本文主要是介绍大语言模型实战——最小化agent,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. agent是什么
大模型拥有语言理解和推理能力后,就相当于拥有了大脑,要让模型发挥更大的潜力,就需要给它安装上手臂,让它拥有行动的能力。
而Agent就是一个将语言模型和外部工具结合起来的智能体,它使用语言模型的推理能力做出决策,再调用外部工具来完成具体的行动,并将行动结果反馈给语言模型,这样语言模型可以通过行动的结果来做出进一步的决策,直到得出结果(工作流程如下图所示)。
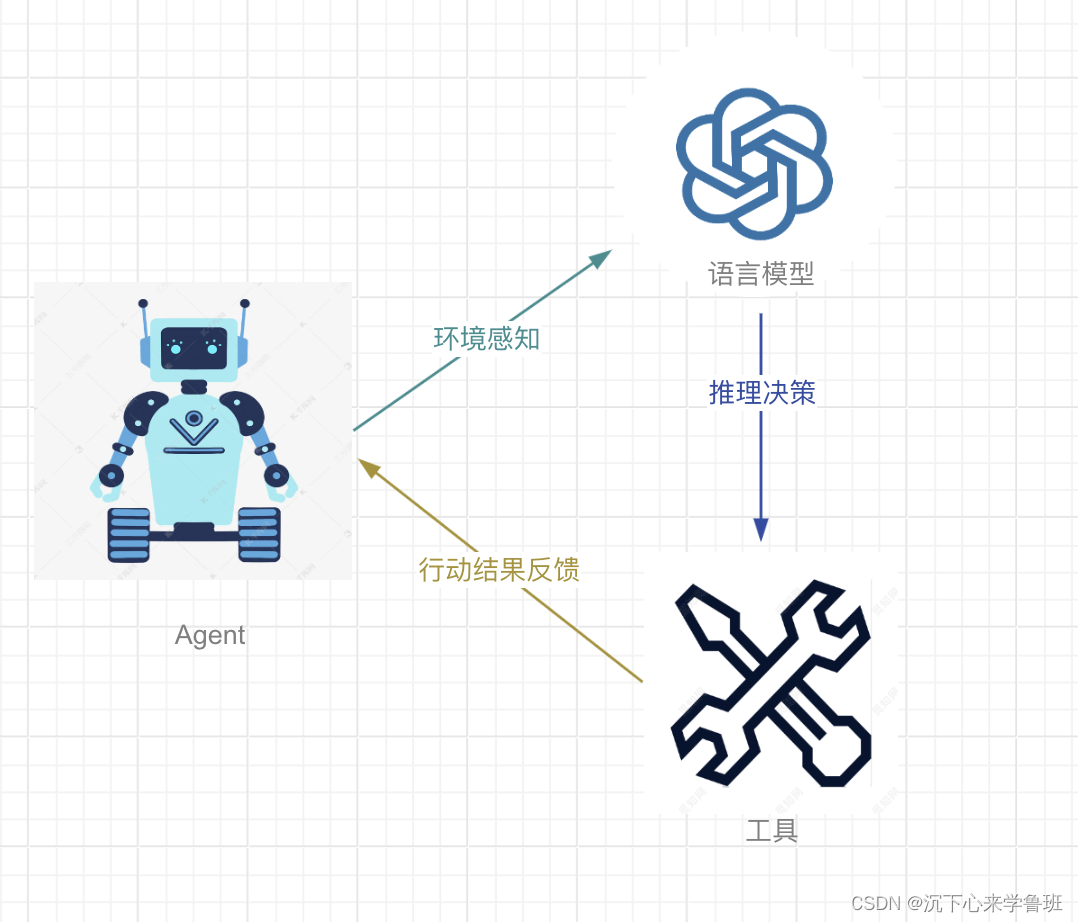
由上可知,一个智能体系统最少由以下几部分组成:
- 语言模型
- 工具集
- Agent
本文将动手搭建一个最小化的agent,下面将分别就这几部分进行展开。
2. 语言模型
首先需要一个具有functionCalling能力的语言模型,来理解用户问题,并针对问题进行思考和规划行动方案。这里使用qwen:7b作为我们的 Agent 模型。
这里和前面一篇文章RAG所用的语言模型相似。
class OllamaChat:def __init__(self, model: str = "qwen") -> None:self.model = modeldef _build_messages(self, prompt: str, content: str):……def chat(self, prompt: str, history: List[Dict], content: str) -> str:……
2.1 构造提示词
将用户的问题、历史聊天记录和系统提示词,按照语言模型的格式要求,拼成一个完整的提示词。
def _build_messages(self, prompt: str, history: List[dict], system_prompt: str):messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt}]for item in history:messages.append({"role": "user", "content": item["prompt"]})messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": item["response"]})messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})print(f"prompt messages: {messages}")return messages
2.2 聊天对话
这里与前面RAG实现的相同,详情参考搭建纯本地迷你版RAG。
def chat(self, prompt: str, history: List[dict], meta_instruction:str ='') -> str:
import ollamaresponse = ollama.chat(model=self.model,messages=self._build_messages(prompt, history, meta_instruction),stream=True)final_response = ''for chunk in response:if type(chunk) == "str":chunk = to_json(chunk)if 'content' in chunk.get('message', {}):final_response += chunk['message']['content']history.append({"prompt": prompt, "response": final_response})return final_response, history
2. 工具
工具包括两部分信息,工具的实现和工具的使用描述。
2.1 工具封装
这里实现一个最简单的本地时间函数来作为大语言模型可以调用的工具。
