本文主要是介绍unicloud where 使用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
where介绍
在uniCloud中,WHERE是一个用于指定查询条件的关键字。它允许用户根据特定的条件来筛选和查询云数据库中的数据。WHERE语句的基本语法格式是WHERE condition,其中condition表示查询条件,可以是一个或多个逻辑表达式组成的条件。
在uniCloud的查询操作中,WHERE子句的使用非常灵活,可以支持多种查询条件,包括等于、不等于、大于、小于、范围查询等。同时,它还可以支持多个条件的组合查询,通过逻辑运算符(如AND、OR)将多个条件连接起来,实现更复杂的查询需求。
此外,WHERE子句还支持正则表达式查询,可以使用正则表达式来匹配和筛选符合特定模式的数据。这使得在处理文本数据时,能够更加精确地定位到所需的信息。
WHERE在uniCloud中是一个强大的查询工具,能够帮助用户快速、准确地获取所需的数据。无论是简单的条件查询还是复杂的组合查询,都可以通过WHERE子句来实现。
要查看本文章,请先阅读unicloud 集合 Collection 详解及其使用示例
示例教程如下
where 简单使用(查询对象)
使用where查询时,如果传入的参数是一个对象,将按照字段的值进行相等匹配,包含字段顺序。
如查看users表内年龄是38岁的人
示例代码如下
云函数代码
'use strict';
exports.main = async (event, context) => {const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({age:38}).get()//返回数据给客户端return result
};页面引用代码
const where = async _=>{const result = await uniCloud.callFunction({name:'where'})console.log(result)
}
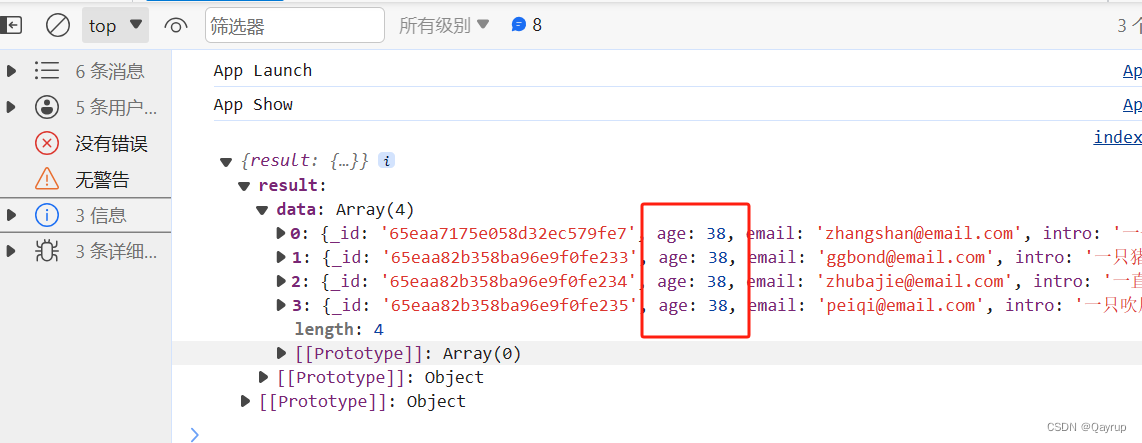
输出结果如下
可以看到,将age为38的都查询出来了
where 高级使用(查询指令)
查询指令以dbCmd.开头,包括等于、不等于、大于、大于等于、小于、小于等于、in、nin、and、or。
tips:
- 以下指令挂载在 db.command 下
指令图表如下
| 指令 | 描述 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| eq | 等于 | name:dbCmd.eq(‘qayrup’) |
| neq | 不等于 | 删除字段 |
| gt | 大于 | 加一个数值,原子自增 |
| gte | 大于等于 | 乘一个数值,原子自乘 |
| it | 小于 | 数组类型字段追加尾元素,支持数组 |
| ite | 小于等于 | 数组类型字段删除尾元素,支持数组 |
