本文主要是介绍【深度学习】序列生成模型(六):评价方法计算实例:计算ROUGE-N得分【理论到程序】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 一、BLEU-N得分(Bilingual Evaluation Understudy)
- 二、ROUGE-N得分(Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation)
- 1. 定义
- 2. 计算
- N=1
- N=2
- 3. 程序
给定一个生成序列“The cat sat on the mat”和两个参考序列“The cat is on the mat”“The bird sat on the bush”分别计算BLEU-N和ROUGE-N得分(N=1或N =2时).
- 生成序列 x = the cat sat on the mat \mathbf{x}=\text{the cat sat on the mat} x=the cat sat on the mat
- 参考序列
- s ( 1 ) = the cat is on the mat \mathbf{s}^{(1)}=\text{the cat is on the mat} s(1)=the cat is on the mat
- s ( 2 ) = the bird sat on the bush \mathbf{s}^{(2)}=\text{the bird sat on the bush} s(2)=the bird sat on the bush
一、BLEU-N得分(Bilingual Evaluation Understudy)
【深度学习】序列生成模型(五):评价方法计算实例:计算BLEU-N得分
二、ROUGE-N得分(Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation)
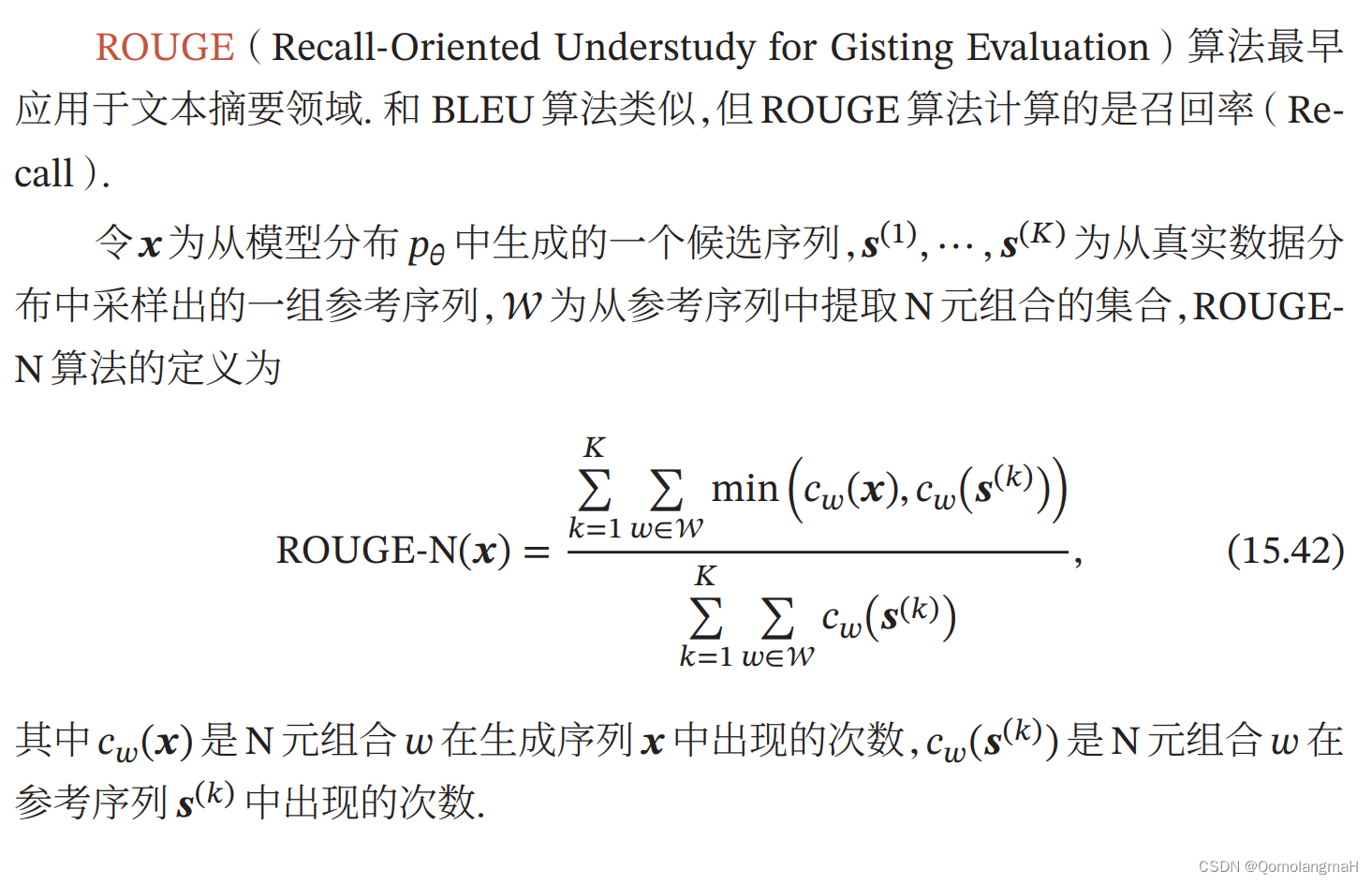
1. 定义
设 x \mathbf{x} x 为从模型分布 p θ p_{\theta} pθ 中生成的一个候选序列, s ( 1 ) , ⋯ , s ( K ) \mathbf{s^{(1)}}, ⋯ , \mathbf{s^{(K)}} s(1),⋯,s(K) 为从真实数据分布中采样得到的一组参考序列, W \mathcal{W} W 为从参考序列中提取N元组合的集合,ROUGE-N算法的定义为:
ROUGE-N ( x ) = ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) \text{ROUGE-N}(\mathbf{x}) = \frac{\sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}))}{\sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k))}} ROUGE-N(x)=∑k=1K∑w∈Wcw(s(k))∑k=1K∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))
其中 c w ( x ) c_w(\mathbf{x}) cw(x) 是N元组合 w w w 在生成序列 x \mathbf{x} x 中出现的次数, c w ( s ( k ) ) ) c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k))}) cw(s(k))) 是N元组合 w w w 在参考序列 s ( k ) \mathbf{s}^{(k)} s(k) 中出现的次数。
2. 计算
N=1
- 生成序列 x = the cat sat on the mat \mathbf{x}=\text{the cat sat on the mat} x=the cat sat on the mat
- 参考序列
- s ( 1 ) = the cat is on the mat \mathbf{s}^{(1)}=\text{the cat is on the mat} s(1)=the cat is on the mat
- s ( 2 ) = the bird sat on the bush \mathbf{s}^{(2)}=\text{the bird sat on the bush} s(2)=the bird sat on the bush
- W = the, cat, is, on, mat, bird, sat, bush \mathcal{W}=\text{ {the, cat, is, on, mat, bird, sat, bush }} W= the, cat, is, on, mat, bird, sat, bush
| w w w | c w ( x ) c_w(\mathbf{x}) cw(x) | c w ( s ( 1 ) ) c_w(\mathbf{s^{(1)}}) cw(s(1)) | c w ( s ( 2 ) ) c_w(\mathbf{s^{(2)}}) cw(s(2)) | min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 1 ) ) \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)}) min(cw(x),cw(s(1)) | min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 2 ) ) \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)}) min(cw(x),cw(s(2)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| the | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| cat | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| is | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| on | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| mat | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| bird | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| sat | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| bush | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
- 分子 ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) \sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)})) ∑k=1K∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))
- ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 1 ) ) = 2 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 1 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 5 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)})=2+1+0+1+1+0+0+0=5 ∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(1))=2+1+0+1+1+0+0+0=5
- ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 2 ) ) = 2 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 0 = 4 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)})=2+0+0+1+0+0+1+0=4 ∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(2))=2+0+0+1+0+0+1+0=4
- ∑ k = 1 2 ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) = ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 1 ) ) ) + ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 2 ) ) ) = 5 + 4 = 9 \sum_{k=1}^{2} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}))=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)}))+\sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)}))=5+4=9 ∑k=12∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))=∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(1)))+∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(2)))=5+4=9
- 分母 ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) \sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}) ∑k=1K∑w∈Wcw(s(k))
- ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 1 ) ) = 6 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1))}=6 ∑w∈Wcw(s(1))=6
- ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 2 ) ) = 6 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)})=6 ∑w∈Wcw(s(2))=6
- ∑ k = 1 2 ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) = ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 1 ) ) + ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 2 ) ) = 12 \sum_{k=1}^{2} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)})= \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)})+ \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)})=12 ∑k=12∑w∈Wcw(s(k))=∑w∈Wcw(s(1))+∑w∈Wcw(s(2))=12
- ROUGE-N ( x ) = ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) = 5 + 4 6 + 6 = 9 12 = 0.75 \text{ROUGE-N}(\mathbf{x}) = \frac{\sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}))}{\sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k))}}=\frac{5+4}{6+6}=\frac{9}{12}=0.75 ROUGE-N(x)=∑k=1K∑w∈Wcw(s(k))∑k=1K∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))=6+65+4=129=0.75
N=2
- 生成序列 x = the cat sat on the mat \mathbf{x}=\text{the cat sat on the mat} x=the cat sat on the mat
- 参考序列
- s ( 1 ) = the cat is on the mat \mathbf{s}^{(1)}=\text{the cat is on the mat} s(1)=the cat is on the mat
- s ( 2 ) = the bird sat on the bush \mathbf{s}^{(2)}=\text{the bird sat on the bush} s(2)=the bird sat on the bush
- W = the cat, cat is, is on, on the, the mat, the bird, bird sat, sat on, the bush \mathcal{W}=\text{ {the cat, cat is, is on, on the, the mat, the bird, bird sat, sat on, the bush }} W= the cat, cat is, is on, on the, the mat, the bird, bird sat, sat on, the bush
| w w w | c w ( x ) c_w(\mathbf{x}) cw(x) | c w ( s ( 1 ) ) c_w(\mathbf{s^{(1)}}) cw(s(1)) | c w ( s ( 2 ) ) c_w(\mathbf{s^{(2)}}) cw(s(2)) | min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 1 ) ) \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)}) min(cw(x),cw(s(1)) | min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 2 ) ) \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)}) min(cw(x),cw(s(2)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| the cat | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| cat is | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| is on | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| on the | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| the mat | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| the bird | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| bird sat | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| sat on | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| the bush | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
