本文主要是介绍标准库标头 <filesystem> (C++17)学习,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
此头文件是文件系统支持库的一部分。本篇介绍filesystem命名空间的一些函数。
函数 | |
| 在命名空间 | |
| absolute (C++17) | 组成一个绝对路径 (函数) |
| canonicalweakly_canonical (C++17) | 组成一个规范路径 (函数) |
| relativeproximate (C++17) | 组成一个相对路径 (函数) |
| copy (C++17) | 复制文件或目录 (函数) |
| copy_file (C++17) | 复制文件内容 (函数) |
| copy_symlink (C++17) | 复制一个符号链接 (函数) |
| create_directorycreate_directories (C++17)(C++17) | 创建新目录 (函数) |
| create_hard_link (C++17) | 创建一个硬链接 (函数) |
| create_symlinkcreate_directory_symlink (C++17)(C++17) | 创建一个符号链接 (函数) |
| current_path (C++17) | 返回或设置当前工作目录 (函数) |
| exists (C++17) | 检查路径是否指代既存的文件系统对象 (函数) |
| equivalent (C++17) | 检查两个路径是否指代同一文件系统对象 (函数) |
| file_size (C++17) | 返回文件的大小 (函数) |
| hard_link_count (C++17) | 返回指代特定文件的硬链接数 (函数) |
| last_write_time (C++17) | 获取或设置最近一次数据修改的时间 (函数) |
| permissions (C++17) | 修改文件访问权限 (函数) |
| read_symlink (C++17) | 获得符号链接的目标 (函数) |
| removeremove_all (C++17)(C++17) | 移除一个文件或空目录 移除一个文件或递归地移除一个目录及其所有内容 (函数) |
| rename (C++17) | 移动或重命名一个文件或目录 (函数) |
| resize_file (C++17) | 以截断或填充零更改一个常规文件的大小 (函数) |
| space (C++17) | 确定文件系统上的可用空闲空间 (函数) |
| statussymlink_status (C++17)(C++17) | 确定文件属性 确定文件属性,检查符号链接目标 (函数) |
| temp_directory_path (C++17) | 返回一个适用于临时文件的目录 (函数) |
示例代码:
#include <filesystem>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdint>
#include <system_error>namespace fs = std::filesystem;void show(std::filesystem::path x, std::filesystem::path y)
{std::cout << "x:\t\t " << x << "\ny:\t\t " << y << '\n'<< "relative(x, y): "<< std::filesystem::relative(x, y) << '\n'<< "proximate(x, y): "<< std::filesystem::proximate(x, y) << "\n\n";
}void demo_exists(const fs::path& p, fs::file_status s = fs::file_status{})
{std::cout << p;if (fs::status_known(s) ? fs::exists(s) : fs::exists(p))std::cout << " exists\n";elsestd::cout << " does not exist\n";
}struct HumanReadable
{std::uintmax_t size{};private:friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, HumanReadable hr){int o{};double mantissa = hr.size;for (; mantissa >= 1024.; mantissa /= 1024., ++o);os << std::ceil(mantissa * 10.) / 10. << "BKMGTPE"[o];return o ? os << "B (" << hr.size << ')' : os;}
};int main(int, char const* argv[])
