本文主要是介绍Codeforces Round 943 (Div. 3 ABCDEFG1G2题) 视频讲解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
A. Maximize?
Problem Statement
You are given an integer x x x. Your task is to find any integer y y y ( 1 ≤ y < x ) (1\le y<x) (1≤y<x) such that gcd ( x , y ) + y \gcd(x,y)+y gcd(x,y)+y is maximum possible.
Note that if there is more than one y y y which satisfies the statement, you are allowed to find any.
gcd ( a , b ) \gcd(a,b) gcd(a,b) is the Greatest Common Divisor of a a a and b b b. For example, gcd ( 6 , 4 ) = 2 \gcd(6,4)=2 gcd(6,4)=2.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1000 1 \le t \le 1000 1≤t≤1000) — the number of test cases.
Each of the following t t t lines contains a single integer x x x ( 2 ≤ x ≤ 1000 2 \le x \le 1000 2≤x≤1000).
Output
For each test case, output any y y y ( 1 ≤ y < x 1 \le y < x 1≤y<x), which satisfies the statement.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 7 |
| 10 |
| 7 |
| 21 |
| 100 |
| 2 |
| 1000 |
| 6 |
| output |
|---|
| 5 |
| 6 |
| 18 |
| 98 |
| 1 |
| 750 |
| 3 |
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;void solve() {int x;cin >> x;int mx = 0, p;for (int y = 1; y < x; y ++) {if (__gcd(x, y) + y > mx) {mx = __gcd(x, y) + y, p = y;}}cout << p << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
B. Prefiquence
Problem Statement
You are given two binary strings a a a and b b b. A binary string is a string consisting of the characters ‘0’ and ‘1’.
Your task is to determine the maximum possible number k k k such that a prefix of string a a a of length k k k is a subsequence of string b b b.
A sequence a a a is a subsequence of a sequence b b b if a a a can be obtained from b b b by the deletion of several (possibly, zero or all) elements.
Input
The first line consists of a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n and m m m ( 1 ≤ n , m ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1\le n,m \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤n,m≤2⋅105) — the length of string a a a and the length of string b b b, respectively.
The second line of each test case contains a binary string a a a of length n n n.
The third line of each test case contains a binary string b b b of length m m m.
It is guaranteed that the sum of values n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105. Similarly, the sum of values m m m over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output a single number — the maximum k k k, such that the first k k k characters of a a a form a subsequence of b b b.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 6 |
| 5 4 |
| 10011 |
| 1110 |
| 3 3 |
| 100 |
| 110 |
| 1 3 |
| 1 |
| 111 |
| 4 4 |
| 1011 |
| 1111 |
| 3 5 |
| 100 |
| 11010 |
| 3 1 |
| 100 |
| 0 |
| output |
|---|
| 2 |
| 2 |
| 1 |
| 1 |
| 3 |
| 0 |
Note
In the first example, the string ‘ 10 10 10’ is a subsequence of ‘ 1 11 0 1\color{red}11\color{red}0 1110’ but the string ‘ 100 100 100’ is not. So the answer is 2 2 2.
In the fifth example, a a a=‘ 100 100 100’, b b b=‘ 1 101 0 1\color{red}{10}1\color{red}0 11010’, whole string a a a is a subsequence of string b b b. So the answer is 3 3 3.
In the sixth example, string b b b does not contain ‘ 1 1 1’ so the answer is 0 0 0.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;int n, m;
string a, b;bool check(int x) {for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i ++) {if (a[j + 1] == b[i])j ++;if (j == x)return 1;}return 0;
}void solve() {cin >> n >> m >> a >> b;a = ' ' + a, b = ' ' + b;int l = 0, r = min(n, m);while (l < r) {int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;if (check(mid)) l = mid;else r = mid - 1;}cout << l << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
C. Assembly via Remainders
Problem Statement
You are given an array x 2 , x 3 , … , x n x_2,x_3,\dots,x_n x2,x3,…,xn. Your task is to find any array a 1 , … , a n a_1,\dots,a_n a1,…,an, where:
- 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1\le a_i\le 10^9 1≤ai≤109 for all 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1\le i\le n 1≤i≤n.
