本文主要是介绍基于模因框架的包装过滤特征选择算法,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
#引用
##LaTex
@ARTICLE{4067093,
author={Z. Zhu and Y. S. Ong and M. Dash},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics)},
title={Wrapper ndash;Filter Feature Selection Algorithm Using a Memetic Framework},
year={2007},
volume={37},
number={1},
pages={70-76},
keywords={biology computing;genetic algorithms;learning (artificial intelligence);pattern classification;search problems;classification problem;feature selection algorithm;genetic algorithm;local search;memetic framework;microarray data set;wrapper filter;Acceleration;Classification algorithms;Computational efficiency;Filters;Genetic algorithms;Machine learning;Machine learning algorithms;Pattern recognition;Pervasive computing;Spatial databases;Chi-square;feature selection;filter;gain ratio;genetic algorithm (GA);hybrid GA (HGA);memetic algorithm (MA);relief;wrapper;Algorithms;Artificial Intelligence;Biomimetics;Computer Simulation;Models, Theoretical;Pattern Recognition, Automated;Software;Systems Theory},
doi={10.1109/TSMCB.2006.883267},
ISSN={1083-4419},
month={Feb},}
##Normal
Z. Zhu, Y. S. Ong and M. Dash, “Wrapper–Filter Feature Selection Algorithm Using a Memetic Framework,” in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 70-76, Feb. 2007.
doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2006.883267
keywords: {biology computing;genetic algorithms;learning (artificial intelligence);pattern classification;search problems;classification problem;feature selection algorithm;genetic algorithm;local search;memetic framework;microarray data set;wrapper filter;Acceleration;Classification algorithms;Computational efficiency;Filters;Genetic algorithms;Machine learning;Machine learning algorithms;Pattern recognition;Pervasive computing;Spatial databases;Chi-square;feature selection;filter;gain ratio;genetic algorithm (GA);hybrid GA (HGA);memetic algorithm (MA);relief;wrapper;Algorithms;Artificial Intelligence;Biomimetics;Computer Simulation;Models, Theoretical;Pattern Recognition, Automated;Software;Systems Theory},
URL: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=4067093&isnumber=4067063
#摘要
a novel hybrid wrapper and filter feature selection algorithm for a classification problem using a memetic framework
a filter ranking method
genetic algorithm
univariate feature ranking information
the University of California, Irvine repository and microarray data sets
classification accuracy, number of selected features, and computational efficiency.
memetic algorithm (MA) — balance between local search and genetic search
to maximize search quality and efficiency
#主要内容
- filter methods
- wrapper methods
##wrapper–filter feature selection algorithm (WFFSA) using a memetic framework
WFFSA
Lamarckian learning
local improvement
Genetic operators
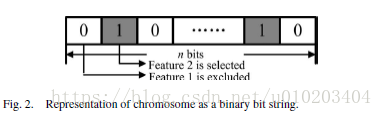
###A 编码表示与初始化
a chromosome is a binary string of length equal to the total number of features
randomly initialized
###B 目标函数
the classification accuracy
S c S_c Sc — the corresponding selected feature subset encoded in chromosome c c c
J ( S c ) J \left( S_c \right) J(Sc) — criterion function
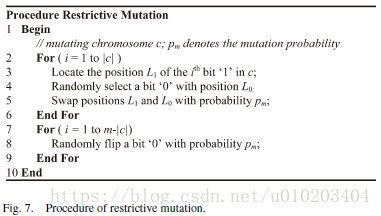
###C LS改进过程
domain knowledge and heuristics
filter ranking methods as memes or LS heuristics
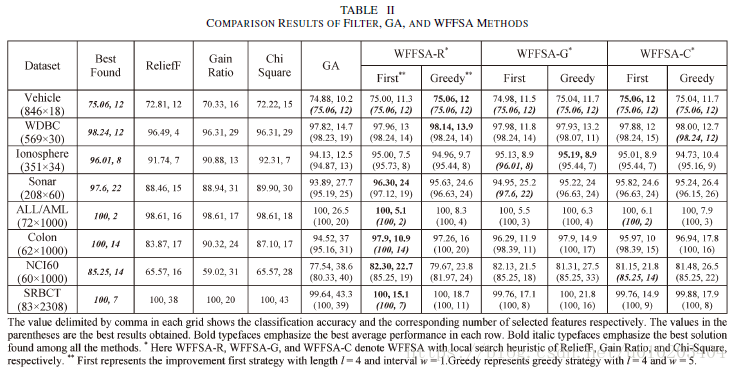
three different filter ranking methods, namely:
- ReliefF;
- gain ratio;
- chi-square.
based on different criteria:
- Euclidean distance,
- information entropy,
- chi-square statistics
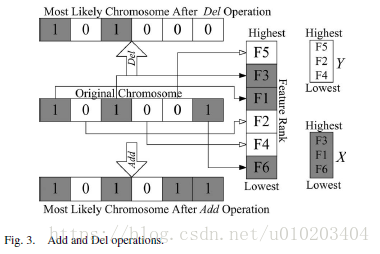
basic LS operators:
- “Add”: select a feature from Y using the linear ranking selection and move it to X.
- “Del”: select a feature from X using the linear ranking selection and move it to Y .
