本文主要是介绍连接查询、自关联、子查询,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
连接查询
连接查询概述
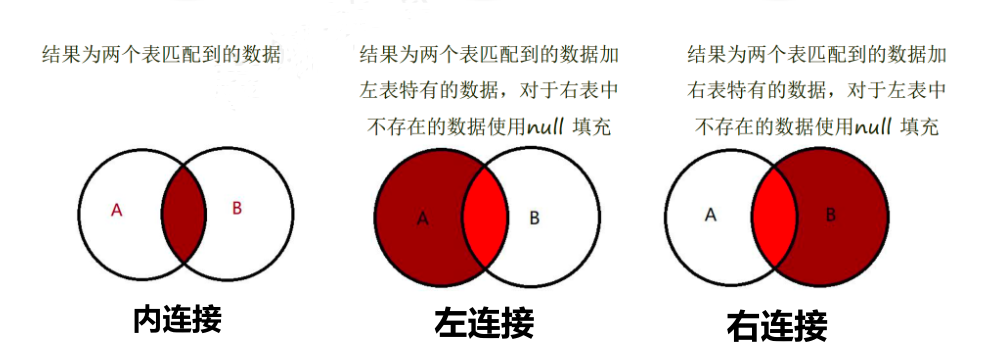
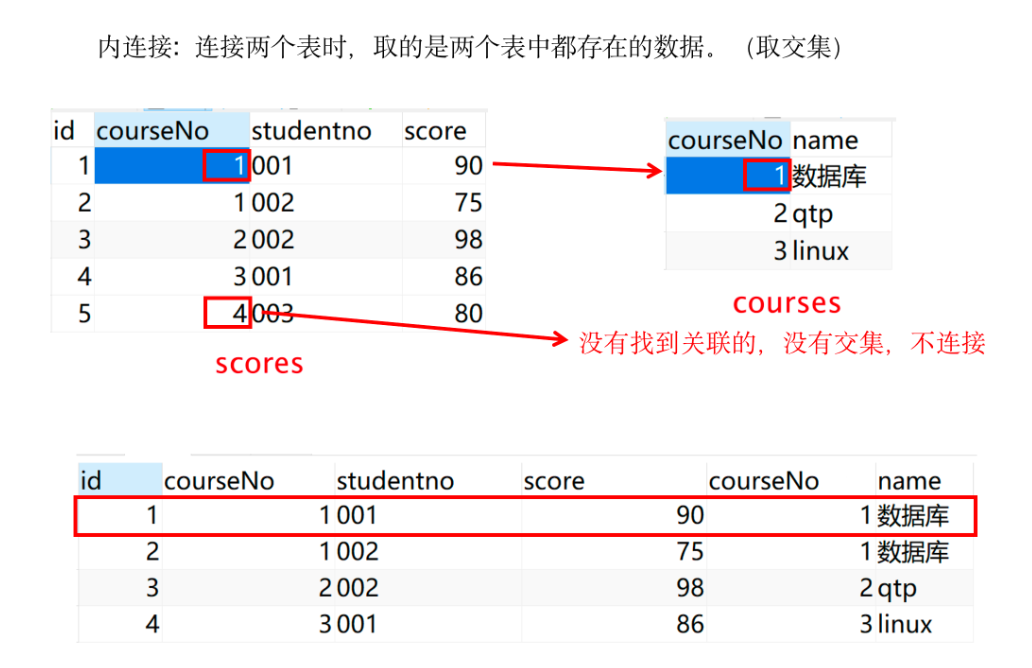
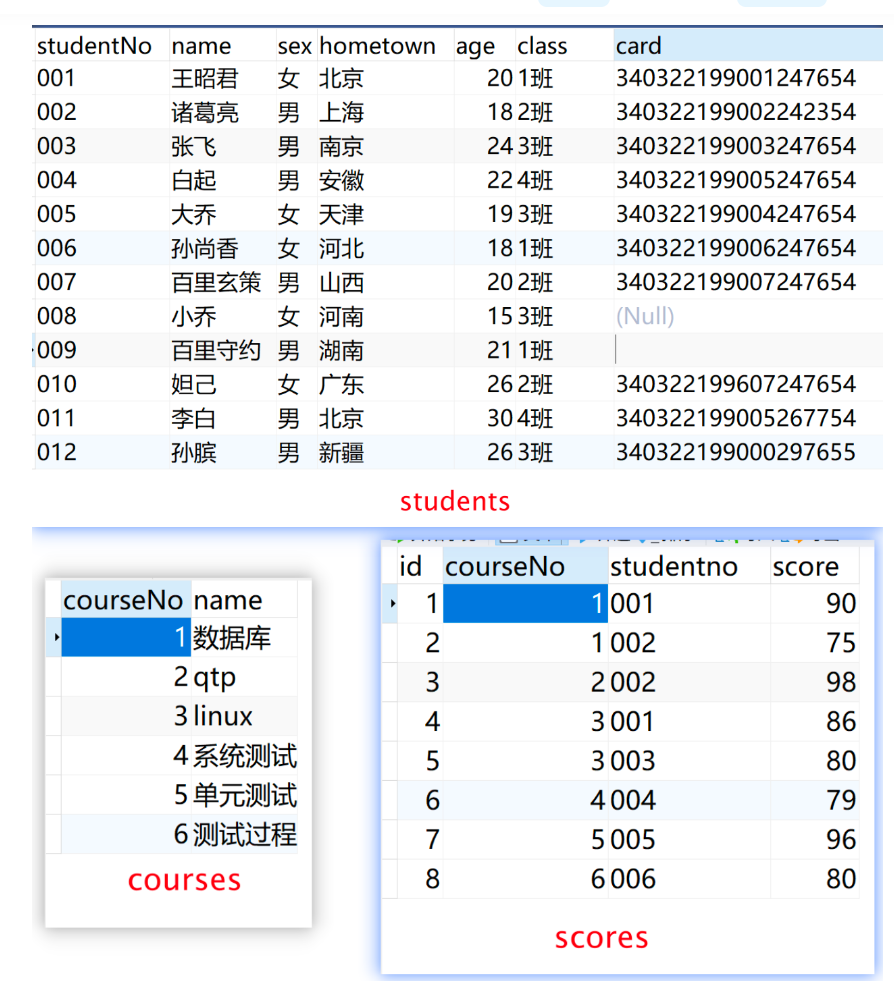
- 内连接:连接两个表时,取的是两个表中都存在的数据(取交集)
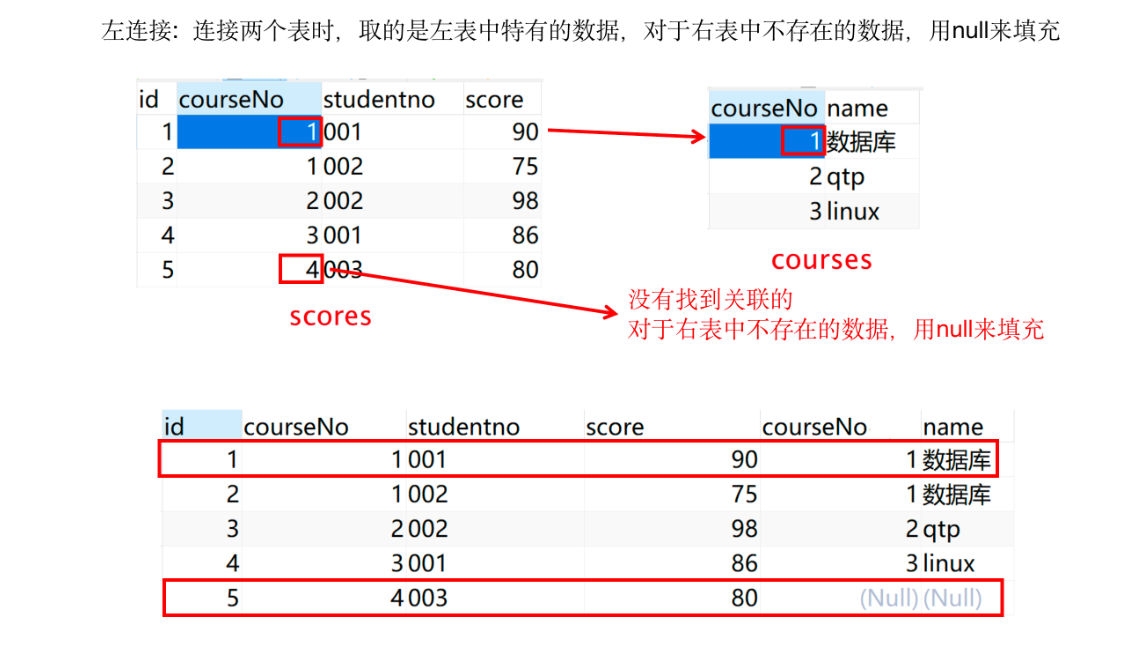
- 左连接:连接两个表时,取的是左表中特有的数据,对于右表中不存在的数据,用null来填充。
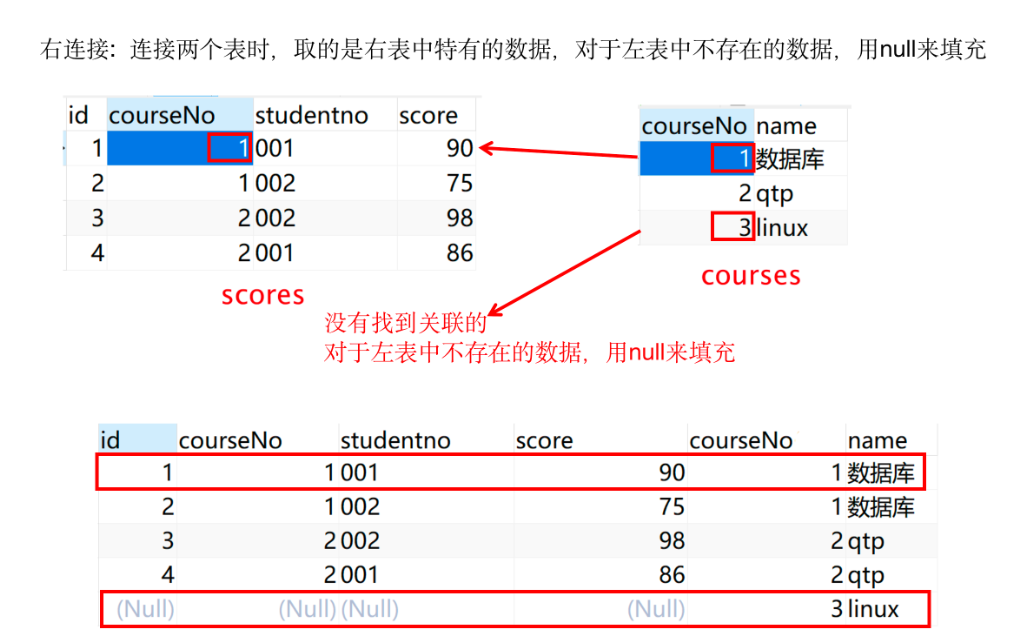
- 右连接:连接两个表时,取的时右表中特有的数据,对于左表中不存在的数据,用null来填充。
- 数据准备
drop table if exists courses;
create table courses (
courseNo int(10) unsigned primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(10)
);
insert into courses values ('1', '数据库'), ('2', 'qtp'), ('3', 'linux'),
('4', '系统测试'), ('5', '单元测试'), ('6', '测试过程');
drop table if exists scores;
create table scores (
id int(10) unsigned primary key auto_increment,
courseNo int(10),
studentno varchar(10),
score tinyint(4)
);
insert into scores values ('1', '1', '001', '90'), ('2', '1', '002', '75'),
('3', '2', '002', '98'),('4', '3', '001', '86'),('5', '3', '003', '80'),
('6', '4', '004', '79'),('7', '5', '005', '96'),('8', '6', '006', '80');
内连接
-
语法格式
select * from 表名1 inner join 表名2 on 表1.列=表2.列;- 查询的时两个表的交集的数据
- 表1的列与表2的列一定是存在关联关系
- 内连接连接时可以连接多个表
-
案例
-- 例1:查询学生信息及学生的成绩 select * from students inner join scores on students.studentNo=scores.studentNo; -- students 起别名为stu,scores起别名为sc select * from students as stu inner join scores as sc on stu.studentNo=sc.studentNo; -- 起别名可以不写as select * from students stu inner join scores