本文主要是介绍手把手教程:RT-DETR如何训练自己的数据集 | NEU-DET钢材缺陷检测,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
🚀🚀🚀本文内容:1)RT-DETR原理介绍;2)RT-DETR如何训练自己的数据集
🚀🚀🚀RT-DETR改进创新专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/vuQTz
学姐带你学习YOLOv8,从入门到创新,轻轻松松搞定科研;
RT-DETR模型创新优化,涨点技巧分享,科研小助手;
目录
1.RT-DETR介绍
2.如何训练 RT-DETR模型
2.1数据集介绍
2.2配置NEU-DET.yaml
2.3 超参数修改ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml
2.4如何开启训练
2.5 训练正式开始
3.RT-DETR训练结果可视化分析
1.RT-DETR介绍

论文: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08069.pdf
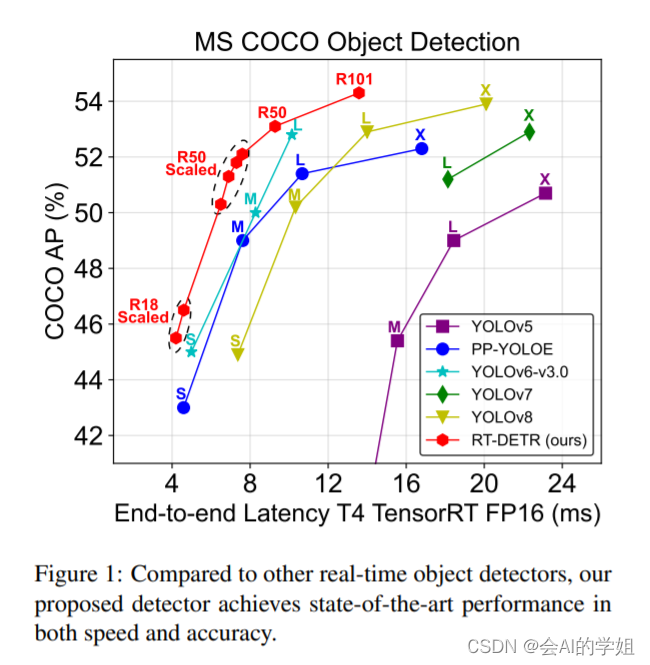
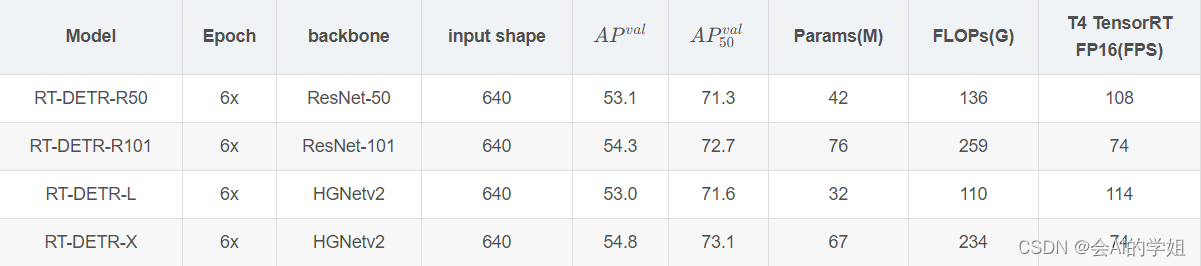
摘要: RT-DETR是第一个实时端到端目标检测器。具体而言,我们设计了一个高效的混合编码器,通过解耦尺度内交互和跨尺度融合来高效处理多尺度特征,并提出了IoU感知的查询选择机制,以优化解码器查询的初始化。此外,RT-DETR支持通过使用不同的解码器层来灵活调整推理速度,而不需要重新训练,这有助于实时目标检测器的实际应用。RT-DETR-L在COCO val2017上实现了53.0%的AP,在T4 GPU上实现了114FPS,RT-DETR-X实现了54.8%的AP和74FPS,在速度和精度方面都优于相同规模的所有YOLO检测器。RT-DETR-R50实现了53.1%的AP和108FPS,RT-DETR-R101实现了54.3%的AP和74FPS,在精度上超过了全部使用相同骨干网络的DETR检测器。
YOLO的问题点是什么?
