本文主要是介绍利用大型语言模型协作提升甲状腺结节超声诊断的一致性和准确性| 文献速递-基于深度学习的癌症风险预测与疾病预后应用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Title
题目
Collaborative Enhancement of Consistency and Accuracy in US Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules Using Large Language Models
利用大型语言模型协作提升甲状腺结节超声诊断的一致性和准确性
Background
背景
Large language models (LLMs) hold substantial promise for medical imaging interpretation. However, there is a lack of studies on their feasibility in handling reasoning questions associated with medical diagnosis.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在医学影像解读中具有巨大的潜力。然而,关于其在处理与医学诊断相关的推理问题方面的可行性研究尚不足够。
Method
方法
US images of thyroid nodules with pathologic results were retrospectively collected from a tertiary referral hospital between July 2022 and December 2022 and used to evaluate malignancy diagnoses generated by three LLMs—OpenAI’s ChatGPT 3.5, ChatGPT 4.0, and Google’s Bard. Inter- and intra-LLM agreement of diagnosis were evaluated. Then, diagnostic performance, including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), was evaluated and compared for the LLMs and three interactive approaches: human reader combined with LLMs, image-to-text model combined with LLMs, and an end-to-end convolutional neural network model.
2022年7月至2022年12月期间,从一家三级转诊医院回顾性收集了具有病理结果的甲状腺结节超声图像,并用于评估由三个大型语言模型(LLMs)生成的恶性肿瘤诊断——OpenAI的ChatGPT 3.5、ChatGPT 4.0和Google的Bard。评估了诊断的一致性,包括模型之间和模型内部的一致性。随后对LLMs的诊断性能进行了评估和比较,包括准确性、敏感性、特异性和受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC),并比较了三种互动方法:人类读片者与LLMs结合,图像到文本模型与LLMs结合,以及端到端卷积神经网络模型。
Conclusion
结论
LLMs, particularly integrated with image-to-text approaches, show potential in enhancing diagnostic medical imaging. ChatGPT 4.0 was optimal for consistency and diagnostic accuracy when compared with Bard and ChatGPT 3.5.
大型语言模型(LLMs),特别是与图像到文本的方法相结合时,在提升医学影像诊断方面显示出潜力。与Bard和ChatGPT 3.5相比,ChatGPT 4.0在一致性和诊断准确性方面表现最佳。
Results
结果
A total of 1161 US images of thyroid nodules (498 benign, 663 malignant) from 725 patients (mean age, 42.2 years ± 14.1 [SD]; 516 women) were evaluated. ChatGPT 4.0 and Bard displayed substantial to almost perfect intra-LLM agreement (κ range, 0.65–0.86 [95% CI: 0.64, 0.86]), while ChatGPT 3.5 showed fair to substantial agreement (κ range, 0.36–0.68 [95% CI: 0.36, 0.68]). ChatGPT 4.0 had an accuracy of 78%–86% (95% CI: 76%, 88%) and sensitivity of 86%–95% (95% CI: 83%, 96%), compared with 74%–86% (95% CI: 71%, 88%) and 74%–91% (95% CI: 71%, 93%), respectively, for Bard. Moreover, with ChatGPT 4.0, the image-to-text–LLM strategy exhibited an AUC (0.83 [95% CI: 0.80, 0.85]) and accuracy (84% [95% CI: 82%, 86%]) comparable to those of the human-LLM interaction strategy with two senior readers and one junior reader and exceeding those of the human-LLM interaction strategy with one junior reader.
