本文主要是介绍【QT教程】使用qcustomplot完成对图像的拖动、框选缩放、自动缩放、游标等操作,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 1.Qt 配置qcustomplot
- 2.图像拖拽功能
- 3.图像框选放大
- 4.曲线自动缩放
- 5.图像游标
- 6.【完整代码】将曲线抽象成一个类,以便复用
1.Qt 配置qcustomplot
首先下载qcustomplot官网(qcustomplot下载地址)下载最近的源码,我用的是2.1.1版本。下载完成后解压,得到如下文件。

将.h和.cpp文件加入到工程中

如果使用的是Qt creator的话,在.pro文件中加入printsupport。

打开.ui文件,选中Widget模块拖入到界面当中

右键这个Widget,选择【提升为】
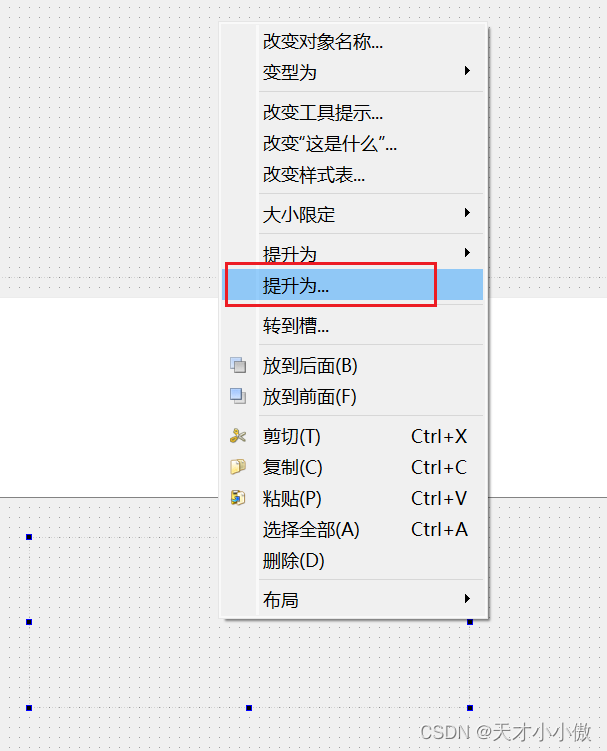
输入 QCustomPlot,点击添加、提升为

之后我们为这个控件改个名字就可以操作它啦。这里我给他重命名为widget_Force。
2.图像拖拽功能
首先在主线程中声明qcustomplot类,并实现一个对象。
QTimer *plotTimer;//曲线刷新定时器/***************曲线绘制**********************//*选中的曲线画笔*/QVector<QPen> selectedPen;/*选中的图例字体*/QFont YHfontBold;/*力曲线*/QCustomPlot *widget_Force;CurvePlot *curves_Force;
图像拖拽功能
//禁用选择矩形widget_Force->setSelectionRectMode(QCP::SelectionRectMode::srmNone);//使能拖动widget_Force->setInteraction(QCP::iRangeDrag, true);
演示

3.图像框选放大
widget_Force->setInteraction(QCP::iRangeDrag, false);//取消拖动widget_Force->setSelectionRectMode(QCP::SelectionRectMode::srmZoom);
演示

4.曲线自动缩放
右键曲线实现自动缩放功能需要添加一个右键菜单栏。
首先定义信号槽
//右键菜单connect(widget_Force, &QCustomPlot::customContextMenuRequested, this, &MainWindow::contextMenuRequestForce);
槽函数如下
void MainWindow::contextMenuRequestForce(QPoint pos)
{QMenu *menu = new QMenu(this);menu->setStyleSheet("font:11pt;font-family:Microsoft YaHei");menu->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose);menu->popup(widget_Force->mapToGlobal(pos));menu->addAction("调整范围", curves_Force, &CurvePlot::rescaleAxes);menu->addAction("清除选中曲线", curves_Force, &CurvePlot::clearCurve);
}
rescaleAxes 函数如下
void CurvePlot::rescaleAxes()//曲线全部显示
{//给第一个graph设置rescaleAxes(),后续所有graph都设置rescaleAxes(true)即可实现显示所有曲线。//rescaleAxes(true)时如果plot的X或Y轴本来能容纳下本graph的X或Y数据点,//那么plot的X或Y轴的可视范围就无需调整,只有plot容纳不下本graph时,才扩展plot两个轴的显示范围。//见博客https://www.csdn.net/gather_26/MtTaYg2sMzgxNDgtYmxvZwO0O0OO0O0O.htmlmyPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes();myPlot->graph(1)->rescaleAxes(true);myPlot->replot();
