本文主要是介绍20:kotlin 类和对象 --泛型(Generics),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
类可以有类型参数
class Box<T>(t: T) {var value = t
}
要创建类实例,需提供类型参数
val box: Box<Int> = Box<Int>(1)
如果类型可以被推断出来,可以省略
val box = Box(1)
通配符
在JAVA泛型中有通配符?、? extends E、? super E,在kotlin中没有这个概念,取而代之的是Declaration-site variance和type projections
Declaration-site variance
out 协变
对于如下代码
interface Source<T> {fun next():T
}fun demo(x : Source<Number>){val objects: Source<Any> = x
}
编译器报错 – 类型不匹配
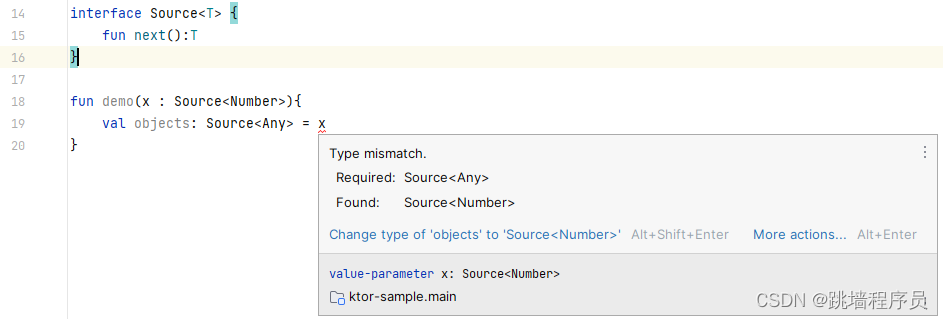
想要代码成立需要在泛型定义时使用out
interface Source<T> {fun next():T
}fun demo(x : Source<Number>){val objects: Source<Any> = x
}
in 逆变
对于代码
interface Comparable<T> {operator fun compareTo(other: T): Int
}fun demo(x: Comparable<Number>) {x.compareTo(1.0)val y: Comparable<Int> = x
}
报错类型不匹配
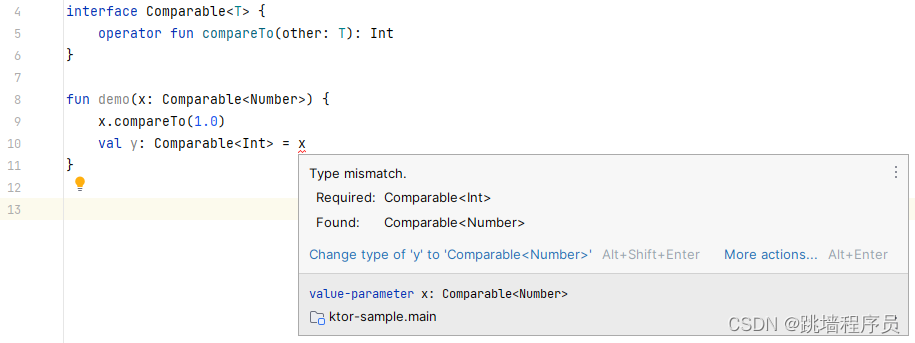
想要代码成立需要在泛型定义时使用in
interface Comparable<in T> {operator fun compareTo(other: T): Int
}fun demo(x: Comparable<Number>) {x.compareTo(1.0)val y: Comparable<Int> = x
}
如果
T类型作为参数(消费)就是用in,如果作为返回值(生产)就用out
Consumer in, Producer out!
