0, 189:205] = ")
print(data[0, 189:205])
print("data[1, 189:205] = ")
print(data[1, 189:205])data_normalized, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=True)
print("data_normalized.size() =", data_normalized.size())
print("sample_rate =", sample_rate)data_normalized = data_normalized.numpy()
print("data_normalized[0, 189:205] = ")
print(data_normalized[0, 189:205])
print("data_normalized[1, 189:205] = ")
print(data_normalized[1, 189:205])print("yongqiang cheng")/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/envs/pt-1.4_py-3.6/bin/python /home/yongqiang/pytorch_work/end2end-asr-pytorch-example/yongqiang.py
data.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100
data[0, 189:205] =
[ 65536. -131072. 131072. -131072. 131072. -262144.196608. -327680. 327680. -524288. 524288. -1179648.5308416. 8847360. 196608. -19660800.]
data[1, 189:205] =
[ 0. -131072. 65536. -131072. 131072. -131072.262144. -262144. 262144. -458752. 458752. -1048576.4390912. 7602176. 327680. -16777216.]
data_normalized.size() = torch.Size([2, 17504])
sample_rate = 44100
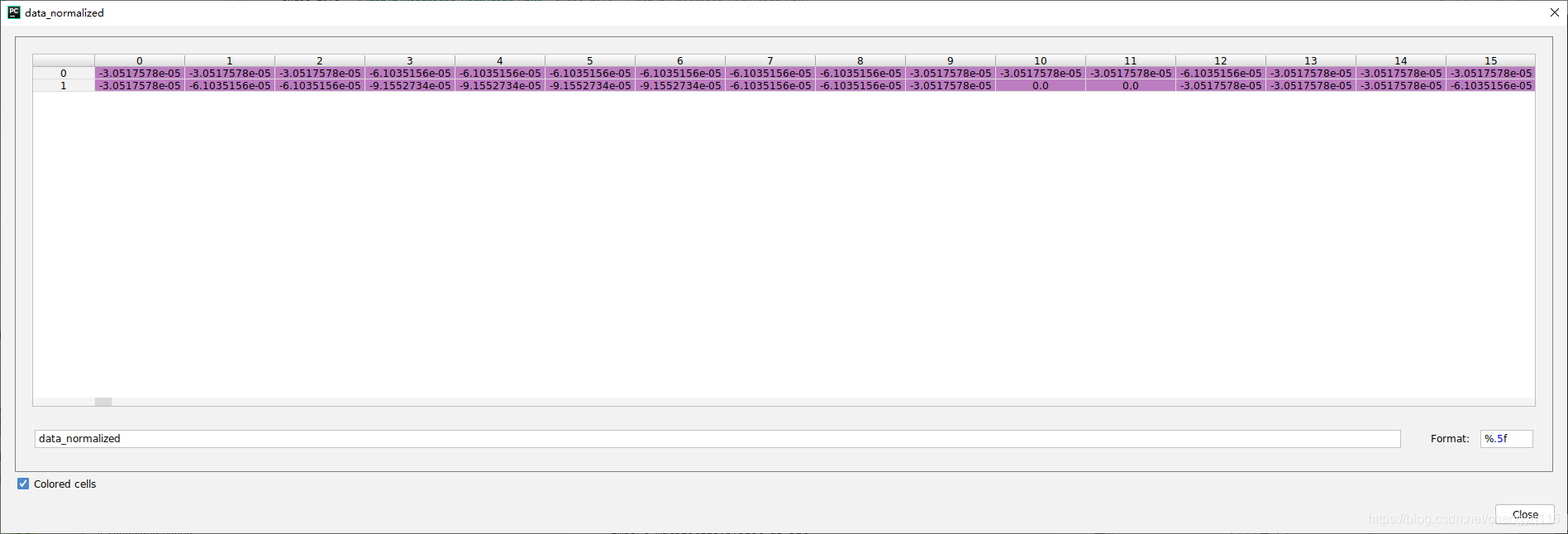
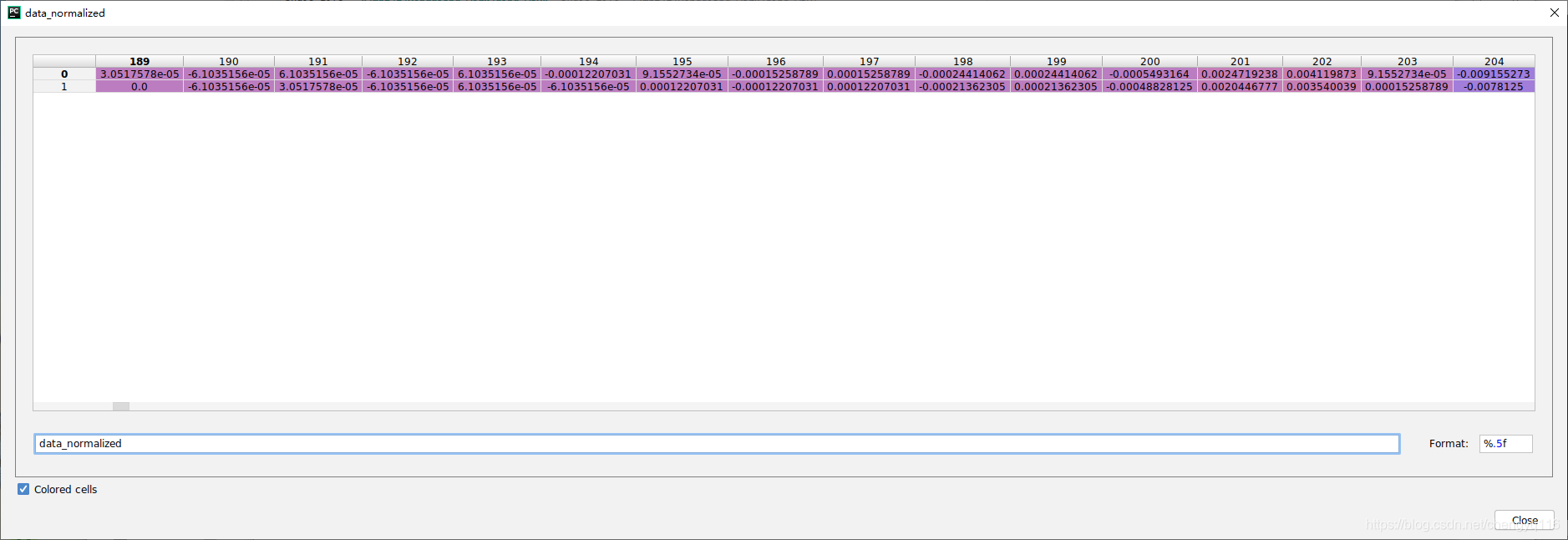
data_normalized[0, 189:205] =
[ 3.0517578e-05 -6.1035156e-05 6.1035156e-05 -6.1035156e-056.1035156e-05 -1.2207031e-04 9.1552734e-05 -1.5258789e-041.5258789e-04 -2.4414062e-04 2.4414062e-04 -5.4931641e-042.4719238e-03 4.1198730e-03 9.1552734e-05 -9.1552734e-03]