sc on stu.studentNo=sc.studentNo; select * from students stu , scores sc where stu.studentNo=sc.studentNo;-- 例2:查询课程信息及课程的成绩 select * from courses cs inner join scores sc on cs.courseNo=sc.courseNo-- 例3、查询王昭君的成绩,要求显示姓名,课程号,成绩 select stu.name,sc.courseNo,sc.score from students stu inner join scores sc on stu.studentNo=sc.studentNo where stu.name='王昭君'-- 1、查询学生信息及学生的课程对应的成绩 select * from students inner join scores on students.studentNo=scores.studentno inner join courses on scores.courseNo=courses.courseNo -- 2、查询所有学生的数据库成绩,要求显示姓名,课程名,成绩 select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students inner join scores on students.studentNo=scores.studentno inner join courses on scores.courseNo=courses.courseNo -- 3、查询王昭君的数据库成绩,要求显示姓名,课程名,成绩 select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students inner join scores on students.studentNo=scores.studentno inner join courses on scores.courseNo=courses.courseNo where students.name='王昭君'-- 4、 查询男生中最高成绩,要求显示姓名、课程名、成绩 select students.name,courses.name,scores.score from students inner join scores on students.studentNo=scores.studentno inner join courses on scores.courseNo=courses.courseNo where students.sex='男' order by scores.score desc LIMIT 0,1 -- 等价于limit 1
左连接
-
语法格式
select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 表1.列=表2.列- 左连接查询的是左表特有的数据,对于右表中不存在的数据用null来填充
-
案例