逆变就是大类型变小类型,协变就是小类型变大类型
type projections(类型投影)
Use-site variance: type projections(使用点位变异:类型投影)
对于以下代码
class Demo<T>{fun copy(from: Array<T>, to: Array<T>) {assert(from.size == from.size)for (i in from.indices) {to[i] = from.get(i)}}
}fun main() {val str: Array<String> = arrayOf("hello", "world")val obj: Array<Any> = arrayOf(123, 432)Demo<Any>().copy(str, obj)
}
报错
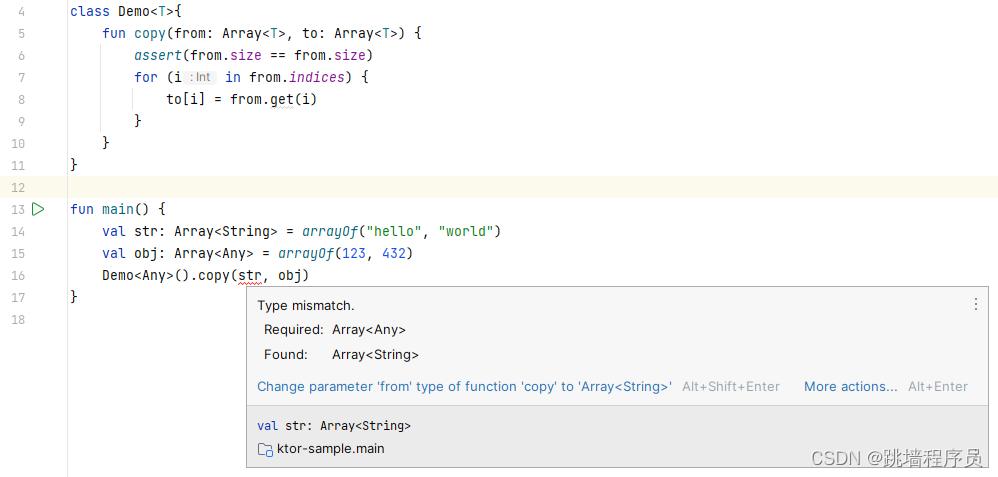
在类声明时,不管是使用class Demo<in T>还是class Demo<out T>都会报错,为解决这种情况,可以修改copy方法的from参数类型为from: Array<out T>,因为from作为生产者,生产数组中的值
class Demo<T>{fun copy(from: Array<out T>, to: Array<T>) {assert(from.size == from.size)for (i in from.indices) {to[i] = from.get(i)}}
}
当然也可以改成下边写法
class Demo<T>{fun copy(from: Array<T>, to: Array<in T>) {assert(from.size == from.size)for (i in from.indices) {to[i] = from.get(i)}}
}fun main() {val str: Array<String> = arrayOf("hello", "world")val obj: Array<Any> = arrayOf(123, 432)Demo<String>().copy(str, obj)
}
星号投影(*)
有时候参数是一个泛型类型,但是在定义方法的时候不能确定泛型的具体类型,需要用到*投影
语法如下
- 对于泛型类型
Foo<out T : TUpper>,T是一个具有上界TUpper的协变类型参数,Foo<*>等价于Foo<out TUpper>。这意味着当T未知时,你可以安全地从Foo<*>中读取TUpper的值。 - 对于泛型类型
Foo<in T>,T是一个逆变类型参数,Foo<*>等价于Foo<in Nothing>。这意味着当T未知时,你无法以安全的方式向Foo<*>写入任何值。 - 对于泛型类型
Foo<T : TUpper>,T是一个不变类型参数,具有上界TUpper,Foo<*>在读取值时等价于Foo<out TUpper>,在写入值时等价于Foo<in Nothing>。
举个例子
class Box<out T : Any>(private val value: T) {fun getValue(): T {return value}
}fun printBoxValue(box: Box<*>) {val value = box.getValue()println(value)
}fun main(){printBoxValue(Box(123)) // 123printBoxValue(Box("hello world")) // hello world
}
printBoxValue方法的参数使用*投影
如果一个泛型类型有多个类型参数,每个参数可以独立进行投影
泛型函数
不仅类可以有类型参数,函数也可以有类型参数。类型参数位于函数名称之前
fun <T> singletonList(item: T): List<T> {// ...
}fun <T> T.basicToString(): String { // 扩展函数// ...
}
要调用泛型函数,在调用点的函数名称之后指定类型参数
val l = singletonList<Int>(1)
如果可以从上下文中推断出类型参数,则可以省略类型参数
val l = singletonList(1)
泛型约束
对于给定的类型参数,可以通过泛型约束来限制可替代的所有可能类型。
最常见的约束类型是上界(upper bounds)
fun <T : Comparable<T>> sort(list: List<T>) { ... }
在冒号后指定的类型是上界,表示只有Comparable<T>的子类型可以替代T
sort(listOf(1, 2, 3)) // 正确。Int是Comparable<Int>的子类型
sort(listOf(HashMap<Int, String>())) // 错误:HashMap<Int, String>不是Comparable<HashMap<Int, String>>的子类型
如果不指定上界,则默认为Any?类型的
当一个类型参数需要满足多个上界时,需要使用 where 子句来指定这些上界条件
fun <T> processValues(list: List<T>) where T : CharSequence, T : Comparable<T> {val sortedValues = list.sorted()for (value in sortedValues) {println(value)}
}val stringList: List<String> = listOf("apple", "banana", "cherry")
val intList: List<Int> = listOf(1, 2, 3)
val mixedList: List<Any> = listOf("hello", 42, true)processValues(stringList) // apple, banana, cherry
processValues(intList) // 报错 -- Int 不满足 CharSequence 的上界
processValues(mixedList) // 报错 --Any 不满足 CharSequence 的上界
绝对非空类型(Definitely non-nullable types)
为了方便和java接口和类交互,如果有如下java接口
import org.jetbrains.annotations.*;public interface Game<T> {public T save(T x) {}@NotNullpublic T load(@NotNull T x) {}
}
要继承该接口并重写load方法,使用& Any来声明一个非空参数
interface ArcadeGame<T1> : Game<T1> {override fun save(x: T1): T1// T1 is definitely non-nullableoverride fun load(x: T1 & Any): T1 & Any
}
如果是纯kotlin项目,不需要使用此方法声明,kotlin的类型推断会做这件事
class ArcadeGame<T> {fun load(x: T & Any){println(x)}
}fun main(){ArcadeGame<String?>().load(null) // 这里String?即使可以为空,调用load方法时传入null依旧报错
}
类型擦除
kotlin对泛型声明的类型安全检查是在编译时进行的。在运行时,泛型类型的实例不保存有关其实际类型参数的任何信息。这种类型信息被称为擦除。例如,Foo<Bar> 和 Foo<Baz?> 的实例在擦除后变为 Foo<*>
泛型类型的检查和转换
由于类型擦除的存在,不能使用is进行如下检查
class ArcadeGame<T>{fun check(x:Any){if (x is T){} // 报错 -- Cannot check for instance of erased type: T}
