本文主要是介绍数据结构——10.24,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
这里写目录标题
- 回文
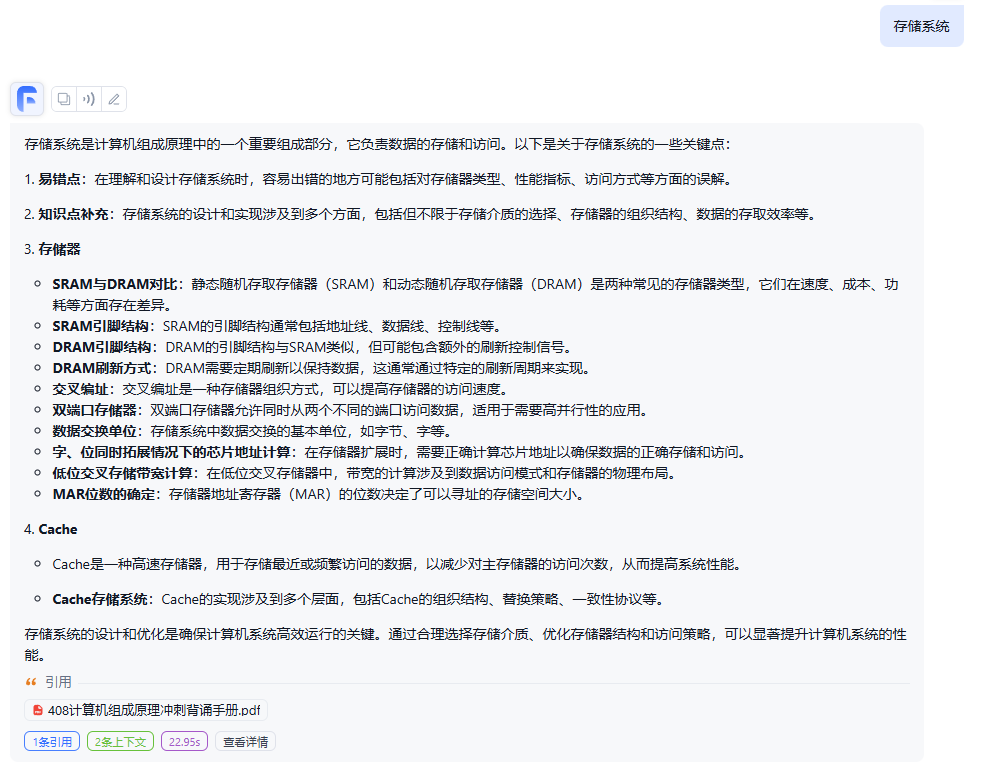
- 双向栈
- 双向队列1
- 双向队列2
回文
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;bool is_huiwen( string s)
{for(int i = 0; i < s.size() / 2; i++){if( s[i] != s[ s.size() - i - 1 ] ){return false;}}return true;
}int main(){string ss;int option;while( 1 ){cout << "请选择你的操作,1判断回文,0退出\n";cin >> option;if( option == 0 ){break;}else{cout << "qing input a string\n"; cin >> ss;if( is_huiwen( ss ) ){cout << "YES!该字符串 是 回文的\n";}else{cout << "NO!该字符串 不是 回文的\n";} }}return 0;
}
双向栈
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define maxsize 10
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct {int data[maxsize];int left; int right;
}DoubleStack,*Double;int Init(Double &L){L=(Double)malloc(sizeof(DoubleStack));if(L==NULL) return -1;L->left=-1; L->right=maxsize; return 1; }
//入栈
int push(Double &L,int status,int x){ if(L->left+1==L->right){printf("栈满!");return -1;} if(status==1){L->left++; L->data[L->left]=x; }else if(status==2){L->right--; L->data[L->right]=x; }
}
//出栈
int pop(Double &L,int status) {if(status==1){if(L->left<0) {printf("左栈为空!\n"); return -1;}else{printf("出%d ",L->data[L->left]); L->data[L->left]=0; L->left--;}}else if(status==2){if(L->right>maxsize-1){printf("右栈为空!\n"); return -1;}else{printf("出%d ",L->data[L->right]); L->data[L->right]=0; L->right++;}}
}void Print(Double &L) {int i,j;for(i=0;i<=maxsize-1;i++){ if(L->data[i]!=0){ printf("%d ",L->data[i]);}else{printf(" * ");} }}
int main(){DoubleStack *s;char L,R;if(Init(s)==1){printf("初始化成功!\n");}while (1){int a;int xxx;int x_val;cout << "\n 1左入栈\n 2右入栈\n 3左出栈\n 4右出栈\n 5遍历栈(左到右) 0退出" << endl;cout << "请选择要进行的操作:";cin >> a;switch (a){case 1:cout << "请选择左入栈个数:";cin >> xxx;cout << "请依次输入入栈元素:\n";for(int i = 1; i <= xxx ; i++){cin >> x_val;push(s,1,x_val); }break;case 2:cout << "请选择右入栈个数:";//int xxx;cin >> xxx;cout << "请依次输入入栈元素:\n";for(int i = 1; i <= xxx ; i++){cin >> x_val;push(s,2,x_val); }break;case 3:cout << "请选择左出栈个数:";int xxx;cin >> xxx;//cout << "请依次输入入栈元素:\n";for(int i = 1; i <= xxx ; i++){//cin >> x_val;pop(s,1);}break;case 4:cout << "请选择右出栈个数:";//int xxx;cin >> xxx;//cout << "请依次输入入栈元素:\n";for(int i = 1; i <= xxx ; i++){//cin >> x_val;pop(s,2);}break;case 5:printf("此时栈的元素为:");Print(s);break; case 0: return 1;default:return 1;}}} 双向队列1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define OK 1
