本文主要是介绍【cmu15445c++入门】(5)C++ 包装类(管理资源的类),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、背景
c++包装类
二、运行代码
// A C++ wrapper class is a class that manages a resource. A resource
// could be memory, file sockets, or a network connection. Wrapper classes
// often use the RAII (Resource Acquisition is Initialization) C++
// programming technique. Using this technique implies that the resource's
// lifetime is tied to its scope. When an instance of the wrapper class is
// constructed, this means that the underlying resource it is managing is
// available, and when this instance is destructed, the resource also
// is unavailable. //C++ 包装类是管理资源的类。资源可以是内存、文件套接字或网络连接。
//包装类通常使用 RAII(资源获取即初始化)C++ 编程技术。
//使用此技术意味着资源的生存期与其范围相关联。
//当构造包装类的实例时,这意味着它所管理的基础资源是可用的,而当此实例被销毁时,该资源也是不可用的。// Here are a couple resources on RAII that are useful:
// https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/raii (RAII docs on the CPP
// docs website)
// Interesting Stack Overflow answers to "What is meant by RAII?":
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2321511/what-is-meant-by-resource-acquisition-is-initialization-raii// In this file, we will look at a basic implementation of a wrapper class that
// manages an int*. We will also look at usage of this class.// Includes std::cout (printing) for demo purposes.
#include <iostream>
// Includes the utility header for std::move.
#include <utility>// The IntPtrManager class is a wrapper class that manages an int*. The
// resource that this class is managing is the dynamic memory accessible via
// the pointer ptr_. By the principles of the RAII technique, a wrapper class
// object should not be copyable, since one object is supposed to manage one
// resource. Therefore, the copy assignment operator and copy constructor are
// deleted from this class. However, the class is still moveable from different
// lvalues/owners, and has a move constructor and move assignment operator.
// Another reason that wrapper classes forbid copying is because they destroy
// their resource in the destructor, and if two objects are managing the same
// resource, there is a risk of double deletion of the resource.
// IntPtrManager 类是管理 int* 的包装类。此类管理的资源是通过指针ptr_访问的动态内存。
// 根据 RAII 技术的原则,包装类对象不应该是可复制的,因为一个对象应该管理一个资源。
// 因此,从此类中删除复制赋值运算符和复制构造函数。但是,该类仍然可以从不同的左值/所有者移动,并且具有移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符。
// 包装类禁止复制的另一个原因是在析构函数中进行做资源销毁,如果两个对象管理同一资源,则存在双重删除资源的风险。class IntPtrManager {public:// All constructors of a wrapper class are supposed to initialize a resource.// In this case, this means allocating the memory that we are managing.// The default value of this pointer's data is 0.IntPtrManager() {ptr_ = new int;*ptr_ = 0;}// Another constructor for this wrapper class that takes a initial value.IntPtrManager(int val) {ptr_ = new int;*ptr_ = val;}// Destructor for the wrapper class. The destructor must destroy the// resource that it is managing; in this case, the destructor deletes// the pointer!~IntPtrManager() {// Note that since the move constructor marks objects invalid by setting// their ptr_ value to nullptr, we have to account for this in the // destructor. We don't want to be calling delete on a nullptr!std::cout << "~IntPtrManager()" << std::endl;if (ptr_) {std::cout << "ptr is " << ptr_ <<std::endl;delete ptr_;}}// Move constructor for this wrapper class. Note that after the move// constructor is called, effectively moving all of other's data into// the specified instance being constructed, the other object is no// longer a valid instance of the IntPtrManager class, since it has// no memory to manage. IntPtrManager(IntPtrManager&& other) {ptr_ = other.ptr_;other.ptr_ = nullptr;}// Move assignment operator for class Person. Similar techniques as// the move constructor.IntPtrManager &operator=(IntPtrManager &&other) {ptr_ = other.ptr_;other.ptr_ = nullptr;return *this;}// We delete the copy constructor and the copy assignment operator,// so this class cannot be copy-constructed. IntPtrManager(const IntPtrManager &) = delete;IntPtrManager &operator=(const IntPtrManager &) = delete;// Setter function.void SetVal(int val) {*ptr_ = val;}// Getter function.int GetVal() const {return *ptr_;}private:int *ptr_;};int main() {// We initialize an instance of IntPtrManager. After it is initialized, this// class is managing an int pointer.IntPtrManager a(445);// Getting the value works as expected.std::cout << "1. Value of a is " << a.GetVal() << std::endl;// Setting the value goes through, and the value can retrieved as expected.a.SetVal(645);std::cout << "2. Value of a is " << a.GetVal() << std::endl;// Now, we move the instance of this class from the a lvalue to the b lvalue// via the move constructor.IntPtrManager b(std::move(a));// Retrieving the value of b works as expected because b is now managing the// data originally constructed by the constructor that created a. Note that// calling GetVal() on a will segfault, and a is supposed to effectively be// empty and unusable in this state.std::cout << "Value of b is " << b.GetVal() << std::endl;// 此时去访问a必然会报错退出//std::cout << "Value of a is " << a.GetVal() << std::endl;IntPtrManager c = std::move(b);std::cout << "Value of c is " << c.GetVal() << std::endl;c.SetVal(123);// Once this function ends, the destructor for both a and b will be called.// a's destructor will note that the ptr_ it is managing has been set to // nullptr, and will do nothing, while b's destructor should free the memory// it is managing.// 在函数退出之后,会有析构函数return 0;
}三、运行结果
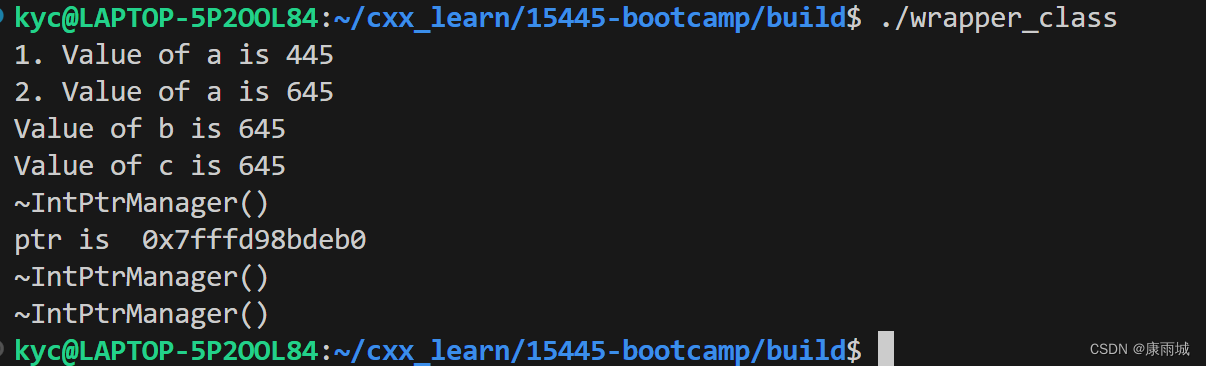
这篇关于【cmu15445c++入门】(5)C++ 包装类(管理资源的类)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





