本文主要是介绍[SQL调优] “查询SQL过滤和排序条件涉及的表字段未创建索引”引起慢查询问题,优化后执行时间从70+s下降到0.01s以下,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
# 查询SQL
select d.type,d.value,e.fraud_type,e.evidence_time,e.evidence_origin,d.uuid,d.refuuid from evidence_details d inner join evidence e on d.refuuid= e.uuid order by gmt_create desc limit 0,10;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: evidence_details
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `evidence_details` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`refuuid` char(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`type` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
`value` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`partner_code` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`app_name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`uuid` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`evidence_type_displayname` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`partnercode_display_name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`app_display_name` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`evidence_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`fraud_type` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uuid` (`uuid`),
KEY `idx_value` (`value`),
KEY `dex_uuid` (`refuuid`)
) ENGINE= InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=16421615 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: evidence
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `evidence` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`evidence_origin` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`uuid` char(32) NOT NULL,
`fraud_type` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
`evidence_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`fraud_details` text,
`fraud_displayname` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uuid` (`uuid`),
KEY `dex_time` (`gmt_create`)
) ENGINE= InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=15438435 DEFAULT CHARSET= utf8
经验教训
只要涉及到SQL查询条件(WHERE、ORDER BY)的相关字段,都应建立索引(唯一索引、联合索引)。
分析过程
1. 核实“SQL的执行时间”
select d.type,d.value,e.fraud_type,e.evidence_time,e.evidence_origin,d.uuid,d.refuuid from evidence_details d inner join evidence e on d.refuuid=e.uuid order by gmt_create desc limit 0,10;
.....
10 rows in set (1 min 11.27 sec)
哇哦,该条SQL执行时间尽然需要1分11秒,太恐怖啦!!!
2. 分析“该条SQL的查询执行计划”
explain select d.type,d.value,e.fraud_type,e.evidence_time,e.evidence_origin,d.uuid,d.refuuid from evidence_details d inner join evidence e on d.refuuid=e.uuid order by gmt_create desc limit 0,10;
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+------+---------+-------------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+------+---------+-------------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | d | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 6452641 | Using where; Using temporary; Using filesort |
| 1 | SIMPLE | e | eq_ref | uuid | uuid | 96 | riskbase_core.d.refuuid | 1 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+--------+---------------+------+---------+-------------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------+
从上面可以看出,查询第一步使用全表扫描(ALL),还涉及到临时表和文件排序(Using where; Using temporary; Using filesort)。所以,为了提高查询速度,尽量针对相关查询字段(`evidence_details`.`refuuid`、`evidence`.`uuid`、`evidence`.`gmt_create`)建立合理的索引。
3. 查看相应的索引是否创建
show index from `riskbase_core`.`evidence`;
+----------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+----------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| evidence | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 6471176 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| evidence | 0 | uuid | 1 | uuid | A | 6471176 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+----------+------------+----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
从上面看,`evidence`.`uuid` 字段的索引已创建。还需要创建`evidence`.`gmt_create`字段的索引,创建语句如下:
CREATE INDEX `dex_time` on `riskbase_core`.`evidence` (`gmt_create`);
show index from `riskbase_core`.`evidence_details`;
+------------------+------------+-----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+------------------+------------+-----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| evidence_details | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 6452885 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
| evidence_details | 0 | uuid | 1 | uuid | A | 6452885 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| evidence_details | 1 | idx_value | 1 | value | A | 6452885 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+------------------+------------+-----------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
从上面看,未对`evidence_details`.`refuuid`字段创建索引。所以,需要对`evidence_details`.`refuuid`字段创建索引,创建语句如下:
CREATE INDEX `dex_uuid` on `riskbase_core`.`evidence_details` (`refuuid`);
4. 再次查看“该SQL的查询执行计划”
explain select d.type,d.value,e.fraud_type,e.evidence_time,e.evidence_origin,d.uuid,d.refuuid from evidence_details d inner join evidence e on d.refuuid=e.uuid order by gmt_create desc limit 0,10; +----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+----------------------+------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+----------------------+------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | e | index | uuid | dex_time | 6 | NULL | 10 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | d | ref | dex_uuid | dex_uuid | 97 | riskbase_core.e.uuid | 1 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+----------------------+------+-------+
从SQL查询执行计划看,相关索引都使用上了,看起来应该没问题了。现在就用SQL语句测试一下执行时间吧
5. 再次执行该SQL,用“执行时间”来验证优化效果
select d.type,d.value,e.fraud_type,e.evidence_time,e.evidence_origin,d.uuid,d.refuuid from evidence_details d inner join evidence e on d.refuuid=e.uuid order by gmt_create desc limit 0,10;
......