- x i = a i m o d a i − 1 x_i=a_i \bmod a_{i-1} xi=aimodai−1 for all 2 ≤ i ≤ n 2\le i\le n 2≤i≤n.
Here c m o d d c\bmod d cmodd denotes the remainder of the division of the integer c c c by the integer d d d. For example 5 m o d 2 = 1 5 \bmod 2 = 1 5mod2=1, 72 m o d 3 = 0 72 \bmod 3 = 0 72mod3=0, 143 m o d 14 = 3 143 \bmod 14 = 3 143mod14=3.
Note that if there is more than one a a a which satisfies the statement, you are allowed to find any.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 ) (1\le t\le 10^4) (1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 500 ) (2\le n\le 500) (2≤n≤500) — the number of elements in a a a.
The second line of each test case contains n − 1 n-1 n−1 integers x 2 , … , x n x_2,\dots,x_n x2,…,xn ( 1 ≤ x i ≤ 500 ) (1\le x_i\le 500) (1≤xi≤500) — the elements of x x x.
It is guaranteed that the sum of values n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case output any a 1 , … , a n a_1,\dots,a_n a1,…,an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le a_i \le 10^9 1≤ai≤109) which satisfies the statement.
Example
| input |
|---|
| 5 |
| 4 |
| 2 4 1 |
| 3 |
| 1 1 |
| 6 |
| 4 2 5 1 2 |
| 2 |
| 500 |
| 3 |
| 1 5 |
| output |
|---|
| 3 5 4 9 |
| 2 5 11 |
| 5 14 16 5 11 24 |
| 501 500 |
| 2 7 5 |
Note
In the first test case a = [ 3 , 5 , 4 , 9 ] a=[3,5,4,9] a=[3,5,4,9] satisfies the conditions, because:
- a 2 m o d a 1 = 5 m o d 3 = 2 = x 2 a_2\bmod a_1=5\bmod 3=2=x_2 a2moda1=5mod3=2=x2;
- a 3 m o d a 2 = 4 m o d 5 = 4 = x 3 a_3\bmod a_2=4\bmod 5=4=x_3 a3moda2=4mod5=4=x3;
- a 4 m o d a 3 = 9 m o d 4 = 1 = x 4 a_4\bmod a_3=9\bmod 4=1=x_4 a4moda3=9mod4=1=x4;
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;void solve() {int n;cin >> n;std::vector<int> a(n + 1);for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)cin >> a[i];cout << 501 << " ";int lst = 501;for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)cout << lst + a[i] << " ", lst += a[i];cout << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
D. Permutation Game
Problem Statement
Bodya and Sasha found a permutation p 1 , … , p n p_1,\dots,p_n p1,…,pn and an array a 1 , … , a n a_1,\dots,a_n a1,…,an. They decided to play a well-known “Permutation game”.
A permutation of length n n n is an array consisting of n n n distinct integers from 1 1 1 to n n n in arbitrary order. For example, [ 2 , 3 , 1 , 5 , 4 ] [2,3,1,5,4] [2,3,1,5,4] is a permutation, but [ 1 , 2 , 2 ] [1,2,2] [1,2,2] is not a permutation ( 2 2 2 appears twice in the array), and [ 1 , 3 , 4 ] [1,3,4] [1,3,4] is also not a permutation ( n = 3 n=3 n=3 but there is 4 4 4 in the array).
Both of them chose a starting position in the permutation.
The game lasts k k k turns. The players make moves simultaneously. On each turn, two things happen to each player:
- If the current position of the player is x x x, his score increases by a x a_x ax.
- Then the player either stays at his current position x x x or moves from x x x to p x p_x px.
The winner of the game is the player with the higher score after exactly k k k turns.
Knowing Bodya’s starting position P B P_B PB and Sasha’s starting position P S P_S PS, determine who wins the game if both players are trying to win.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1\le t\le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of testcases.
The first line of each testcase contains integers n n n, k k k, P B P_B PB, P S P_S PS ( 1 ≤ P B , P S ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1\le P_B,P_S\le n\le 2\cdot 10^5 1≤PB,PS≤n≤2⋅105, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1 0 9 1\le k\le 10^9 1≤k≤109) — length of the permutation, duration of the game, starting positions respectively.