YOLO 检测器有个较大的待改进点是需要 NMS 后处理,其通常难以优化且不够鲁棒,因此检测器的速度存在延迟。为避免该问题,我们将目光移向了不需要 NMS 后处理的 DETR,一种基于 Transformer 的端到端目标检测器。然而,相比于 YOLO 系列检测器,DETR 系列检测器的速度要慢的多,这使得"无需 NMS "并未在速度上体现出优势。上述问题促使我们针对实时的端到端检测器进行探索,旨在基于 DETR 的优秀架构设计一个全新的实时检测器,从根源上解决 NMS 对实时检测器带来的速度延迟问题。
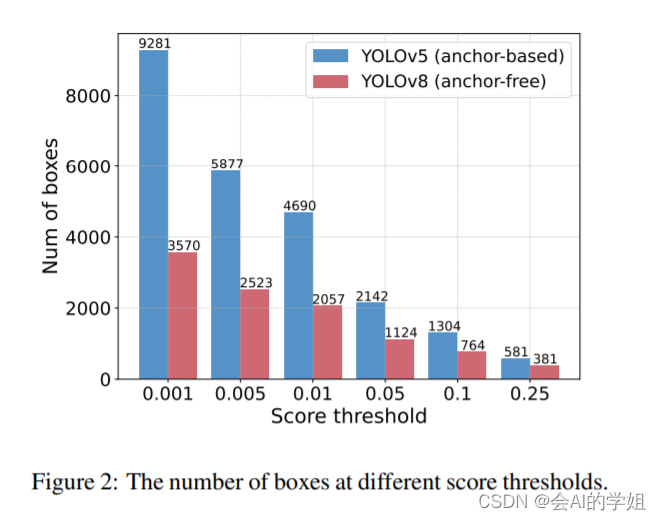
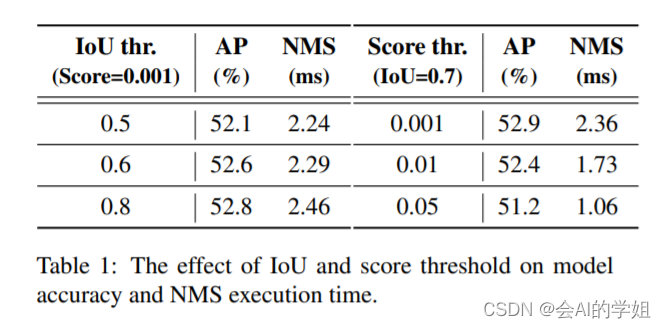
NMS 是目标检测领域常用的后处理技术,用于去除检测器产生的重叠较多的检测框,其包含两个超参数:置信度阈值和 IoU 阈值。具体来说,低于置信度阈值的框被直接过滤,并且如果两个检测框的交并比大于 IoU 阈值,那么其中置信度低的框会被滤除。该过程迭代执行,直到所有类别都被处理完毕。因此,NMS 算法的执行时间取决于预测框数量和上述两个阈值。为了更好地说明这一点,我们使用 YOLOv5 (anchor-based) 和 YOLOv8 (anchor-free) 进行了统计和实测,测量指标包括不同置信度阈值下剩余的检测框的数量,以及在不同的超参数组合下检测器在 COCO 验证集上的精度和 NMS 的执行时间。实验结果表明,NMS 不仅会延迟推理速度,并且不够鲁棒,需要挑选合适的超参数才能达到最优精度。这一实验结果有力证明设计一种实时的端到端检测器是具有重要意义的。
RT-DETR模型结构
(1)Backbone: 采用了经典的ResNet和百度自研的HGNet-v2两种,backbone是可以Scaled,HGNetv2的L和X两个版本,分别对标经典的ResNet50和ResNet101,不同于DINO等DETR类检测器使用最后4个stage输出,RT-DETR为了提速只需要最后3个,这样也符合YOLO的风格;
(2) Neck: 起名为HybridEncoder,其实是相当于DETR中的Encoder,其也类似于经典检测模型模型常用的FPN,论文里分析了Encoder计算量是比较冗余的,作者解耦了基于Transformer的这种全局特征编码,设计了AIFI (尺度内特征交互)和 CCFM(跨尺度特征融合)结合的新的高效混合编码器也就是 Efficient Hybrid Encoder ,此外把encoder_layer层数由6减小到1层,并且由几个通道维度区分L和X两个版本,配合CCFM中RepBlock数量一起调节宽度深度实现Scaled RT-DETR;
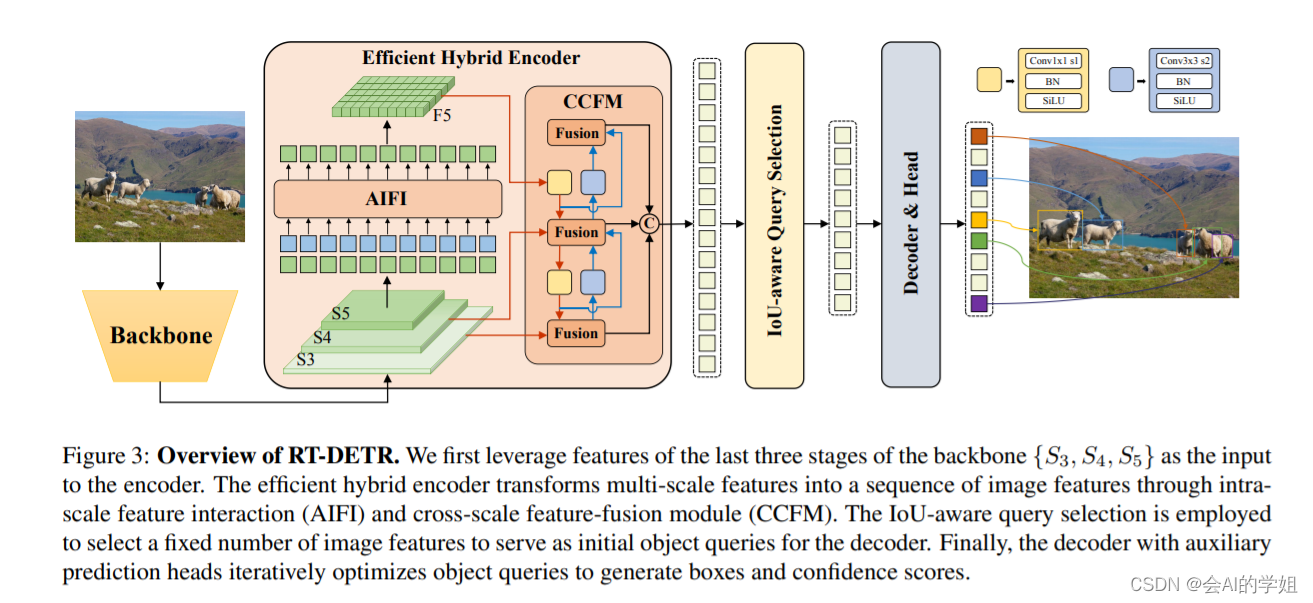 颈部
颈部
RT-DETR采用了一层Transformer的Encoder,只处理主干网络输出的 S5 特征,即AIFI(Attention-based Intra-scale Feature Interaction)模块。
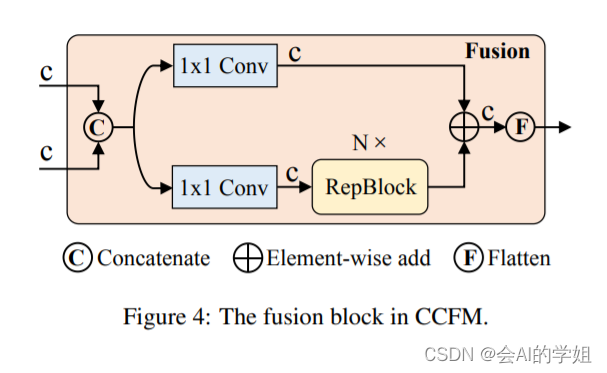
 实验结果
实验结果
RT-DETR-R50 在 COCO val2017 上的精度为 53.1% AP,在 T4 GPU 上的 FPS 为 108,RT-DETR-R101 的精度为 54.3% AP,FPS 为 74。总结来说,RT-DETR 比具有相同 backbone 的 DETR 系列检测器有比较显著的精度提升和速度提升。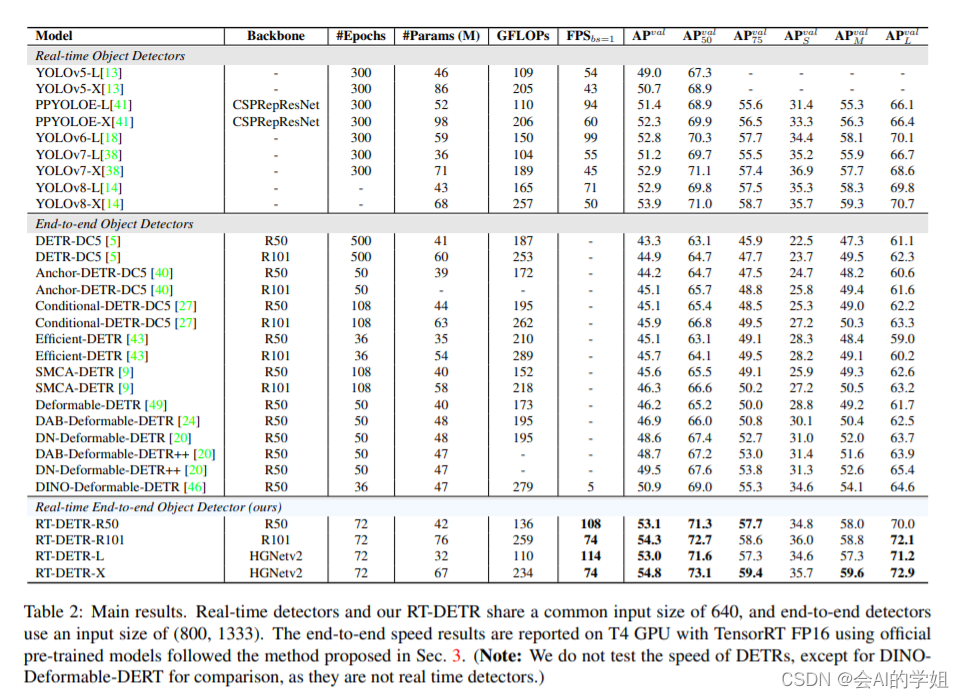
2.如何训练 RT-DETR模型
2.1数据集介绍
经典的NEU-DET数据集,数据集大小1800张,按照train:val:test 7:2:1随机划分
2.2配置NEU-DET.yaml
path: ./ultralytics-rt-detr/data/NEU-DET # dataset root dir
train: train.txt # train images
val: val.txt # val images# number of classes
nc: 6# class names
