本文主要是介绍C++标准模板(STL)- 类型支持 (数值极限,max_digits10,radix,min_exponent),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
数值极限
定义于头文件 <limits>
| 定义于头文件 | ||
| template< class T > class numeric_limits; |
numeric_limits 类模板提供查询各种算术类型属性的标准化方式(例如 int 类型的最大可能值是 std::numeric_limits<int>::max() )。
区别所有此类型值所需的十进制位数
std::numeric_limits<T>::max_digits10| static constexpr int max_digits10 | (C++11 起) |
std::numeric_limits<T>::max_digits10 的值是唯一地表示所有类型 T 值的底 10 位数,是为序列化/反序列化到文本所需。此常量对所有浮点类型有意义。
标准特化
T | std::numeric_limits<T>::max_digits10 的值 |
| /* non-specialized */ | 0 |
| bool | 0 |
| char | 0 |
| signed char | 0 |
| unsigned char | 0 |
| wchar_t | 0 |
| char8_t | 0 |
| char16_t | 0 |
| char32_t | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| unsigned short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| unsigned int | 0 |
| long | 0 |
| unsigned long | 0 |
| long long | 0 |
| unsigned long long | 0 |
| float | FLT_DECIMAL_DIG 或 std::ceil(std::numeric_limits<float>::digits * std::log10(2) + 1) |
| double | DBL_DECIMAL_DIG 或 std::ceil(std::numeric_limits<double>::digits * std::log10(2) + 1) |
| long double | DECIMAL_DIG 或 LDBL_DECIMAL_DIG 或 std::ceil(std::numeric_limits<long double>::digits * std::log10(2) + 1) |
注意
不同于多数数学运算,只要用至少 max_digits10 (对于 float 为 9 ,对于 double 为 17 )位,则从浮点值转换到文本并转换回来是准确的:保证产生同一浮点值,即使不确定的文本表示不准确。以小数点记法,可能需要超过一百个十进制小数位表示 float 的精确值。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cfloat>struct SName
{
};//偏特化
struct SPartSpec
{
};namespace std
{
template<>
struct numeric_limits<SPartSpec>
{static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_specialized = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_signed = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_integer = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_exact = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_infinity = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_quiet_NaN = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_signaling_NaN = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_denorm_style has_denorm = denorm_present;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_denorm_loss = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_round_style round_style = round_toward_neg_infinity;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_iec559 = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_bounded = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_modulo = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits = CHAR_BIT;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits10 = CHAR_BIT;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_digits10 = DECIMAL_DIG;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int radix = FLT_RADIX;
};
}int main()
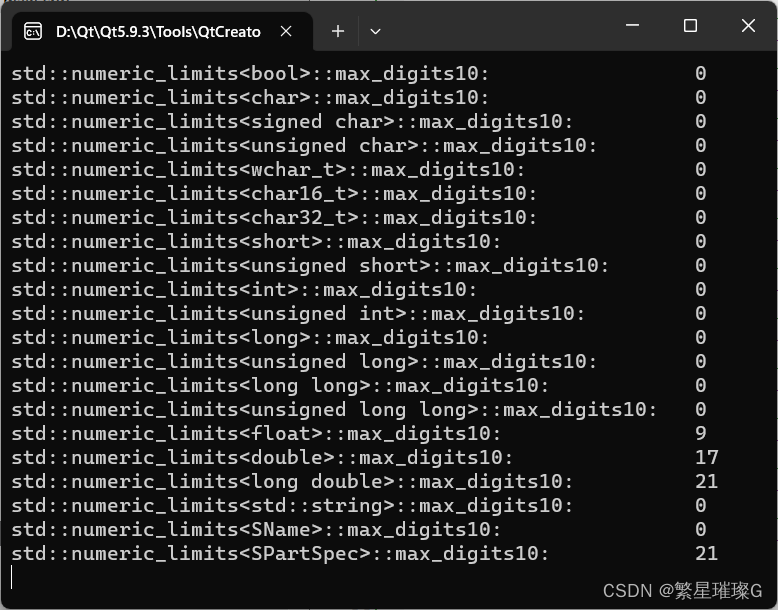
{std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<bool>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<bool>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<char>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<signed char>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<signed char>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<short>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<short>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<int>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<int>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<long>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long long>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<long long>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<float>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<float>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<double>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long double>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<long double>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<std::string>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<std::string>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SName>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<SName>::max_digits10 << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::max_digits10: "<< std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::max_digits10 << std::endl;return 0;