#define MAXQSIZE 5typedef struct
{int* base; int front; int rear;
}SqQueue;int InitQueue(SqQueue&);
int EnQueue(SqQueue&, int);
int DeQueue(SqQueue&, int &);
int GetHead(SqQueue);
int QueueTraverse(SqQueue);
//int QueueLength( SqQueue );
void is_full( SqQueue );int flag;int main()
{SqQueue S;int e, a;if (InitQueue(S))cout << "循环队列初始化成功!" << endl;elsecout << "循环队列初始化失败!" << endl;while (1){cout << "\n 1入队\n 2出队\n 3取队头元素\n 4输出队列\n 5求队列状态\n 0退出" << endl;cout << "请选择要进行的操作:";cin >> a;switch (a){case 1:int x, n;cout << "请输入要插入的元素个数:";cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "元素值:";cin >> x;EnQueue(S, x);}cout << "入队完成!" << endl;break;case 2:cout << "请输入要删除的元素个数:";cin >> n;for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (!DeQueue(S, e))cout << "出队失败!" << endl;elsecout << "第【" << j+1 << "】个元素:" << e << " 出队成功!" << endl;}break;case 3:cout << "队头元素为:" << GetHead(S) << endl;break;case 4:if(!QueueTraverse(S))cout << "队列为空!" << endl;break;
// case 6:
// QueueLength(S);
// break;case 5:is_full( S );if( flag == 0 ){cout << "队列为空!\n"; }else cout << "队列是满的!\n";break; case 0: return OK;default:return OK;}}return 0;
}int InitQueue(SqQueue& Q)
{Q.base = new int[MAXQSIZE];if(!Q.base)return 0; Q.front = Q.rear = 0;return OK;
}int EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, int e)
{if ((Q.rear + 1) % MAXQSIZE == Q.front) return 0; Q.base[Q.rear] = e;Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MAXQSIZE;return OK;
}int DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, int &e)
{if (Q.front == Q.rear)return 0;e = Q.base[Q.front];Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MAXQSIZE;return OK;
}int GetHead(SqQueue Q)
{if (Q.front != Q.rear) return Q.base[Q.front];
}int QueueTraverse(SqQueue Q)
{cout << "当前队列为:";if (Q.front == Q.rear)return 0;while (Q.front != Q.rear) {cout << Q.base[Q.front] << " ";Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MAXQSIZE;}cout << endl;
}/*int QueueLength(SqQueue Q)
{int len = (Q.rear - Q.front + MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE;cout << "循环队列的长度为:" << len << endl;return OK;
}
*/
void is_full( SqQueue Q ){if( Q.front == Q.rear ){int len = (Q.rear - Q.front + MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE;if( len == MAXQSIZE ){flag = 1;}else flag = 0;}else flag = 1;
}双向队列2
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define OK 1
#define MAXQSIZE 5typedef struct
{int* base; int front; int rear;