-- 例1、查询所有学生的成绩,包括没有成绩的学生 select * from students stu left join scores sc on stu.studentNo=sc.studentno -- 例2、查询所有学生的成绩,包括没有成绩的学生,需要显示课程名 select * from students stu left join scores sc on stu.studentNo=sc.studentno left join courses cs on sc.courseNo=cs.courseNo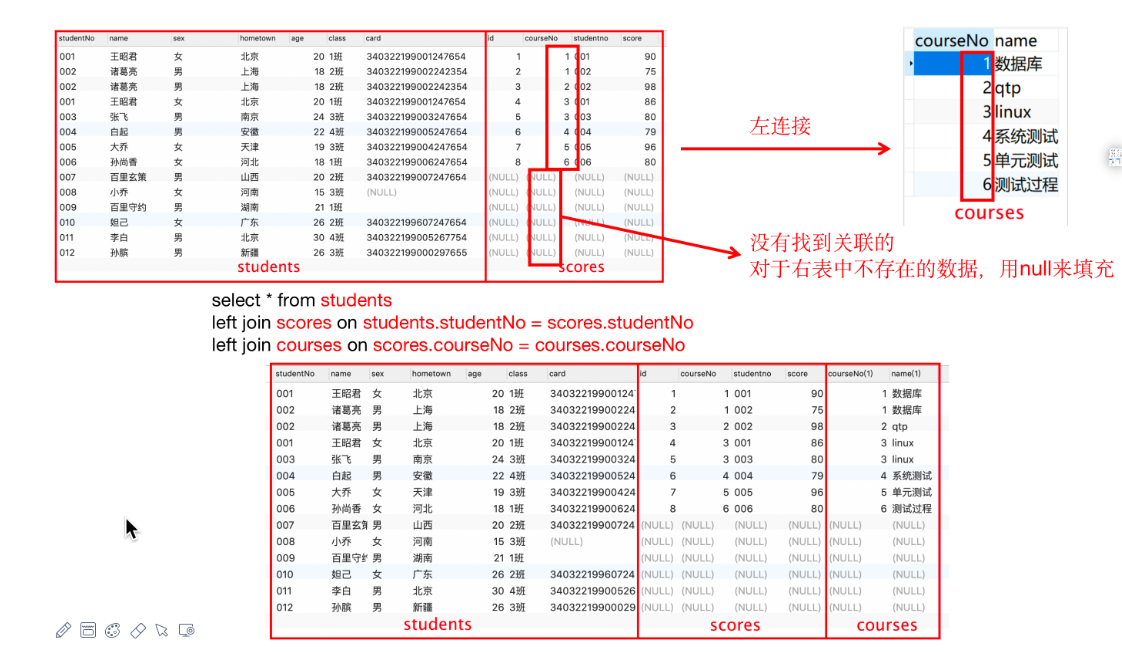
右连接
-
语法格式
select * from 表1 right join 表2 on 表1.列=表2.列- 右连接查询的是右表特有的数据,对于左表中不存在的数据用null来填充
-
案例
-- 例1、查询所有学生的成绩,包括没有成绩的学生 select * from scores sc right join students stu on sc.studentno=stu.studentNo -- 例2、查询所有学生的成绩,包括没有成绩的学生,需要显示课程名 select * from scores sc right join courses cs on sc.courseNo=cs.courseNo right join students stu on stu.studentNo=sc.studentno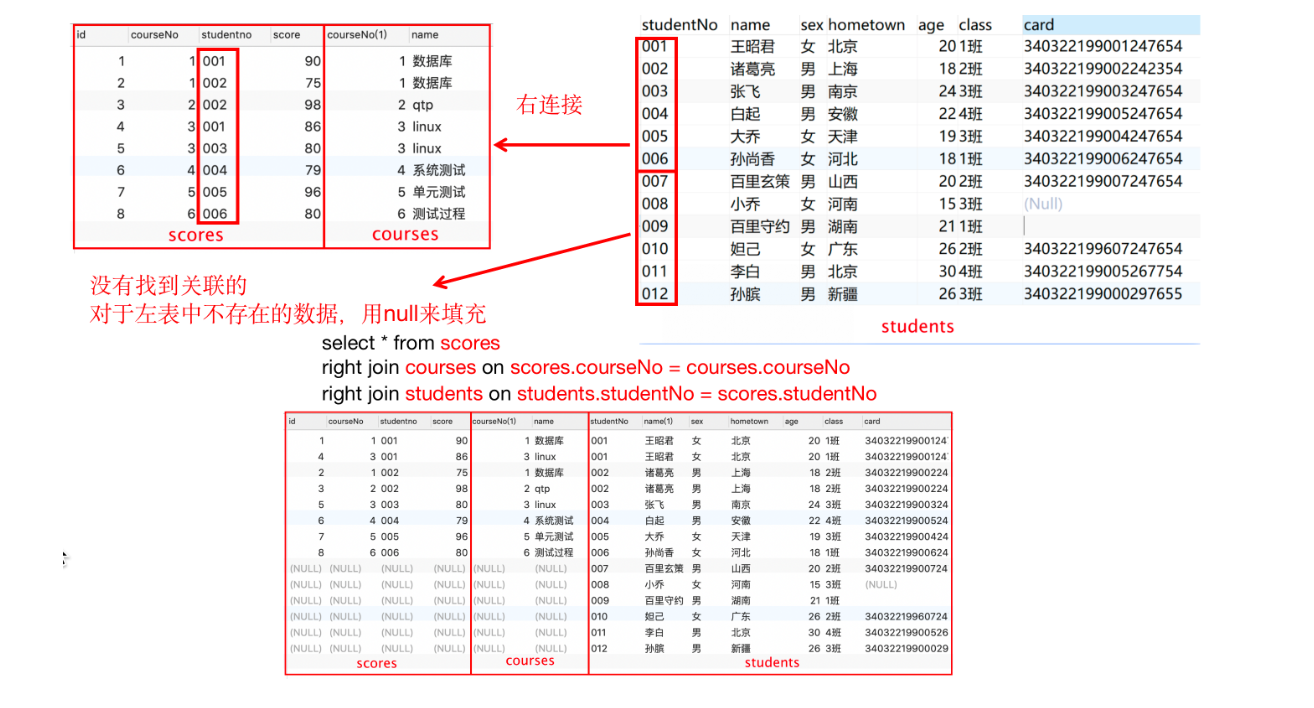
自关联
自关联介绍
- 自连接的应用场景
- 省、市、区的信息,一般不会分开放在不同的表里面进行存储,而是放在同一个表当中。
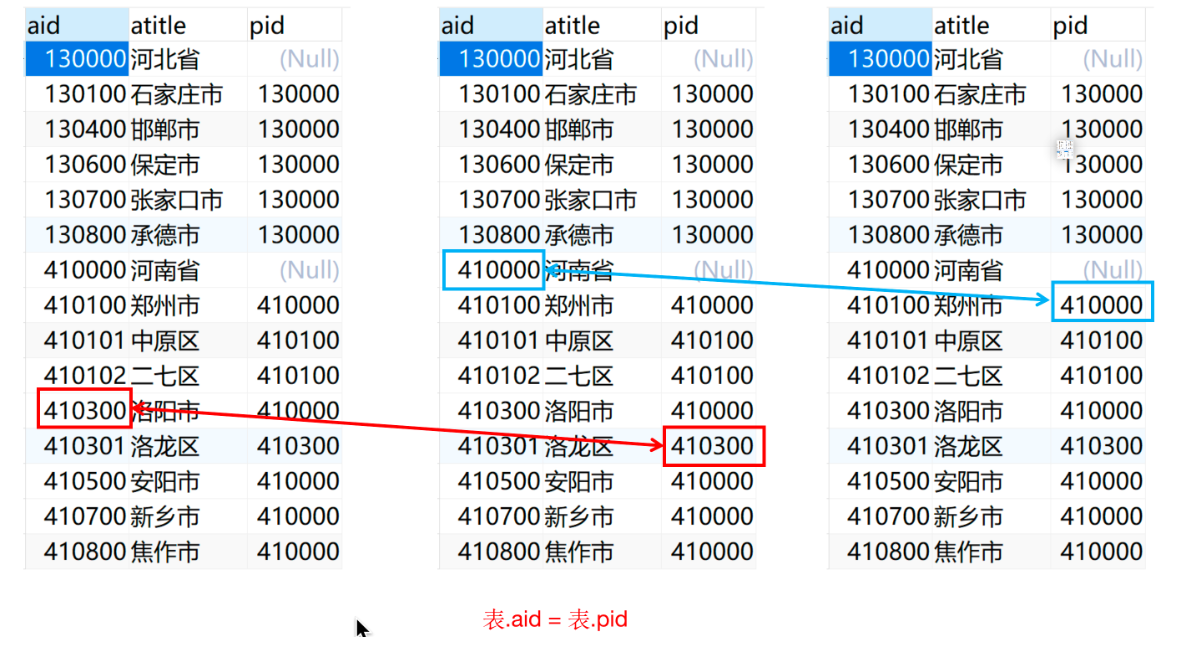
- 数据准备
drop table if exists areas;
create table areas(aid int primary key, atitle varchar(20),pid int);
insert into areas values ('130000', '河北省', NULL), ('130100', '石家庄市','130000'),
('130400','邯郸市','130000'), ('130600', '保定市', '130000'),('130700','张家口市', '130000'),
('130800', '承德市', '130000'),('410000', '河南省', NULL), ('410100', '郑州市', '410000'),
('410300', '洛阳市', '410000'),('410500', '安阳市', '410000'),('410700', '新乡市', '410000'),
('410800', '焦作市', '410000'),('410101', '中原区', '410100'),('410102', '二七区', '410100'),
('410301', '洛龙区', '410300');自关联实现
-
要通过自关联进行查询时,当前自关联的表当中一定会存在两个相关联的字段。
-
自关联要用别名
-
语法格式
select * from 表名 as 别名1 inner join 表名 as 别名2 on 别名1.列=别名2.列 -
案例
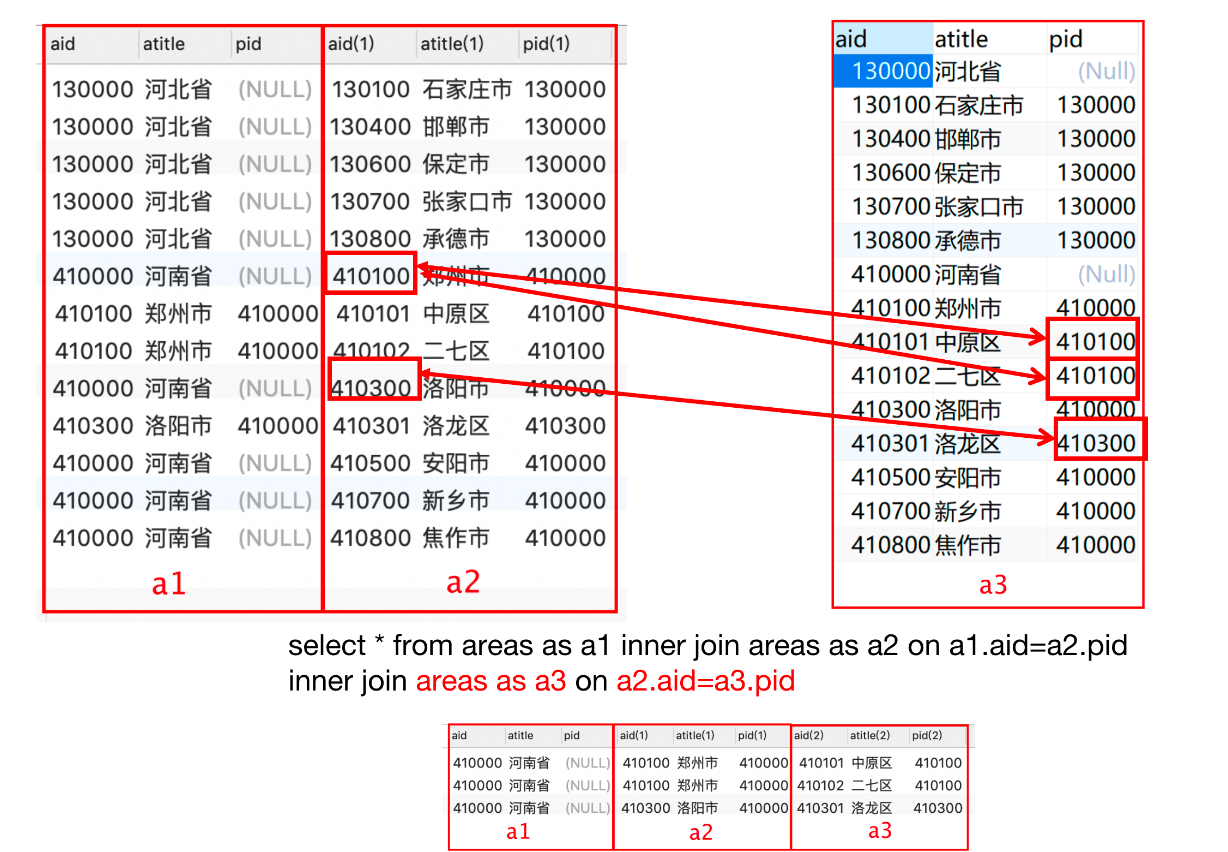