names:0: crazing1: inclusion2: patches3: pitted_surface4: rolled-in_scale 5: scratches2.3 超参数修改ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml
初版算法选择默认参数即可
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# Default training settings and hyperparameters for medium-augmentation COCO trainingtask: detect # (str) YOLO task, i.e. detect, segment, classify, pose
mode: train # (str) YOLO mode, i.e. train, val, predict, export, track, benchmark# Train settings -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
model: # (str, optional) path to model file, i.e. yolov8n.pt, yolov8n.yaml
data: # (str, optional) path to data file, i.e. coco128.yaml
epochs: 100 # (int) number of epochs to train for
patience: 50 # (int) epochs to wait for no observable improvement for early stopping of training
batch: 16 # (int) number of images per batch (-1 for AutoBatch)
imgsz: 640 # (int | list) input images size as int for train and val modes, or list[w,h] for predict and export modes
save: True # (bool) save train checkpoints and predict results
save_period: -1 # (int) Save checkpoint every x epochs (disabled if < 1)
cache: True # (bool) True/ram, disk or False. Use cache for data loading
device: # (int | str | list, optional) device to run on, i.e. cuda device=0 or device=0,1,2,3 or device=cpu
workers: 0 # (int) number of worker threads for data loading (per RANK if DDP)
project: # (str, optional) project name
name: # (str, optional) experiment name, results saved to 'project/name' directory
exist_ok: False # (bool) whether to overwrite existing experiment
pretrained: True # (bool | str) whether to use a pretrained model (bool) or a model to load weights from (str)
optimizer: auto # (str) optimizer to use, choices=[SGD, Adam, Adamax, AdamW, NAdam, RAdam, RMSProp, auto]
verbose: True # (bool) whether to print verbose output
seed: 0 # (int) random seed for reproducibility
deterministic: True # (bool) whether to enable deterministic mode