The next line contains n n n integers p 1 , … , p n p_1,\dots,p_n p1,…,pn ( 1 ≤ p i ≤ n 1 \le p_i \le n 1≤pi≤n) — elements of the permutation p p p.
The next line contains n n n integers a 1 , … , a n a_1,\dots,a_n a1,…,an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1\le a_i\le 10^9 1≤ai≤109) — elements of array a a a.
It is guaranteed that the sum of values of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each testcase output:
- “Bodya” if Bodya wins the game.
- “Sasha” if Sasha wins the game.
- “Draw” if the players have the same score.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 10 |
| 4 2 3 2 |
| 4 1 2 3 |
| 7 2 5 6 |
| 10 8 2 10 |
| 3 1 4 5 2 7 8 10 6 9 |
| 5 10 5 1 3 7 10 15 4 3 |
| 2 1000000000 1 2 |
| 1 2 |
| 4 4 |
| 8 10 4 1 |
| 5 1 4 3 2 8 6 7 |
| 1 1 2 1 2 100 101 102 |
| 5 1 2 5 |
| 1 2 4 5 3 |
| 4 6 9 4 2 |
| 4 2 3 1 |
| 4 1 3 2 |
| 6 8 5 3 |
| 6 9 5 4 |
| 6 1 3 5 2 4 |
| 6 9 8 9 5 10 |
| 4 8 4 2 |
| 2 3 4 1 |
| 5 2 8 7 |
| 4 2 3 1 |
| 4 1 3 2 |
| 6 8 5 3 |
| 2 1000000000 1 2 |
| 1 2 |
| 1000000000 2 |
| output |
|---|
| Bodya |
| Sasha |
| Draw |
| Draw |
| Bodya |
| Sasha |
| Sasha |
| Sasha |
| Sasha |
| Bodya |
Note
Below you can find the explanation for the first testcase, where the game consists of k = 2 k=2 k=2 turns.
| Turn | Bodya’s position | Bodya’s score | Bodya’s move | Sasha’s position | Sasha’s score | Sasha’s move |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| first | 3 3 3 | 0 + a 3 = 0 + 5 = 5 0 + a_3 = 0 + 5 = 5 0+a3=0+5=5 | stays on the same position | 2 2 2 | 0 + a 2 = 0 + 2 = 2 0 + a_2 = 0 + 2 = 2 0+a2=0+2=2 | moves to p 2 = 1 p_2=1 p2=1 |
| second | 3 3 3 | 5 + a 3 = 5 + 5 = 10 5 + a_3 = 5 + 5 = 10 5+a3=5+5=10 | stays on the same position | 1 1 1 | 2 + a 1 = 2 + 7 = 9 2 + a_1 = 2 + 7 = 9 2+a1=2+7=9 | stays on the same position |
| final results | 3 3 3 | 10 10 10 | 1 1 1 | 9 9 9 |
As we may see, Bodya’s score is greater, so he wins the game. It can be shown that Bodya always can win this game.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, k, pb, ps;
int a[N], p[N];
int vis[N];void solve() {cin >> n >> k >> pb >> ps;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cin >> p[i];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cin >> a[i];int r1 = 0, tot = 0, r2 = 0, left = k;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) vis[i] = 0;while (!vis[pb] && left) {vis[pb] = 1, tot += a[pb], left --;r1 = max(tot + left * a[pb], r1), pb = p[pb];}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) vis[i] = 0;left = k, tot = 0;while (!vis[ps] && left) {vis[ps] = 1, tot += a[ps], left --;r2 = max(tot + left * a[ps], r2), ps = p[ps];}// cout << r1 << " " << r2 << endl;if (r1 == r2) cout << "Draw" << endl;else if (r1 > r2) cout << "Bodya" << endl;else cout << "Sasha" << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
E. Cells Arrangement
Problem Statement
You are given an integer n n n. You choose n n n cells ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , … , ( x n , y n ) (x_1,y_1), (x_2,y_2),\dots,(x_n,y_n) (x1,y1),(x2,y2),…,(xn,yn) in the grid n × n n\times n n×n where 1 ≤ x i ≤ n 1\le x_i\le n 1≤xi≤n and 1 ≤ y i ≤ n 1\le y_i\le n 1≤yi≤n.
