本文主要是介绍【Python游戏开发】使用Python编写拼图益智游戏教程,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
使用Python编写拼图益智游戏

大家一般都玩过拼图益智游戏,或者类似的游戏。今天,就给大家使用pygame库在Python中构建一个拼图益智小游戏。这个拼图小游戏是构建一个围绕着将1-15个数字排列在16个方块的网格中的游戏。
现在,让我们从今天的惊人项目“使用PyGame的Python益智游戏”开始。首先,我们将对游戏背后的主要逻辑有一个基本的想法,然后我们将继续讨论我们将添加到这个项目中的功能,然后我们将会继续讨论这个项目的实际编码部分——Python益智游戏
游戏的基本规则和玩法:
在Python中的这个拼图益智小游戏,玩家必须按升序排列从1到15的块。游戏将显示16个方块,其中一个方块为空,玩家可以移动这些方块。一旦所有的方块都按顺序排好了,比赛就结束了。
既然我们已经对到底需要开发什么有了基本的想法,让我们继续往下看Python中拼图益智游戏需要实现的功能列表:
Python中益智游戏的特点:
Python中益智游戏的自动洗牌功能。
重置、新游戏和自动求解选项。
Python中的益智游戏块可以使用箭头键或鼠标移动。
下面直接给出Python拼图益智游戏的完整代码:
# baic library imports pygame and random
import pygame
import sys
import random
from pygame.locals import *# this section holds all the variables that we will use in Puzzle Game In Python
w_of_board = 4 # total number of columns in the board of Puzzle Game In Python
h_of_board = 4 # total number of rows in the board
block_size = 80
win_width = 640
win_height = 480
FPS = 30
BLANK = None# this is bascially for managing the different colors of the component
# we have also used variables for mantaining the text size in Puzzle Game In Python
BLACK = (0, 0, 0)
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
BRIGHTBLUE = (0, 50, 255)
DARKTURQUOISE = (255, 255, 255)
BLUE = (0, 0, 0)
GREEN = (0, 128, 0)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
BGCOLOR = DARKTURQUOISE
TILECOLOR = BLUE
TEXTCOLOR = WHITE
BORDERCOLOR = RED
BASICFONTSIZE = 20
TEXT = GREENBUTTONCOLOR = WHITE
BUTTONTEXTCOLOR = BLACK
MESSAGECOLOR = GREEN# this is to leave the space on both the sides of the block
XMARGIN = int((win_width - (block_size * w_of_board + (w_of_board - 1))) / 2)
YMARGIN = int((win_height - (block_size * h_of_board + (h_of_board - 1))) / 2)# these are the variables for handling the keyboard keys
UP = 'up'
DOWN = 'down'
LEFT = 'left'
RIGHT = 'right'# this is the main functiondef main():global FPSCLOCK, DISPLAYSURF, BASICFONT, RESET_SURF, RESET_RECT, NEW_SURF, NEW_RECT, SOLVE_SURF, SOLVE_RECTpygame.init()FPSCLOCK = pygame.time.Clock()DISPLAYSURF = pygame.display.set_mode((win_width, win_height))# we gave a title using set_caption function in pygamepygame.display.set_caption('Slide Puzzle - CopyAssignment')BASICFONT = pygame.font.Font('freesansbold.ttf', BASICFONTSIZE)# these variables stores the various options that will be displayed to the right side of our main grid# these below only handles the design part of the optionsRESET_SURF, RESET_RECT = makeText('重置', TEXT, BGCOLOR, win_width - 120, win_height - 310)NEW_SURF, NEW_RECT = makeText('新游戏', TEXT, BGCOLOR, win_width - 120, win_height - 280)SOLVE_SURF, SOLVE_RECT = makeText('求解', TEXT, BGCOLOR, win_width - 120, win_height - 250)mainBoard, solutionSeq = generateNewPuzzle(80)# this is simply the board that is same as that of the solved board in Puzzle Game In Python# bascially the game will shuffle all blocks of the solved gameSOLVEDBOARD = start_playing()# a list that tracks the moves made from the solved configurationallMoves = []# main game loopwhile True:slideTo = None# the below variable contains the message