single_cls: False # (bool) train multi-class data as single-class
rect: False # (bool) rectangular training if mode='train' or rectangular validation if mode='val'
cos_lr: False # (bool) use cosine learning rate scheduler
close_mosaic: 10 # (int) disable mosaic augmentation for final epochs (0 to disable)
resume: False # (bool) resume training from last checkpoint
amp: True # (bool) Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) training, choices=[True, False], True runs AMP check
fraction: 1.0 # (float) dataset fraction to train on (default is 1.0, all images in train set)
profile: False # (bool) profile ONNX and TensorRT speeds during training for loggers
freeze: None # (int | list, optional) freeze first n layers, or freeze list of layer indices during training
# Segmentation
overlap_mask: True # (bool) masks should overlap during training (segment train only)
mask_ratio: 4 # (int) mask downsample ratio (segment train only)
# Classification
dropout: 0.0 # (float) use dropout regularization (classify train only)# Val/Test settings ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
val: True # (bool) validate/test during training
split: val # (str) dataset split to use for validation, i.e. 'val', 'test' or 'train'
save_json: False # (bool) save results to JSON file
save_hybrid: False # (bool) save hybrid version of labels (labels + additional predictions)
conf: # (float, optional) object confidence threshold for detection (default 0.25 predict, 0.001 val)
iou: 0.7 # (float) intersection over union (IoU) threshold for NMS
max_det: 300 # (int) maximum number of detections per image
half: False # (bool) use half precision (FP16)
dnn: False # (bool) use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference
plots: True # (bool) save plots during train/val# Prediction settings --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
source: # (str, optional) source directory for images or videos