}SqQueue;int InitQueue(SqQueue&);
int EnQueue(SqQueue&, int);
int DeQueue(SqQueue&, int &);
int GetHead(SqQueue);
int QueueTraverse(SqQueue);
//int QueueLength( SqQueue );
void is_full( SqQueue );int flag;int main()
{SqQueue S;int e, a;if (InitQueue(S))cout << "循环队列初始化成功!" << endl;elsecout << "循环队列初始化失败!" << endl;S.base[MAXQSIZE ] = 0;while (1){cout << "\n 1入队\n 2出队\n 3取队头元素\n 4输出队列\n 5求队列状态\n 0退出" << endl;cout << "请选择要进行的操作:";cin >> a;switch (a){case 1:int x, n;cout << "请输入要插入的元素个数:";cin >> n;cout << "请依次输入要插入的元素:";for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> x;EnQueue(S, x);}cout << "入队完成!" << endl;break;case 2:cout << "请输入要删除的元素个数:";cin >> n;for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (!DeQueue(S, e))cout << "出队失败!" << endl;elsecout << "第" << j+1 << "个元素:" << e << " 出队成功!" << endl;}break;case 3:cout << "队头元素为:" << GetHead(S) << endl;break;case 4:if(!QueueTraverse(S))cout << "队列为空!" << endl;break;
// case 6:
// QueueLength(S);
// break;case 5:is_full( S );break; case 0: return OK;default:return OK;}}return 0;
}int InitQueue(SqQueue& Q)
{Q.base = new int[MAXQSIZE + 1];if(!Q.base)return 0; Q.front = 10;Q.rear = 0;return OK;
}int EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, int e)
{//cout << "wei " << Q.rear<< endl;if ((Q.rear + 1) % (MAXQSIZE ) == Q.front) {//cout << "wei " << Q.rear<< endl;cout << "full!\n";return 0;}Q.base[Q.rear] = e;Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % (MAXQSIZE - 1 );Q.base[MAXQSIZE]++; //cout << "wei " << Q.rear<< endl;return 1;
}int DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, int &e)
{if (Q.front == Q.rear)return 0;e = Q.base[Q.front];Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % (MAXQSIZE );Q.base[MAXQSIZE ]--;return OK;
}int GetHead(SqQueue Q)
{if (Q.front != Q.rear) return Q.base[Q.front];
}int QueueTraverse(SqQueue Q)
{cout << "当前队列为:";if (Q.front == Q.rear)return 0;while (Q.front != Q.rear) {cout << Q.base[Q.front] << " ";Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % (MAXQSIZE );}cout << endl;
}/*int QueueLength(SqQueue Q)
{int len = (Q.rear - Q.front + MAXQSIZE) % MAXQSIZE;cout << "循环队列的长度为:" << len << endl;return OK;
}
*/
void is_full( SqQueue Q ){if( Q.base[MAXQSIZE ] == (MAXQSIZE ) ){cout << "队列是满的!\n";}else if( Q.base[MAXQSIZE ] == 0 ){cout << "队列是空的!\n";}else{cout << "队列长度为:" << Q.base[MAXQSIZE] << endl;;}
}这篇关于数据结构——10.24的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!