本文主要是介绍python-装饰器骗局,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
装 饰 器 骗 局
Python 函数装饰器:https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/python-func-decorators.html
装饰器的本意:
加上装饰器—>除了自身功能还有被装饰的内容
不加装饰器—>只有自身的功能
先来看一个装饰器的使用范例:
#计算程序运算时间的装饰器 --- 需要有一个形参 接受待验证运行时间的函数
def get_time(func):def wrapper():import timestart = time.time()func()stop = time.time()print("执行时间", stop - start)return wrapper'''
怎么为对应的功能添加装饰器使用@语法糖 在被需要添加装饰器的功能上方 @装饰器的外部函数
'''
@get_time
def print_nine_table():for r in range(1, 10):for c in range(1, r + 1):print(f"{c} * {r} = {r*c}", end="\t")print()
print_nine_table()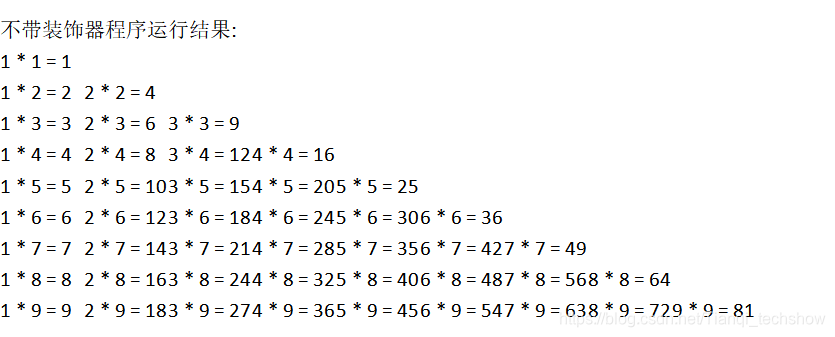

装饰器----->原有函数功能增加 or 函数重构 ?
咱们先来看下 Python 中的函数的一些操作:
def hi(name="yasoob"):return "hi " + nameprint(hi())
# output: 'hi yasoob'# 我们甚至可以将一个函数赋值给一个变量,比如
greet = hi
# 我们这里没有在使用小括号,因为我们并不是在调用hi函数
# 而是在将它放在greet变量里头。我们尝试运行下这个print(greet())
# output: 'hi yasoob'# 如果我们删掉旧的hi函数,看看会发生什么!
del hi
print(hi())
# outputs: NameErrorprint(greet())
# outputs: 'hi yasoob'在函数中定义函数:
def hi(name="yasoob"):print("now you are inside the hi() function")def greet():return "now you are in the greet() function"def welcome():return "now you are in the welcome() function"print(greet())print(welcome())print("now you are back in the hi() function")hi()
# output:now you are inside the hi() function
# now you are in the greet() function
# now you are in the welcome() function
# now you are back in the hi() function# 上面展示了无论何时你调用hi(), greet()和welcome()将会同时被调用。
# 然后greet()和welcome()函数在hi()函数之外是不能访问的,比如:greet()
# outputs: NameError: name 'greet' is not defined从函数中返回函数:
def hi(name="yasoob"):def greet():return "now you are in the greet() function"def welcome():return "now you are in the welcome() function"if name == "yasoob":return greetelse:return welcomea = hi()
print(a)
# outputs: <function greet at 0x7f2143c01500># 上面清晰地展示了`a`现在指向到hi()函数中的greet()函数
# 现在试试这个print(a())
# outputs: now you are in the greet() function将函数作为参数传给另一个函数:
def hi():return "hi yasoob!"def doSomethingBeforeHi(func):print("I am doing some boring work before executing hi()")print(func())doSomethingBeforeHi(hi)
# outputs:I am doing some boring work before executing hi()
# hi yasoob!装饰器实例:
def a_new_decorator(a_func):def wrapTheFunction():print("I am doing some boring work before executing a_func()")a_func()print("I am doing some boring work after executing a_func()")return wrapTheFunctiondef a_function():print("I am the function which needs some decoration to remove my foul smell")a_function()
# outputs: "I am the function which needs some decoration to remove my foul smell"a_function =a_new_decorator(a_functionn)
# now a_function is wrapped by wrapTheFunction()a_function()
# outputs:I am doing some boring work before executing a_func()
# I am the function which needs some decoration to remove my foul smell
# I am doing some boring work after executing a_func()语法糖@:
@a_new_decorator
def a_function():"""Hey you! Decorate me!"""print("I am the function which needs some decoration to ""remove my foul smell")a_function()
# outputs: I am doing some boring work before executing a_func()
# I am the function which needs some decoration to remove my foul smell
# I am doing some boring work after executing a_func()# the @a_new_decorator is just a short way of saying:
a_function= a_new_decorator(a_function)重构的问题:函数被warpTheFunction替代了。它重写了我们函数的名字和注释文档(docstring)
print(a_function.__name__)
# Output: wrapTheFunctionfunctools.wraps的引入:
from functools import wrapsdef a_new_decorator(a_func):@wraps(a_func)def wrapTheFunction():print("I am doing some boring work before executing a_func()")a_func()print("I am doing some boring work after executing a_func()")return wrapTheFunction
@a_new_decorator
def a_function():"""Hey yo! Decorate me!"""print("I am the function which needs some decoration to ""remove my foul smell")print(a_function.__name__)
# Output: a_function综上所述:装饰器本质上是通过程序内容上的一系列操作,把某一个函数的函数体进行了重写,只是名称还是当初那个函数名称,对于计算机来说,只要函数名称一样就会执行相应的函数.
这篇关于python-装饰器骗局的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