}fun main() {val game = ArcadeGame<String?>()if (game is ArcadeGame<String>) {} // 报错 -- Cannot check for instance of erased type: ArcadeGame<String>
}
可以使用型号投影进行检查
class ArcadeGame<T>fun main() {val game = ArcadeGame<String?>()if (game is ArcadeGame<*>) {}
}
对于x is T这种检查方式,可以进行如下改造
class ArcadeGame<T>(private val type: Class<T>) {fun check(x: Any) {if (type.isInstance(x)) {// x 是 T 类型的实例}}
}fun main() {val game = ArcadeGame<String>(String::class.java)
}
The type arguments of generic function calls are also only checked at compile time. Inside the function bodies, the type parameters cannot be used for type checks, and type casts to type parameters (foo as T) are unchecked. The only exclusion is inline functions with reified type parameters, which have their actual type arguments inlined at each call site. This enables type checks and casts for the type parameters. However, the restrictions described above still apply for instances of generic types used inside checks or casts. For example, in the type check arg is T, if arg is an instance of a generic type itself, its type arguments are still erased.
inline fun <reified A, reified B> Pair<*, *>.asPairOf(): Pair<A, B>? {if (first !is A || second !is B) return nullreturn first as A to second as B
}val somePair: Pair<Any?, Any?> = "items" to listOf(1, 2, 3)val stringToSomething = somePair.asPairOf<String, Any>()
val stringToInt = somePair.asPairOf<String, Int>()
val stringToList = somePair.asPairOf<String, List<*>>()
val stringToStringList = somePair.asPairOf<String, List<String>>() // Compiles but breaks type safety!
// Expand the sample for more details
未经检查的类型转换(Unchecked casts)
对于泛型类型转换,无法在运行时进行检查。
fun gen(): Map<String, *> {return mapOf("one" to "你好", "two" to 123)
}fun main() {val gen = gen()gen as Map<Int, Int> // 提示 -- Unchecked cast: Map<String, *> to Map<Int, Int>println(gen) // {one=你好, two=123}
}
因为类型擦除的缘故,gen as Map<Int, Int>并不会报错,只是在编译期做出提醒
如果是这样转换则会报错
fun main() {val gen = gen()gen["one"] as Int // 报错 -- java.lang.ClassCastException: class java.lang.String cannot be cast to class java.lang.Integer (java.lang.String and java.lang.Integer are in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap')println(gen)
}
如果不想提示,使用注解@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
fun main() {val gen = gen()@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")gen as Map<Int, Int>println(gen)
}
在 JVM上,数组类型保留有关其元素被擦除的类型的信息,并且对数组类型的类型转换进行了部分检查:元素类型的可为空性和实际类型参数仍然被擦除。
fun gen(): Array<*> {return arrayOf("hello", "world")
}fun main() {val gen = gen()gen as Array<Int> // java.lang.ClassCastException: class [Ljava.lang.String; cannot be cast to class [Ljava.lang.Integer; ([Ljava.lang.String; and [Ljava.lang.Integer; are in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap')println(gen)
}
类型参数的下划线操作符
当其他类型被显式指定时,可以使用下划线操作符来自动推断参数的类型
abstract class SomeClass<T> {abstract fun execute() : T
}class SomeImplementation : SomeClass<String>() {override fun execute(): String = "Test"
}class OtherImplementation : SomeClass<Int>() {override fun execute(): Int = 42
}object Runner {inline fun <reified S: SomeClass<T>, T> run() : T {return S::class.java.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance().execute()}
}fun main() {// T 是 String 类型,因为SomeImplementation为SomeClass<String>val s = Runner.run<SomeImplementation, _>()assert(s == "Test")// T 是 Int 类型 ,因为SomeImplementation为SomeClass<Int>val n = Runner.run<OtherImplementation, _>()assert(n == 42)
}
这篇关于20:kotlin 类和对象 --泛型(Generics)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