def current_time():"""获取本地时间信息,返回yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss格式"""timestamp = time.time()# 将时间戳转换为本地时间time_tuple = time.localtime(timestamp)return time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time_tuple)
2.2 工具描述
封装好工具实现后,我们需要对它进行一些描述,目的是让大语言模型知道什么时候调用此工具以及如何调用此工具。具体包括如下信息:
- name_for_model: 用以给程序识别的工具标识。
- name_for_human:人类可以理解的工具名称。
- description_for_model:功能描述,工具能用来做什么。
- parameters:工具需要的参数。
tool_config = [{'name_for_human': '当前系统时间查询','name_for_model': 'current_time','description_for_model': '当前系统时间查询是一个简单的工具,用于获取系统本地当前的时间信息。','parameters': []}
]
3. Agent
Agent是核心类,通过提示词和一定的逻辑,将外部工具整合进大语言模型推理决策的流程中,最终完成用户交给的任务。它有以下核心方法:
- build_system_input: 构造系统提示词
- parse_latest_plugin_call: 解析大语言模型需要调用的工具信息
- call_plugin: 调用工具
- text_completion:对外提供给用户调用的主方法,负责将其它三个方法的功能串联成一个自动解决问题的业务流程。
class Agent:def __init__(self, model: str = '') -> None:self.system_prompt = self.build_system_input()self.model = OllamaChat(model)def build_system_input(self):……def parse_latest_plugin_call(self, text):……def call_plugin(self, plugin_name, plugin_args):……def text_completion(self, text, history=[], max_loops=5):……
3.1 构造system-prompt
作用:根据提示词来告诉大模型可以凋用哪些工具,并且以什么样的方式输出。
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:{tool_descs}Use the following format:Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can be repeated zero or more times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input questionBegin!
这里的thought->Action->Action Input->Observation结构是一种典型的Reasoning(推理) 和 Action(行动)的思想,旨在使模型能够基于观察到的信息进行推理,然后采取适当行动,从而实现更高级的应用。
工具可能会有多个,我们先为每个工具定义一个给语言模型的通用描述模板,这里就简单的将工具标识、工具描述、工具参数三者以一定的格式接起来。如下:
TOOL_DESC = """{name_for_model}: {description_for_model} Parameters: {parameters} Format the arguments as a JSON object."""