}输出
给定类型的表示所用的基或整数底
std::numeric_limits<T>::radix| static const int radix; | (C++11 前) | |
| static constexpr int radix; | (C++11 起) |
std::numeric_limits<T>::radix 的值是用于表示该类型的数字系统的底。对于所有二进制数值类型为 2 ,但它可以,譬如对 IEEE 754 十进制浮点类型或第三方二进制编码十进制整数为 10 。此常量对所有特化有意义。
标准特化
T | std::numeric_limits<T>::radix 的值 |
| /* non-specialized */ | 0 |
| bool | 2 |
| char | 2 |
| signed char | 2 |
| unsigned char | 2 |
| wchar_t | 2 |
| char8_t | 2 |
| char16_t | 2 |
| char32_t | 2 |
| short | 2 |
| unsigned short | 2 |
| int | 2 |
| unsigned int | 2 |
| long | 2 |
| unsigned long | 2 |
| long long | 2 |
| unsigned long long | 2 |
| float | FLT_RADIX |
| double | FLT_RADIX |
| long double | FLT_RADIX |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cfloat>struct SName
{
};//偏特化
struct SPartSpec
{
};namespace std
{
template<>
struct numeric_limits<SPartSpec>
{static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_specialized = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_signed = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_integer = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_exact = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_infinity = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_quiet_NaN = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_signaling_NaN = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_denorm_style has_denorm = denorm_present;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_denorm_loss = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_round_style round_style = round_toward_neg_infinity;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_iec559 = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_bounded = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_modulo = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits = CHAR_BIT;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits10 = CHAR_BIT;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_digits10 = DECIMAL_DIG;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int radix = FLT_RADIX;
};
}int main()
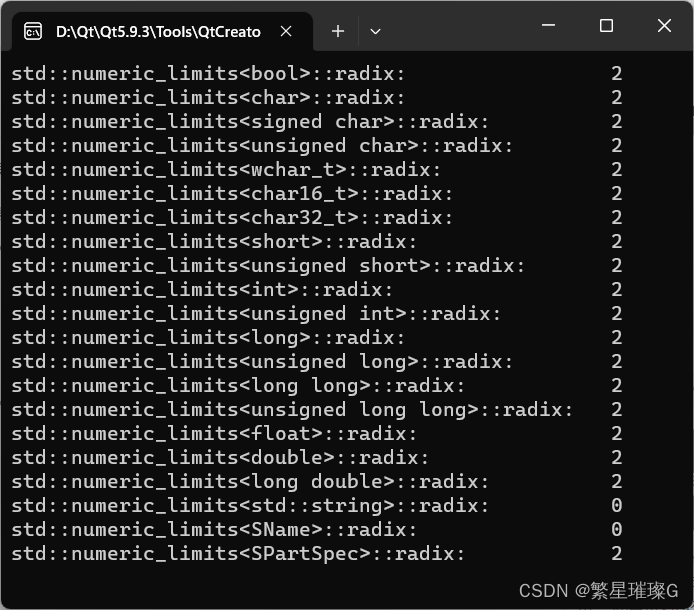
{std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<bool>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<bool>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<char>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<signed char>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<signed char>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<short>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<short>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<int>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<int>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<long>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long long>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<long long>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<float>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<float>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<double>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long double>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<long double>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<std::string>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<std::string>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SName>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<SName>::radix << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::radix: "<< std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::radix << std::endl;return 0;
}输出
底的该数次幂是合法正规浮点值的最小负数加一
std::numeric_limits<T>::min_exponent| static const int min_exponent; | (C++11 前) | |
| static constexpr int min_exponent; | (C++11 起) |
