本文主要是介绍[原创]产生多个随机不重复打乱不重复的最优性能代码实现探索,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在接手键盘项目的时候发现某些代码写的比较奇怪,看半天才知道原来通过巧妙的方式实现了,刚开始还以为存在bug - -,..
那么既然已经发车,那就继续优化性能呗.发现公司的那种写法效率还不是很高,但是至少比网上百分之80的效率高太多了
下面是我写的这几种方法,很多方法和和网上的方法差不多的,
容器优化
首先说说 java集合中哪些增删快,哪些查询快吧.
具体参考这个地址包含详细的图
不重复的set,以及hashmap结构
根据index查询快 但是 增删 慢的arraylist
增删快查询慢的 linkedlisthttp://www.cnblogs.com/laotan/p/3644238.html
所谓算法优化
有的人认为这些又不叫算法,叫实现方式,等等,ok,这配不上是算法,那就不扯算法,就扯几种实现方式的效率 .
方法包含多种,
如random()控制永远不会包含 通过 创建拷贝的集合,然后根据随机index取出插入,然后删除随机位,然后减少随机最大数实现.
我目前研究和发现想到了这几种,如果各位发现了新的方式,欢迎补充哦!!!
通过反复循环包含的判断
通过系统的方式
暴力循环判断包含
初始arraylist容量总数的方式
使用linkedlist的方式暴力 添加和判断包含
使用有序插入方式不重复的linkedhashset插入
经过测试 系统的方式速度>linkedhashset暴力>非暴力random()永远不重复方式>arraylist暴力随机>linkedslist暴力随机
测试效果:
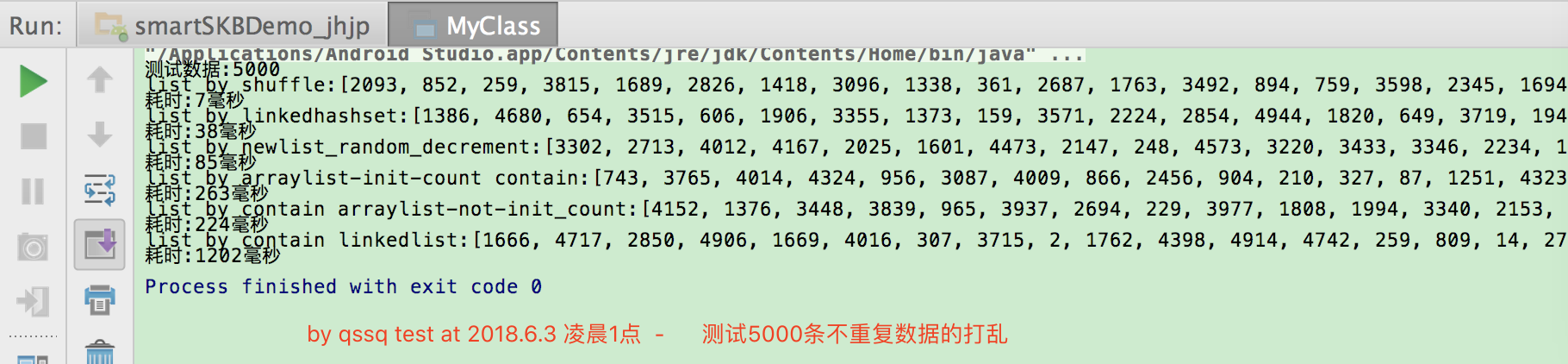
从上图清晰的看出来了java自带的打乱顺序是最优秀的,其次依然是使用暴力+系统优势的有序而且去重复(免查询)和插入都有优势.
某个方式和我这里的非暴力方式相似,但是也不是最优的方式 在我这里排行老三https://blog.csdn.net/albertfly/article/details/51383410这篇2011年的文章和这里某种比较类似,还算比较可以的,但是最牛逼的还是官方自带的实现.
参考基础https://www.cnblogs.com/wl0000-03/p/6019627.html
源码想了想,还是发给大家吧.如果我自己是牛人,我也不应该怕别人超越不是么.