Let H \mathcal{H} H be the set of distinct Manhattan distances between any pair of cells. Your task is to maximize the size of H \mathcal{H} H. Examples of sets and their construction are given in the notes.
If there exists more than one solution, you are allowed to output any.
Manhattan distance between cells ( x 1 , y 1 ) (x_1,y_1) (x1,y1) and ( x 2 , y 2 ) (x_2,y_2) (x2,y2) equals ∣ x 1 − x 2 ∣ + ∣ y 1 − y 2 ∣ |x_1-x_2|+|y_1-y_2| ∣x1−x2∣+∣y1−y2∣.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 50 1\le t\le 50 1≤t≤50) — the number of test cases.
Each of the following t t t lines contains a single integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 3 2\le n\le 10^3 2≤n≤103).
Output
For each test case, output n n n points which maximize the size of H \mathcal{H} H. It is not necessary to output an empty line at the end of the answer for each test case.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 5 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
| output |
|---|
| 1 1 |
| 1 2 |
2 1
2 3
3 1
1 1
1 3
4 3
4 4
1 1
1 3
1 4
2 1
5 5
1 4
1 5
1 6
5 2
5 5
6 1
Note
In the first testcase we have n = 2 n=2 n=2. One of the possible arrangements is:
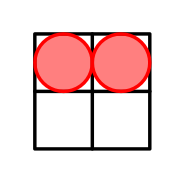 The arrangement with cells located in ( 1 , 1 ) (1,1) (1,1) and ( 1 , 2 ) (1,2) (1,2).
The arrangement with cells located in ( 1 , 1 ) (1,1) (1,1) and ( 1 , 2 ) (1,2) (1,2).
In this case H = { ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ + ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ , ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ + ∣ 2 − 2 ∣ , ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ + ∣ 1 − 2 ∣ } = { 0 , 0 , 1 } = { 0 , 1 } \mathcal{H}=\{|1-1|+|1-1|,|1-1|+|2-2|,|1-1|+|1-2|\}=\{0,0,1\}=\{0,1\} H={∣1−1∣+∣1−1∣,∣1−1∣+∣2−2∣,∣1−1∣+∣1−2∣}={0,0,1}={0,1}. Hence, the size of H \mathcal{H} H is 2 2 2. It can be shown that it is the greatest possible answer.
In the second testcase we have n = 3 n=3 n=3. The optimal arrangement is:
 The arrangement with cells located in ( 2 , 1 ) (2,1) (2,1), ( 2 , 3 ) (2,3) (2,3) and ( 3 , 1 ) (3,1) (3,1).
The arrangement with cells located in ( 2 , 1 ) (2,1) (2,1), ( 2 , 3 ) (2,3) (2,3) and ( 3 , 1 ) (3,1) (3,1).
H \mathcal{H} H= { ∣ 2 − 2 ∣ + ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ , ∣ 2 − 2 ∣ + ∣ 3 − 3 ∣ , ∣ 3 − 3 ∣ + ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ , ∣ 2 − 2 ∣ + ∣ 1 − 3 ∣ , ∣ 2 − 3 ∣ + ∣ 1 − 1 ∣ , ∣ 2 − 3 ∣ + ∣ 3 − 1 ∣ } \{|2-2|+|1-1|,|2-2|+|3-3|,|3-3|+|1-1|,|2-2|+|1-3|,|2-3|+|1-1|,|2-3|+|3-1|\} {∣2−2∣+∣1−1∣,∣2−2∣+∣3−3∣,∣3−3∣+∣1−1∣,∣2−2∣+∣1−3∣,∣2−3∣+∣1−1∣,∣2−3∣+∣3−1∣}= { 0 , 0 , 0 , 2 , 1 , 3 } \{0,0,0,2,1,3\} {0,0,0,2,1,3}= { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 } \{0,1,2,3\} {0,1,2,3}.
