本文主要是介绍JavaScript:js实现在线五子棋人机(人人)对弈,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在线五子棋人机对弈
全部使用前端技术,使用HTML,CSS以及JS进行实现.
棋盘在后端就是一个15*15的二维数组
页面设计
页面设计的比较粗糙
主要使用js自带的canvas画布进行绘画
HTML代码如下:
<div class="outer"><canvas id="canvas" height="900" width="900"></canvas><div class="button"><div id="reset"><button v-on:click="reset()">重试</button></div><!-- <div id="check"><button v-on:click="check()">开始</button></div> --><div id="jump"><button v-on:click="jump()">玩家本地对战</button></div></div>
</div>
CSS样式设计如下:
给canvas加了个居中和看上去像棋盘的颜色
按钮使用fixed布局跟随视口移动
#canvas {margin: 0 auto;display: block;margin: auto;background:burlywood ;border: 5px solid black;border-radius: 5px;
}.outer {background: grey;padding: 20px;
}.button{position: fixed;top: 100px;left: 100px;
}.button button{color: black;font-size: 20px;background-color:powderblue
}#reset{float: left;
}#check{float: left;margin-left: 10px;
}
JS代码如下:
简而言之:就是画了一堆横线和竖线
var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");for (let index = 0; index <= 15; index += 1) {ctx.moveTo(0, 60 * index);ctx.lineTo(900, 60 * index);ctx.stroke()ctx.moveTo(60 * index, 0);ctx.lineTo(60 * index, 900);ctx.stroke()};
落子
效果如下
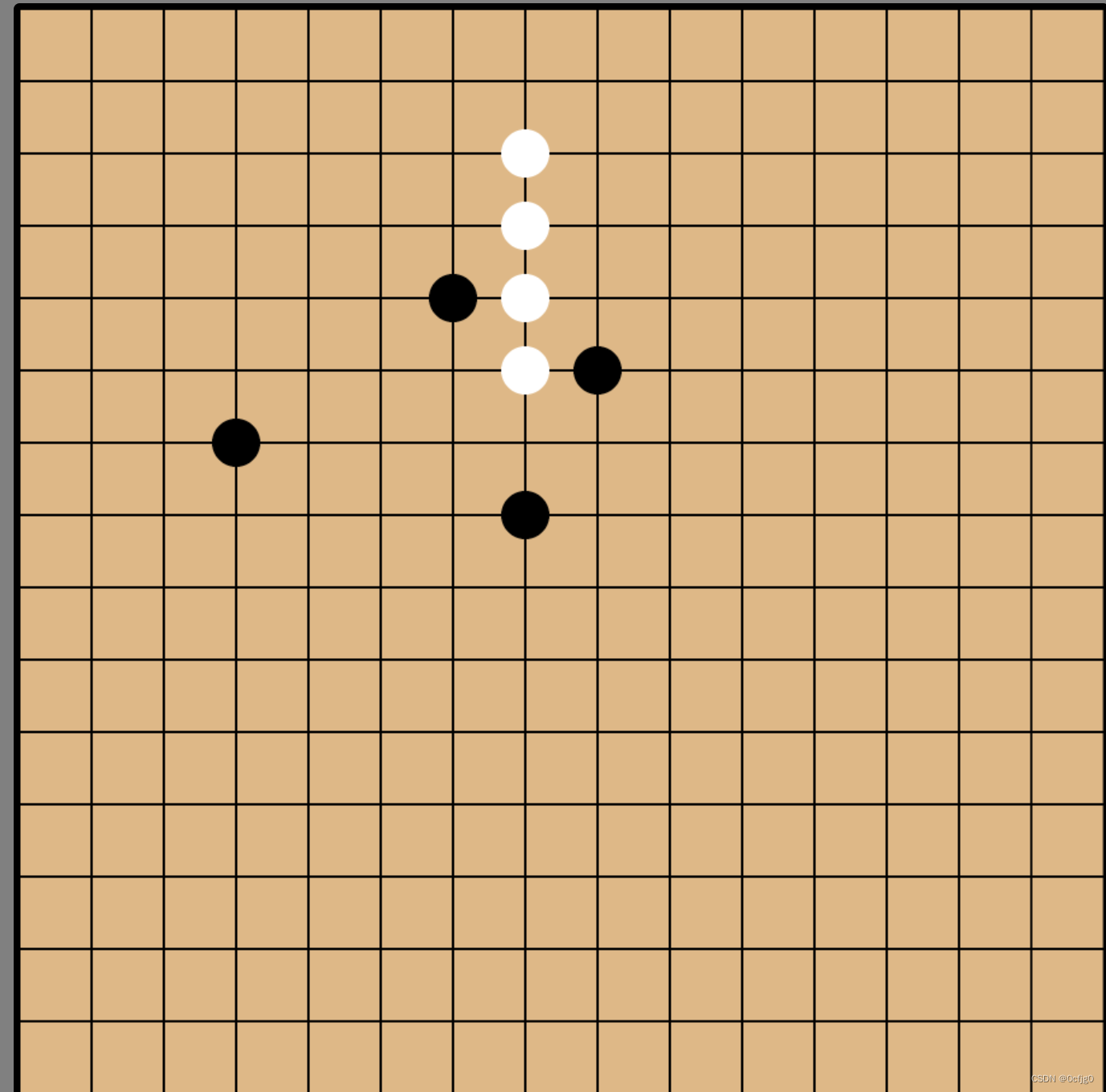
同样使用canvas进行绘画,代码如下
canvas.addEventListener('click', e => {//获取坐标距离父级的偏移量var { offsetX, offsetY } = e;//边界判断 不能点击格子外面的范围if (offsetX < 30 || offsetY < 30 || offsetX > 870 || offsetY > 870) {return;} else if (flag === "black") {let x = Math.round(e.offsetX / 60) * 60;let y = Math.round(e.offsetY / 60) * 60;if (arr[y / 60][x / 60] != 0) {alert("此处已有棋子")return;}arr[y / 60][x / 60] = "black";ctx.fillStyle = '#000';ctx.beginPath();ctx.arc(x, y, 20, 0, 2 * Math.PI)ctx.fill();ctx.closePath();if (test()) {return;}// setTimeout(// () => {// clear(arrai);// aitest();// ai();// }// , 100);flag = "white"} else {let x = Math.round(e.offsetX / 60) * 60;let y = Math.round(e.offsetY / 60) * 60;if (arr[y / 60][x / 60] != 0) {alert("此处已有棋子")return;}arr[y / 60][x / 60] = "white";ctx.fillStyle = '#fff';ctx.beginPath();ctx.arc(x, y, 20, 0, 2 * Math.PI)ctx.fill();ctx.closePath();test();flag = "black";}});