-- 查询出河南省的所有的市 select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid where a1.atitle='河南省'; -- 查询出郑州市所有的区 select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid where a1.atitle='郑州市'; -- 查询出河南省所有的市区信息 select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid left join areas as a3 on a2.pid=a3.pid where a1.atitle='河南省'-- 1、查询河北省所有市的信息 select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid where a1.atitle='河北省' -- 2、查询洛阳市所有区的信息 select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid where a1.atitle='洛阳市'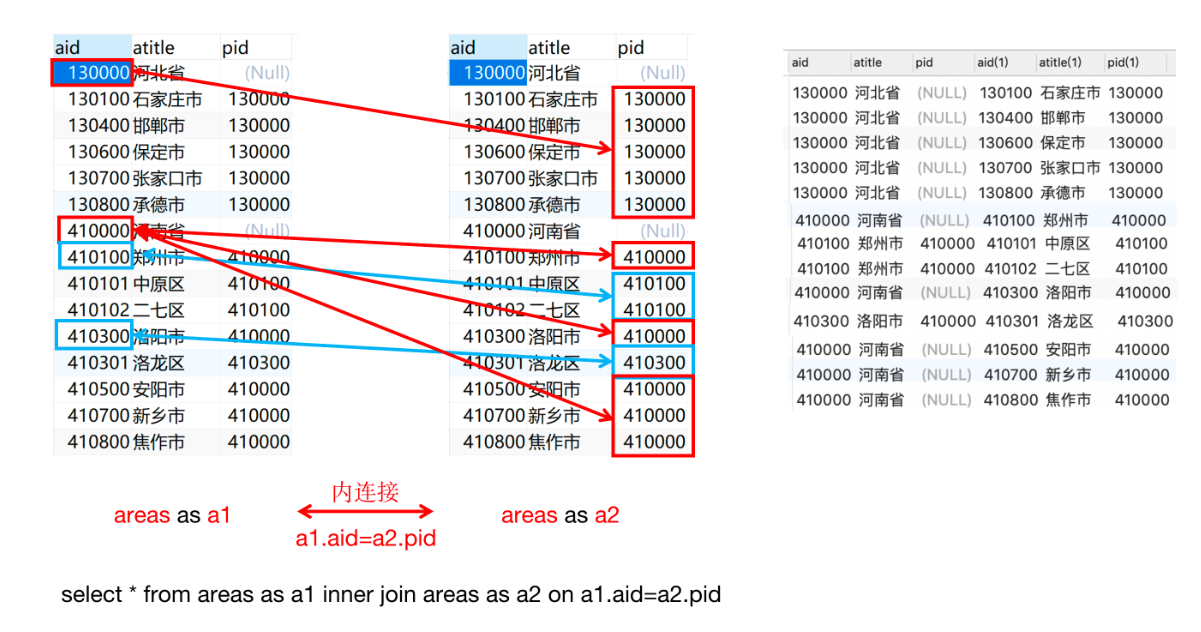
子查询
- 将一条SQL查询的语句嵌入在其他的SQL语句中,被嵌入的SQL语句称之为子查询,其他的SQL称之为主查询
- 子查询select语句,要么是充当条件,要么充当数据源
- 子查询语句是一条完整的select语句,且可以单独执行
子查询充当条件
-- 例1、查询王昭君的成绩,要求显示成绩(标量子查询)
select studentNo from students where name='王昭君';
select * from scores where studentNO=(select studentNo from students where name='王昭君');-- 例2、查询18岁的学生的成绩,要求显示成绩(列子查询)
select studentNO from students where age=18;
select score from scores where studentNo in (select studentNO from students where age=18);-- 例3、查询和王昭君同班、同龄的学生信息(行子查询)
select class,age from students where name='王昭君';
select * from students where (class,age)=(select class,age from students where name='王昭君')
子查询充当数据源
-- 例1、查询数据库和系统测试的课程成绩
select * from scores as sc inner join (select * from courses where name in ('数据库','系统测试'))
as co on sc.courseNo=co.courseNo
- 子查询-特定关键字

-- 例1、查询18岁的学生的成绩,要求显示成绩(列子查询)
select studentNo from students where age=18;