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
好了,从“执行时间”看,问题已彻底修复了。
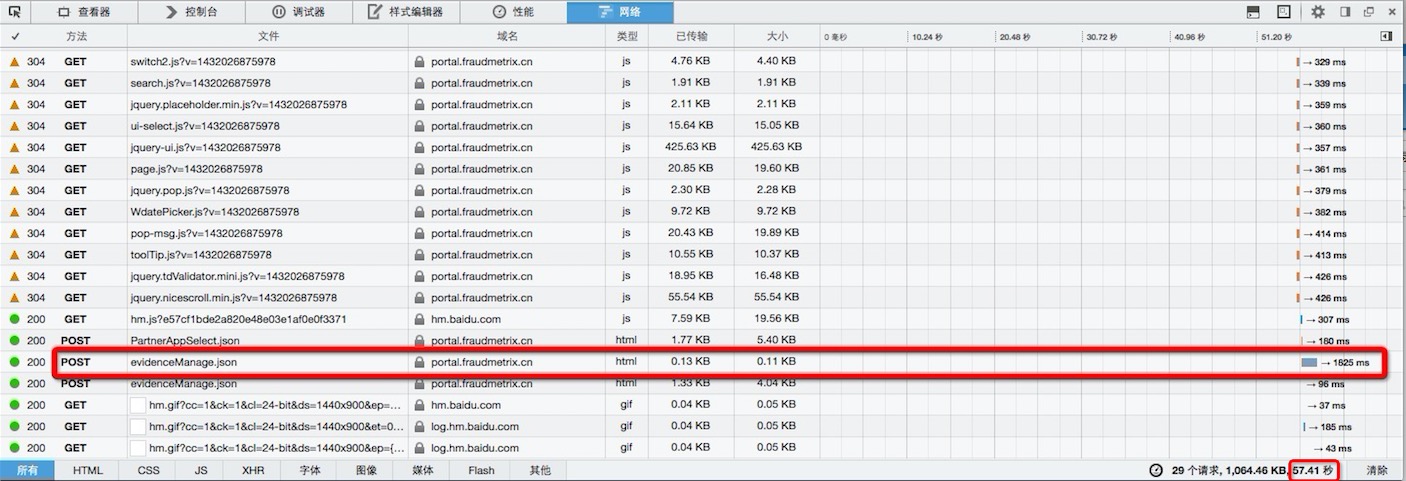
6. 看一下优化前后,页面的加载效果
# 优化前 57.41s
# 优化后 1.79s
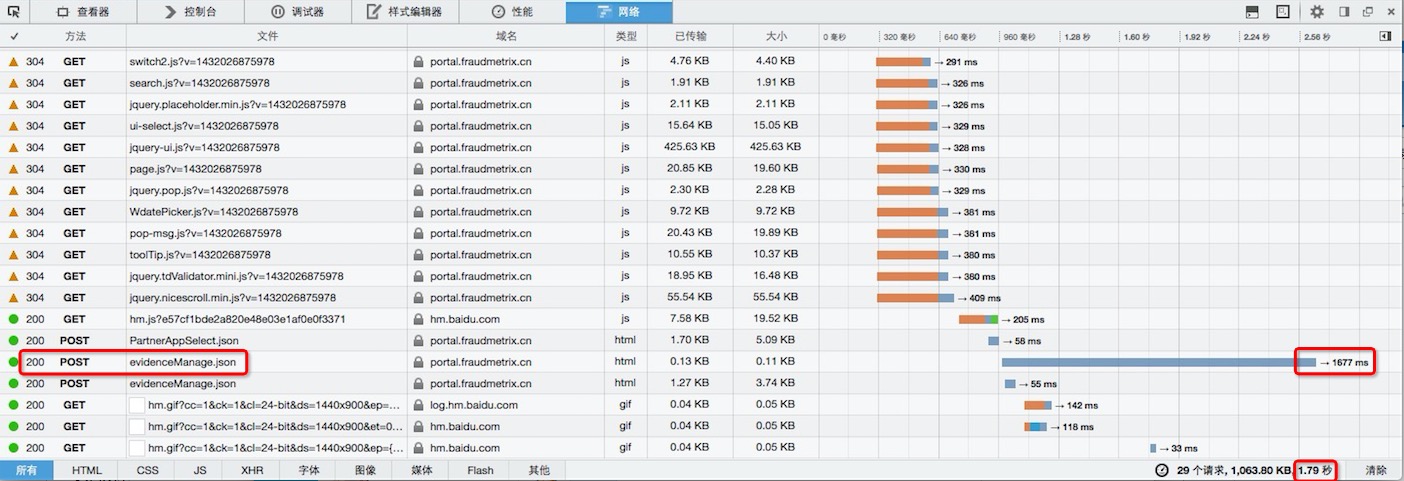
页面加载时间,从优化前的 57.41s 降低到 1.79s。
但可能细心的朋友已经发现,优化后 evidenceManage.json 的响应时间还需要 1.677s,而上面那条SQL的执行时间已经降低到10ms之内。那其它的时间都消耗在哪里啦?
其它故事
其实 evidenceManage.json 接口除了执行上面那条SQL语句,还执行了一条count(*)的SQL语句。而正是count(*) SQL语句耗时了 1.67s,哦哦,原来这里还有其它故事啊~~~
# 总行数统计
select count(*) from evidence_details
但通过对“count(*) SQL语句”的查询执行计划的分析,发现对于InnoDB引擎(14.2 InnoDB Concepts and Architecture),很难对此再优化了。
(建议:有count(*)相关的操作,数据表的存储引擎(ENGINE)尽量设计为MyISAM(15.2 The MyISAM Storage Engine),除非该表涉及事务操作!)
总结
针对 InnoDB 存储引擎:
- 索引(index)查询类型的查询要快于范围(range)查询类型
- 二级索引(dex_uuid)类型的查询要快于主键索引(PRIMARY)类型
参考
[MySQL FAQ系列] 为何 InnoDB 表 select count(*) 很慢 -- 叶金荣(yejr)
[InnoDB系列] InnoDB 表如何更快得到 count(*) 结果 -- 叶金荣(yejr)
分析过程
mysql> explain select count(*) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: dex_uuid
key_len: 97
ref: NULL
rows: 6479241
Extra: Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(*): 7640484
1 row in set (1.67 sec)
mysql> explain select count(*) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 3239629
Extra: Using where; Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(*): 7640505
1 row in set (2.51 sec)
mysql> explain select count(id) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: dex_uuid
key_len: 97
ref: NULL
rows: 6479287
Extra: Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(id) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(id): 7640530
1 row in set (1.83 sec)
mysql> explain select count(id) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 3239652
Extra: Using where; Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(id) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(id): 7640547
1 row in set (2.64 sec)
mysql> explain select count(`uuid`) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: uuid
key_len: 99
ref: NULL
rows: 6479323
Extra: Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(`uuid`) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(`uuid`): 7640564
1 row in set (2.20 sec)
mysql> explain select count(`uuid`) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 3239705
Extra: Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(`uuid`) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(`uuid`): 7640657
1 row in set (3.13 sec)
mysql> explain select count(`refuuid`) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: dex_uuid
key_len: 97
ref: NULL
rows: 6479554
Extra: Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(`refuuid`) from evidence_details \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(`refuuid`): 7640812
1 row in set (2.09 sec)
mysql> explain select count(`refuuid`) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: evidence_details
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 3239794
Extra: Using where
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(`refuuid`) from evidence_details where id >= 0 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
count(`refuuid`): 7640852
1 row in set (3.31 sec)
这篇关于[SQL调优] “查询SQL过滤和排序条件涉及的表字段未创建索引”引起慢查询问题,优化后执行时间从70+s下降到0.01s以下的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