对725名患者(平均年龄42.2岁,标准差±14.1;其中516名女性)的1161张甲状腺结节超声图像(498个良性,663个恶性)进行了评估。ChatGPT 4.0和Bard在模型内部显示出高度至几乎完美的一致性(κ范围为0.65–0.86 [95% CI: 0.64, 0.86]),而ChatGPT 3.5显示出中等至高度一致性(κ范围为0.36–0.68 [95% CI: 0.36, 0.68])。ChatGPT 4.0的准确率为78%–86%(95% CI: 76%, 88%),敏感性为86%–95%(95% CI: 83%, 96%),而Bard的准确率和敏感性分别为74%–86%(95% CI: 71%, 88%)和74%–91%(95% CI: 71%, 93%)。此外,使用ChatGPT 4.0时,图像到文本与LLM结合的策略表现出与两名高级读片者和一名初级读片者的人机交互策略相当的AUC(0.83 [95% CI: 0.80, 0.85])和准确性(84% [95% CI: 82%, 86%]),并且超过了仅有一名初级读片者的人机交互策略的表现。
Figure
图
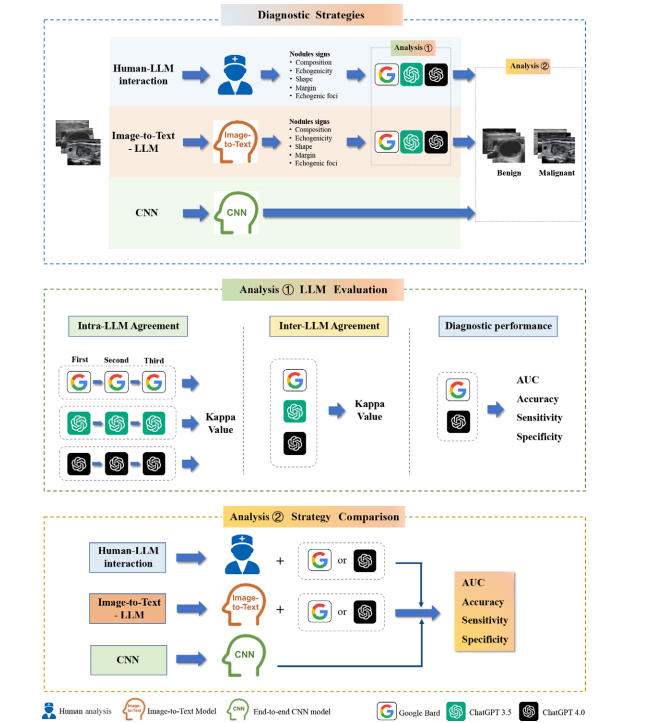
Figure 1: Diagram of study profile. The top box depicts three distinct model deployment strategies: human–large language model (LLM) interaction, in which a human reader initially interprets the image and the LLM generates a diagnosis; image-to-text–LLM, which employs an image-to-text model followed by LLM diagnosis; and convolutional neural network (CNN), which uses an end-to-end CNN model for image analysis and diagnosis. The middle box illustrates the analysis of LLM agreement and diagnostic performance using American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System criteria. The bottom box illustrates the comparison of the three strategies in distinguishing between benign and malignant thyroid nodules.
图1:研究概况示意图。顶部框显示了三种不同的模型部署策略:人类与大型语言模型(LLM)的互动,其中人类读片者首先解读图像,然后由LLM生成诊断结果;图像到文本与LLM结合的策略,先使用图像到文本模型,然后由LLM进行诊断;以及卷积神经网络(CNN)策略,使用端到端的CNN模型进行图像分析和诊断。中间框展示了使用美国放射学会甲状腺影像报告和数据系统标准分析LLM的一致性和诊断性能。底部框则展示了三种策略在区分良性和恶性甲状腺结节中的比较。
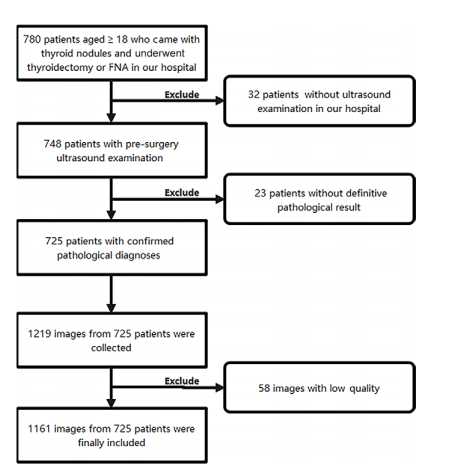
Figure 2: Flowchart of inclusion and exclusion criteria for patients and US im ages. FNA = fine-needle aspiration.
图2:患者和超声图像的纳入和排除标准流程图。FNA = 细针穿刺。

Figure 3: Screenshots show the input prompts used and responses generated by ChatGPT 3.5 (OpenAI; https://chat.openai.com/) based on a single thyroid nodule. This response was recorded as a diagnosis of malignant.