select score from scores where studentNo in (select studentNo from students where age=18);
-- =any 和in等价
select score from scores where studentNo =any(select studentNo from students where age=18);
-- some:是any的别称,很少用
select score from scores where studentNo =some(select studentNo from students where age=18);
-- !=all 和not in 等价
select score from scores where studentNo not in (select studentNo from students where age=18);
select score from scores where studentNo !=all (select studentNo from students where age=18);
- 练习
-- 1、查询大于平均年龄的学生
-- 先查平均年龄
select avg(age) from students ;
select * from students where age>(select avg(age) from students);
-- 2、查询年龄在18-20之间的学生的成绩
-- 先查18-20之间的学生的学号
select studentNo from students where age between 18 and 20;
-- 子查询充当条件
select * from scores where studentNo in (select studentNo from students where age between 18 and 20);
-- 子查询充当数据源
select * from scores as sc inner join(select * from students where age between 18 and 20) as stu
on sc.studentNo=stu.studentNo;
查询演练
-
准备数据
/* **创建部门表 */ drop table if exists departments; create table departments ( deptid int(10) primary key, deptname varchar(20) not null -- 部门名称 ); insert into departments values ('1001', '市场部'); insert into departments values ('1002', '测试部'); insert into departments values ('1003', '开发部');/* **创建员工表 */ drop table if exists employees; create table employees ( empid int(10) primary key, empname varchar(20) not null, -- 姓名 sex varchar(4) default null, -- 性别 deptid int(20) default