本文主要是介绍C++的stack和queue类(一):适配器模式、双端队列与优先级队列,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
基本概念
stack的使用
queue的使用
适配器模式
stack.h
test.cpp
双端队列-deque
仿函数
优先队列
priority_queue的使用
queue.h文件
stack.h文件
test.cpp文件
日期类的比较
商品的比较
结论
基本概念
1、stack和queue不是容器而是容器适配器,它们没有迭代器
2、适配stack和queue的默认容器是deque,因为:
- stack和queue不需要遍历,只需要在固定的一端或者两端进行操作
- 在stack中元素增加需要扩容时,deque比vector的效率高(不需要搬移大量数据)
- queue中的元素增长时,deque不仅效率高,而且内存使用率高
stack的使用
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| stack | 构造空的栈 |
| empty | 检测stack是否为空 |
| size | 返回stack中元素的个数 |
| top | 返回栈顶元素的引用 |
| push | 将元素val压入stack中 |
| pop | 将stack中尾部的元素弹出 |
queue的使用
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| queue | 构造空的队列 |
| empty | 检测队列是否为空 |
| size | 返回队列中有效元素的个数 |
| front | 返回队头元素的引用 |
| back | 返回队尾元素的引用 |
| push | 在队尾将元素val入队列 |
| empty | 将队头元素出队列 |
适配器模式
适配器模式是一种设计模式,用于将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另一个接口,这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它涉及到单个类的功能增强,适配器模式中有三个主要角色:
- 目标接口:客户端所期待使用的接口,适配器通过实现这个目标接口来与用户进行交互
- 被适配者:需要被适配以符合目标接口规范的现有类
- 适配器:实现了目标接口,并持有一个对被适配者对象的引用,在其方法内部调用被适配者对象来完成特定操作
stack.h
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
namespace bit
{//适配器模式//stack<int,vector<int>> st1;//stack<int,list<int>> st2;template<class T, class Container>class stack{public://入栈void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);}//出栈void pop(){_con.pop_back();}//求大小size_t size(){return _con.size();}//判空bool empty(){return _con.empty();}//获取栈顶元素const T& top(){return _con.back();}private:Container _con;};
}- 目标接口:构成栈所需的操作接口
- 被适配者:实现栈的底层数据结构(数组或链表)
- 适配器:bit::stack类
test.cpp
#include "Queue.h"
#include "Stack.h"
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void test_stack1()