data_normalized[1, 189:205] =
[ 0.0000000e+00 -6.1035156e-05 3.0517578e-05 -6.1035156e-056.1035156e-05 -6.1035156e-05 1.2207031e-04 -1.2207031e-041.2207031e-04 -2.1362305e-04 2.1362305e-04 -4.8828125e-042.0446777e-03 3.5400391e-03 1.5258789e-04 -7.8125000e-03]
yongqiang chengProcess finished with exit code 0
- Python wave
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# yongqiang chengfrom __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_functionimport wave
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# WAV file
audio_file = "/mnt/f/yongqiang_work/ding.wav"
object = wave.open(audio_file, "rb")# (nchannels, sampwidth, framerate, nframes, comptype, compname)
params = object.getparams()
nchannels, sampwidth, framerate, nframes, comptype, compname = params[:6]
print("nchannels =", nchannels)
print("sampwidth =", sampwidth)
print("framerate =", framerate)
print("nframes =", nframes)
print("comptype =", comptype)
print("compname =", compname)# Returns number of audio channels (1 for mono, 2 for stereo).
print("object.getnchannels() =", object.getnchannels())# Returns sample width in bytes.
print("object.getsampwidth() =", object.getsampwidth())# Returns sampling frequency.
print("object.getframerate() =", object.getframerate())# Returns number of audio frames.
print("object.getnframes() =", object.getnframes())# Returns compression type ('NONE' is the only supported type).
