本文主要是介绍CMap在用CString做key类型时,ARG_KEY要选LPCTSTR,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章来源:http://blog.csdn.net/flyingxu/archive/2005/12/26/562852.aspx
遇到好几个人说CMap在用CString做key类型时有问题,说用int和DWORD就可以,用CString就不行。因此很多人推荐使用MFC中的CMapStringToPtr之类。
看下面的代码:
//.h
CMap<CString, LPCTSTR, int, int> typeMap;
//.cpp
typeMap.SetAt(_T("ONE"),1);
typeMap.SetAt(_T("TWO"),2);
int nValue = 0;
BOOL ret = typeMap.Lookup(_T("ONE"), nValue);
ret = typeMap.Lookup(_T("THREE"), nValue);
ret = typeMap.Lookup(_T("TWO"), nValue);
我的代码运行的很好,我觉得关键是ARG_KEY要选LPCTSTR
原因: referencehttp://www.codeproject.com/KB/architecture/cmap_howto.aspx
Introduction
Programmers like me, who learnt STL::map before CMap, always think CMap is difficult to use, and always try to useCMap in the way as a STL::map. In this article, I will explain about CMap and what you should do to use it for your own custom classes. And at the end of this article, I will show an example of how to use CMap correctly withCString* (note, I mean CString pointer and not CString :>)
CMap Internal
The first thing to be noted is that CMap is actually a hash map, and not a tree map (and usually a Red-black tree) asSTL::map. Shown below is the internal structure of a CMap.
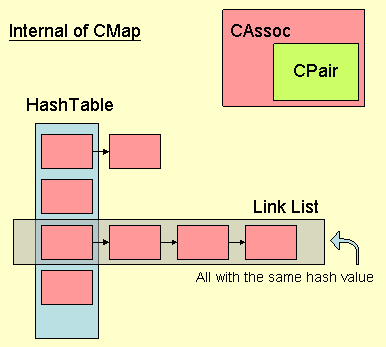
How to declare a CMap
Many people get confused about CMap's declaration CMap<KEY, ARG_KEY, VALUE, ARG_VALUE>, why not justCMap<KEY, VALUE>?
In fact, the ultimate data container in CMap is CPair, and the internal of CPair is {KEY, VALUE}. Therefore, CMapwill really store a KEY, and not ARG_KEY. However, if you check with the MFC source code, almost all the internal parameters passing within CMap itself is called with ARG_KEY and ARG_VALUE, therefore, using KEY& as ARG_KEYseems always a correct thing, except when:
- You are using primitive date types like
int,char, where pass-by-value makes no difference (may be even faster) with pass-by-reference. - If you use
CStringasKEY, you should useLPCTSTRasARG_KEYand notCString&, we will talk more about this later.
So what should I do to make CMap work with my ClassX
Well, as I mentioned earlier, CMap is a hash map, a hash map will try to get the "hash value" -- a UINT -- from the key, and use that hash value as the index in the hash table (well, actually it is hash value % hash table size). If more then one key have the same hash value, they will be linked in a linked list. Therefore, the first thing you have to do is to provide a hash function.
CMap will call a templated function HashKey() to do the hashing. The default implementation and specialized version for LPCSTR and LPCWSTR are listed as follows:
// inside <afxtemp.h> template<class ARG_KEY> AFX_INLINE UINT AFXAPI HashKey(ARG_KEY key) {// default identity hash - works for most primitive values return (DWORD)(((DWORD_PTR)key)>>4); }// inside <strcore.cpp> // specialized implementation for LPCWSTR #if _MSC_VER >= 1100 template<> UINT AFXAPI HashKey<LPCWSTR> (LPCWSTR key) #else UINT AFXAPI HashKey(LPCWSTR key) #endif {UINT nHash = 0;while (*key)nHash = (nHash<<5) + nHash + *key++;return nHash; }// specialized implementation for LPCSTR #if _MSC_VER >= 1100 template<> UINT AFXAPI HashKey<LPCSTR> (LPCSTR key) #else UINT AFXAPI HashKey(LPCSTR key) #endif {UINT nHash = 0;while (*key)nHash = (nHash<<5) + nHash + *key++;return nHash; }
As you can see, the default behavior is to "assume" that the key is a pointer, and convert it to DWORD, and that's why you will get "error C2440: 'type cast': cannot convert from 'ClassXXX' to 'DWORD_PTR'" if you don't provide a specialized HashKey() for your ClassX.