show: False # (bool) show results if possible
save_txt: False # (bool) save results as .txt file
save_conf: False # (bool) save results with confidence scores
save_crop: False # (bool) save cropped images with results
show_labels: True # (bool) show object labels in plots
show_conf: True # (bool) show object confidence scores in plots
vid_stride: 1 # (int) video frame-rate stride
stream_buffer: False # (bool) buffer all streaming frames (True) or return the most recent frame (False)
line_width: # (int, optional) line width of the bounding boxes, auto if missing
visualize: False # (bool) visualize model features
augment: False # (bool) apply image augmentation to prediction sources
agnostic_nms: False # (bool) class-agnostic NMS
classes: # (int | list[int], optional) filter results by class, i.e. classes=0, or classes=[0,2,3]
retina_masks: False # (bool) use high-resolution segmentation masks
boxes: True # (bool) Show boxes in segmentation predictions# Export settings ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
format: torchscript # (str) format to export to, choices at https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/#export-formats
keras: False # (bool) use Kera=s
optimize: False # (bool) TorchScript: optimize for mobile
int8: False # (bool) CoreML/TF INT8 quantization
dynamic: False # (bool) ONNX/TF/TensorRT: dynamic axes
simplify: False # (bool) ONNX: simplify model
opset: # (int, optional) ONNX: opset version
workspace: 4 # (int) TensorRT: workspace size (GB)
nms: False # (bool) CoreML: add NMS# Hyperparameters ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
lr0: 0.01 # (float) initial learning rate (i.e. SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
lrf: 0.01 # (float) final learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
momentum: 0.937 # (float) SGD momentum/Adam beta1