图3:截图显示了基于单个甲状腺结节使用ChatGPT 3.5(OpenAI;https://chat.openai.com/)的输入提示和生成的响应。此响应被记录为恶性诊断。

Figure 4: Screenshots show the input prompts used and responses generated by ChatGPT 4.0 (OpenAI; https://chat.openai.com/) based on a single thyroid nodule. This response was recorded as a diagnosis of malignant.
图4:截图显示了基于单个甲状腺结节使用ChatGPT 4.0(OpenAI;https://chat.openai.com/)的输入提示和生成的响应。此响应被记录为恶性诊断。
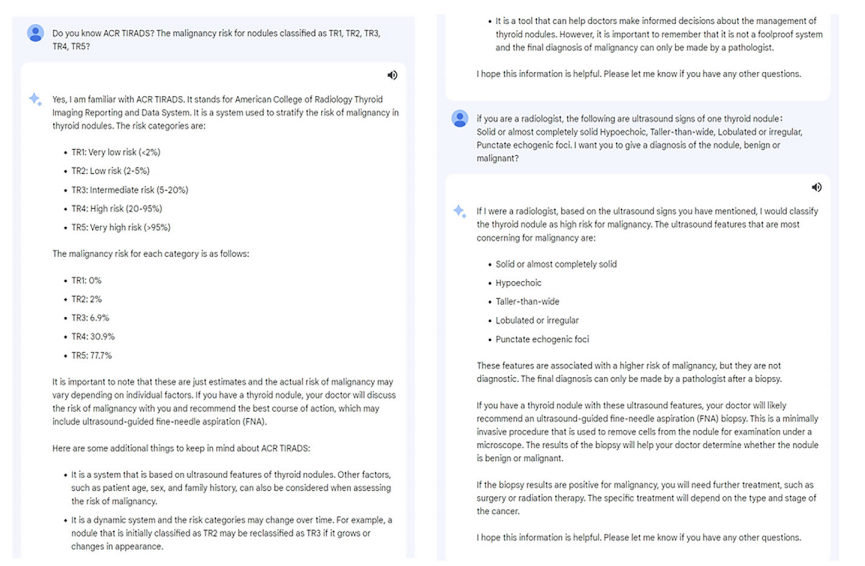
Figure 5: Screenshots show the input prompts used and responses generated by Bard (Google; https://bard.google.com/) based on a single thyroid nodule. This response was recorded as a diagnosis of malignant.
图5:截图显示了基于单个甲状腺结节使用Bard(Google;https://bard.google.com/)的输入提示和生成的响应。此响应被记录为恶性诊断。
Table
表
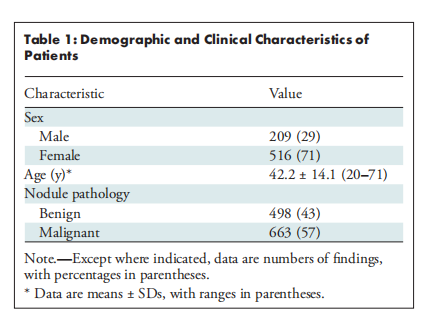