}
演示

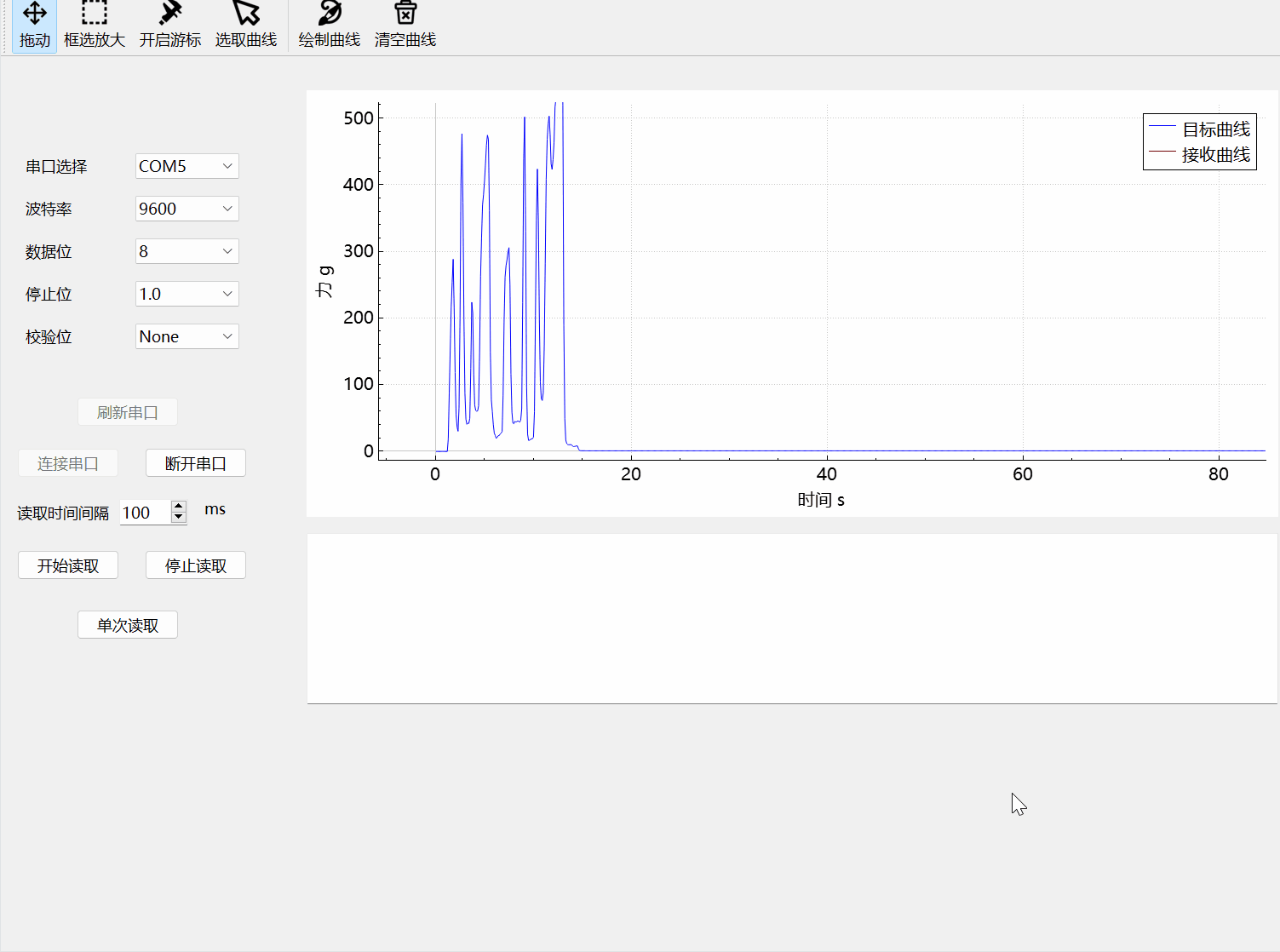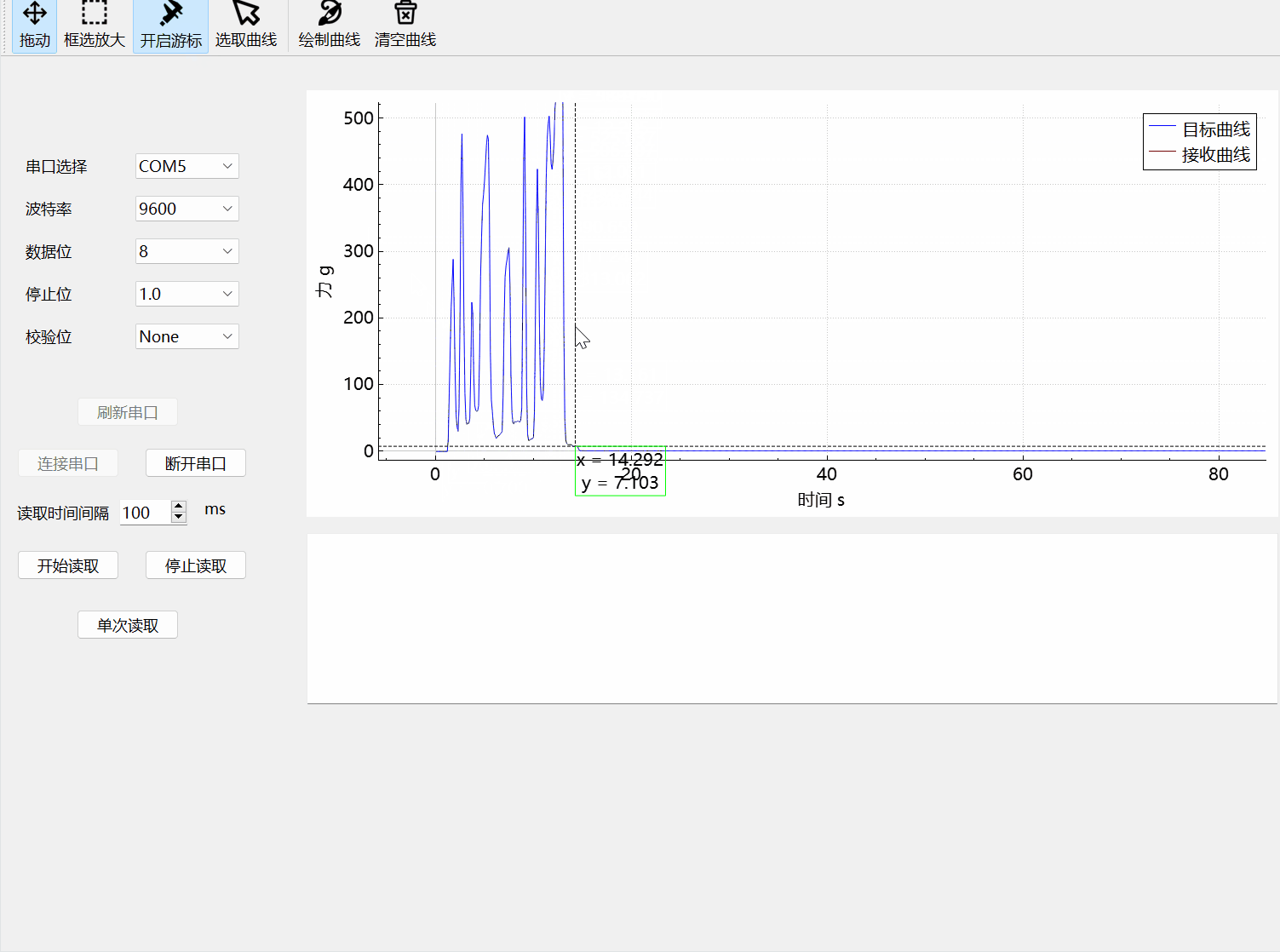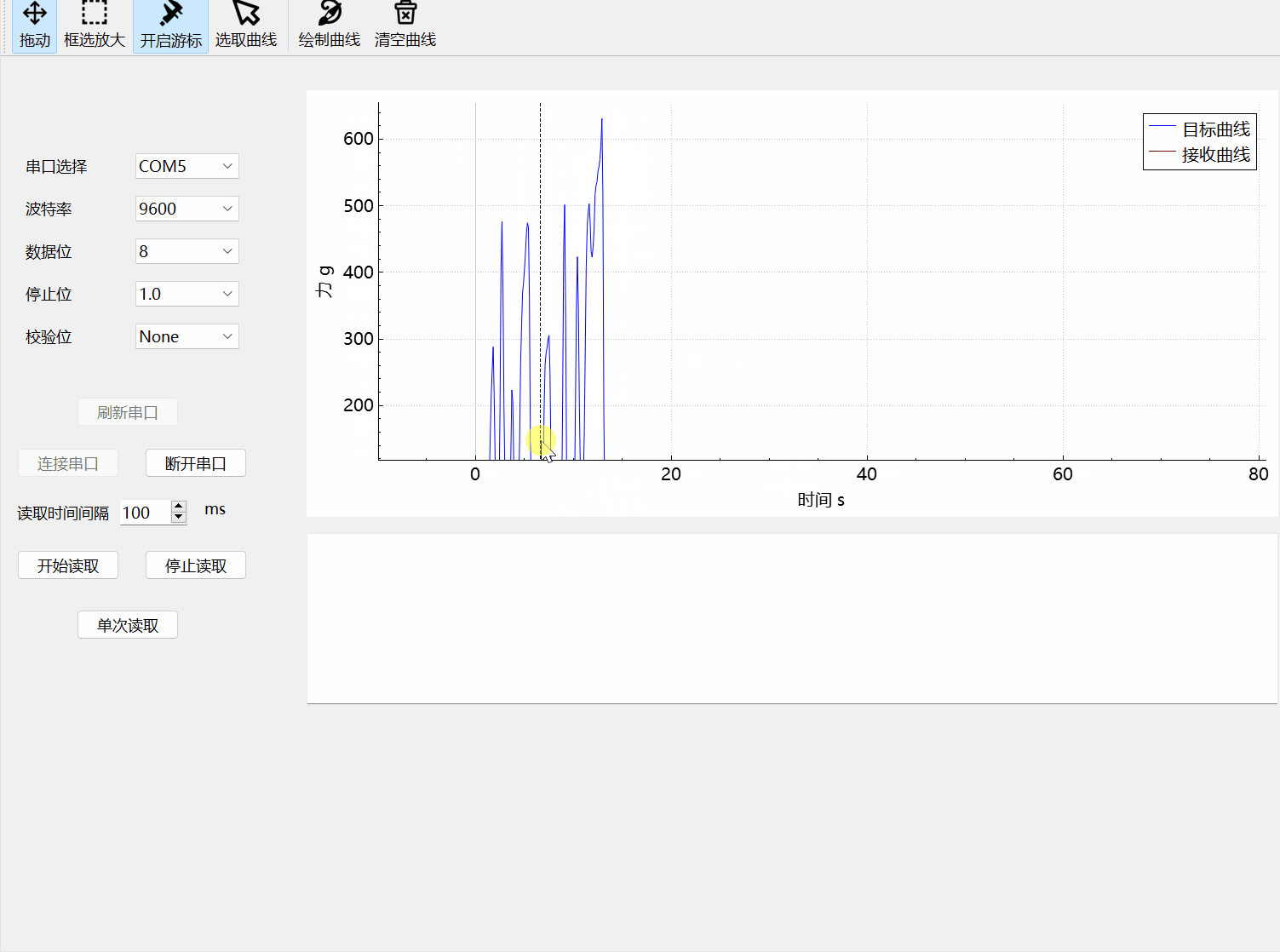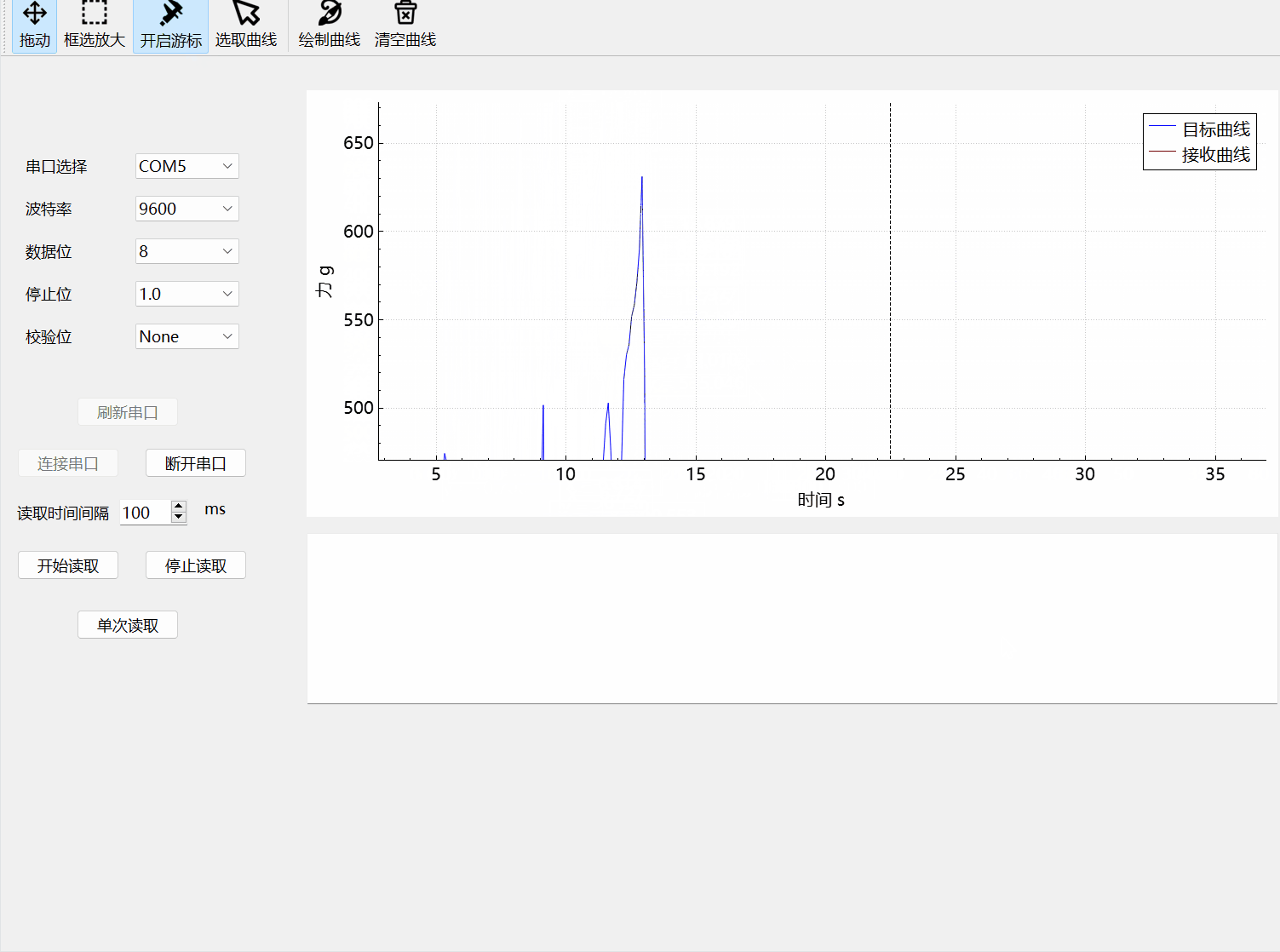
5.图像游标
使用游标的话需要配合鼠标事件完成
首先声明一下游标
/*************游标*************/bool tracerEnable;//游标使能QCPItemTracer *tracer0 = nullptr; // 0号曲线游标QCPItemTracer *tracer1 = nullptr; // 1号曲线游标QCPItemText *tracer0Label = nullptr; // 0号曲线X游标标签QCPItemText *tracer1Label = nullptr;// 1号曲线Y轴游标标签void setVisibleTracer(bool trueorfalse);//游标可见/不可见 true/false
然后配置游标的属性
if (arg1){qDebug() << "act_tracer is on!";tracerEnable = true;tracer0 = new QCPItemTracer(myPlot);tracer0->setStyle(QCPItemTracer::tsCrosshair);//游标样式:十字星、圆圈、方框tracer0->setPen(QPen(Qt::green));//设置tracer的颜色绿色tracer0->setPen(QPen(Qt::DashLine));//虚线游标tracer0->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::red));tracer0->setSize(10);tracer0->setInterpolating(true);//false禁用插值tracer1 = new QCPItemTracer(myPlot);tracer1->setStyle(QCPItemTracer::tsCrosshair);//游标样式:十字星、圆圈、方框tracer1->setPen(QPen(Qt::green));//设置tracer的颜色绿色tracer1->setPen(QPen(Qt::DashLine));//虚线游标tracer1->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::red));tracer1->setSize(10);tracer1->setInterpolating(true);//false禁用插值tracer0Label = new QCPItemText(myPlot);tracer0Label->setClipToAxisRect(false);tracer0Label->setLayer("overlay");tracer0Label->setPen(QPen(Qt::green));tracer0Label->setFont(QFont("Microsoft YaHei", 10));tracer0Label->setPadding(QMargins(2, 2, 2, 2));tracer0Label->setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop);//下面这个语句很重要,它将游标说明锚固在tracer位置处,实现自动跟随tracer0Label->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptAxisRectRatio);//位置类型(当前轴范围的比例为单位/实际坐标为单位)tracer0Label->position->setParentAnchor(tracer0->position);tracer1Label = new QCPItemText(myPlot);tracer1Label->setClipToAxisRect(false);tracer1Label->setLayer("overlay");tracer1Label->setPen(QPen(Qt::red));tracer1Label->setFont(QFont("Microsoft