| in | 在数组中 | 数组类型字段删除头元素,支持数组 |
| nin | 不再数组中 | 数组类型字段追加头元素,支持数组 |
| and | 且 | 数组类型字段追加头元素,支持数组 |
| or | 或 | 数组类型字段追加头元素,支持数组 |
eq 等于
表示字段等于某个值。eq 指令接受一个字面量 (literal),可以是 number, boolean, string, object, array。
事实上在uniCloud的数据库中,等于有两种写法。
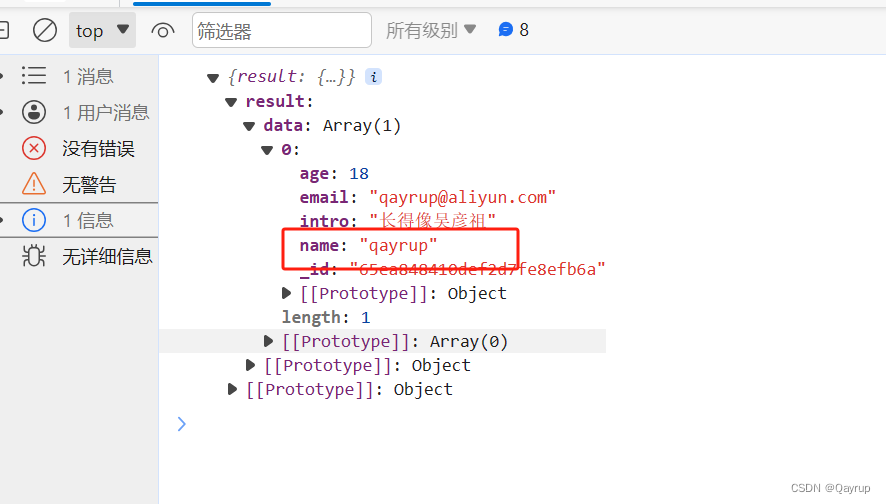
比如筛选名字为qayrup的
第一种写法使用对象
云函数示例代码
'use strict';
exports.main = async (event, context) => {const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()//返回数据给客户端return result
};输出结果
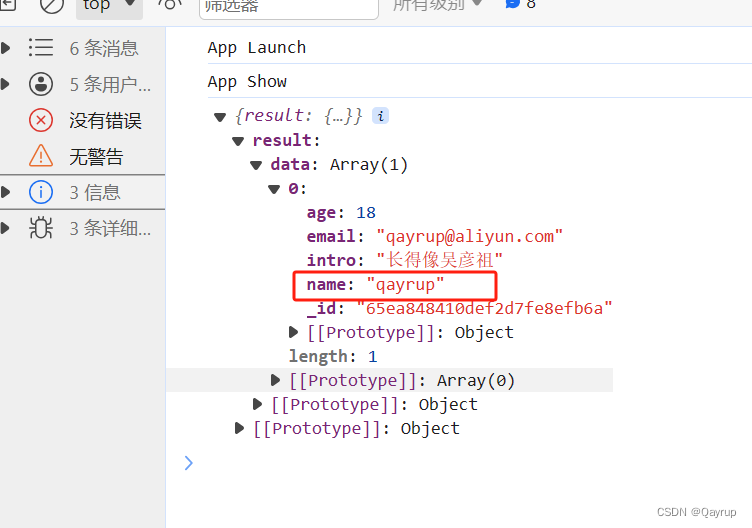
第二种写法使用eq指令
云函数代码如下
'use strict';
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eqconst result = await uniCloud.database().collection().where({name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')})return result
};输出结果如下
neq 不等于
字段不等于。neq 指令接受一个字面量 (literal),可以是 number, boolean, string, object, array。
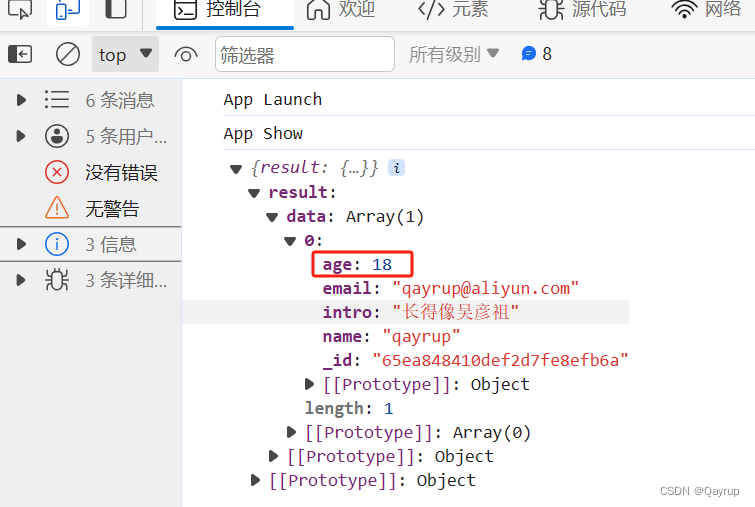
例如筛选出age不为38的数据
示例代码如下
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.neq(38)}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
gt 大于
字段大于指定值。
如筛选年龄大于20的
示例代码如下
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.gt(20)}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
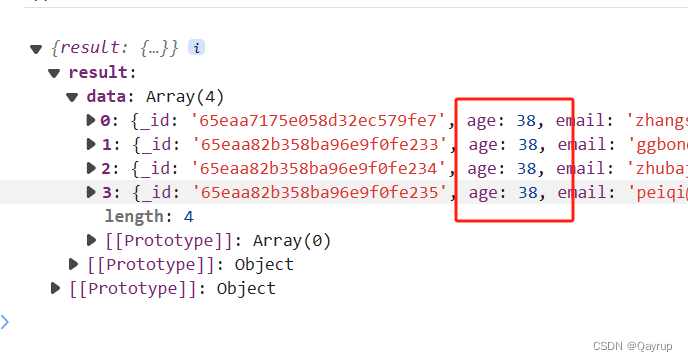
gte 大于等于
字段大于或等于指定值。
筛选年龄大于等于18的
示例代码如下
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.gte(18)}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