weight_decay: 0.0005 # (float) optimizer weight decay 5e-4
warmup_epochs: 3.0 # (float) warmup epochs (fractions ok)
warmup_momentum: 0.8 # (float) warmup initial momentum
warmup_bias_lr: 0.1 # (float) warmup initial bias lr
box: 7.5 # (float) box loss gain
cls: 0.5 # (float) cls loss gain (scale with pixels)
dfl: 1.5 # (float) dfl loss gain
pose: 12.0 # (float) pose loss gain
kobj: 1.0 # (float) keypoint obj loss gain
label_smoothing: 0.0 # (float) label smoothing (fraction)
nbs: 64 # (int) nominal batch size
hsv_h: 0.015 # (float) image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
hsv_s: 0.7 # (float) image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
hsv_v: 0.4 # (float) image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
degrees: 0.0 # (float) image rotation (+/- deg)
translate: 0.1 # (float) image translation (+/- fraction)
scale: 0.5 # (float) image scale (+/- gain)
shear: 0.0 # (float) image shear (+/- deg)
perspective: 0.0 # (float) image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
flipud: 0.0 # (float) image flip up-down (probability)
fliplr: 0.5 # (float) image flip left-right (probability)
mosaic: 1.0 # (float) image mosaic (probability)
mixup: 0.0 # (float) image mixup (probability)
copy_paste: 0.0 # (float) segment copy-paste (probability)# Custom config.yaml ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
cfg: # (str, optional) for overriding defaults.yaml# Tracker settings ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
tracker: botsort.yaml # (str) tracker type, choices=[botsort.yaml, bytetrack.yaml]
2.4如何开启训练
from ultralytics.cfg import entrypoint
arg="yolo detect train model=rtdetr-l.yaml data=ultralytics/cfg/datasets/NEU-DET.yaml"entrypoint(arg)2.5 训练正式开始
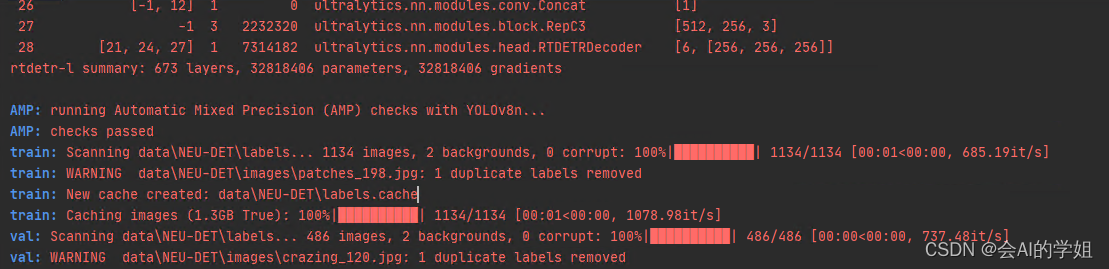
3.RT-DETR训练结果可视化分析
训练中,后续更新以及改进优化
这篇关于手把手教程:RT-DETR如何训练自己的数据集 | NEU-DET钢材缺陷检测的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