For n = 4 n=4 n=4 a possible arrangement is:

For n = 5 n=5 n=5 a possible arrangement is:

For n = 6 n=6 n=6 a possible arrangement is:

Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 7;int n;
bool vis[N][N], res[N][N];
int mx;void dfs(int u) {if (!u) {set<int> s;std::vector<PII> point;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)if (vis[i][j])point.emplace_back(i, j);for (auto i : point)for (auto j : point)s.insert(abs(i.fi - j.fi) + abs(i.se - j.se));if (s.size() > mx) {mx = s.size();memcpy(res, vis, sizeof vis);}return;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)if (!vis[i][j]) {vis[i][j] = 1;dfs(u - 1);vis[i][j] = 0;}
}void solve() {cin >> n;if (n == 2) {cout << "1 2\n2 2\n";} else {for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i ++)cout << 1 << " " << i << endl;cout << 2 << " " << n << endl << n << " " << n << endl;}cout << endl;// set<int> s;// std::vector<PII> point;// int x, y;// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)// cin >> x >> y, point.emplace_back(x, y);// for (auto i : point)// for (auto j : point)// s.insert(abs(i.fi - j.fi) + abs(i.se - j.se));// cout << s.size() << endl;// mx = 0;// dfs(n);// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)// for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)// if (res[i][j])// cout << i << " " << j << endl;// cout << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
F. Equal XOR Segments
Problem Statement
Let us call an array x 1 , … , x m x_1,\dots,x_m x1,…,xm interesting if it is possible to divide the array into k > 1 k>1 k>1 parts so that bitwise XOR of values from each part are equal.
More formally, you must split array x x x into k k k consecutive segments, each element of x x x must belong to exactly 1 1 1 segment. Let y 1 , … , y k y_1,\dots,y_k y1,…,yk be the XOR of elements from each part respectively. Then y 1 = y 2 = ⋯ = y k y_1=y_2=\dots=y_k y1=y2=⋯=yk must be fulfilled.
For example, if x = [ 1 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 0 ] x = [1, 1, 2, 3, 0] x=[1,1,2,3,0], you can split it as follows: [ 1 ] , [ 1 ] , [ 2 , 3 , 0 ] [\color{blue}1], [\color{green}1], [\color{red}2, \color{red}3, \color{red}0] [1],[1],[2,3,0]. Indeed 1 = 1 = 2 ⊕ 3 ⊕ 0 \color{blue}1=\color{green}1=\color{red}2 \oplus \color{red}3\oplus \color{red}0 1=1=2⊕3⊕0.
You are given an array a 1 , … , a n a_1,\dots,a_n a1,…,an. Your task is to answer q q q queries:
- For fixed l l l, r r r, determine whether the subarray a l , a l + 1 , … , a r a_l,a_{l+1},\dots,a_r al,al+1,…,ar is interesting.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1\le t\le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n and q q q ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 2≤n≤2⋅105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le q \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤q≤2⋅105) — the number of elements in the array and the number of queries respectively.
The next line contains n n n integers a 1 , … , a n a_1,\dots,a_n a1,…,an ( 0 ≤ a i < 2 30 0 \le a_i < 2^{30} 0≤ai<230) — elements of the array.
Each of the next q q q lines contains two integers l l l and r r r ( 1 ≤ l < r ≤ n 1 \le l < r \le n 1≤l<r≤n) describing the query.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all testcases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
It is guaranteed that the sum of q q q over all testcases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each query, output “YES” if the subarray is interesting and “NO” otherwise.
You can output “Yes” and “No” in any case (for example, the strings “yES”, “yes”, and “Yes” will be recognized as correct answers).
Example
| input |
|---|
| 4 |
| 5 5 |
| 1 1 2 3 0 |
| 1 5 |
| 2 4 |
| 3 5 |
| 1 3 |
| 3 4 |
| 5 5 |
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
| 1 5 |
| 2 4 |
| 3 5 |
| 1 3 |
| 2 3 |
| 7 4 |
| 12 9 10 9 10 11 9 |
| 1 5 |
| 1 7 |
| 2 6 |
| 2 7 |
| 11 4 |
| 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 |
| 1 2 |
| 2 5 |
| 6 9 |
| 7 11 |
| output |
|---|
| YES |
| YES |
| NO |
| NO |
| NO |
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
YES
Note
Explanation for the first test case:
The first query is described in the statement.
