本文主要是介绍北邮22信通:二叉树 书上重要知识点补充 例4.3 统计结点总数 深度和叶子结点数,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
北邮22信通一枚~
跟随课程进度每周更新数据结构与算法的代码和文章
持续关注作者 解锁更多邮苑信通专属代码~
获取更多文章 请访问专栏:
北邮22信通_青山如墨雨如画的博客-CSDN博客
目录
一.统计结点总个数
二.统计二叉树深度
三.统计叶子结点总数
四.完整代码
4.1测试int存储类型:
代码部分:
运行结果:
4.2测试class储存类型:
代码部分:
运行结果:
***说明***
书上例4.3的代码和思考题~
对上一篇文章的功能有了新补充~
函数主要思想:递归调用。
***说明完毕***
一.统计结点总个数
思路:二叉树结点总数等于其左子树的节点总数+右子树的结点总数+根结点。
代码部分:
template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::nodecount(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;if (r->leftchild == NULL && r->rightchild == NULL)return 1;else{int m = nodecount(r->leftchild);int n = nodecount(r->rightchild);return m + n + 1;}
}二.统计二叉树深度
代码部分:
思路:保存现场截止。
template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::height(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;else{int m = height(r->leftchild);int n = height(r->rightchild);return m > n ? m + 1 : n + 1;}
}三.统计叶子结点总数
思路:判断某一处的结点是不是叶子结点,判断条件就是看它左右孩子是否没有。如果都没有,那就是叶子结点。然后调用函数递归来实现整体。
代码部分:
template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::leafcount(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;if (r->leftchild == NULL && r->rightchild == NULL)return 1;else{int m = leafcount(r->leftchild);int n = leafcount(r->rightchild);return m + n;}
}
四.完整代码
4.1测试int存储类型:
代码部分:
#include<iostream>
#define MAXSIZE 100000
//注意:不能将上面这行宏定义写成
//#define MAXSIZE 1e5
//上面这样写会报错!!
using namespace std;template<class temp>
struct binnode
{temp data;binnode<temp>* leftchild;binnode<temp>* rightchild;
};template<class temp>
class bintree
{
private:void create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n);void release(binnode<temp>* r);
public:binnode<temp>* root;bintree(temp data[], int n);void preorder(binnode<temp>* r);void inorder(binnode<temp>* r);void postorder(binnode<temp>* r);void levelorder(binnode<temp>* r);int nodecount(binnode<temp>* r);int height(binnode<temp>* r);int leafcount(binnode<temp>* r);~bintree();
};template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n)
{if (i <= n && data[i - 1] != 0){r = new binnode<temp>;r->data = data[i - 1];r->leftchild = r->rightchild = NULL;create(r->leftchild, data, 2 * i, n);/*书上代码错误1:向函数传入实参时少传入一个n*/create(r->rightchild, data, 2 * i + 1, n);/*书上代码错误同上*/}
}template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n)
/*书上代码错误2:构造函数不能有返回值类型,但是书上多加了一个void*/
/*如果构造函数的声明语句写成
void bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n),
程序会报错:不能在构造函数上指定返回值类型*/
{create(this->root, data, 1, n);
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::preorder(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){cout << r->data;//访问结点;preorder(r->leftchild);//遍历左子树preorder(r->rightchild);//遍历右子树}
