本文主要是介绍CPM(Cluster Percolation method)派系过滤算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
原文地址
一、概念
(1)完全子图/全耦合网络/k-派系:所有节点全部两两相连
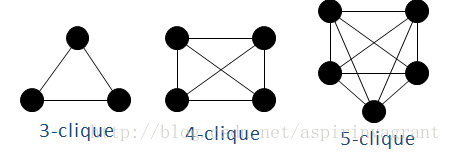
图1
这些全耦合网络也成为派系,k-派系表示该全耦合网络的节点数目为k
1)k-派系相邻:两个不同的k-派系共享k-1个节点,认为他们相邻
2)k-派系连通:一个k-派系可以通过若干个相邻的k-派系到达另一个k-派系,则称这两个k-派系彼此联通
二、思路
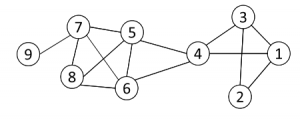
图2
1- first find all cliques of size k in the graph
第一步首先找到网络中大小为K的完全子图,例如图2中k=3的完全子图有{1, 2, 3} {1, 3, 4} {4, 5, 6} {5, 6, 7} {5, 6, 8} {5, 7, 8} {6, 7, 8}
2- then create graph where nodes are cliques of size k
第二步将每个完全子图定义为一个节点,建立一个重叠矩阵
a=[3 2 0 0 0 0 0;
2 3 1 0 0 0 0;
0 1 3 2 2 1 1;
0 0 2 3 2 2 2;
0 0 2 2 3 2 2;
0 0 1 2 2 3 2;
0 0 1 2 2 2 3 ]
3- add edges if two nodes (cliques) share k-1 common nodes
第三步将重叠矩阵变成社团邻接矩阵,其中重叠矩阵中对角线小于k,非对角线小于k-1的元素全置为0
a=[1 1 0 0 0 0 0;
1 1 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 1 1 1 0 0;
0 0 1 1 1 1 1;
0 0 1 1 1 1 1;
0 0 0 1 1 1 1;
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 ]
4- each connected component is a community
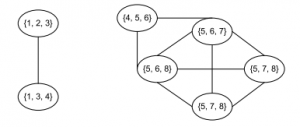
画出派系图,如上所示
从图中可以看出包含了两个社区{1,2,3,4}和{4,5,6,7,8},节点4属于两个社区的重叠节点
三、代码实现
R实现代码和Java实现代码可在GitHub网站上下载,R下载地址
https://github.com/angelosalatino/CliquePercolationMethod-R
四、References
Palla, G., Derényi, I., Farkas, I., & Vicsek, T. (2005). Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature, 435(7043), 814-818.
注意事项:
CPM算法不适用于稀疏矩阵,K的取值对结果影响不大,一般实验证明4-6为最佳
2017年4.16更新
用matlab算法实现,其中做了一点小变动,k是最小派系范围,寻找的是大于等于k的完全子图数,得到结果与上述描述结果一致,节点4是重叠节点
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 | function [components,cliques,CC] = k_clique(k,M) % k-clique algorithm for detecting overlapping communities in a network % as defined in the paper "Uncovering the overlapping % community structure of complex networks in nature and society" - % G. Palla, I. Derényi, I. Farkas, and T. Vicsek - Nature 435, 814–818 (2005) % % [X,Y,Z] = k_clique(k,A) % % Inputs: % k - clique size % A - adjacency matrix % % Outputs: % X - detected communities % Y - all cliques (i.e. complete subgraphs that are not parts of larger % complete subgraphs) % Z - k-clique matrix % % Author : Anh-Dung Nguyen % Email : anh-dung.nguyen@isae.fr % The adjacency matrix of the example network presented in the paper % M = [1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1; % 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1; % 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0; % 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0; % 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0; % 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0; % 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1; % 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1; % 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1; % 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1]; nb_nodes = size (M,1); % number of nodes % Find the largest possible clique size via the degree sequence: % Let {d1,d2,...,dk} be the degree sequence of a graph. The largest % possible clique size of the graph is the maximum value k such that % dk >= k-1 degree_sequence = sort ( sum (M,2) - 1, 'descend' ); max_s = 0; for i = 1: length (degree_sequence) if degree_sequence( i ) >= i - 1 max_s = i ; else break ; end end cliques = cell (0); % Find all s-size kliques in the graph for s = max_s:-1:3 M_aux = M; % Looping over nodes for n = 1:nb_nodes A = n; % Set of nodes all linked to each other B = setdiff ( find (M_aux(n,:)==1),n); % Set of nodes that are linked to each node in A, but not necessarily to the nodes in B C = transfer_nodes(A,B,s,M_aux); % Enlarging A by transferring nodes from B if ~ isempty (C) for i = size (C,1) cliques = [cliques;{C( i ,:)}]; end end M_aux(n,:) = 0; % Remove the processed node M_aux(:,n) = 0; end end % Generating the clique-clique overlap matrix CC = zeros ( length (cliques)); for c1 = 1: length (cliques) for c2 = c1: length (cliques) if c1==c2 CC(c1,c2) = numel (cliques{c1}); else CC(c1,c2) = numel ( intersect (cliques{c1},cliques{c2})); CC(c2,c1) = CC(c1,c2); end end end % Extracting the k-clique matrix from the clique-clique overlap matrix % Off-diagonal elements <= k-1 --> 0 % Diagonal elements <= k --> 0 CC( eye ( size (CC))==1) = CC( eye ( size (CC))==1) - k; CC( eye ( size (CC))~=1) = CC( eye ( size (CC))~=1) - k + 1; CC(CC >= 0) = 1; CC(CC < 0) = 0; % Extracting components (or k-clique communities) from the k-clique matrix components = []; for i = 1: length (cliques) linked_cliques = find (CC( i ,:)==1); new_component = []; for j = 1: length (linked_cliques) new_component = union (new_component,cliques{linked_cliques( j )}); end found = false; if ~ isempty (new_component) for j = 1: length (components) if all ( ismember (new_component,components{ j })) found = true; end end if ~found components = [components; {new_component}]; end end end function R = transfer_nodes(S1,S2,clique_size,C) % Recursive function to transfer nodes from set B to set A (as % defined above) % Check if the union of S1 and S2 or S1 is inside an already found larger % clique found_s12 = false; found_s1 = false; for c = 1: length (cliques) for cc = 1: size (cliques{c},1) if all ( ismember (S1,cliques{c}(cc,:))) found_s1 = true; end if all ( ismember ( union (S1,S2),cliques{c}(cc,:))) found_s12 = true; break ; end end end if found_s12 || ( length (S1) ~= clique_size && isempty (S2)) % If the union of the sets A and B can be included in an % already found (larger) clique, the recursion is stepped back % to check other possibilities R = []; elseif length (S1) == clique_size; % The size of A reaches s, a new clique is found if found_s1 R = []; else R = S1; end else % Check the remaining possible combinations of the neighbors % indices if isempty ( find (S2>= max (S1),1)) R = []; else R = []; for w = find (S2>= max (S1),1): length (S2) S2_aux = S2; S1_aux = S1; S1_aux = [S1_aux S2_aux(w)]; S2_aux = setdiff (S2_aux(C(S2(w),S2_aux)==1),S2_aux(w)); R = [R;transfer_nodes(S1_aux,S2_aux,clique_size,C)]; end end end end end |
这篇关于CPM(Cluster Percolation method)派系过滤算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