{bit::stack<int,vector<int>> st;st.push(1);st.push(2);st.push(3);st.push(4);while (!st.empty()){cout << st.top() << " ";st.pop();}cout << endl;}int main()
{test_stack1();return 0;
}注意事项:函数参数传递的是对象,模板参数传递的是类型,函数参数可以传递缺省值,模板参数也可以传递缺省值
template<class T, class Container = vector<int>>
bit::stack<int> st; //此时就等价于bit::stack<int,vector<int>> st双端队列-deque
vector优缺点
- 优点:支持下标随机访问
- 缺点:头部或中间插入删除效率低,扩容有消耗
list的优缺点:
- 优点:任意位置插入删除效率都不错
- 缺点:不支持下标的随机访问
(第一个stack和queue的2:30:00处)
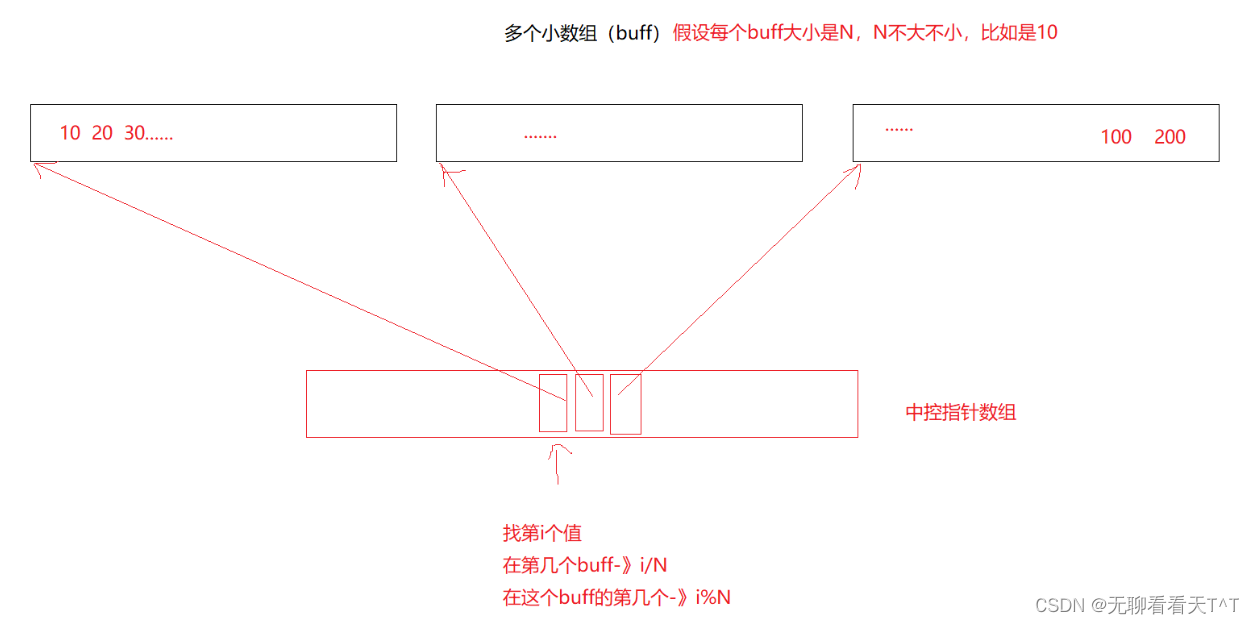
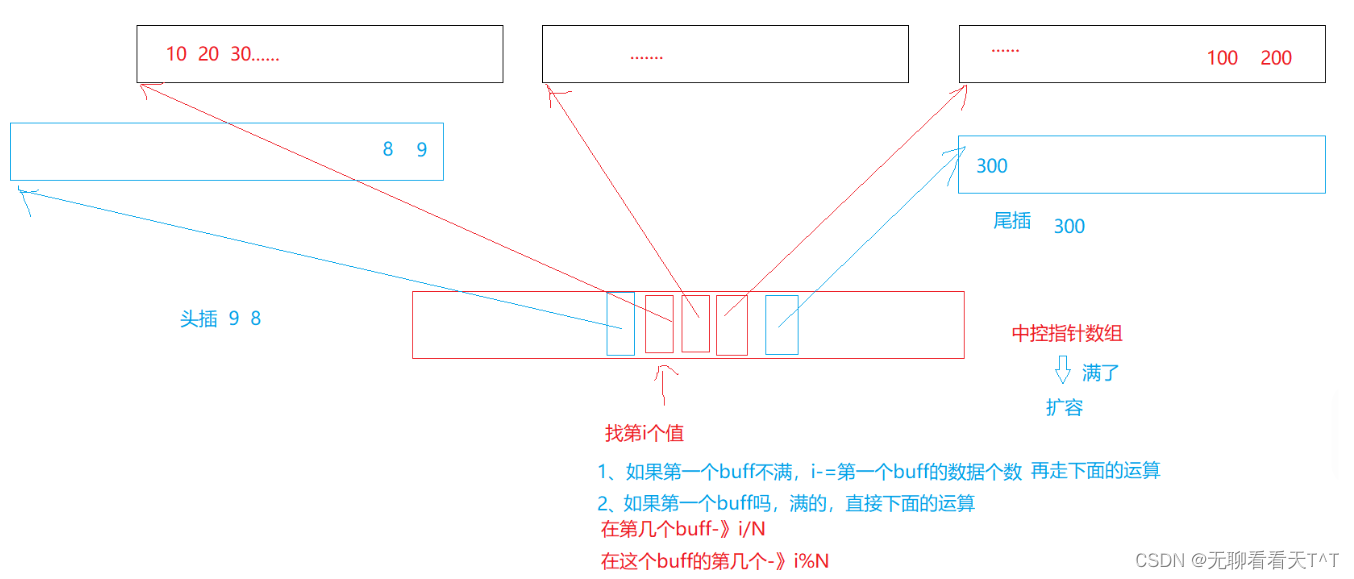
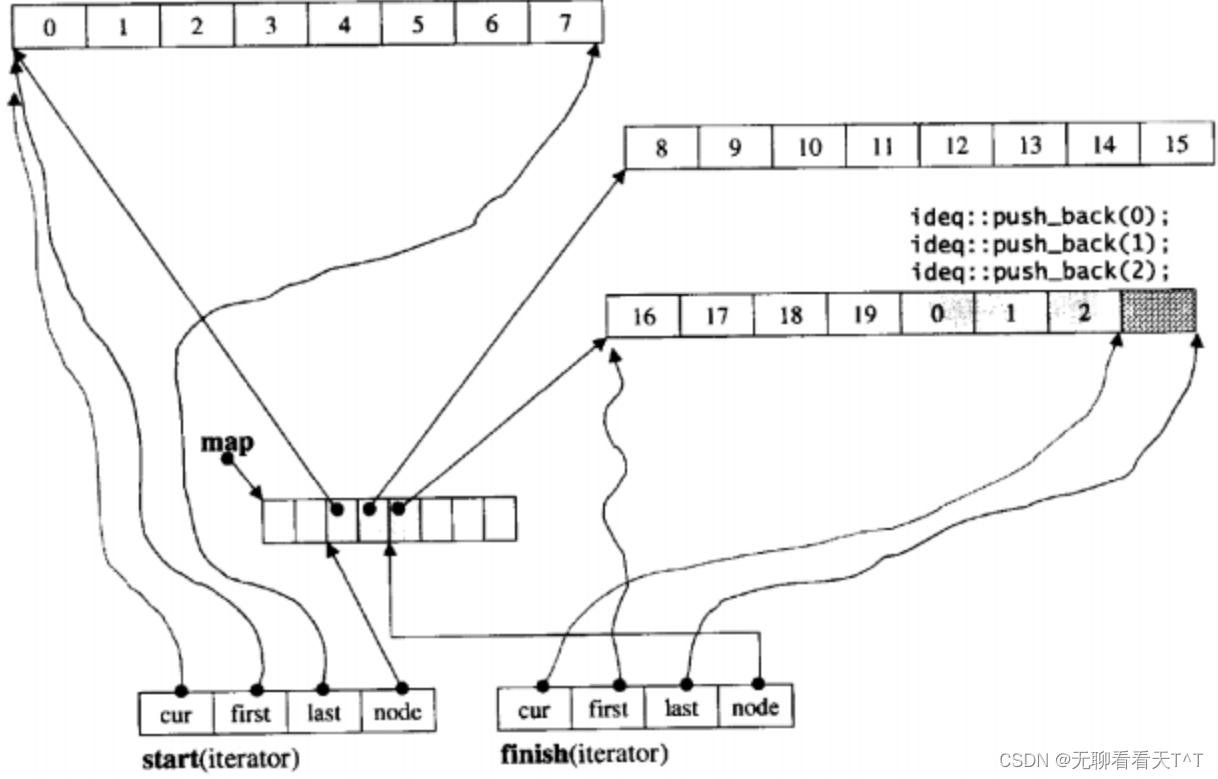
基本概念:deque是一种双开口的”连续“空间的数据结构,与vector相比,头插效率高,不需要搬移元素,与list相比,空间利用率更高,deque不是真正连续的空间,而是由一段段连续的小空间拼接而成的,实际deque类似于一个动态的二维数组
优点:deque 允许在两端进行高效插入和删除操作,且支持下标的随机访问
缺点:中间插入删除效率一般、[]效率一般(遍历时deque要频繁的检查是否移动到小空间边界)
仿函数
基本概念:仿函数是一个类或结构体,它重载了函数调用运算符 operator(),通过重载该运算符,这个类的实例就可以被像函数一样调用
#include <iostream>//仿函数 + 函数模板
template <class T>
struct MyComparator
{bool operator()(const T& x,const T& y) {return x < y;}
};int main() {MyComparator<int> cmp;cout<< cmp(1, 2) << endl;//有名对象cout<< cmp.operator()(1, 2) << endl;//有名对象cout<< MyComparator<int>()(1, 2) << endl;//匿名对象cout<< MyComparator<int>().operator()(1, 2) << endl;//匿名对象return 0;
}
优先队列
文档:cplusplus.com/reference/queue/priority_queue/
基本概念
1、优先队列是一种容器适配器
2、优先队列的底层容器的虚拟逻辑是一个堆,只能获取堆顶元素
3、底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他特定设计的容器类。容器应该可以通过随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下操作 (标准容器类vector和deque满足以下需求) :
- empty():检测容器是否为空
- size():返回容器中有效元素个数
- front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
- push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
- pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