标准特化
T | std::numeric_limits<T>::min_exponent 的值 |
| /* non-specialized */ | 0 |
| bool | 0 |
| char | 0 |
| signed char | 0 |
| unsigned char | 0 |
| wchar_t | 0 |
| char8_t | 0 |
| char16_t | 0 |
| char32_t | 0 |
| short | 0 |
| unsigned short | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| unsigned int | 0 |
| long | 0 |
| unsigned long | 0 |
| long long | 0 |
| unsigned long long | 0 |
| float | FLT_MIN_EXP |
| double | DBL_MIN_EXP |
| long double | LDBL_MIN_EXP |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cfloat>struct SName
{
};//偏特化
struct SPartSpec
{
};namespace std
{
template<>
struct numeric_limits<SPartSpec>
{static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_specialized = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_signed = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_integer = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_exact = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_infinity = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_quiet_NaN = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_signaling_NaN = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_denorm_style has_denorm = denorm_present;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool has_denorm_loss = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR float_round_style round_style = round_toward_neg_infinity;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_iec559 = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_bounded = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR bool is_modulo = true;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits = CHAR_BIT;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int digits10 = CHAR_BIT;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int max_digits10 = DECIMAL_DIG;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int radix = FLT_RADIX;static _GLIBCXX_USE_CONSTEXPR int min_exponent = FLT_MIN_EXP;
};
}int main()
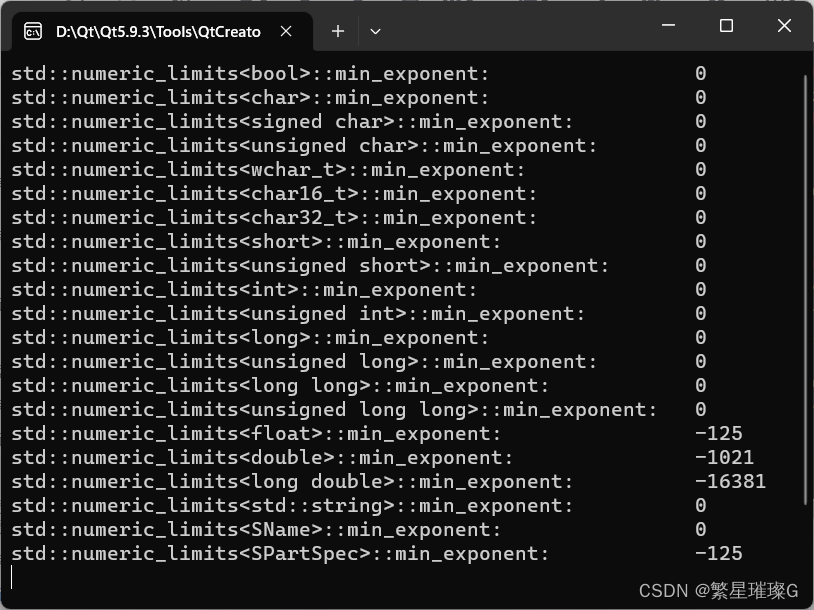
{std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<bool>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<bool>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<char>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<signed char>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<signed char>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<wchar_t>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<char16_t>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<char32_t>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<short>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<short>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned short>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<int>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<int>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned int>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<long>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long long>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<long long>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<unsigned long long>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<float>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<float>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<double>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<long double>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<long double>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<std::string>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<std::string>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SName>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<SName>::min_exponent << std::endl;std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::min_exponent: "<< std::numeric_limits<SPartSpec>::min_exponent << std::endl;return 0;
}输出
这篇关于C++标准模板(STL)- 类型支持 (数值极限,max_digits10,radix,min_exponent)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