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::inorder(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){inorder(r->leftchild);cout << r->data;inorder(r->rightchild);}
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::postorder(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){postorder(r->leftchild);postorder(r->rightchild);cout << r->data;}
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::levelorder(binnode<temp>* R)
{binnode<temp>* queue[MAXSIZE];int f = 0, r = 0;if (R != NULL)queue[++r] = R;//根节点入队while (f != r){binnode<temp>* p = queue[++f];//队头元素入队cout << p->data;//出队打印if (p->leftchild != NULL)queue[++r] = p->leftchild;//左孩子入队if (p->rightchild != NULL)queue[++r] = p->rightchild;//右孩子入队}
}template <class temp>
void bintree<temp>::release(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){release(r->leftchild);release(r->rightchild);delete r;}
}/*书上代码错误3:不能在析构函数上指定返回值类型,但是书上代码多了一个void*/
template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::~bintree()
{release(this->root);
}template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::nodecount(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;if (r->leftchild == NULL && r->rightchild == NULL)return 1;else{int m = nodecount(r->leftchild);int n = nodecount(r->rightchild);return m + n + 1;}
}template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::height(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;else{int m = height(r->leftchild);int n = height(r->rightchild);return m > n ? m + 1 : n + 1;}
}template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::leafcount(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;if (r->leftchild == NULL && r->rightchild == NULL)return 1;else{int m = leafcount(r->leftchild);int n = leafcount(r->rightchild);return m + n;}
}int main()
{system("color 0A");int a[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };bintree<int>bintreee(a, 5);cout << "前序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.preorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "中序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.inorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "后序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.postorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "层序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.levelorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "二叉树中的节点总数为:";cout << bintreee.nodecount(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "二叉树的深度为:";cout << bintreee.height(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "二叉树的叶子结点数为:";cout << bintreee.leafcount(bintreee.root);cout << endl;
}运行结果:

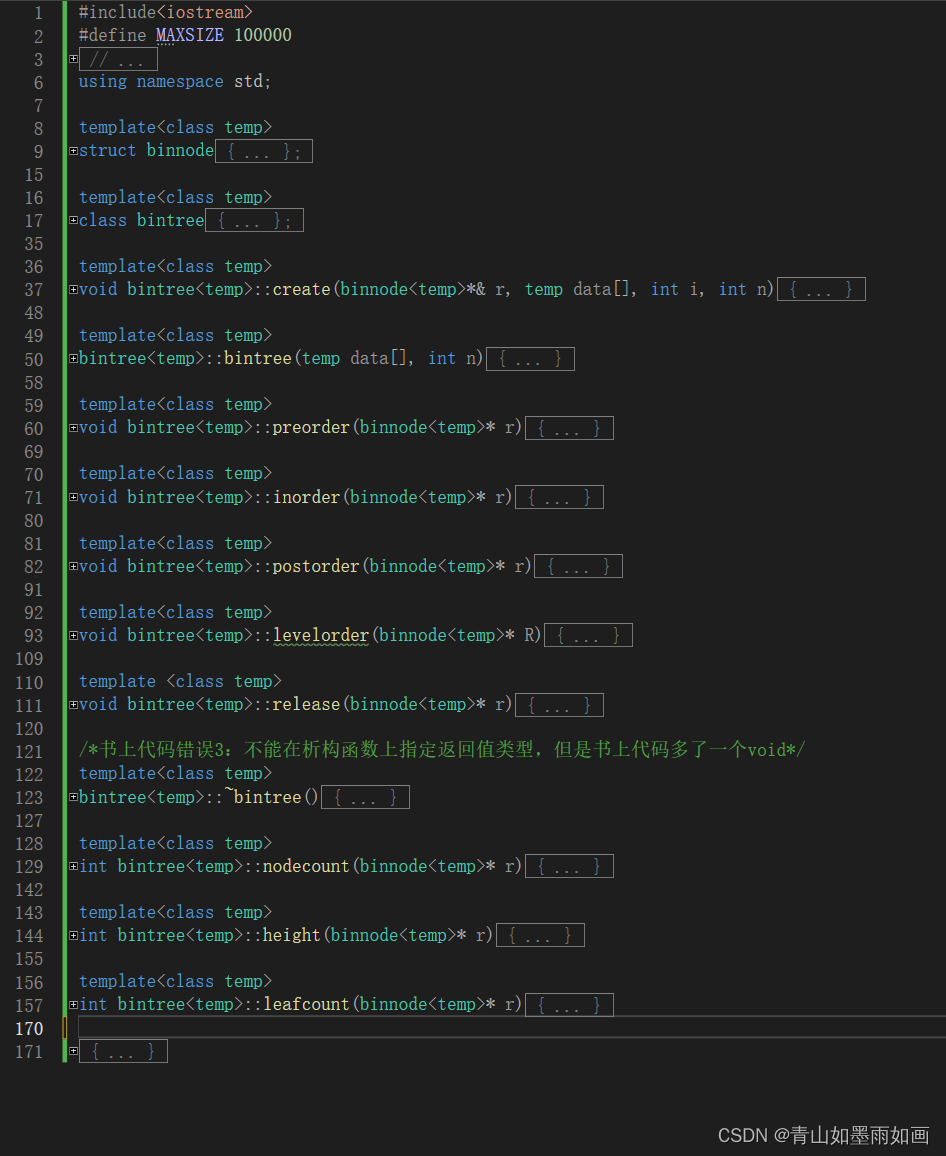
4.2测试class储存类型:
代码部分:
#include<iostream>
#define MAXSIZE 100000
//注意:不能将上面这行宏定义写成
//#define MAXSIZE 1e5
//上面这样写会报错!!