YaHei", 10));tracer1Label->setPadding(QMargins(2, 2, 2, 2));tracer1Label->setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop);//下面这个语句很重要,它将游标说明锚固在tracer位置处,实现自动跟随tracer1Label->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptAxisRectRatio);//位置类型(当前轴范围的比例为单位/实际坐标为单位)tracer1Label->position->setParentAnchor(tracer1->position);}else{qDebug() << "act_tracer is off !";tracerEnable = false;setVisibleTracer(false);}
然后编写鼠标事件,并进行信号槽绑定。
//游标鼠标事件信号槽connect(widget_Force, &QCustomPlot::mouseMove, curves_Force, &CurvePlot::myMouseMoveEvent);
void CurvePlot::myMouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent * event)//鼠标移动事件
{if (tracerEnable)//游标使能判断{double x = myPlot->xAxis->pixelToCoord(event->pos().x());//鼠标点的像素坐标转plot坐标foundRange = true;QrangeX0 = myPlot->graph(0)->getKeyRange(foundRange, QCP::sdBoth);//获取0号曲线X轴坐标范围QrangeX0_lower = QrangeX0.lower;QrangeX0_upper = QrangeX0.upper;QrangeX1 = myPlot->graph(1)->getKeyRange(foundRange, QCP::sdBoth);//获取1号曲线X轴坐标范围QrangeX1_lower = QrangeX1.lower;QrangeX1_upper = QrangeX1.upper;//如果鼠标移动超出0号曲线X轴范围,则0号曲线隐藏游标if (x < QrangeX0_upper && x > QrangeX0_lower){tracer0->setGraph(myPlot->graph(0));//设置游标吸附在traceGraph这条曲线上tracer0->setGraphKey(x);//将游标横坐标(key)设置成刚获得的横坐标数据x (这就是游标随动的关键代码)tracer0->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效double traceX0 = tracer0->position->key();double traceY0 = tracer0->position->value();tracer0Label->setText(QString::number(traceX0, 'f', 3));//游标文本框,指示游标的X值tracer0Label->setText(QString("x = %1\ny = %2").arg(QString::number(traceX0, 'f', 3)).arg(QString::number(traceY0, 'f', 3)));tracer0->setVisible(true);tracer0Label->setVisible(true);}else{tracer0->setVisible(false);tracer0Label->setVisible(false);}//如果鼠标移动超出1号曲线X轴范围,则1号曲线隐藏游标if (x < QrangeX1_upper && x > QrangeX1_lower){double traceX1 = tracer1->position->key();double traceY1 = tracer1->position->value();tracer1->setGraph(myPlot->graph(1));//设置游标吸附在traceGraph这条曲线上tracer1->setGraphKey(x);tracer1->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效tracer1Label->setText(QString("x = %1\ny = %2").arg(QString::number(traceX1, 'f', 3)).arg(QString::number(traceY1, 'f', 3)));tracer1->setVisible(true);tracer1Label->setVisible(true);}else{tracer1->setVisible(false);tracer1Label->setVisible(false);}myPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot); //刷新图标,不能省略}
}
效果展示
6.【完整代码】将曲线抽象成一个类,以便复用
这里我写了一个CurvePlot的类,如果界面上同时有多个绘图窗口,那么就可以方便的进行复用。通过这个类可以设置曲线范围等参数,也将一些鼠标事件写了进去。这个是根据之前的一个项目做的,绘图框中绘制两条曲线,一条是目标曲线,一条是实时采集到的曲线。.大家可以在这个基础上进行修改。
CurvePlot.h如下
#ifndef CURVEPLOT_H
#define CURVEPLOT_H
#include "qcustomplot.h"#pragma execution_character_set("utf-8")
class CurvePlot :public QObject
{Q_OBJECT
public:explicit CurvePlot(QCustomPlot * Plot);virtual ~CurvePlot();void setxAxisName(QString name);void setyAxisName(QString name);void setxAxisRange(double lower, double upper);void setyAxisRange(double lower, double upper);void setGraphName(QString name0, QString name1);void setSelectLegend(bool enabled);void setLegendFont(QFont font);/*************曲线数据*************/int curIndex;//当前曲线号 = 0, = 1, = -1时未选中曲线//0号曲线(目标曲线)QVector<double> x0;//存储x坐标的向量QVector<double> y0;//存储y坐标的向量QList<QList<QVariant>> x_y0;//1号曲线(采集曲线)QVector<double> x1;//存储x坐标的向量QVector<double> y1;//存储y坐标的向量QList<QList<QVariant>> x_y1;public slots:void on_act_tracerToggled(bool arg1);void myMouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent* event);//鼠标事件void rescaleAxes();//自动调整void clearCurve();//清除曲线void clearAllCurves();//清除所有曲线
private:/*绘图窗口*/QCustomPlot * myPlot = nullptr;/*画笔*/QVector<QPen> pen;/*************游标*************/bool tracerEnable;//游标使能QCPItemTracer *tracer0 = nullptr; // 0号曲线游标QCPItemTracer *tracer1 = nullptr; // 1号曲线游标QCPItemText *tracer0Label = nullptr; // 0号曲线X游标标签QCPItemText *tracer1Label = nullptr;// 1号曲线Y轴游标标签void setVisibleTracer(bool trueorfalse);//游标可见/不可见 true/false/*********曲线X轴范围**********/QCPRange QrangeX0;//0号曲线X轴范围double QrangeX0_lower;double QrangeX0_upper;QCPRange QrangeX1;//1号曲线X轴范围double QrangeX1_lower;double QrangeX1_upper;bool foundRange;