Table 1: Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Patients
表1:患者的人口统计和临床特征
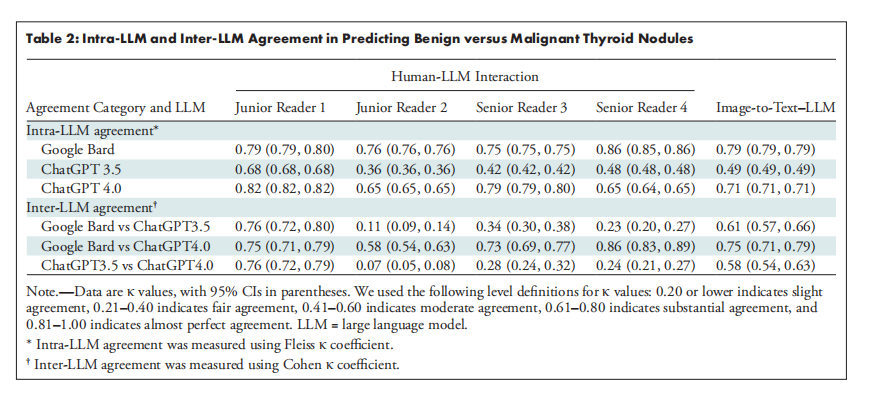
Table 2: Intra-LLM and Inter-LLM Agreement in Predicting Benign versus Malignant Thyroid Nodules
表2:大型语言模型(LLM)内部及不同LLM之间在预测良性与恶性甲状腺结节方面的一致性分析
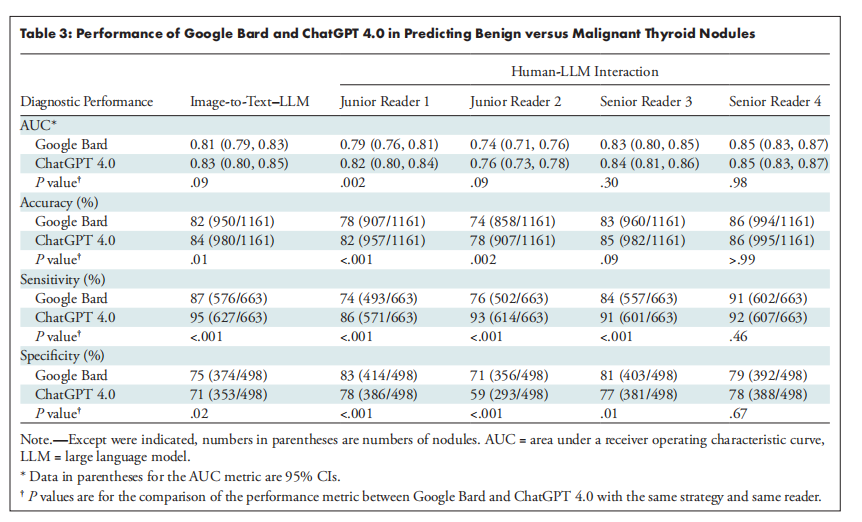
Table 3: Performance of Google Bard and ChatGPT 4.0 in Predicting Benign versus Malignant Thyroid Nodules
表3:Google Bard 和 ChatGPT 4.0 在预测良性与恶性甲状腺结节中的表现
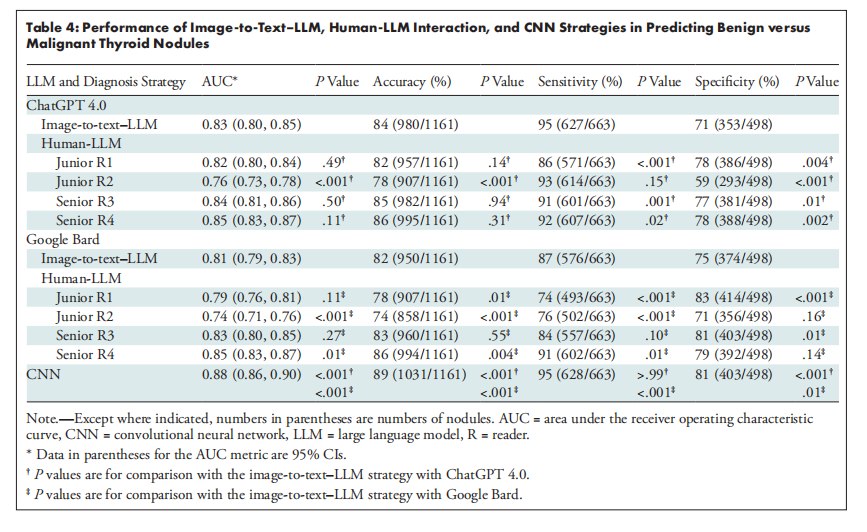
Table 4: Performance of Image-to-Text–LLM, Human-LLM Interaction, and CNN Strategies in Predicting Benign versus Malignant Thyroid Nodules
表4:图像到文本-LLM、人类-LLM交互和CNN策略在预测良性与恶性甲状腺结节中的表现
这篇关于利用大型语言模型协作提升甲状腺结节超声诊断的一致性和准确性| 文献速递-基于深度学习的癌症风险预测与疾病预后应用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