And because MFC only has specialized implementations for the LPCSTR and LPCWSTR, and not for CStringA norCStringW, if you want to use CString in CMap, you have to declare CMap<CString, LPCTSTR....>.
OK, now you know how CMap calculates the hash value, but since more than one key may have the same hash value,CMap needs to traverse the whole linked list to find the one with exactly the same key "content", not only with the same "hash value". And when CMap does the matching, it will call CompareElements(), another templated function.
// inside <afxtemp.h> // noted: when called from CMap, // TYPE=KEY, ARG_TYPE=ARG_TYPE // and note pElement1 is TYPE*, not TYPE template<class TYPE, class ARG_TYPE> BOOL AFXAPI CompareElements(const TYPE* pElement1, const ARG_TYPE* pElement2) {ASSERT(AfxIsValidAddress(pElement1, sizeof(TYPE), FALSE));ASSERT(AfxIsValidAddress(pElement2, sizeof(ARG_TYPE), FALSE));// for CMap<CString, LPCTSTR...> // we are comparing CString == LPCTSTR return *pElement1 == *pElement2; }
Therefore, if you want to use CMap with your own custom ClassX, you will have to provide a specialized implementation for HashKey() and CompareElements().
Example: CMap with CString*
Provided as an example, below is what you need to do to make CMap work with CString*, and of course, using the string content as the key, and not the address of the pointer.
template<> UINT AFXAPI HashKey<CString*> (CString* key) {return (NULL == key) ? 0 : HashKey((LPCTSTR)(*key)); }// I don't know why, but CompareElements can't work with CString* // have to define this typedef CString* LPCString;template<> BOOL AFXAPI CompareElements<LPCString, LPCString> (const LPCString* pElement1, const LPCString* pElement2) {if ( *pElement1 == *pElement2 ) {// true even if pE1==pE2==NULL return true;} else if ( NULL != *pElement1 && NULL != *pElement2 ) {// both are not NULL return **pElement1 == **pElement2;} else {// either one is NULL return false;} }
And the main program is as simple as:
int _tmain(int argc, TCHAR* argv[], TCHAR* envp[]) {CMap<CString*, CString*, int, int> map;CString name1 = "Microsoft";CString name2 = "Microsoft";map[&name1] = 100;int x = map[&name2];printf("%s = %d\n", (LPCTSTR)name1, x);*/return 0; }
--------- console output ---------
Microsoft = 100 Please note that the program can compile without error even without the specialized HashKey() andCompareElements(), but of course, the output will then be 0, probably not what you want.
My final note about CMap
CMapis a hash map andSTL::mapis a tree map, there is no meaning comparing the two for performance (it would be like comparing apples and oranges!). But if you will retrieve the keys in sorted order, then you will have to useSTL::map.- The design of
HashKey()is critical to the overall performance. You should provide aHashKey()that has a low collision rate (different keys generally would have different hash values) and is easy to calculate (not a MD5 of the string, etc..). And we have to note that -- at least for some of the classes -- this is not easy. - When using
CMap(as well asSTL::hash_map), always beware of the hash table size. As quoted in MSDN, "the hash table size should be a prime number. To minimize collisions, the size should be roughly 20 percent larger than the largest anticipated data set". By default,CMaphash table size is 17, which should be okay for around 10 keys. You can change the hash table size withInitHashTable(UINT nHashSize), and can only do so before the first element is added to the map. You can find more prime numbers here. (And don't mix-up withCMap(UINT nBlockSize),nBlockSizeis to acquire more than oneCAssocto speed up the creation of a new node.)
这篇关于CMap在用CString做key类型时,ARG_KEY要选LPCTSTR的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