5. 默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector注意事项:1、默认情况下,priority_queue是大堆#include <vector> #include <queue> #include <functional> // greater算法的头文件 void TestPriorityQueue() {// 默认情况下,创建的是大堆,其底层按照小于号比较vector<int> v{3,2,7,6,0,4,1,9,8,5};priority_queue<int> q1;for (auto& e : v){q1.push(e);}cout << q1.top() << endl;//如果要创建小堆,将第三个模板参数换成greater比较方式priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q2(v.begin(), v.end());cout << q2.top() << endl; }int main() {TestPriorityQueue();return 0 }2. 若在priority_queue中放自定义类型的数据,需要在自定义类型中提供> 或者< 的重载
priority_queue的使用
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| priority_queue | 构造一个空的优先级队列 |
| empty | 检测优先级队列是否为空 |
| top | 返回优先级队列中最大(最小元素),即堆顶元素 |
| push | 在优先级队列中插入元素x |
| pop | 删除优先级队列中最大(最小)元素,即堆顶元素 |
queue.h文件
#pragma once
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;namespace bit
{//基于deque实现的队列template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>class queue{public://入队void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);}//出队void pop(){_con.pop_front();}//求大小size_t size(){return _con.size();}//判空bool empty(){return _con.empty();}//获取队头const T& front(){return _con.front();}//获取队尾const T& back(){return _con.back();}private:Container _con;};//实现小堆逻辑的仿函数template<class T>class less{public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x < y;}};//实现大堆逻辑的仿函数template<class T>class greater{public:bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y){return x > y;}};//优先级队列(底层数据结构是vector,比较部分调用了仿函数)template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>//不传入指的大小堆实现逻辑则按默认实现小堆逻辑class priority_queue{public://向上调整void adjust_up(size_t child){Compare com;int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){//if (_con[child] > _con[parent]):求大堆逻辑:将孩子与父亲间大的向上移动//if (_con[parent] < _con[child]):求小堆逻辑:将孩子与父亲间小的向前移动if (com(_con[child],_con[parent]))//实现大堆还是小队基于使用的仿函数{swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else{ break;}}}void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);//直接调用现有的尾插函数adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);//向上调整建(大/小)堆}void adjust_down(size_t parent){Compare com;size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;//不到叶子就继续while (child < _con.size()){//找出最大的那个孩子//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] > _con[child])//大堆逻辑//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] > _con[child])//小堆逻辑if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child + 1], _con[child])){++child;}//if (_con[child] > _con[parent])//大堆逻辑//if (_con[child] < _con[parent])//小堆逻辑if (com(_con[child], _con[parent])){swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}}//删除堆顶元素void pop(){swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);//交换堆顶元素和最后一个元素_con.pop_back();//直接用现有的尾删函数adjust_down(0);//向下调整建(大/小)堆}//判空bool empty(){return _con.empty();}//获取堆中元素个数size_t size(){return _con.size;}//获取堆顶元素const T& top(){return _con[0];}private:Container _con;};
}stack.h文件
#pragma once
namespace bit
{//基于双端队列实现的栈template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>class stack{public:void push(const T& x){_con.push_back(x);}void pop(){_con.pop_back();}size_t size(){return _con.size();}bool empty(){return _con.empty();}const T& top(){return _con.back();}private:Container _con;};
}test.cpp文件
#include"Stack.h"
#include"Queue.h"//尝试基于deque实现的队列
void test_queue()
{bit::queue<int> q;q.push(1);q.push(2);cout << q.front() << " ";q.pop();q.push(3);q.push(4);while (!q.empty()){cout << q.front() << " ";q.pop();}cout << endl;
}//优先级队列
void test_priority_queue()
{bit::priority_queue<int,vector<int>,bit::greater<int>> pq;//存放int类型的数据,底层数据结构为vector,实现大堆的逻辑pq.push(2);pq.push(1);pq.push(3);pq.push(4);pq.push(5);pq.push(7);pq.push(8);pq.push(6);while (!pq.empty()){cout << pq.top() << " ";pq.pop();}cout << endl;