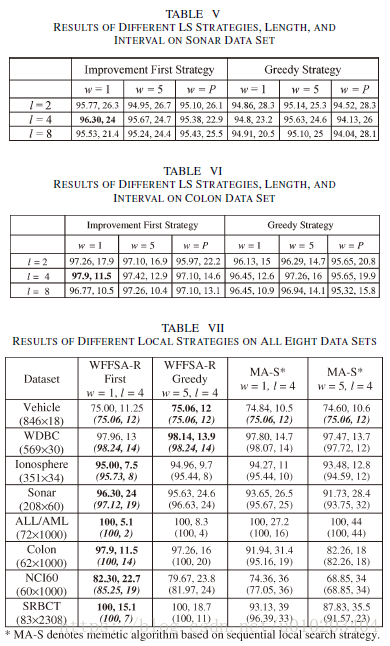
The intensity of LS — the LS length l l l and interval w w w
LS length l l l — the maximum number of Del and Add operations in each LS — l 2 l^2 l2 possible combinations of Add and Del operations
interval w w w — the w w w elite chromosomes in the population
until a local optimum or an improvement is reached
- Improvement First Strategy: a random choice from the l 2 l^2 l2 combinations. stops once an improvement is obtained either in terms of classification accuracy or a reduction in the number of selected features without deterioration in accuracy greater than ε ε ε.
- Greedy Strategy: carries out all possible l 2 l^2 l2 combinations — the best improved solution
- Sequential Strategy: the Add operation searches for the most significant feature y y y in Y Y Y in a sequential manner; the Del operation searches for the least significant feature x from X in a sequential manner
- Evolutionary Operators:
- Computational Complexity:
The ranking of features based on the filter methods — linear time complexity — a one-time offline cost — negligible
the computational cost of a single fitness evaluation — the basic unit of computational cost
GA — O ( p g ) O(pg) O(pg): p p p — the size of population, g g g — the number of search generations
+improvement first strategy — O ( p g + l 2 w g / 2 ) O (pg + l^2wg/2) O(pg+l2wg/2)
+the greedy strategy ( l 2 w / p l^2w/p l2w/p) — O ( p g + l 2 w g ) O (pg + l^2wg) O(pg+l2wg)
+the sequential strategy ( ( 2 ∣ Y ∣ − l ) l / 2 (2|Y | − l)l/2 (2∣Y∣−l)l/2 and ( 2 ∣ X ∣ + l ) l / 2 2|X| + l)l/2 2∣X∣+l)l/2 — Add and Del operations — n l w nlw nlw) — O ( p g + n l w g ) O(pg + nlwg) O(pg+nlwg)
KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 8: n \gg ̲ l — KaTeX parse error: Unexpected character: '' at position 8: nlw \gg̲ l^2w > l^2w/2 — sequential LS strategy requires significantly more computations
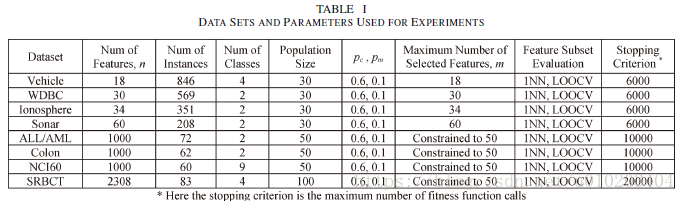
##试验
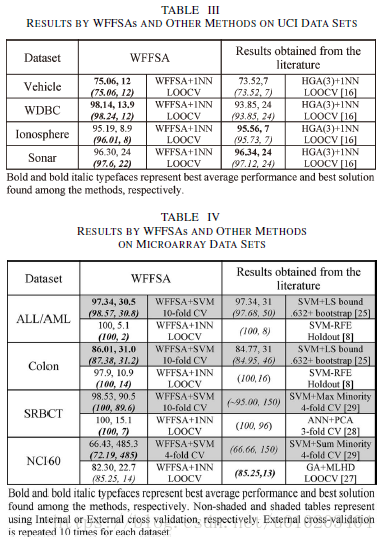
UCI data sets
ALL/AML, Colon, NCI60, and SRBCT
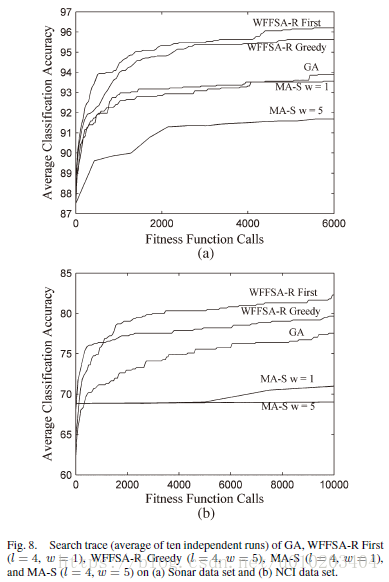
population size — 30 30 30 and 50 50 50 or 100 100 100 (microarray data sets)
fitness function calls — 6000 6000 6000 and 10000 10000 10000 or 20000 20 000 20000 (microarray data sets)
the one nearest neighbor (1NN) classifier
the leave-one-out cross validation (LOOCV)
这篇关于基于模因框架的包装过滤特征选择算法的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!