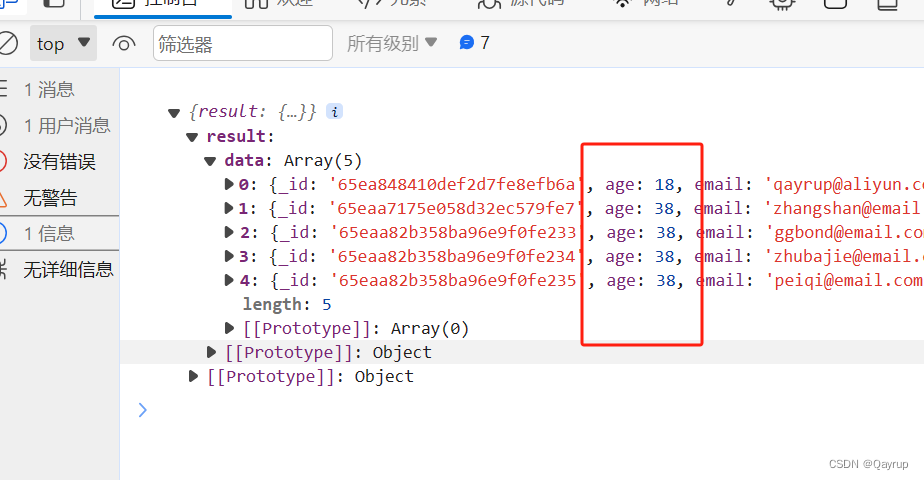
lt 小于
字段小于指定值。
筛选年龄小于20的
示例代码如下
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gte(18)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于20的const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.lt(20)}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
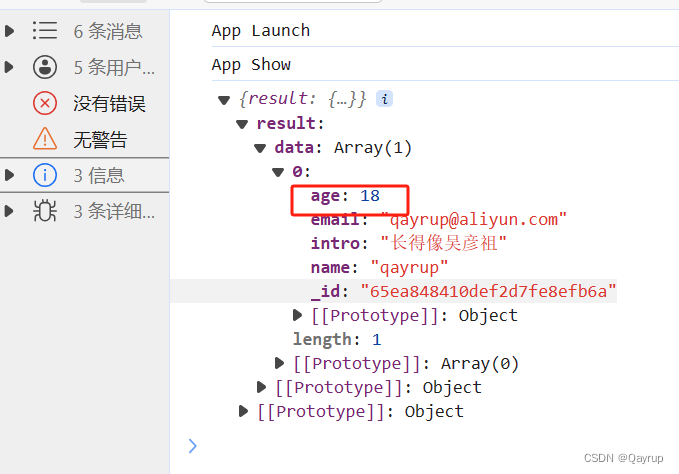
lte 小于等于
字段小于或等于指定值。
筛选小于等于18的
示例代码如下
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gte(18)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于等于十八的const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.lte(18)}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
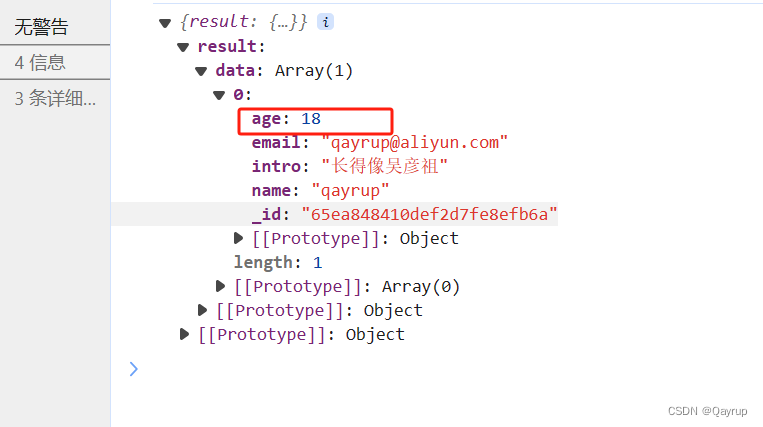
in 在数组中
字段值在给定的数组中。
'use strict';const { setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback } = require("process");const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gte(18)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于等于十八的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lte(18)// }).get()// return result// 名字在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内const result = await db.collection('users').where({name:dbCmd.in(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
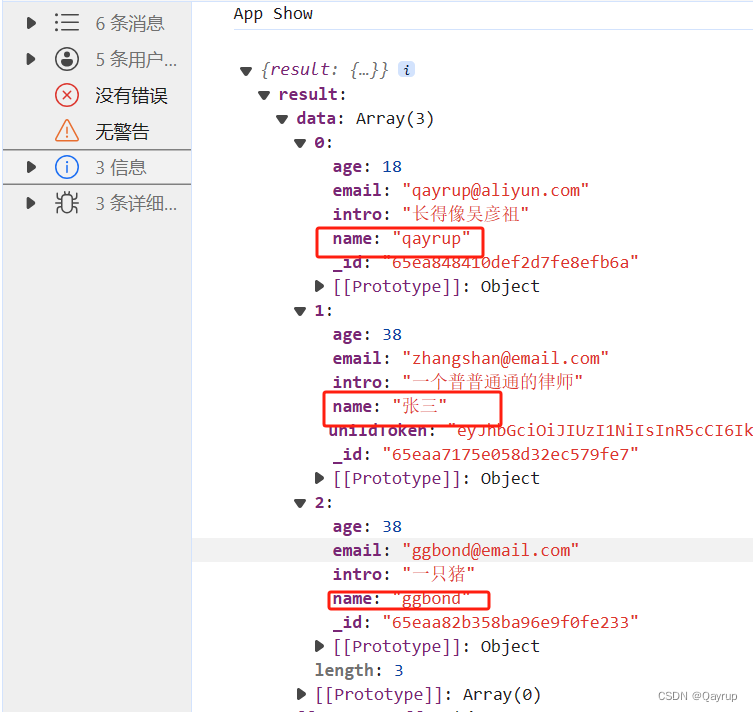
nin 不在数组中
字段值不在给定的数组中。
名字不在[‘qayrup’,‘张三’,‘ggbond’] 内
示例代码如下