};#endif
CurvePlot.cpp如下
#include "CurvePlot.h"CurvePlot::CurvePlot(QCustomPlot * Plot)
{myPlot = Plot;tracerEnable = false;/*************绘图模块***************///设置坐标轴字体QFont YHfont("Microsoft YaHei", 10, QFont::Normal);myPlot->setFont(YHfont);myPlot->xAxis->setLabelFont(YHfont);myPlot->xAxis->setTickLabelFont(YHfont);myPlot->yAxis->setLabelFont(YHfont);myPlot->yAxis->setTickLabelFont(YHfont);//设定右上角图例标注的字体myPlot->legend->setFont(YHfont);//设定右上角图例标注可见myPlot->legend->setVisible(true);//添加图形myPlot->addGraph();myPlot->addGraph();//曲线全部可见myPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes();myPlot->graph(1)->rescaleAxes(true);//设置画笔QPen pen0(Qt::blue, 1, Qt::SolidLine, Qt::RoundCap, Qt::RoundJoin);QPen pen1(Qt::red, 1, Qt::SolidLine, Qt::RoundCap, Qt::RoundJoin);pen.append(pen0);pen.append(pen1);myPlot->graph(0)->setPen(pen[0]);myPlot->graph(1)->setPen(pen[1]);//设置线型myPlot->graph(0)->setLineStyle(QCPGraph::lsLine);myPlot->graph(1)->setLineStyle(QCPGraph::lsLine);//设置线上点的风格myPlot->graph(0)->setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle::ssNone);myPlot->graph(1)->setScatterStyle(QCPScatterStyle::ssNone);//右键菜单自定义myPlot->setContextMenuPolicy(Qt::CustomContextMenu);/**********鼠标操作图像模块************/myPlot->selectionRect()->setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1, Qt::DashLine));//设置选框的样式:虚线myPlot->selectionRect()->setBrush(QBrush(QColor(0, 0, 100, 50)));//设置选框的样式:半透明浅蓝myPlot->setInteraction(QCP::iRangeDrag, true); //鼠标单击拖动 QCPAxisRect::mousePressEvent() 左键拖动myPlot->setInteraction(QCP::iRangeZoom, true); //滚轮滑动缩放myPlot->setInteraction(QCP::iSelectAxes, true);myPlot->setInteraction(QCP::iSelectLegend, true); //图例可选myPlot->selectionRect()->setPen(QPen(Qt::black, 1, Qt::DashLine));myPlot->selectionRect()->setBrush(QBrush(QColor(0, 0, 100, 50)));