给页面的鼠标点击绑了个监听事件.
画棋子也是依靠canvas实现
就是相当于先画一个圆,再往里面填颜色.
ctx.fillStyle = '#000';ctx.beginPath();ctx.arc(x, y, 20, 0, 2 * Math.PI)ctx.fill();ctx.closePath();
判断输赢
js逻辑判断,代码如下
就是遍历棋盘,然后判断横向纵向以及斜向是否连成五子
function test() {let countx = 1;for (let i = 0; i <= 14; i++) {for (let j = 0; j <= 14; j++) {if (arr[i][j] !== 0 && arr[i][j] === arr[i][j + 1]) {countx++;if (countx == 5) {alert(flag == "black" ? "黑棋获胜" : "白棋获胜");setTimeout(() => location.reload(), 1000);return true;}} else {countx = 1;}}}let county = 1;for (let j = 0; j <= 14; j++) {for (let i = 0; i <= 14; i++) {if (arr[i][j] !== 0 && arr[i][j] === arr[i + 1][j]) {county++;if (county == 5) {alert(flag == "black" ? "黑棋获胜" : "白棋获胜");setTimeout(() => location.reload(), 1000);return true;}} else {county = 1;}}}let countob = 1;let orii = 0;let orij = 0;for (let i = 0; i <= 14; i++) {for (let j = 0; j <= 14; j++) {if (arr[i][j] === arr[i + 1][j + 1]) {orii = i;orij = j;while (1 <= i <= 14 && j <= 14) {if (arr[i][j] === arr[i + 1][j + 1] && arr[i][j] !== 0) {countob++;// console.log(countob);i++;j++;if (countob == 5) {alert(flag == "black" ? "黑棋获胜" : "白棋获胜");setTimeout(() => location.reload(), 1000);return true;}} else {break;}}i = orii;j = orij;countob = 1;}}}let countob1 = 1;let orii1 = 0;let orij1 = 0;for (let i = 1; i <= 14; i++) {for (let j = 0; j <= 14; j++) {if (arr[i][j] === arr[i + 1][j - 1]) {orii = i;orij = j;while (i <= 14 && 1 <= j <= 14) {if (arr[i][j] === arr[i + 1][j - 1] && arr[i][j] !== 0) {countob1++;// console.log(countob);i++;j--;if (countob1 == 5) {alert(flag == "black" ? "黑棋获胜" : "白棋获胜");setTimeout(() => location.reload(), 1000);return true;}} else {break;}}i = orii;j = orij;countob1 = 1;}}}return false;}
到此为止,五子棋的人人对弈功能已经完全实现.