'use strict';const { setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback } = require("process");const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gte(18)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于等于十八的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lte(18)// }).get()// return result// 名字在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// name:dbCmd.in(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )// }).get()// 名字不在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内const result = await db.collection('users').where({name:dbCmd.nin(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
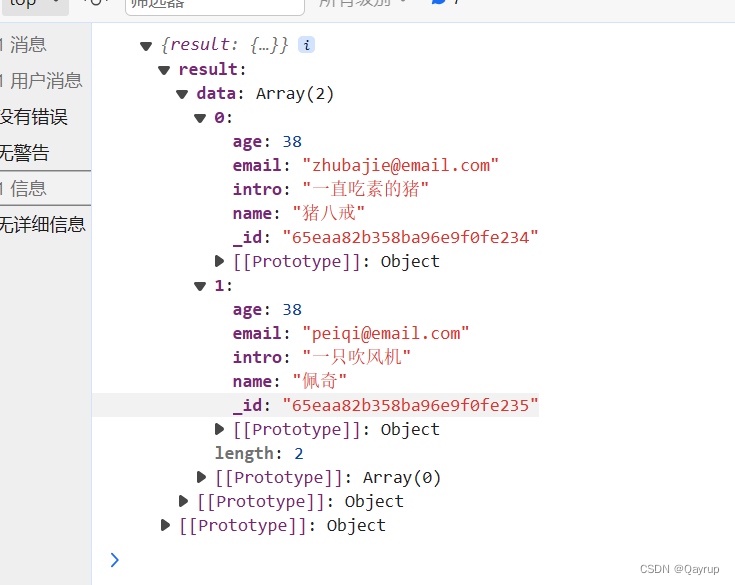
and 且
表示需同时满足指定的两个或以上的条件。
筛选出 年龄大于20且小于50的
示例代码如下
'use strict';const { setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback } = require("process");const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gte(18)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于等于十八的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lte(18)// }).get()// return result// 名字在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// name:dbCmd.in(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )// }).get()// 名字不在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// name:dbCmd.nin(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )// }).get()// 筛选出 年龄大于20且小于50的const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.gt(20).and(dbCmd.lt(50))}).get()return result