In the second query, we should divide [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] [1,2,3] [1,2,3]. A possible division is [ 1 , 2 ] , [ 3 ] [1,2],[3] [1,2],[3], since 1 ⊕ 2 = 3 1\oplus 2=3 1⊕2=3.
It can be shown that for queries 3 , 4 , 5 3,4,5 3,4,5, the subarrays are not interesting.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, q;
int s[N];
map<int, vector<int>> p;void solve() {cin >> n >> q;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cin >> s[i], s[i] ^= s[i - 1], p[s[i]].emplace_back(i);while (q -- ){int l, r;cin >> l >> r;if ((s[r] ^ s[l - 1]) == 0) {cout << "YES" << endl;} else {auto it = lower_bound(p[s[r]].begin(), p[s[r]].end(), l);if (it == p[s[r]].end()) {cout << "NO" << endl;continue;}int t1 = *it;auto it2 = upper_bound(p[s[l - 1]].begin(), p[s[l - 1]].end(), t1);if (it2 == p[s[l - 1]].end()) {cout << "NO" << endl;continue;}int t2 = *it2;if (t1 < r && t2 < r) cout << "YES" << endl;else cout << "NO" << endl;}}p.clear();cout << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
G1. Division + LCP (easy version)
Problem Statement
This is the easy version of the problem. In this version l = r l=r l=r.
You are given a string s s s. For a fixed k k k, consider a division of s s s into exactly k k k continuous substrings w 1 , … , w k w_1,\dots,w_k w1,…,wk. Let f k f_k fk be the maximal possible L C P ( w 1 , … , w k ) LCP(w_1,\dots,w_k) LCP(w1,…,wk) among all divisions.
L C P ( w 1 , … , w m ) LCP(w_1,\dots,w_m) LCP(w1,…,wm) is the length of the Longest Common Prefix of the strings w 1 , … , w m w_1,\dots,w_m w1,…,wm.
For example, if s = a b a b a b c a b s=abababcab s=abababcab and k = 4 k=4 k=4, a possible division is a b a b a b c a b \color{red}{ab}\color{blue}{ab}\color{orange}{abc}\color{green}{ab} abababcab. The L C P ( a b , a b , a b c , a b ) LCP(\color{red}{ab},\color{blue}{ab},\color{orange}{abc},\color{green}{ab}) LCP(ab,ab,abc,ab) is 2 2 2, since a b ab ab is the Longest Common Prefix of those four strings. Note that each substring consists of a continuous segment of characters and each character belongs to exactly one substring.
Your task is to find f l , f l + 1 , … , f r f_l,f_{l+1},\dots,f_r fl,fl+1,…,fr. In this version l = r l=r l=r.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n, l l l, r r r ( 1 ≤ l = r ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le l = r \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤l=r≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the string and the given range.
The second line of each test case contains string s s s of length n n n, all characters are lowercase English letters.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2\cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output r − l + 1 r-l+1 r−l+1 values: f l , … , f r f_l,\dots,f_r fl,…,fr.
Example
| input |
|---|
| 7 |
| 3 3 3 |
| aba |
| 3 3 3 |
| aaa |
| 7 2 2 |
| abacaba |
| 9 4 4 |
| abababcab |
| 10 1 1 |
| codeforces |
| 9 3 3 |
| abafababa |
| 5 3 3 |
| zpozp |
| output |
|---|
| 0 |
| 1 |
| 3 |
| 2 |
| 10 |
| 2 |
| 0 |
Note
In the first sample n = k n=k n=k, so the only division of a b a aba aba is a b a \color{red}a\color{blue}b\color{orange}a aba. The answer is zero, because those strings do not have a common prefix.