null, -- 部门编号 jobs varchar(20) default null, -- 岗位 politicalstatus varchar(20) default null, -- 政治面貌 leader int(10) default null ); insert into employees values ('1', '王昭君', '女', '1003', '开发', '群众', '9'); insert into employees values ('2', '诸葛亮', '男', '1003', '开发经理', '群众', null); insert into employees values ('3', '张飞', '男', '1002', '测试', '团员', '4'); insert into employees values ('4', '白起', '男', '1002', '测试经理', '党员', null); insert into employees values ('5', '大乔', '女', '1002', '测试', '党员', '4'); insert into employees values ('6', '孙尚香', '女', '1001', '市场', '党员', '12'); insert into employees values ('7', '百里玄策', '男', '1001', '市场', '团员', '12'); insert into employees values ('8', '小乔', '女', '1002', '测试', '群众', '4'); insert into employees values ('9', '百里守约', '男', '1003', '开发', '党员', '9'); insert into employees values ('10', '妲己', '女', '1003', '开发', '团员', '9'); insert into employees values ('11', '李白', '男', '1002', '测试', '团员', '4'); insert into employees values ('12', '孙膑', '男', '1001', '市场经理', '党员', null);/* **创建工资表 */ drop table if exists salary; create table salary ( sid int(10) primary key, empid int(10) not null, salary int(10) not null -- 工资 ); insert into salary values ('1', '7', '2100'); insert into salary values ('2', '6', '2000'); insert into salary values ('3', '12', '5000'); insert into salary values ('4', '9', '1999'); insert into salary values ('5', '10', '1900'); insert into salary values ('6', '1', '3000'); insert into