using namespace std;
class student
{
private:int ID;string name;
public:int existence;student(){this->ID = 0;this->name = "unknown name";this->existence = 0;}student(int ID, string name){this->ID = ID;this->name = name;this->existence = 1;}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& output, student& s){output << s.ID << " " << s.name << endl;return output;}
};template<class temp>
struct binnode
{temp data;binnode<temp>* leftchild;binnode<temp>* rightchild;
};template<class temp>
class bintree
{
private:void create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n);void release(binnode<temp>* r);
public:binnode<temp>* root;bintree(temp data[], int n);void preorder(binnode<temp>* r);void inorder(binnode<temp>* r);void postorder(binnode<temp>* r);void levelorder(binnode<temp>* r);int nodecount(binnode<temp>* r);int height(binnode<temp>* r);int leafcount(binnode<temp>* r);~bintree();
};template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::create(binnode<temp>*& r, temp data[], int i, int n)
{/*书上代码的一个问题:data[i-1]!=0会报错,这是因为data的数据类型是temp,没法实现!=的运算*///书上原代码//if (i <= n && data[i - 1] != 0)if (i <= n && data[i - 1].existence != 0){r = new binnode<temp>;r->data = data[i - 1];r->leftchild = r->rightchild = NULL;create(r->leftchild, data, 2 * i, n);/*书上代码错误1:向函数传入实参时少传入一个n*/create(r->rightchild, data, 2 * i + 1, n);/*书上代码错误同上*/}
}template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n)
/*书上代码错误2:构造函数不能有返回值类型,但是书上多加了一个void*/
/*如果构造函数的声明语句写成
void bintree<temp>::bintree(temp data[], int n),
程序会报错:不能在构造函数上指定返回值类型*/
{create(this->root, data, 1, n);
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::preorder(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){cout << r->data;//访问结点;preorder(r->leftchild);//遍历左子树preorder(r->rightchild);//遍历右子树}
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::inorder(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){inorder(r->leftchild);cout << r->data;inorder(r->rightchild);}
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::postorder(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){postorder(r->leftchild);postorder(r->rightchild);cout << r->data;}
}template<class temp>
void bintree<temp>::levelorder(binnode<temp>* R)