}int main()
{//test_queue();test_priority_queue();return 0;
}
- 实例化优先级队列类类型的对象pq时会将默认的less<T>变为指定的greater<T>
- 向pq中尾插2,_con是pq对象的底层数据结构vector类类型的对象,_con[size-1]可以获取2
- 尾插后为了维护大/小堆性质要调用向上调整函数(新插入的元素后进行向上调整)
- 向上调整函数会实例化一个greater类类型的对象com
- 将vector中父子下标存放的数据放入com中进行比较并返回比较结果
- 根据比较结果将父子下标在vector中存放的数据进行交换
注意事项:vs2022报内部编译器错误一般是涉及模板的内容出错
日期类的比较
#pragma once
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//日期类
class Date
{
public:friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1): _year(year), _month(month), _day(day){}bool operator<(const Date& d)const{return (_year < d._year) ||(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);}bool operator>(const Date& d)const{return (_year > d._year) ||(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;return _cout;
}//处理指针比较的仿函数
class GreaterPDate
{
public:bool operator()(const Date* p1, const Date* p2){return *p1 > *p2;}
};//向优先级队列中放入自定义数据
void test_priority_queue2()
{bit::priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, bit::greater<Date>> pq;Date d1(2024, 4, 8);pq.push(d1);//有名对象pq.push(Date(2024, 4, 10));//匿名对象pq.push({ 2024, 2, 15 });//多参数隐式类型转换while (!pq.empty()){cout << pq.top() << " ";pq.pop();}cout << endl;//向优先级队列中存放指针bit::priority_queue<Date*, vector<Date*>, GreaterPDate> pqptr;//不能对内置类型Date*进行重载operator<pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 14));//new了一个日期类类型的匿名对象,返回的类型是地址,如果仅根据传入的地址进行建堆则每次的值是不一样的pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 11));pqptr.push(new Date(2024, 4, 15));while (!pqptr.empty()){cout << *(pqptr.top()) << " ";pqptr.pop();}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test_priority_queue2();return 0;
}向优先级队列中传入自定义类型的对象数据:

- 实例化优先级队列类类型的对象pq,less变greater,vector中存放的是日期类类型的数据
- 尾插日期类类型的对象(会先调用日期类构造一个日期类类型的对象)
- 向上调整