接下来是人机对弈
ai判断
逻辑就是算出棋盘上己方的最高分位置和对方的最高分位置,进行分数相加,最终的最高分位置就是最优位置.
js逻辑,代码如下:
遍历棋盘对所有位置的所有方向进行判断,得出得分
function aitest() {let sum1 = 0;let sum2 = 0;for (let i = 0; i <= 14; i++) {for (let j = 0; j <= 14; j++) {sum1 += aitestx(i, j);sum1 += aitesty(i, j);sum1 += aitestobl(i, j);sum1 += aitestobr(i, j);flag = (flag == "black") ? "white" : "black";sum2 += aitestx(i, j);sum2 += aitesty(i, j);sum2 += aitestobl(i, j);sum2 += aitestobr(i, j);flag = (flag == "black") ? "white" : "black";arrai[i][j] = sum1 + sum2;console.log(arrai[i][j]);sum1 = 0;sum2 = 0;}}}
横向判断
function aitestx(x, y) {let temp = arr[x][y];let deadr = false;let deadl = false;let count = 1;for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (y + i > 14) {deadr = true;break;}if (arr[x][y + i] != flag) {if (arr[x][y + i] != 0) {deadr = true;}break;} else {count++;}}for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (y - i < 0) {deadl = true;break;}if (arr[x][y - i] != flag) {if (arr[x][y - i] != 0) {deadl = true;}break;} else {count++;}}if (deadl == true && deadr == true) {return 0;} else {if (count > 5) {count = 5;count = 5;}return (score(count, deadl == deadr ? false : true));}}
纵向判断
function aitesty(x, y) {let temp = arr[x][y];let deadr = false;let deadl = false;let count = 1;for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (x + i > 14) {deadr = true;break;}if (arr[x + i][y] != flag) {if (arr[x + i][y] != 0) {deadr = true;}break;} else {count++;}}for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (x - i < 0) {deadl = true;break;}if (arr[x - i][y] != flag) {if (arr[x - i][y] != 0) {deadl = true;}break;} else {count++;}}if (deadl == true && deadr == true) {return 0;} else {return (score(count, deadl == deadr ? false : true));}}
斜向判断
function aitestobl(x, y) {let temp = arr[x][y];let deadr = false;let deadl = false;let count = 1;for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (x + i > 14 || y + i > 14) {deadr = true;break;}if (arr[x + i][y + i] != flag) {if (arr[x + i][y + i] != 0) {deadr = true;}break;} else {count++;}}for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (x - i < 0 || y - i < 0) {deadl = true;break;}if (arr[x - i][y - i] != flag) {if (arr[x - i][y - i] != 0) {deadl = true;}break;} else {count++;}}if (deadl == true && deadr == true) {return 0;} else {return (score(count, deadl == deadr ? false : true));}}
反斜向判断
function aitestobr(x, y) {let temp = arr[x][y];let deadr = false;let deadl = false;let count = 1;for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (x - i < 0 || y + i > 14) {deadr = true;break;}if (arr[x - i][y + i] != flag) {if (arr[x - i][y + i] != 0) {deadr = true;}break;} else {count++;}}for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {if (x + i > 14 || y - i < 0) {deadl = true;break;}if (arr[x + i][y - i] != flag) {if (arr[x + i][y - i] != 0) {deadl = true;}break;} else {count++;}}if (deadl == true && deadr == true) {return 0;} else {return (score(count, deadl == deadr ? false : true));}}
根据上面方法得出的连子数调用方法算出得分返回给aitest()
function score(num, dead) {if (dead) {switch (num) {case 1:return 1;case 2:return 10;case 3:return 50;case 4:return 400;case 5:return 500000;}} else {switch (num) {case 1:return 5;case 2:return 30;case 3:return 250;case 4:return 10000;case 5:return 500000;}}}
当玩家落子时,调用回调函数settimeout()调用ai落子
setTimeout(() => {clear(arrai);aitest();ai();}, 100);flag = "white"
ai()落子函数
遍历棋盘,将分数和映射到另一个二维数组
如果发现此处已有棋子则递归调用本方法.
最后在相应位置完成落子
大功告成
function ai() {let max = -1;let maxarr = new Array(-1, -1);for (let i = 1; i <= 14; i++) {for (let j = 1; j <= 14; j++) {if (max < arrai[i][j] && arr[i][j] == 0) {max = arrai[i][j];maxarr[0] = i;maxarr[1] = j;}}}console.log(maxarr);console.log(arr);if (arr[maxarr[0]][maxarr[1]] != 0) {arrai[maxarr[0]][maxarr[1]] = -1;ai();console.log("重新来过");return;}console.log("max:" + max);console.log("max数组:" + maxarr[0] + " " + maxarr[1]);x = 60 * maxarr[1];y = 60 * maxarr[0];arr[maxarr[0]][maxarr[1]] = "white";ctx.fillStyle = '#fff';ctx.beginPath();ctx.arc(x, y, 20, 0, 2 * Math.PI)ctx.fill();ctx.closePath();test();flag = "black";clear(arrai);}
总结
一个不难的小游戏,逻辑存在一定漏洞,主要是对js也不熟悉,包括对var和let的理解等等都比较欠缺,以现在的知识储备应该是改不明白了,再多学点把这个做成线上人人对战.
这篇关于JavaScript:js实现在线五子棋人机(人人)对弈的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