上面的系统提示词中,有tool_descs和tool_names两个占位符,我们需要用前面定义好的工具作替换:
def build_system_input(self):tool_descs, tool_names = [], []for item in tool.toolConfig:tool_descs.append(TOOL_DESC.format(**item))tool_names.append(item['name_for_model'])tool_descs = '\n\n'.join(tool_descs)tool_names = ','.join(tool_names)sys_prompt = REACT_PROMPT.format(tool_descs=tool_descs, tool_names=tool_names)return sys_prompt
这样,就能得到一个能用并完整的系统提示词,剩下的只需要用户提问题即可。
3.2 解析工具信息
LLM返回的response中可能带有工具调用信息,我们需要从中查找并解析出要调用的工具和参数。
def parse_latest_plugin_call(self, text):plugin_name, plugin_args = '', ''i = text.rfind('\nAction:')j = text.rfind('\nAction Input:')k = text.rfind('\nObservation:')if 0 <= i < j: # If the text has `Action` and `Action input`,if k < j: # but does not contain `Observation`,text = text.rstrip() + '\nObservation:' # Add it back.k = text.rfind('\nObservation:')plugin_name = text[i + len('\nAction:') : j].strip()plugin_args = text[j + len('\nAction Input:') : k].strip()text = text[:k]return plugin_name, plugin_args, text
3.3 调用工具
这里只有一个工具,直接根据plugin_name调用即可。
def call_plugin(self, plugin_name, plugin_args):1tool.current_time(**plugin_args)elif plugin_name == 'local_file_search':return '\nObservation:' + tool.local_file_search(**plugin_args)
3.4 主方法
流程为:
- 先和模型进行第一次交互,返回一个response。
- 解析response中要调用的工具信息,如果不需要工具,直接返回。
- 否则,调用工具,并将工具返回的结果拼接模型第一次的输出上,目的是为了给模型提供前一步的上下文。
- 和模型进行第二次交互,语言模型根据上下文以及工具调用返回的信息来生成最终的结果。
def text_completion(self, text, history=[], max_loops=5):text = "\nQuestion:" + textresponse, his = self.model.chat(text, history, self.system_prompt)plugin_name, plugin_args, response = self.parse_latest_plugin_call(response)if not plugin_name:return response, hisresponse += self.call_plugin(plugin_name, plugin_args)response, his = self.model.chat(response, history, self.system_prompt)return response, his
4. 运行流程
启动方式:创建agent并使用agent向大语言模型下一个任务。
agent = Agent('qwen')
response, _ = agent.text_completion(text='告诉我当前系统的本地准确时间?', history=[])
print(response)
这里将详细描述下agent与大语言模型的交互过程。
1)第一次chat
用户prompt:
Question:告诉我当前系统的本地准确时间?
系统提示词:
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:current_time: 当前系统时间查询是一个简单的工具,用于获取系统本地当前的时间信息。 Parameters: [] Format the arguments as a JSON object.Use the following format:Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [google_search,current_time,local_file_search]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can be repeated zero or more times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input questionBegin!
语言模型的response:
Thought: 我应该使用哪个工具来获取当前系统的本地准确时间?
Action: current_time
Action Input: {}
2)工具调用
调用本地方法parse_latest_plugin_call来解析response,得到的工具信息:
plugin_name:current_time
args: {}
调用工具方法tool.current_time拿到本地时间:2024-05-24 23:02:49
3)第二次chat
将本地时间拼接成Observation得到第二次chat用户提示词输入:
Thought: 我应该使用哪个工具来获取当前系统的本地准确时间?
Action: current_time
Action Input: {}
Observation:2024-05-24 23:02:49
第二次chat的系统提示词和第一次相同,这里省略。
第二次chat的response:
Thought: 我现在可以作答了。
Final Answer: 当前系统时间是 2024-05-24 23:02:49。
从第二次chat的response中得到了用户问题的答案。
这样就完成了一个最小化agent,这里主要是演示了下FunctionCalling的调用过程,它是扩展语言模型能力的关键。
作为扩展,我们可以根据需要添加多个tool,例如:
- 搜索本地文件
- 获取文件内容
- …
并且可以修改agent的流程,来支持需要多次调用不同tool的复杂任务,相应的也需要更长的上下文和能力更强的语言模型,有兴趣可以尝试下。
参考资料
- tiny-universe
- 搭建纯本地迷你版RAG
这篇关于大语言模型实战——最小化agent的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