to show in the top left corner.msg = 'Click a block or press arrow keys to slide the block.'if mainBoard == SOLVEDBOARD:msg = 'Solved!'drawBoard(mainBoard, msg)check_exit_req()# the below for loop is to handle the various events of keyboardfor event in pygame.event.get():if event.type == MOUSEBUTTONUP:spotx, spoty = getSpotClicked(mainBoard, event.pos[0], event.pos[1])if (spotx, spoty) == (None, None):# this is to check if the user clicked on an option buttonif RESET_RECT.collidepoint(event.pos):# this below linw will come into action of the user clicked on Reset buttonrst_animation(mainBoard, allMoves)allMoves = []elif NEW_RECT.collidepoint(event.pos):# this below linw will come into action of the user clicked on New Game buttonmainBoard, solutionSeq = generateNewPuzzle(80)allMoves = []elif SOLVE_RECT.collidepoint(event.pos):# this below linw will come into action of the user clicked on Solve buttonrst_animation(mainBoard, solutionSeq + allMoves)allMoves = []else:# this else block in Puzzle Game In Python is just to check that the moved tile has a blankblankx, blanky = getBlankPosition(mainBoard)if spotx == blankx + 1 and spoty == blanky:slideTo = LEFTelif spotx == blankx - 1 and spoty == blanky:slideTo = RIGHTelif spotx == blankx and spoty == blanky + 1:slideTo = UPelif spotx == blankx and spoty == blanky - 1:slideTo = DOWNelif event.type == KEYUP:# this elif block will handle the checking if the user pressed a key to slide a tileif event.key in (K_LEFT, K_a) and isValidMove(mainBoard, LEFT):slideTo = LEFTelif event.key in (K_RIGHT, K_d) and isValidMove(mainBoard, RIGHT):slideTo = RIGHTelif event.key in (K_UP, K_w) and isValidMove(mainBoard, UP):slideTo = UPelif event.key in (K_DOWN, K_s) and isValidMove(mainBoard, DOWN):slideTo = DOWN# this block will handle the fucntionality of displaying the message for controlsif slideTo:# show slide on screensliding_animation(mainBoard, slideTo, 'Click a block or press arrow keys to slide the block.', 8)take_turn(mainBoard, slideTo)allMoves.append(slideTo)pygame.display.update()FPSCLOCK.tick(FPS)def terminate():pygame.quit()sys.exit()def check_exit_req():# get all the QUIT eventsfor event in pygame.event.get(QUIT):# terminate() will kill all the events. terminate if any QUIT events are presentterminate()# this for loop will get all the KEYUP eventsfor event in pygame.event.get(KEYUP):if event.key == K_ESCAPE:# if the user presses the ESC key then it will terminate the session and if the KEYUP event was for the Esc keyterminate()# put the other KEYUP event objects backpygame.event.post(event)def start_playing():# Return a board structure with blocks in the solved state.counter = 1board = []for x in range(w_of_board):column = []for y in range(h_of_board):column.append(counter)counter += w_of_boardboard.append(column)counter -= w_of_board * (h_of_board - 1) + w_of_board - 1board[w_of_board-1][h_of_board-1] = BLANKreturn boarddef getBlankPosition(board):# Return the x and y of board coordinates of the blank space.for x in range(w_of_board):for y in range(h_of_board):if board[x][y] == BLANK:return (x, y)def take_turn(board, move):blankx, blanky = getBlankPosition(board)if move == UP:board[blankx][blanky], board[blankx][blanky +1] = board[blankx][blanky + 1], board[blankx][blanky]elif move == DOWN:board[blankx][blanky], board[blankx][blanky -1] = board[blankx][blanky - 1], board[blankx][blanky]elif move == LEFT:board[blankx][blanky], board[blankx +1][blanky] = board[blankx + 1][blanky], board[blankx][blanky]elif move == RIGHT:board[blankx][blanky], board[blankx -1][blanky] = board[blankx - 1][blanky], board[blankx][blanky]def isValidMove(board, move):blankx, blanky = getBlankPosition(board)return (move == UP and blanky != len(board[0]) - 1) or \(move == DOWN and blanky != 0) or \(move == LEFT and blankx != len(board) - 1) or \(move == RIGHT and blankx != 0)def ramdom_moves(board, lastMove=None):# start with a full list of all four movesvalidMoves = [UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT]# remove moves from the list as they are disqualifiedif lastMove == UP or not isValidMove(board, DOWN):validMoves.remove(DOWN)if lastMove == DOWN or not isValidMove(board, UP):validMoves.remove(UP)if lastMove == LEFT or not isValidMove(board, RIGHT):validMoves.remove(RIGHT)if lastMove == RIGHT or not isValidMove(board, LEFT):validMoves.remove(LEFT)# this will perform the return nad it will return a random move from the list of remaining movesreturn random.choice(validMoves)def getLeftTopOfTile(block_x, block_y):left = XMARGIN + (block_x * block_size) + (block_x - 1)top = YMARGIN + (block_y * block_size) + (block_y - 1)return (left, top)def getSpotClicked(board, x, y):# from the x & y pixel coordinates, this for loop below will get the x & y board coordinatesfor block_x in range(len(board)):for block_y in range(len(board[0])):left, top = getLeftTopOfTile(block_x, block_y)tileRect = pygame.Rect(left, top, block_size, block_size)if tileRect.collidepoint(x, y):return (block_x, block_y)return (None, None)def draw_block(block_x, block_y, number, adjx=0, adjy=0):# draw a tile at board coordinates block_x and block_y, optionally a fewleft, top = getLeftTopOfTile(block_x, block_y)pygame.draw.rect(DISPLAYSURF, TILECOLOR, (left + adjx,top + adjy, block_size, block_size))text_renderign = BASICFONT.render(str(number), True, TEXTCOLOR)text_in_rect = text_renderign.get_rect()text_in_rect.center = left + \int(block_size / 2) + adjx, top + int(block_size / 2) + adjyDISPLAYSURF.blit(text_renderign, text_in_rect)def makeText(text, color, bgcolor, top, left):# create the Surface and Rect objects for some text.text_renderign = BASICFONT.render(text, True, color, bgcolor)text_in_rect = text_renderign.get_rect()text_in_rect.topleft = (top, left)return (text_renderign, text_in_rect)# this function will draw the board wherein the player can play.