};结果如下
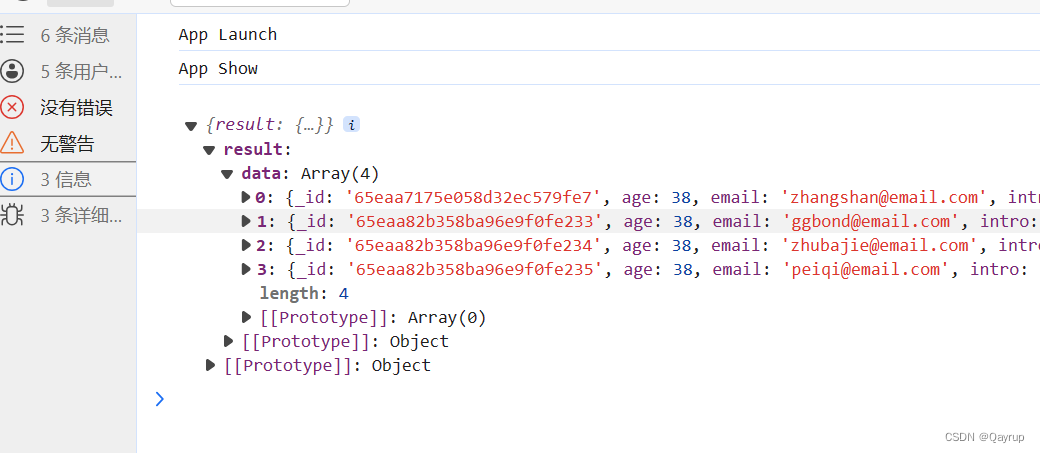
or 或
表示需满足所有指定条件中的至少一个。
筛选 年龄等于18或年龄等38的
示例代码如下
'use strict';const { setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback } = require("process");const db = uniCloud.database()
const dbCmd = db.command
exports.main = async (event, context) => {// 查询字段等于某个值 第一种写法// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({name:'qayrup'}).get()// 查询字段等于某个值 第二个写法 使用eq// const result = await uniCloud.database().collection('users').where({// name:uniCloud.database().command.eq('qayrup')// }).get()// 查询 age 不等于38的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.neq(38)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄大于等于18的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gte(18)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于20的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lt(20)// }).get()// 筛选年龄小于等于十八的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.lte(18)// }).get()// return result// 名字在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// name:dbCmd.in(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )// }).get()// 名字不在['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] 内// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// name:dbCmd.nin(['qayrup','张三','ggbond'] )// }).get()// 筛选出 年龄大于20且小于50的// const result = await db.collection('users').where({// age:dbCmd.gt(20).and(dbCmd.lt(50))// }).get()// 筛选 年龄等于18或年龄等38的const result = await db.collection('users').where({age:dbCmd.eq(18).or(dbCmd.eq(38))}).get()return result
};输出结果如下
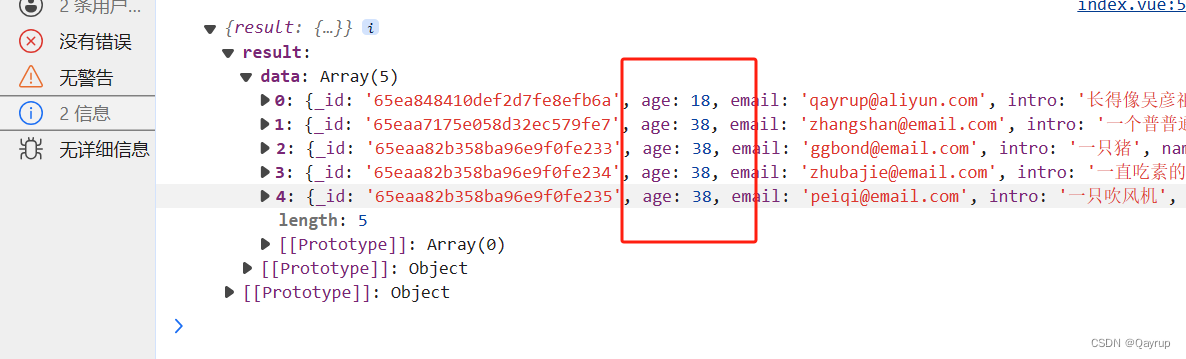
正则表达式查询
db.RegExp
根据正则表达式进行筛选
正则表达式忘得差不多了,这里就不做示例了
以上指令所示例的数据集
[{"_id":"65ea848410def2d7fe8efb6a","age":18,"email":"qayrup@aliyun.com","intro":"长得像吴彦祖","name":"qayrup"},
{"_id":"65eaa7175e058d32ec579fe7","age":38,"email":"zhangshan@email.com","intro":"一个普普通通的律师","name":"张三","uniIdToken":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1aWQiOiI2NTg4M2Y3MTZlNWQyZDcxODc5MDAxYjEiLCJyb2xlIjpbXSwicGVybWlzc2lvbiI6W10sInVuaUlkVmVyc2lvbiI6IjEuMC4xNiIsImlhdCI6MTcwMzQyNzk0NCwiZXhwIjoxNzAzNDM1MTQ0fQ.hy40ZsKGvtnm4IDA0HpOFYwhE-5x69OZXQcZ57EoTO8"},
{"_id":"65eaa82b358ba96e9f0fe233","age":38,"email":"ggbond@email.com","intro":"一只猪","name":"ggbond"},
{"_id":"65eaa82b358ba96e9f0fe234","age":38,"email":"zhubajie@email.com","intro":"一直吃素的猪","name":"猪八戒"},
{"_id":"65eaa82b358ba96e9f0fe235","age":38,"email":"peiqi@email.com","intro":"一只吹风机","name":"佩奇"}]
这篇关于unicloud where 使用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