}CurvePlot::~CurvePlot()
{
}
//X轴名称
void CurvePlot::setxAxisName(QString name)
{myPlot->xAxis->setLabel(name);
}
//Y轴名称
void CurvePlot::setyAxisName(QString name)
{myPlot->yAxis->setLabel(name);
}
//X轴范围
void CurvePlot::setxAxisRange(double lower, double upper)
{myPlot->xAxis->setRange(lower, upper);
}
//Y轴范围
void CurvePlot::setyAxisRange(double lower, double upper)
{myPlot->yAxis->setRange(lower, upper);
}
//曲线图例名称
void CurvePlot::setGraphName(QString name0, QString name1)
{//设置右上角图形标注名称myPlot->graph(0)->setName(name0);myPlot->graph(1)->setName(name1);
}
void CurvePlot::setSelectLegend(bool enabled)
{if (enabled){myPlot->setInteraction(QCP::iSelectLegend, true); //图例可选}else{myPlot->setInteraction(QCP::iSelectLegend, false); //图例可选}
}
void CurvePlot::setLegendFont(QFont font)
{myPlot->legend->setFont(font);
}
void CurvePlot::on_act_tracerToggled(bool arg1)
{if (arg1){qDebug() << "act_tracer is on!";tracerEnable = true;tracer0 = new QCPItemTracer(myPlot);tracer0->setStyle(QCPItemTracer::tsCrosshair);//游标样式:十字星、圆圈、方框tracer0->setPen(QPen(Qt::green));//设置tracer的颜色绿色tracer0->setPen(QPen(Qt::DashLine));//虚线游标tracer0->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::red));tracer0->setSize(10);tracer0->setInterpolating(true);//false禁用插值tracer1 = new QCPItemTracer(myPlot);tracer1->setStyle(QCPItemTracer::tsCrosshair);//游标样式:十字星、圆圈、方框tracer1->setPen(QPen(Qt::green));//设置tracer的颜色绿色tracer1->setPen(QPen(Qt::DashLine));//虚线游标tracer1->setBrush(QBrush(Qt::red));tracer1->setSize(10);tracer1->setInterpolating(true);//false禁用插值tracer0Label = new QCPItemText(myPlot);tracer0Label->setClipToAxisRect(false);tracer0Label->setLayer("overlay");tracer0Label->setPen(QPen(Qt::green));tracer0Label->setFont(QFont("Microsoft YaHei", 10));tracer0Label->setPadding(QMargins(2, 2, 2, 2));tracer0Label->setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop);//下面这个语句很重要,它将游标说明锚固在tracer位置处,实现自动跟随tracer0Label->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptAxisRectRatio);//位置类型(当前轴范围的比例为单位/实际坐标为单位)tracer0Label->position->setParentAnchor(tracer0->position);tracer1Label = new QCPItemText(myPlot);tracer1Label->setClipToAxisRect(false);tracer1Label->setLayer("overlay");tracer1Label->setPen(QPen(Qt::red));tracer1Label->setFont(QFont("Microsoft YaHei", 10));tracer1Label->setPadding(QMargins(2, 2, 2, 2));tracer1Label->setPositionAlignment(Qt::AlignLeft | Qt::AlignTop);//下面这个语句很重要,它将游标说明锚固在tracer位置处,实现自动跟随tracer1Label->position->setType(QCPItemPosition::ptAxisRectRatio);//位置类型(当前轴范围的比例为单位/实际坐标为单位)tracer1Label->position->setParentAnchor(tracer1->position);}else{qDebug() << "act_tracer is off !";tracerEnable = false;setVisibleTracer(false);}
}
void CurvePlot::myMouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent * event)//鼠标移动事件
{if (tracerEnable)//游标使能判断{double x = myPlot->xAxis->pixelToCoord(event->pos().x());//鼠标点的像素坐标转plot坐标foundRange = true;QrangeX0 = myPlot->graph(0)->getKeyRange(foundRange, QCP::sdBoth);//获取0号曲线X轴坐标范围QrangeX0_lower = QrangeX0.lower;QrangeX0_upper = QrangeX0.upper;QrangeX1 = myPlot->graph(1)->getKeyRange(foundRange, QCP::sdBoth);//获取1号曲线X轴坐标范围QrangeX1_lower = QrangeX1.lower;QrangeX1_upper = QrangeX1.upper;//如果鼠标移动超出0号曲线X轴范围,则0号曲线隐藏游标if (x < QrangeX0_upper && x > QrangeX0_lower){tracer0->setGraph(myPlot->graph(0));//设置游标吸附在traceGraph这条曲线上tracer0->setGraphKey(x);//将游标横坐标(key)设置成刚获得的横坐标数据x (这就是游标随动的关键代码)tracer0->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效double traceX0 = tracer0->position->key();double traceY0 = tracer0->position->value();tracer0Label->setText(QString::number(traceX0, 'f', 3));//游标文本框,指示游标的X值tracer0Label->setText(QString("x = %1\ny = %2").arg(QString::number(traceX0, 'f', 3)).arg(QString::number(traceY0, 'f', 3)));tracer0->setVisible(true);tracer0Label->setVisible(true);}else{tracer0->setVisible(false);tracer0Label->setVisible(false);}//如果鼠标移动超出1号曲线X轴范围,则1号曲线隐藏游标if (x < QrangeX1_upper && x > QrangeX1_lower){double