# it holds the code for displaying different color and logic behind the gamedef drawBoard(board, message):DISPLAYSURF.fill(BGCOLOR)if message:text_renderign, text_in_rect = makeText(message, MESSAGECOLOR, BGCOLOR, 5, 5)DISPLAYSURF.blit(text_renderign, text_in_rect)for block_x in range(len(board)):for block_y in range(len(board[0])):if board[block_x][block_y]:draw_block(block_x, block_y, board[block_x][block_y])left, top = getLeftTopOfTile(0, 0)width = w_of_board * block_sizeheight = h_of_board * block_sizepygame.draw.rect(DISPLAYSURF, BORDERCOLOR, (left - 5,top - 5, width + 11, height + 11), 4)DISPLAYSURF.blit(RESET_SURF, RESET_RECT)DISPLAYSURF.blit(NEW_SURF, NEW_RECT)DISPLAYSURF.blit(SOLVE_SURF, SOLVE_RECT)# this function is to handle the animation that are displayed when a user starts a new Game
# a user can see the sliding animation over the blocks
# this is made possible using the below functiondef sliding_animation(board, direction, message, animationSpeed):blankx, blanky = getBlankPosition(board)if direction == UP:move_in_xaxis = blankxmove_in_yaxis = blanky + 1elif direction == DOWN:move_in_xaxis = blankxmove_in_yaxis = blanky - 1elif direction == LEFT:move_in_xaxis = blankx + 1move_in_yaxis = blankyelif direction == RIGHT:move_in_xaxis = blankx - 1move_in_yaxis = blanky# prepare the base surfacedrawBoard(board, message)baseSurf = DISPLAYSURF.copy()# draw a blank space over the moving block on the baseSurf Surface.take_left, take_top = getLeftTopOfTile(move_in_xaxis, move_in_yaxis)pygame.draw.rect(baseSurf, BGCOLOR, (take_left,take_top, block_size, block_size))for i in range(0, block_size, animationSpeed):# this is to handle the animation of the tile sliding overcheck_exit_req()DISPLAYSURF.blit(baseSurf, (0, 0))if direction == UP:draw_block(move_in_xaxis, move_in_yaxis,board[move_in_xaxis][move_in_yaxis], 0, -i)if direction == DOWN:draw_block(move_in_xaxis, move_in_yaxis,board[move_in_xaxis][move_in_yaxis], 0, i)if direction == LEFT:draw_block(move_in_xaxis, move_in_yaxis,board[move_in_xaxis][move_in_yaxis], -i, 0)if direction == RIGHT:draw_block(move_in_xaxis, move_in_yaxis,board[move_in_xaxis][move_in_yaxis], i, 0)pygame.display.update()FPSCLOCK.tick(FPS)def generateNewPuzzle(numSlides):# this to display the animation of blockssequence = []board = start_playing()drawBoard(board, '')pygame.display.update()# we used time.wait() to pause 500 milliseconds for effectpygame.time.wait(500)lastMove = Nonefor i in range(numSlides):move = ramdom_moves(board, lastMove)sliding_animation(board, move, 'Generating new puzzle...',animationSpeed=int(block_size / 3))take_turn(board, move)sequence.append(move)lastMove = movereturn (board, sequence)def rst_animation(board, allMoves):# make all of the moves in reversereverse_moves = allMoves[:]reverse_moves.reverse()for move in reverse_moves:if move == UP:opp_moves = DOWNelif move == DOWN:opp_moves = UPelif move == RIGHT:opp_moves = LEFTelif move == LEFT:opp_moves = RIGHTsliding_animation(board, opp_moves, '',animationSpeed=int(block_size / 2))take_turn(board, opp_moves)# this is the call to main fucntion
if __name__ == '__main__':main()输出:

【生成新的拼图】
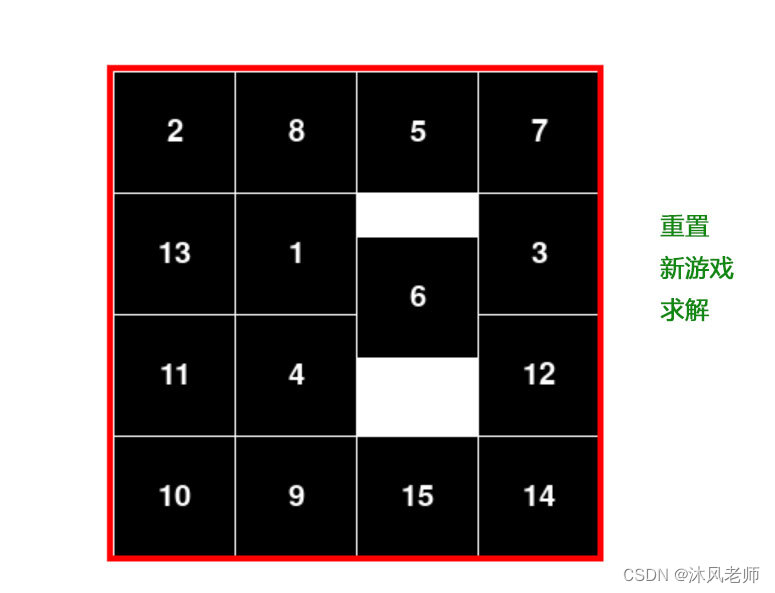
【单击块或按箭头键滑动块】
在这个教程中,尽可能的讲解了每一个步骤方法,希望这篇文章对你有用。
Python拼图益智游戏源码本站下载:https://download.csdn.net/download/mufenglaoshi/88571303
这篇关于【Python游戏开发】使用Python编写拼图益智游戏教程的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