{binnode<temp>* queue[MAXSIZE];int f = 0, r = 0;if (R != NULL)queue[++r] = R;//根节点入队while (f != r){binnode<temp>* p = queue[++f];//队头元素入队cout << p->data;//出队打印if (p->leftchild != NULL)queue[++r] = p->leftchild;//左孩子入队if (p->rightchild != NULL)queue[++r] = p->rightchild;//右孩子入队}
}template <class temp>
void bintree<temp>::release(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r != NULL){release(r->leftchild);release(r->rightchild);delete r;}
}/*书上代码错误3:不能在析构函数上指定返回值类型,但是书上代码多了一个void*/
template<class temp>
bintree<temp>::~bintree()
{release(this->root);
}template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::nodecount(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;if (r->leftchild == NULL && r->rightchild == NULL)return 1;else{int m = nodecount(r->leftchild);int n = nodecount(r->rightchild);return m + n + 1;}
}template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::height(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;else{int m = height(r->leftchild);int n = height(r->rightchild);return m > n ? m + 1 : n + 1;}
}template<class temp>
int bintree<temp>::leafcount(binnode<temp>* r)
{if (r == NULL)return 0;if (r->leftchild == NULL && r->rightchild == NULL)return 1;else{int m = leafcount(r->leftchild);int n = leafcount(r->rightchild);return m + n;}
}int main()
{system("color 0A");student stu[5] = { {1,"zhang"},{2,"wang"},{3,"li"},{4,"zhao"},{5,"liu"} };bintree<student>bintreee(stu, 5);cout << "前序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.preorder(bintreee.root);/*说明:这里体现了将根节点定义为public类型的好处,不然需要通过一个成员函数来实现这个功能,从数据保密性来看,这样做也是可以的:外部如果不通过调用成员函数,就只能访问根节点一个节点内的数据,但是其他任意节点内的数据都无法访问,安全性也相对较高。*/cout << endl << "中序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.inorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "后序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.postorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "层序遍历:" << endl;bintreee.levelorder(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "二叉树中的节点总数为:";cout << bintreee.nodecount(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "二叉树的深度为:";cout << bintreee.height(bintreee.root);cout << endl << "二叉树的叶子结点数为:";cout << bintreee.leafcount(bintreee.root);cout << endl;return 0;
}运行结果:
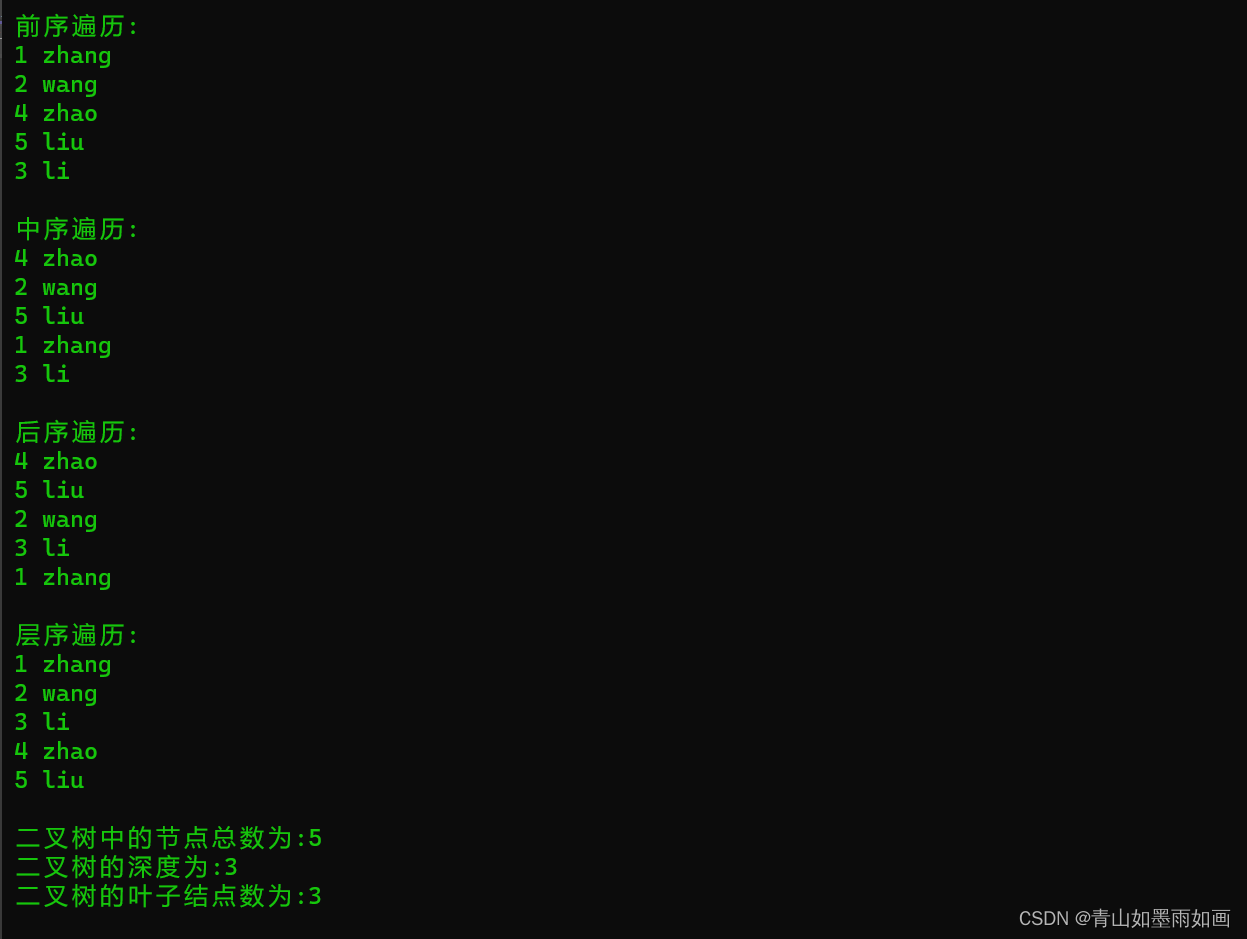
这篇关于北邮22信通:二叉树 书上重要知识点补充 例4.3 统计结点总数 深度和叶子结点数的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




