本文主要是介绍python中struct.pack中的fmt理解(笔记),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
python官方的文档
我们知道python只定义了6种数据类型,字符串,整数,浮点数,列表,元组,字典。但是C语言中有些字节型的变量,在python中该如何实现呢?这点颇为重要,特别是要在网络上进行数据传输的话。
struct.pack(fmt, v1, v2, …)
Return a string containing the values v1, v2, … packed according to the given format. The arguments must match the values required by the format exactly.
野生翻译:返回一个包含v1,v2的,根据所给fmt打包的字符串,其中的参数必须和fmt要求的值匹配
重点来理解一下fmt:
一、下面是讲fmt的第一个字符:
By default, C types are represented in the machine’s native format and byte order, and properly aligned by skipping pad bytes if necessary (according to the rules used by the C compiler).
野生翻译:默认情况下,C类型在机器的本机格式和字节顺序中表示,如果需要的话,可以通过跳过pad字节来正确地对齐(根据C编译器使用的规则)。
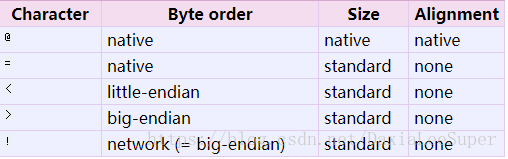
Alternatively, the first character of the format string can be used to indicate the byte order, size and alignment of the packed data, according to the following table:
野生翻译:可以使用格式字符串的第一个字符来指示填充数据的字节顺序、大小和对齐方式(这是可选的),如下表所示
If the first character is not one of these, ‘@’ is assumed.
野生翻译:如果第一个字符不是上面表里面中的一个,@是默认的值
Native byte order is big-endian or little-endian, depending on the host system. For example, Intel x86 and AMD64 (x86-64) are little-endian; Motorola 68000 and PowerPC G5 are big-endian; ARM and Intel Itanium feature switchable endianness (bi-endian). Use sys.byteorder to check the endianness of your system.
野生翻译:原生字节顺序是big-endian还是little-endian,取决于主机系统。例如,Intel x86和AMD64(x86-64)是little-endian ;摩托罗拉68000和PowerPC G5是big-endian; ARM和英特尔的Itanium特性是可切换的(双endian)。可以使用sys.byteorder指令来检查你系统是按照什么排序的
Native size and alignment are determined using the C compiler’s sizeof expression. This is always combined with native byte order.
Standard size depends only on the format character; see the table in the Format Characters section.
Note the difference between ‘@’ and ‘=’: both use native byte order, but the size and alignment of the latter is standardized.
The form ‘!’ is available for those poor souls who claim they can’t remember whether network byte order is big-endian or little-endian.
There is no way to indicate non-native byte order (force byte-swapping); use the appropriate choice of ‘<’ or ‘>’.
野生翻译:本机大小和对齐是使用C编译器的sizeof表达式来确定的。这总是与本机字节顺序相结合。
标准大小只取决于格式字符;请参见格式字符部分中的表格。
注意“@”和“=”之间的区别:两者都使用本机字节顺序,但是后者的大小和对齐是标准化的。
表单”!“对于那些不记得网络字节顺序是big-endian或little-endian的字节顺序的人来说是可行的。”
没有办法指出非本地字节顺序(强制字节交换);使用“<”或“>”的适当选择。
Notes:
- Padding is only automatically added between successive structure members. No padding is added at the beginning or the end of the encoded struct.
- No padding is added when using non-native size and alignment, e.g. with ‘<’, ‘>’, ‘=’, and ‘!’.
- To align the end of a structure to the alignment requirement of a particular type, end the format with the code for that type with a repeat count of zero. See Examples.
野生翻译:
注意:
- 填充只在连续的结构成员之间自动添加。在编码的结构体的开始或结束时没有添加填充物。
- 在使用非本地大小和对齐方式时,不添加任何填充,例如“<”、“”、“=”和“!”。
- 为了使结构的结束与特定类型的对齐要求保持一致,以重复计数为零的方式结束该类型的代码。详见examples
二、 下面是讲fmt后面的内容
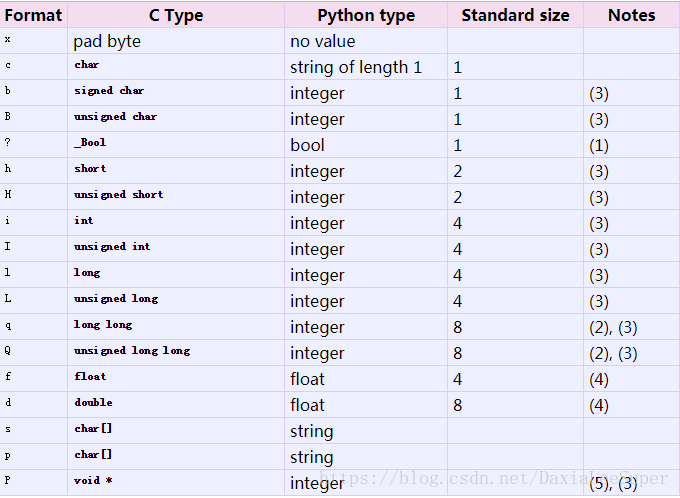
Format characters have the following meaning; the conversion between C and Python values should be obvious given their types. The ‘Standard size’ column refers to the size of the packed value in bytes when using standard size; that is, when the format string starts with one of ‘<’, ‘>’, ‘!’ or ‘=’. When using native size, the size of the packed value is platform-dependent.
野生翻译:fmt字符有以下含义;C和Python值之间的转换应该是明显的,因为它们提供的类型。“标准大小”列指的是在使用标准尺寸时以字节为单位的包装值的大小;也就是说,当fmt以“<”、“”、“!”开头的时候。”或“=”。当使用本机大小时,包装值的大小与平台相关。
Notes:
- The ‘?’ conversion code corresponds to the _Bool type defined by C99. If this type is not available, it is simulated using a char. In standard mode, it is always represented by one byte.
New in version 2.6.
- The ‘q’ and ‘Q’ conversion codes are available in native mode only if the platform C compiler supports C long long, or, on Windows, __int64. They are always available in standard modes.
New in version 2.2.
- When attempting to pack a non-integer using any of the integer conversion codes, if the non-integer has a index() method then that method is called to convert the argument to an integer before packing. If no index() method exists, or the call to index() raises TypeError, then the int() method is tried. However, the use of int() is deprecated, and will raise DeprecationWarning.
Changed in version 2.7: Use of the index() method for non-integers is new in 2.7.
Changed in version 2.7: Prior to version 2.7, not all integer conversion codes would use the int() method to convert, and DeprecationWarning was raised only for float arguments.
-
For the ‘f’ and ‘d’ conversion codes, the packed representation uses the IEEE 754 binary32 (for ‘f’) or binary64 (for ‘d’) format, regardless of the floating-point format used by the platform.
-
The ‘P’ format character is only available for the native byte ordering (selected as the default or with the ‘@’ byte order character). The byte order character ‘=’ chooses to use little- or big-endian ordering based on the host system. The struct module does not interpret this as native ordering, so the ‘P’ format is not available.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………分割线………………………………………………………
以下是一个例子:
如一个消息头
| 名称 | 类型定义 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| MsgType | uInt32 | 消息类型 |
| seqNum | Int64 | 消息序号 |
| BodyLength | uint32 | 消息体长度 |
这篇关于python中struct.pack中的fmt理解(笔记)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!