print("object.getcomptype() =", object.getcomptype())# Human-readable version of getcomptype(). Usually 'not compressed' parallels 'NONE'.
print("object.getcompname() =", object.getcompname())# Reads and returns at most n frames of audio, as a bytes object.
str_data = object.readframes(nframes)
# nframes = 17504, channels = 2, sampwidth = 2
# str_data (bytes: 70016) = nframes * channels * sampwidth = 17504 * 2 * 2 = 70016
num_bytes = len(str_data) # num_bytes = 70016
print("num_bytes =", num_bytes, "bytes")
object.close()wave_data = np.fromstring(str_data, dtype=np.short)
wave_data.shape = -1, 2
wave_data = wave_data.T
time = np.arange(0, nframes) * (1.0 / framerate)plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(time, wave_data[0])
plt.xlabel("left channel - time (seconds)")
plt.subplot(212)
plt.plot(time, wave_data[1], c="g")
plt.xlabel("right channel - time (seconds)")
plt.show()print("wave_data[0, 189:205] = ")
print(wave_data[0, 189:205])
print("wave_data[1, 189:205] = ")
print(wave_data[1, 189:205])print("yongqiang cheng")/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/envs/pt-1.4_py-3.6/bin/python /home/yongqiang/pytorch_work/end2end-asr-pytorch-example/yongqiang.py
nchannels = 2
sampwidth = 2
framerate = 44100
nframes = 17504
comptype = NONE
compname = not compressed
object.getnchannels() = 2
object.getsampwidth() = 2
object.getframerate() = 44100
object.getnframes() = 17504
object.getcomptype() = NONE
object.getcompname() = not compressed
num_bytes = 70016 bytes
wave_data[0, 189:205] =
[ 1 -2 2 -2 2 -4 3 -5 5 -8 8 -18 81 1353 -300]
wave_data[1, 189:205] =
[ 0 -2 1 -2 2 -2 4 -4 4 -7 7 -16 67 1165 -256]
yongqiang chengProcess finished with exit code 0
4.1 data, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=False)
针对 sample width in bytes = 2 bytes,4.1 中数据为 4.3 中对应原始数据乘以 2^16 = 65536。
data[0, 189:205] =
[ 65536. -131072. 131072. -131072.131072. -262144. 196608. -327680.327680. -524288. 524288. -1179648.5308416. 8847360. 196608. -19660800.]data[1, 189:205] =
[ 0. -131072. 65536. -131072.131072. -131072. 262144. -262144.262144. -458752. 458752. -1048576.4390912. 7602176. 327680. -16777216.]
2^31 = 2147483648
2^16 = 65536
2^15 = 32768
4.2 data_normalized, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(audio_file, normalization=True)
4.2 中归一化数据为 4.1 中对应数据除以 2^31 = 2147483648。针对 sample width in bytes = 2 bytes,4.2 中数据为 4.3 中对应原始数据除以 2^(31 - 16) = 2^15 = 32768。
data_normalized[0, 189:205] =
[ 3.0517578e-05 -6.1035156e-05 6.1035156e-05 -6.1035156e-056.1035156e-05 -1.2207031e-04 9.1552734e-05 -1.5258789e-041.5258789e-04 -2.4414062e-04 2.4414062e-04 -5.4931641e-042.4719238e-03 4.1198730e-03 9.1552734e-05 -9.1552734e-03]data_normalized[1, 189:205] =
[ 0.0000000e+00 -6.1035156e-05 3.0517578e-05 -6.1035156e-056.1035156e-05 -6.1035156e-05 1.2207031e-04 -1.2207031e-041.2207031e-04 -2.1362305e-04 2.1362305e-04 -4.8828125e-042.0446777e-03 3.5400391e-03 1.5258789e-04 -7.8125000e-03]
4.3 Python wave
针对 sample width in bytes = 2 bytes,4.1 中数据为 4.3 中对应原始数据乘以 2^16 = 65536。
wave_data[0, 189:205] =
[ 1 -2 2 -22 -4 3 -55 -8 8 -1881 135 3 -300]wave_data[1, 189:205] =
[ 0 -2 1 -22 -2 4 -44 -7 7 -1667 116 5 -256]
这篇关于torchaudio - Python wave 读取音频数据对比的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