salary values ('7', '2', '5500'); insert into salary values ('8', '5', '2000'); insert into salary values ('9', '3', '1500'); insert into salary values ('10', '8', '4000'); insert into salary values ('11', '11', '2600'); insert into salary values ('12', '4', '5300');

-
练习
-- 1、列出总人数大于4的部门号和总人数(要统计所有部门的人数,需要使用分组,同时也要使用聚合函数) select deptid,count(*) from employees GROUP BY deptid having count(*)>4-- 2、列出开发部和测试部的职工号、姓名 select deptid from departments where deptname in ('开发部','测试部') select empid,empname from employees where deptid in ( select deptid from departments where deptname in ('开发部','测试部'))-- 3、求出各部门党员的人数,要求显示部门名称 select * from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid where emp.politicalstatus='党员';select dep.deptname from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid where emp.politicalstatus='党员'select dep.deptname from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid where emp.politicalstatus='党员' GROUP BY emp.deptid;-- 4、列出市场部的所有女职工的姓名和政治面貌 select * from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid where emp.sex='女' and dep.deptname='市场部'select emp.empname, emp.politicalstatus from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid where emp.sex='女' and dep.deptname='市场部'; select emp.empname, dep.deptname, sa.salary from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid;-- 6、显示各部门名和该部门的职工平均工资。 select dep.deptname,avg(sa.salary) from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid group by emp.deptid;-- 7、显示工资最高的前3名职工的职工号和姓名。 select emp.empname, dep.deptname, sa.salary from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid order by sa.salary desc limit 3 -- limit 3 等价于 limit 0, 3-- 8、列出工资在1000-2000之间的所有职工姓名。 select emp.empname, dep.deptname, sa.salary from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid where sa.salary between 1000 and 2000;-- 9、列出工资比王昭君高的员工。(首先查询王昭君的工资) -- 查询王昭君的工资 select sa.salary from employees as emp inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid where emp.empname='王昭君' select emp.empname, sa.salary from employees as emp inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid where sa.salary > ( select sa.salary from employees as empinner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid where emp.empname='王昭君' );-- 10、列出每个部门中工资小于本部门平均工资的员工信息。(首先查询出每个部门的平均工资) -- 查询出每个部门的平均工资 select emp.deptid, avg(sa.salary) as avg_salary from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid group by emp.deptid select emp.deptid, emp.empname, sa.salary from employees as emp inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid inner join ( select emp.deptid, avg(sa.salary) as avg_salary from employees as emp inner join departments as dep on emp.deptid=dep.deptid inner join salary as sa on sa.empid=emp.empid group by emp.deptid ) as c on emp.deptid=c.deptid where sa.salary < c.avg_salary;
这篇关于连接查询、自关联、子查询的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