traceX1 = tracer1->position->key();double traceY1 = tracer1->position->value();tracer1->setGraph(myPlot->graph(1));//设置游标吸附在traceGraph这条曲线上tracer1->setGraphKey(x);tracer1->updatePosition(); //使得刚设置游标的横纵坐标位置生效tracer1Label->setText(QString("x = %1\ny = %2").arg(QString::number(traceX1, 'f', 3)).arg(QString::number(traceY1, 'f', 3)));tracer1->setVisible(true);tracer1Label->setVisible(true);}else{tracer1->setVisible(false);tracer1Label->setVisible(false);}myPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot); //刷新图标,不能省略}
}void CurvePlot::rescaleAxes()//曲线全部显示
{//给第一个graph设置rescaleAxes(),后续所有graph都设置rescaleAxes(true)即可实现显示所有曲线。//rescaleAxes(true)时如果plot的X或Y轴本来能容纳下本graph的X或Y数据点,//那么plot的X或Y轴的可视范围就无需调整,只有plot容纳不下本graph时,才扩展plot两个轴的显示范围。//见博客https://www.csdn.net/gather_26/MtTaYg2sMzgxNDgtYmxvZwO0O0OO0O0O.htmlmyPlot->graph(0)->rescaleAxes();myPlot->graph(1)->rescaleAxes(true);myPlot->replot();
}void CurvePlot::clearCurve()
{switch (this->curIndex){case 0:this->x0.clear();this->y0.clear();this->x_y0.clear();myPlot->graph(0)->setData(this->x0, this->y0);break;case 1:this->x1.clear();this->y1.clear();this->x_y1.clear();myPlot->graph(1)->setData(this->x1, this->y1);break;case -1:qDebug() << "未选中曲线!";break;}myPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot);
}void CurvePlot::clearAllCurves()
{//this->x0.clear();//this->y0.clear();//this->x_y0.clear();//myPlot->graph(0)->setData(this->x0, this->y0);this->x1.clear();this->y1.clear();this->x_y1.clear();myPlot->graph(1)->setData(this->x1, this->y1);myPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot);
}void CurvePlot::setVisibleTracer(bool trueorfalse)
{tracer0->setVisible(trueorfalse);tracer1->setVisible(trueorfalse);tracer0Label->setVisible(trueorfalse);tracer1Label->setVisible(trueorfalse);myPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot); //刷新图标,不能省略
}
这篇关于【QT教程】使用qcustomplot完成对图像的拖动、框选缩放、自动缩放、游标等操作的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