In the second sample, the only division is a a a \color{red}a\color{blue}a\color{orange}a aaa. Their longest common prefix is one.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, k;
string s;
int ne[N];int check(int x) {string p = " ";for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++)p += s[i];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)ne[i] = 0;for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= x; i ++) {while (j && p[j + 1] != p[i]) j = ne[j];if (p[j + 1] == p[i]) j ++;ne[i] = j;}std::vector<PII> res;for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i ++) {while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++;if (j == x) {res.emplace_back(i - x + 1, i);j = ne[j];}}sort(res.begin(), res.end(), [&](PII a, PII b) {return a.se < b.se;});int ans = 0, ed = 0;for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i ++)if (res[i].fi > ed) {ans ++;ed = res[i].se;}return ans;
}void solve() {cin >> n >> k >> k >> s;s = ' ' + s;int l = 0, r = n;while (l < r) {int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;if (check(mid) >= k) l = mid;else r = mid - 1;}cout << l << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
G2. Division + LCP (hard version)
Problem Statement
This is the hard version of the problem. In this version l ≤ r l\le r l≤r.
You are given a string s s s. For a fixed k k k, consider a division of s s s into exactly k k k continuous substrings w 1 , … , w k w_1,\dots,w_k w1,…,wk. Let f k f_k fk be the maximal possible L C P ( w 1 , … , w k ) LCP(w_1,\dots,w_k) LCP(w1,…,wk) among all divisions.
L C P ( w 1 , … , w m ) LCP(w_1,\dots,w_m) LCP(w1,…,wm) is the length of the Longest Common Prefix of the strings w 1 , … , w m w_1,\dots,w_m w1,…,wm.
For example, if s = a b a b a b c a b s=abababcab s=abababcab and k = 4 k=4 k=4, a possible division is a b a b a b c a b \color{red}{ab}\color{blue}{ab}\color{orange}{abc}\color{green}{ab} abababcab. The L C P ( a b , a b , a b c , a b ) LCP(\color{red}{ab},\color{blue}{ab},\color{orange}{abc},\color{green}{ab}) LCP(ab,ab,abc,ab) is 2 2 2, since a b ab ab is the Longest Common Prefix of those four strings. Note that each substring consists of a continuous segment of characters and each character belongs to exactly one substring.
Your task is to find f l , f l + 1 , … , f r f_l,f_{l+1},\dots,f_r fl,fl+1,…,fr.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers n n n, l l l, r r r ( 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le l \le r \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤l≤r≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the string and the given range.
The second line of each test case contains string s s s of length n n n, all characters are lowercase English letters.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2\cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output r − l + 1 r-l+1 r−l+1 values: f l , … , f r f_l,\dots,f_r fl,…,fr.
Example
| input |
|---|
| 7 |
| 3 1 3 |
| aba |
| 3 2 3 |
| aaa |
| 7 1 5 |
| abacaba |
| 9 1 6 |
| abababcab |
| 10 1 10 |
| aaaaaaawac |
| 9 1 9 |
| abafababa |
| 7 2 7 |
| vvzvvvv |
| output |
|---|
| 3 1 0 |
| 1 1 |
| 7 3 1 1 0 |
| 9 2 2 2 0 0 |
| 10 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 |
| 9 3 2 1 1 0 0 0 0 |
| 2 2 1 1 1 0 |
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, L, R;
string s;
int ne[N], f[N];int check(int x) {if (f[x]) return f[x];string p = " ";for (int i = 1; i <= x; i ++)p += s[i];for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)ne[i] = 0;for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= x; i ++) {while (j && p[j + 1] != p[i]) j = ne[j];if (p[j + 1] == p[i]) j ++;ne[i] = j;}int ans = 0, ed = 0;for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i ++) {while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++;if (j == x) {if (i - x + 1 > ed) {ans ++;ed = i;}j = ne[j];}}// int ans = 0, ed = 0;// for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i ++)// if (res[i].fi > ed) {// ans ++;// ed = res[i].se;// }return f[x] = ans;
}void solve() {cin >> n >> L >> R >> s;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) f[i] = 0;s = ' ' + s;int res = n;for (int i = L; i <= R; i ++) {int l = 0, r = res;while (l < r) {int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;if (check(mid) >= i) l = mid;else r = mid - 1;}res = l;cout << res << " ";}cout << endl;
}signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int dt;cin >> dt;while (dt --)solve();return 0;
}
视频讲解
Codeforces Round 943 (Div. 3)(A ~ G2 讲解)
最后祝大家早日
这篇关于Codeforces Round 943 (Div. 3 ABCDEFG1G2题) 视频讲解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