- 实例化一个greater类类型的对象com
- 传数据比较
- 对于自定义类型数据的比较还会调用该自定义函数的比较运算符重载,最后返回比较结果
向优先级队列中传入指针类型的数据:
原因:内置类型不能进行运算符重载(operator<(const Date* d1, const Date* d2)错误)
解决办法:实现一个用于指针比较的仿函数

商品的比较
#pragma once
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;struct Goods
{string _name; // 名字double _price; // 价格int _evaluate; // 评价Goods(const char* str, double price, int evaluate):_name(str), _price(price), _evaluate(evaluate){}
};//根据单价建小堆的仿函数
struct ComparePriceLess
{bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr){return gl._price < gr._price;}
};//根据单价建大堆的仿函数
struct ComparePriceGreater
{bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr){return gl._price > gr._price;}
};//根据个数建小堆的仿函数
struct CompareEvaluateLess
{bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr){return gl._evaluate < gr._evaluate;}
};//根据个数建大堆的仿函数
struct CompareEvaluateGreater
{bool operator()(const Goods& gl, const Goods& gr){return gl._evaluate > gr._evaluate;}
};int main()
{vector<Goods> v = { { "苹果", 2.1, 5 }, { "香蕉", 3, 4 }, { "橙子", 2.2,3 }, { "菠萝", 1.5, 4 } };sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceLess());//按照单价排小堆sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceGreater());//按照单价排大堆sort(v.begin(), v.end(), CompareEvaluateLess());按照个数排小堆sort(v.begin(), v.end(), CompareEvaluateGreater());//按照个数排大堆
}- sort的函数原型:sort(begin,end,cmp)

不写打印函数记得用断点+调试
结论

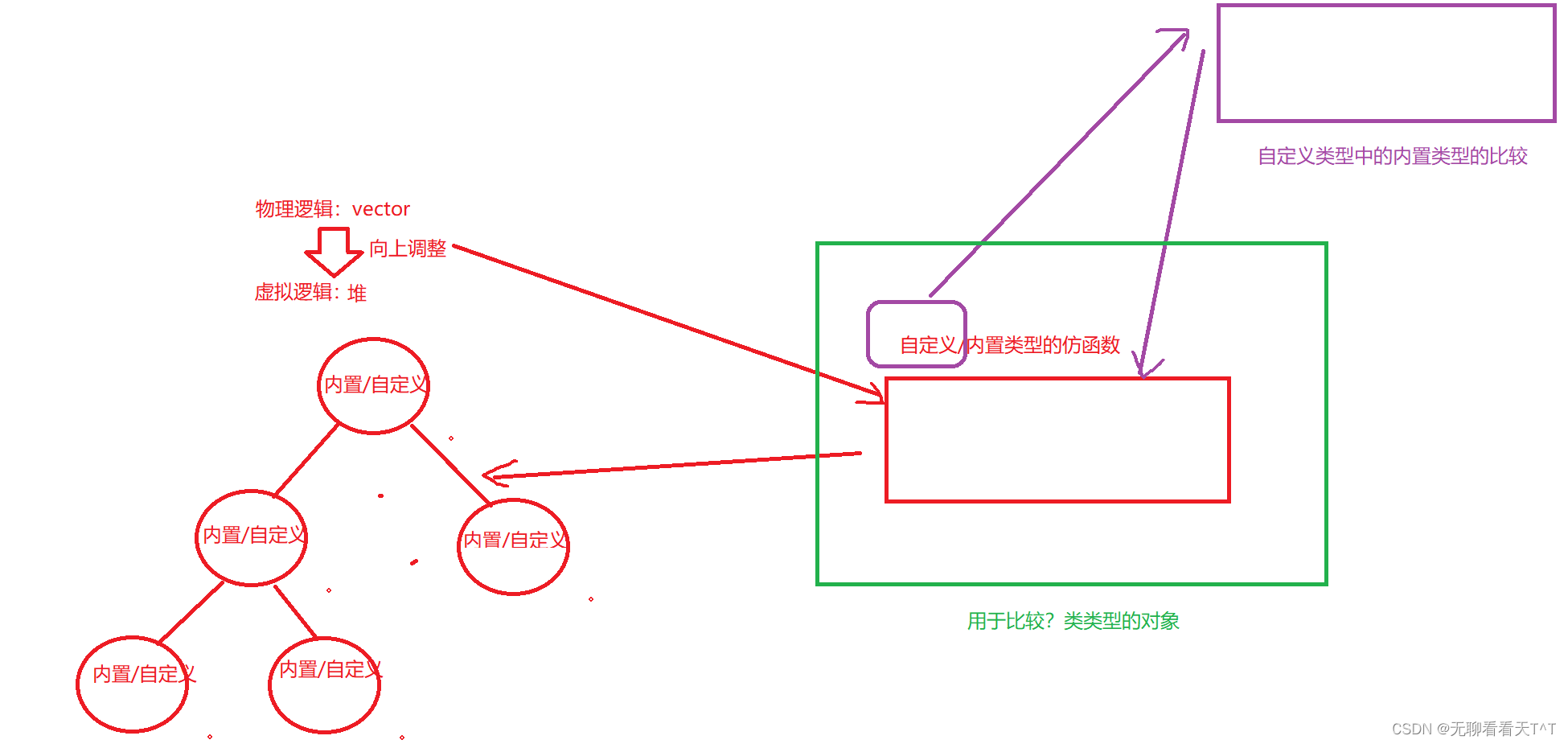
应该是自定义类型的对象
拿日期类来说,pq是优先级队列的对象,_con是vector类类型的对象,该对象中每个下标处存放的都是Data类类型的对象,每次尾插时回去调用pq中的尾插函数先将vector中的尾下标处插入Data类类型的对象,然后将该尾下标的数值(整型数值)传递给向上调整函数,向上调整函数会将父子下标处存放的数据/对象,放入我们预先设计好的获取大/小堆逻辑的仿函数中进行比较,如果vector中父子下标中存放的是自定义类型的对象,在进入仿函数中后还会调用该自定义类型的比较运算符重载函数比较这些自定义类型的对象中的内置类型的数据,然后返回比较结果
~over~
这篇关于C++的stack和queue类(一):适配器模式、双端队列与优先级队列的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