- 分子 ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) \sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)})) ∑k=1K∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))
- ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 1 ) ) = 3 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)})=3 ∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(1))=3
- ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 2 ) ) = 2 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)})=2 ∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(2))=2
- ∑ k = 1 2 ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) = ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 1 ) ) ) + ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( 2 ) ) ) = 3 + 2 = 5 \sum_{k=1}^{2} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}))=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)}))+\sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)}))=3+2=5 ∑k=12∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))=∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(1)))+∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(2)))=3+2=5
- 分母 ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) \sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}) ∑k=1K∑w∈Wcw(s(k))
- ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 1 ) ) = 5 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1))}=5 ∑w∈Wcw(s(1))=5
- ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 2 ) ) = 5 \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)})=5 ∑w∈Wcw(s(2))=5
- ∑ k = 1 2 ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) = ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 1 ) ) + ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( 2 ) ) = 10 \sum_{k=1}^{2} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)})= \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(1)})+ \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(2)})=10 ∑k=12∑w∈Wcw(s(k))=∑w∈Wcw(s(1))+∑w∈Wcw(s(2))=10
- ROUGE-N ( x ) = ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W min ( c w ( x ) , c w ( s ( k ) ) ) ∑ k = 1 K ∑ w ∈ W c w ( s ( k ) ) = 3 + 2 5 + 5 = 5 10 = 0.5 \text{ROUGE-N}(\mathbf{x}) = \frac{\sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} \min(c_w(\mathbf{x}), c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k)}))}{\sum_{k=1}^{K} \sum_{w \in \mathcal{W}} c_w(\mathbf{s}^{(k))}}=\frac{3+2}{5+5}=\frac{5}{10}=0.5 ROUGE-N(x)=∑k=1K∑w∈Wcw(s(k))∑k=1K∑w∈Wmin(cw(x),cw(s(k)))=5+53+2=105=0.5
3. 程序
main_string = 'the cat sat on the mat'
string1 = 'the cat is on the mat'
string2 = 'the bird sat on the bush'words = list(set(string1.split(' ')+string2.split(' '))) # 去除重复元素total_occurrences, matching_occurrences = 0, 0
for word in words:matching_occurrences += min(main_string.count(word), string1.count(word)) + min(main_string.count(word), string2.count(word))total_occurrences += string1.count(word) + string2.count(word)print(matching_occurrences / total_occurrences)bigrams = []
split1 = string1.split(' ')
for i in range(len(split1) - 1):bigrams.append(split1[i] + ' ' + split1[i + 1])split2 = string2.split(' ')
for i in range(len(split2) - 1):bigrams.append(split2[i] + ' ' + split2[i + 1])bigrams = list(set(bigrams)) # 去除重复元素total_occurrences, matching_occurrences = 0, 0
for bigram in bigrams:matching_occurrences += min(main_string.count(bigram), string1.count(bigram)) + min(main_string.count(bigram), string2.count(bigram))total_occurrences += string1.count(bigram) + string2.count(bigram)print(matching_occurrences / total_occurrences)输出:
0.75
0.5
这篇关于【深度学习】序列生成模型(六):评价方法计算实例:计算ROUGE-N得分【理论到程序】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



