本文主要是介绍《PCL点云库学习VS2010(X64)》Part 23 快速双边滤波算法之三线插值,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
《PCL点云库学习&VS2010(X64)》Part 23 快速双边滤波算法之三线插值
一、源代码
快速双边滤波算法的精华部分在3D网格分配、控制网格延伸范围、下采样和上采样线性插值三个主要部分。
核心代码:
#ifndef PCL_FILTERS_IMPL_FAST_BILATERAL_HPP_
#define PCL_FILTERS_IMPL_FAST_BILATERAL_HPP_#include <pcl/common/io.h>//
template <typename PointT> void
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::applyFilter (PointCloud &output)
{if (!input_->isOrganized ()){PCL_ERROR ("[pcl::FastBilateralFilter] Input cloud needs to be organized.\n");return;}copyPointCloud (*input_, output);float base_max = -std::numeric_limits<float>::max (),base_min = std::numeric_limits<float>::max ();bool found_finite = false;for (size_t x = 0; x < output.width; ++x){for (size_t y = 0; y < output.height; ++y){if (pcl_isfinite (output (x, y).z)){if (base_max < output (x, y).z)base_max = output (x, y).z;if (base_min > output (x, y).z)base_min = output (x, y).z;found_finite = true;}}}if (!found_finite){PCL_WARN ("[pcl::FastBilateralFilter] Given an empty cloud. Doing nothing.\n");return;}for (size_t x = 0; x < output.width; ++x)for (size_t y = 0; y < output.height; ++y)if (!pcl_isfinite (output (x, y).z))output (x, y).z = base_max;const float base_delta = base_max - base_min;const size_t padding_xy = 2;const size_t padding_z = 2;const size_t small_width = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (input_->width - 1) / sigma_s_) + 1 + 2 * padding_xy;const size_t small_height = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (input_->height - 1) / sigma_s_) + 1 + 2 * padding_xy;const size_t small_depth = static_cast<size_t> (base_delta / sigma_r_) + 1 + 2 * padding_z;Array3D data (small_width, small_height, small_depth);for (size_t x = 0; x < input_->width; ++x){const size_t small_x = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (x) / sigma_s_ + 0.5f) + padding_xy;for (size_t y = 0; y < input_->height; ++y){const float z = output (x,y).z - base_min;const size_t small_y = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (y) / sigma_s_ + 0.5f) + padding_xy;const size_t small_z = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (z) / sigma_r_ + 0.5f) + padding_z;Eigen::Vector2f& d = data (small_x, small_y, small_z);d[0] += output (x,y).z;d[1] += 1.0f;}}std::vector<long int> offset (3);offset[0] = &(data (1,0,0)) - &(data (0,0,0));offset[1] = &(data (0,1,0)) - &(data (0,0,0));offset[2] = &(data (0,0,1)) - &(data (0,0,0));Array3D buffer (small_width, small_height, small_depth);for (size_t dim = 0; dim < 3; ++dim){const long int off = offset[dim];for (size_t n_iter = 0; n_iter < 2; ++n_iter){std::swap (buffer, data);for(size_t x = 1; x < small_width - 1; ++x)for(size_t y = 1; y < small_height - 1; ++y){Eigen::Vector2f* d_ptr = &(data (x,y,1));Eigen::Vector2f* b_ptr = &(buffer (x,y,1));for(size_t z = 1; z < small_depth - 1; ++z, ++d_ptr, ++b_ptr)*d_ptr = (*(b_ptr - off) + *(b_ptr + off) + 2.0 * (*b_ptr)) / 4.0;}}}if (early_division_){for (std::vector<Eigen::Vector2f >::iterator d = data.begin (); d != data.end (); ++d)*d /= ((*d)[0] != 0) ? (*d)[1] : 1;for (size_t x = 0; x < input_->width; x++)for (size_t y = 0; y < input_->height; y++){const float z = output (x,y).z - base_min;const Eigen::Vector2f D = data.trilinear_interpolation (static_cast<float> (x) / sigma_s_ + padding_xy,static_cast<float> (y) / sigma_s_ + padding_xy,z / sigma_r_ + padding_z);output(x,y).z = D[0];}}else{for (size_t x = 0; x < input_->width; ++x)for (size_t y = 0; y < input_->height; ++y){const float z = output (x,y).z - base_min;const Eigen::Vector2f D = data.trilinear_interpolation (static_cast<float> (x) / sigma_s_ + padding_xy,static_cast<float> (y) / sigma_s_ + padding_xy,z / sigma_r_ + padding_z);output (x,y).z = D[0] / D[1];}}
}//
template <typename PointT> size_t
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::Array3D::clamp (const size_t min_value,const size_t max_value,const size_t x)
{if (x >= min_value && x <= max_value){return x;}else if (x < min_value){return (min_value);}else{return (max_value);}
}//
template <typename PointT> Eigen::Vector2f
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::Array3D::trilinear_interpolation (const float x,const float y,const float z)
{const size_t x_index = clamp (0, x_dim_ - 1, static_cast<size_t> (x));const size_t xx_index = clamp (0, x_dim_ - 1, x_index + 1);const size_t y_index = clamp (0, y_dim_ - 1, static_cast<size_t> (y));const size_t yy_index = clamp (0, y_dim_ - 1, y_index + 1);const size_t z_index = clamp (0, z_dim_ - 1, static_cast<size_t> (z));const size_t zz_index = clamp (0, z_dim_ - 1, z_index + 1);const float x_alpha = x - static_cast<float> (x_index);const float y_alpha = y - static_cast<float> (y_index);const float z_alpha = z - static_cast<float> (z_index);return(1.0f-x_alpha) * (1.0f-y_alpha) * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(x_index, y_index, z_index) +x_alpha * (1.0f-y_alpha) * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(xx_index, y_index, z_index) +(1.0f-x_alpha) * y_alpha * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(x_index, yy_index, z_index) +x_alpha * y_alpha * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(xx_index, yy_index, z_index) +(1.0f-x_alpha) * (1.0f-y_alpha) * z_alpha * (*this)(x_index, y_index, zz_index) +x_alpha * (1.0f-y_alpha) * z_alpha * (*this)(xx_index, y_index, zz_index) +(1.0f-x_alpha) * y_alpha * z_alpha * (*this)(x_index, yy_index, zz_index) +x_alpha * y_alpha * z_alpha * (*this)(xx_index, yy_index, zz_index);