{//path current_path example 返回或设置当前工作目录 std::cout << "当前路径为 " << fs::current_path() << '\n';//path temp_directory_path example 返回一个适用于临时文件的目录 std::cout << "temp_directory_path " << fs::temp_directory_path() << '\n';//absolute example 当前路径/foo.c 组成一个绝对路径 std::filesystem::path p = "foo.c";std::cout << p << " 的绝对路径为 " << fs::absolute(p) << '\n';// create_directory/create_directories example 创建新目录 auto temp = fs::current_path();auto dir1 = temp / "abc";auto dir2 = temp / "abb/c2/e";std::filesystem::create_directory(dir1); //只能创建单个目录std::filesystem::create_directories(dir2);//可以创建多级目录std::filesystem::current_path(dir2);//设置当前路径// canonical/weakly_canonical example 组成一个规范路径//"D:\\vscpp\\cpp20\\cpp20standard\\filesystem"auto p1 = std::filesystem::path("../../c2/./e");auto p2 = std::filesystem::path("../no-such-file");std::cout << "当前路径为 "<< std::filesystem::current_path() << '\n'<< p1 << " 的规范路径为 "<< std::filesystem::canonical(p1) << '\n'<< p2 << " 的弱规范路径为 "<< std::filesystem::weakly_canonical(p2) << '\n';try{[[maybe_unused]] auto x_x = std::filesystem::canonical(p2);// 不会抵达此处}catch (const std::exception& ex){std::cout << p2 << " 的规范路径抛出了异常:\n"<< ex.what() << '\n';}//relative / proximate 组成一个相对路径 show("/a/b/c", "/a/b");show("/a/c", "/a/b");show("c", "/a/b");show("/a/b", "c");//auto temp = fs::current_path();auto dir3 = temp / "abb\\c2";auto dir4 = temp / "abb\\dir4";auto file1 = temp / "abb\\file1.txt";auto file2 = temp / "abb\\file2.txt";std::cout << "dir3======================" << dir3 << "\n";std::ofstream(file1).put('a');fs::copy(file1, file2); // 复制文件fs::copy(dir3, dir4); // 复制目录(非递归)const auto copyOptions = fs::copy_options::update_existing| fs::copy_options::recursive| fs::copy_options::directories_only;auto dirAbc = temp / "abc";auto dir5 = temp / "abb_copy";fs::copy(dirAbc, dir5, copyOptions);static_cast<void>(std::system("tree"));// remove/remove_all 移除一个文件或空目录 / 移除一个文件或递归地移除一个目录及其所有内容fs::remove(file1);fs::remove(file2);fs::remove_all(dirAbc);fs::remove_all(dir5);//exists example 检查路径是否指代既存的文件系统对象 const fs::path sandbox{ temp/"sandbox" };fs::create_directory(sandbox);std::ofstream{ sandbox / "file" }; // 创建常规文件//fs::create_symlink("non-existing", sandbox / "symlink");demo_exists(sandbox);for (const auto& entry : fs::directory_iterator(sandbox))demo_exists(entry, entry.status()); // 使用来自 directory_entry 的缓存状态fs::remove_all(sandbox);// 硬链接等价 equivalent example 检查两个路径是否指代同一文件系统对象 fs::path path1 = ".";fs::path path2 = fs::current_path();if (fs::equivalent(path1, path2))std::cout << path1 << " is equivalent to " << path2 << '\n';// 符号链接等价 for (const fs::path lib : {"/lib/libc.so.6", "/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6"}){try{path2 = lib.parent_path() / fs::read_symlink(lib);}catch (std::filesystem::filesystem_error const& ex){std::cout << ex.what() << '\n';continue;}if (fs::equivalent(lib, path2))std::cout << lib << " is equivalent to " << path2 << '\n';}//file_size example 返回文件的大小 fs::path example = "bug.nc";fs::path path3 = fs::current_path() / example;std::ofstream(path3).put('a'); // 创建大小为 1 的文件std::cout << example << " size = " << fs::file_size(path3) << '\n';fs::remove(path3);path3 = argv[0];std::cout << path3 << " size = " << HumanReadable{ fs::file_size(path3) } << '\n';try{std::cout << "尝试获取目录的大小:\n";[[maybe_unused]] auto x_x = fs::file_size("/dev");}catch (fs::filesystem_error& e){std::cout << e.what() << '\n';}for (std::error_code ec; fs::path bin : {"cat", "mouse"}){bin = "/bin" / bin;if (const std::uintmax_t size = fs::file_size(bin, ec); ec)std::cout << bin << " : " << ec.message() << '\n';elsestd::cout << bin << " size = " << HumanReadable{ size } << '\n';}//rename example 移动或重命名一个文件或目录 std::filesystem::path path4 = std::filesystem::current_path() / "sandbox";std::filesystem::create_directories(path4 / "from");std::ofstream{ path4 / "from/file1.txt" }.put('a');std::filesystem::create_directory(path4 / "to");fs::rename(path4 / "from/file1.txt", path4 / "to/file2.txt"); // OK
// fs::rename(path4 / "from", path4 / "to/subdir"); // OK//space example确定文件系统上的可用空闲空间std::error_code ec;const std::filesystem::space_info si = std::filesystem::space(path4, ec);std::cout << "capacity: " << si.capacity << "\tavailable:" << si.available << "\tfree:" << si.free << '\n';//std::filesystem::remove_all(path4);std::cout << "hello world\n";return 0;
}运行结果:
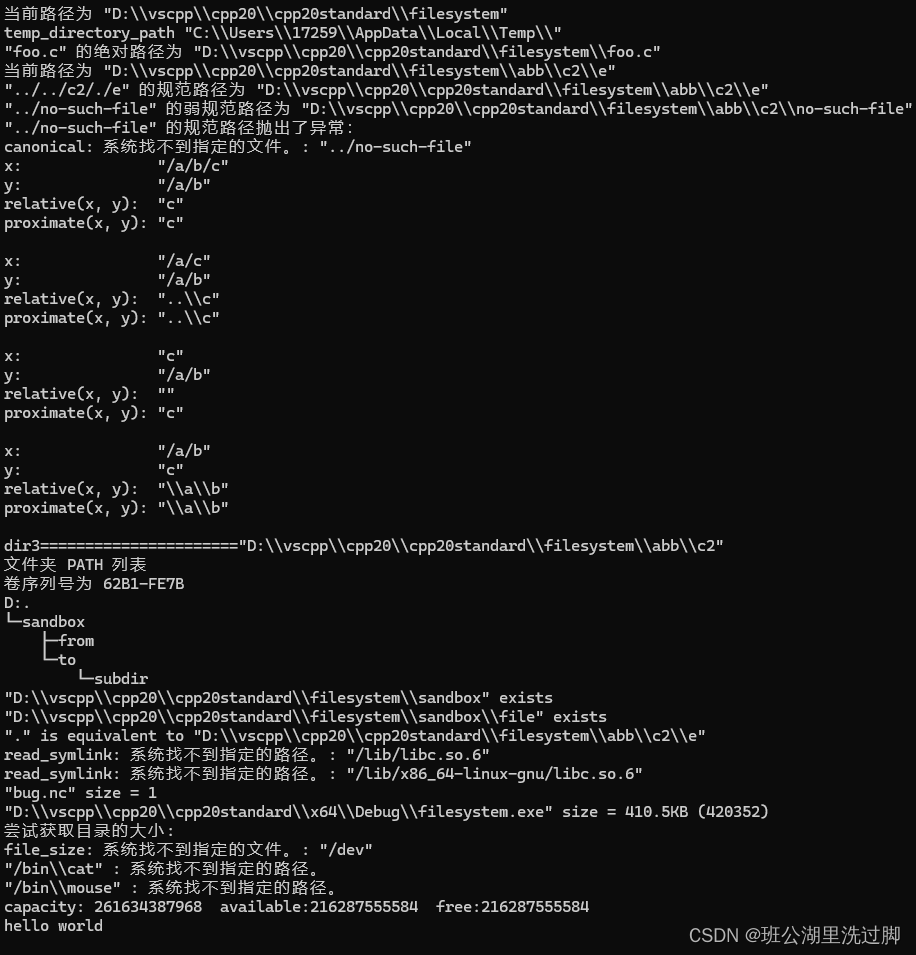
参考:
标准库标头 <filesystem> (C++17) - cppreference.com
这篇关于标准库标头 <filesystem> (C++17)学习的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