}#endif /* PCL_FILTERS_IMPL_FAST_BILATERAL_HPP_ */
二、代码分析——函数
根据上面的代码:主要有三个函数:
1、
template <typename PointT> void
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::applyFilter (PointCloud &output)
template <typename PointT> size_t
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::Array3D::clamp (const size_t min_value,const size_t max_value,const size_t x)
template <typename PointT> Eigen::Vector2f
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::Array3D::trilinear_interpolation (const float x,const float y,const float z)
1、分配3D网格,其中的padding_xy和padding_z用来控制网格的延拓范围,代码如下:
for (size_t x = 0; x < output.width; ++x)for (size_t y = 0; y < output.height; ++y)if (!pcl_isfinite (output (x, y).z))output (x, y).z = base_max;const float base_delta = base_max - base_min;const size_t padding_xy = 2;const size_t padding_z = 2;const size_t small_width = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (input_->width - 1) / sigma_s_) + 1 + 2 * padding_xy;const size_t small_height = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (input_->height - 1) / sigma_s_) + 1 + 2 * padding_xy;const size_t small_depth = static_cast<size_t> (base_delta / sigma_r_) + 1 + 2 * padding_z;
2、对分割的网格进行下采样处理,其核心代码如下:
Array3D data (small_width, small_height, small_depth);for (size_t x = 0; x < input_->width; ++x){const size_t small_x = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (x) / sigma_s_ + 0.5f) + padding_xy;for (size_t y = 0; y < input_->height; ++y){const float z = output (x,y).z - base_min;const size_t small_y = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (y) / sigma_s_ + 0.5f) + padding_xy;const size_t small_z = static_cast<size_t> (static_cast<float> (z) / sigma_r_ + 0.5f) + padding_z;Eigen::Vector2f& d = data (small_x, small_y, small_z);d[0] += output (x,y).z;d[1] += 1.0f;}}3、其中的这段代码不是特别理解:
std::vector<long int> offset (3);offset[0] = &(data (1,0,0)) - &(data (0,0,0));offset[1] = &(data (0,1,0)) - &(data (0,0,0));offset[2] = &(data (0,0,1)) - &(data (0,0,0));Array3D buffer (small_width, small_height, small_depth);for (size_t dim = 0; dim < 3; ++dim){const long int off = offset[dim];for (size_t n_iter = 0; n_iter < 2; ++n_iter){std::swap (buffer, data);for(size_t x = 1; x < small_width - 1; ++x)for(size_t y = 1; y < small_height - 1; ++y){Eigen::Vector2f* d_ptr = &(data (x,y,1));Eigen::Vector2f* b_ptr = &(buffer (x,y,1));for(size_t z = 1; z < small_depth - 1; ++z, ++d_ptr, ++b_ptr)*d_ptr = (*(b_ptr - off) + *(b_ptr + off) + 2.0 * (*b_ptr)) / 4.0;}}}4、clamp函数:限制x的范围,插值过程中控制其size大小。代码如下:
template <typename PointT> size_t
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::Array3D::clamp (const size_t min_value,const size_t max_value,const size_t x)
{if (x >= min_value && x <= max_value){return x;}else if (x < min_value){return (min_value);}else{return (max_value);}
}
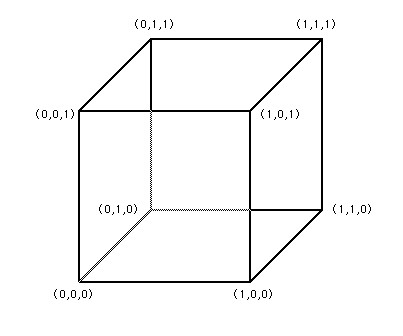
三线插值要先给出六面体的八个顶点;各个顶点的数值分别是:V000, V100, V010, ....V111
计算立方体里面的(x,y,z)的值Vxyz。
Vxyz = V000 (1 - x) (1 - y) (1 - z) +
V100 x (1 - y) (1 - z) +
V010 (1 - x) y (1 - z) +
V001 (1 - x) (1 - y) z +
V101 x (1 - y) z +
V011 (1 - x) y z +
V110 x y (1 - z) +
V111 x y z
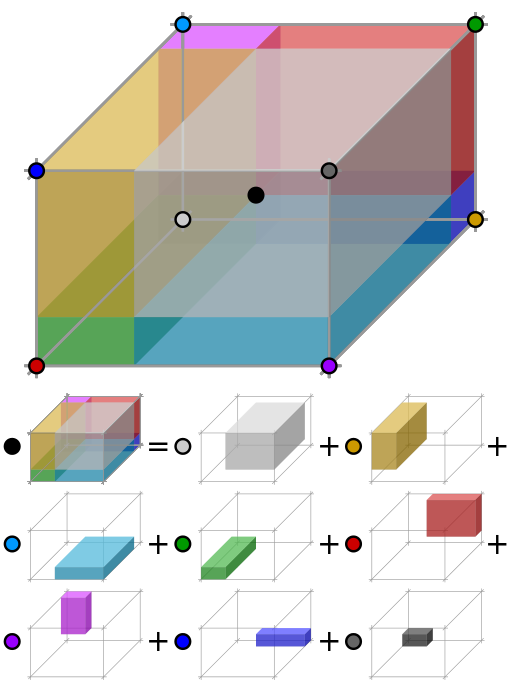
对于更一般的情况就需要对各个维度进行一定的尺度变换操作。其示计算过程意图如下:
三线性插值的几何可视化。在期望点(黑色点)和整个体积值的乘积等于每个顶点处的值的乘积和对角处的部分体积的总和。
template <typename PointT> Eigen::Vector2f
pcl::FastBilateralFilter<PointT>::Array3D::trilinear_interpolation (const float x,const float y,const float z)
{const size_t x_index = clamp (0, x_dim_ - 1, static_cast<size_t> (x));const size_t xx_index = clamp (0, x_dim_ - 1, x_index + 1);const size_t y_index = clamp (0, y_dim_ - 1, static_cast<size_t> (y));const size_t yy_index = clamp (0, y_dim_ - 1, y_index + 1);const size_t z_index = clamp (0, z_dim_ - 1, static_cast<size_t> (z));const size_t zz_index = clamp (0, z_dim_ - 1, z_index + 1);const float x_alpha = x - static_cast<float> (x_index);const float y_alpha = y - static_cast<float> (y_index);const float z_alpha = z - static_cast<float> (z_index);return(1.0f-x_alpha) * (1.0f-y_alpha) * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(x_index, y_index, z_index) +x_alpha * (1.0f-y_alpha) * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(xx_index, y_index, z_index) +(1.0f-x_alpha) * y_alpha * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(x_index, yy_index, z_index) +x_alpha * y_alpha * (1.0f-z_alpha) * (*this)(xx_index, yy_index, z_index) +(1.0f-x_alpha) * (1.0f-y_alpha) * z_alpha * (*this)(x_index, y_index, zz_index) +x_alpha * (1.0f-y_alpha) * z_alpha * (*this)(xx_index, y_index, zz_index) +(1.0f-x_alpha) * y_alpha * z_alpha * (*this)(x_index, yy_index, zz_index) +x_alpha * y_alpha * z_alpha * (*this)(xx_index, yy_index, zz_index);
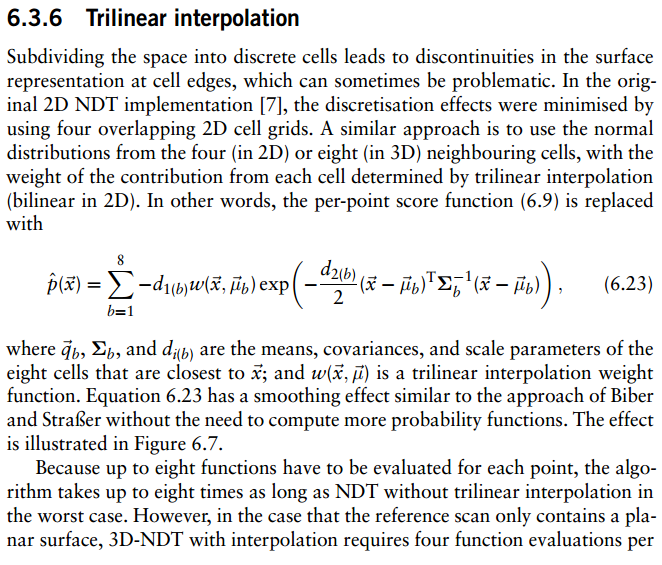
}四:《三维法线分布转换》
The Three-Dimensional Normal-Distributions Transform
论文网址——p86-87
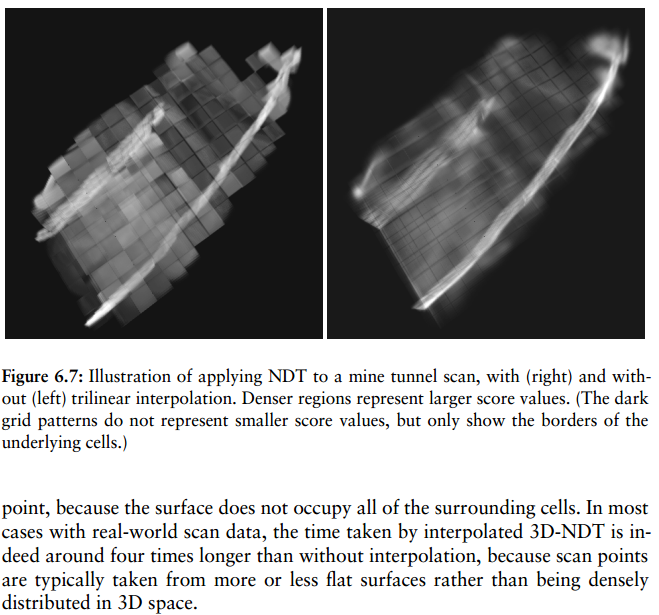
第一句说的很清楚,在空间细分为离散单元格后,单元格边缘处的曲面显示会不连续,所以由二维插值到三维插值的演变过程,出现了三线插值。
五、让该算法的加速计算可以利用线程技术,但是根据论文中的体积,插值过程是由卷积计算来完成的,当然插值的算法有很多,但是总体的思路很重要。
这篇关于《PCL点云库学习VS2010(X64)》Part 23 快速双边滤波算法之三线插值的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!