package cn.qssq666.demo;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Random;public class MyClass {public static void main(String[] args) {/* int count=10;Random rand = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {int num = rand.nextInt(count - i);System.out.println("num:"+num+","+rand.nextInt());*//* KeyModel keyModelTemp = temp.get(num);KeyModel object = new KeyModel(keyModelTemp.getCode(),keyModelTemp.getLable());resultList.add(object);temp.remove(num);*//*}*/
// random(1000);//300个 arraylist 耗时19毫秒 linklist耗时 5毫秒int randomCount = 5000;System.out.println("测试数据:"+randomCount);randomByShuffle(randomCount);//1110毫秒 用的 linklist进行增加,但是这里面也会查询判断是否重复randomByHashSetContain(randomCount);//1110毫秒 用的 linklist进行增加,但是这里面也会查询判断是否重复random(randomCount);//143毫秒randomByArrayListInitCount(randomCount);//5000个 451毫秒randomContainByArrayListNotInitCount(randomCount);//143毫秒randomContainByLinked(randomCount);//1110毫秒 用的 linklist进行增加,但是这里面也会查询判断是否重复}/*** 用系统的方法** @param count*/public static void randomByShuffle(int count) {LinkedList<Integer> integers = new LinkedList<>();int countBackup = count;ConsumeTimeUtil.start();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {integers.add(i);}Collections.shuffle(integers);long consumeTime = ConsumeTimeUtil.end();System.out.println("list by shuffle:" + integers + ",\n耗时:" + consumeTime + "毫秒");}public static void randomByHashSetContain(int count) {LinkedHashSet<Integer> integers = new LinkedHashSet<>();//插入顺序可以保证,而且是唯一的.ConsumeTimeUtil.start();/* for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {integers.add(i);}
*/while (integers.size() < count) {int i = new Random().nextInt(count);integers.add(i);}long consumeTime = ConsumeTimeUtil.end();System.out.println("list by linkedhashset:" + integers + ",\n耗时:" + consumeTime + "毫秒");}/*** 此方法需要先创建一套** @param count*/public static void random(int count) {LinkedList<Integer> integersSrc = new LinkedList<>();//linklist增删快,这里其实也用到了查询,综合测试,还是用linkedlist快. 优化了10多毫秒for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {integersSrc.add(i);}ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(integersSrc.size());//优化1 这里直接初始化已经确定的容量 在1000个的时候能优化几毫秒ConsumeTimeUtil.start();while (count > 0) {int randomIndex = new Random().nextInt(count);Integer currentObj = integersSrc.get(randomIndex);integersSrc.remove(currentObj);// integersSrcintegers.add(currentObj);count--;}long consumeTime = ConsumeTimeUtil.end();System.out.println("list by newlist_random_decrement:" + integers + ",\n耗时:" + consumeTime + "毫秒");}/*** @param count*/public static void randomByArrayListInitCount(int count) {ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>(count);int countBackup = count;ConsumeTimeUtil.start();while (integers.size() < count) {int i = new Random().nextInt(countBackup);if (i == countBackup) {System.out.println("发现刚好末尾,直接减去1,增加随机有效概率");i--;}if (integers.contains(i)) {
// System.out.println("发现重复数值:"+i);continue;} else {integers.add(i);}}long consumeTime = ConsumeTimeUtil.end();System.out.println("list by arraylist-init-count contain:" + integers + ",\n耗时:" + consumeTime + "毫秒");}public static void randomContainByLinked(int count) {LinkedList<Integer> integers = new LinkedList<>();int countBackup = count;ConsumeTimeUtil.start();while (integers.size() < count) {int i = new Random().nextInt(countBackup);if (i == countBackup) {System.out.println("发现刚好末尾,直接减去1,增加随机有效概率");i--;}if (integers.contains(i)) {
// System.out.println("发现重复数值:"+i);continue;} else {integers.add(i);}}long consumeTime = ConsumeTimeUtil.end();System.out.println("list by contain linkedlist:" + integers + ",\n耗时:" + consumeTime + "毫秒");}public static void randomContainByArrayListNotInitCount(int count) {ArrayList<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>();int countBackup = count;ConsumeTimeUtil.start();while (integers.size() < count) {int i = new Random().nextInt(countBackup);if (i == countBackup) {System.out.println("发现刚好末尾,直接减去1,增加随机有效概率");i--;}if (integers.contains(i)) {
// System.out.println("发现重复数值:"+i);continue;} else {integers.add(i);}}long consumeTime = ConsumeTimeUtil.end();System.out.println("list by contain arraylist-not-init_count:" + integers + ",\n耗时:" + consumeTime + "毫秒");}}suffle的原理其实也差不多,只是避免重建
if (objectList instanceof RandomAccess) {for (int i = objectList.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {int index = random.nextInt(i + 1);Keyboard.Key keyRandom = objectList.get(index);Keyboard.Key key = objectList.get(i);key.codes = keyRandom.codes;key.label = keyRandom.label;// objectList.set(index, objectList.set(i, objectList.get(index)));}经过研究发现系统的有缺陷,会导致重复出现。
所以下面的有毛病
public static void shuffle(List<Keyboard.Key> objectList, Random random) {if (objectList instanceof RandomAccess) {for (int i = objectList.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {int index = random.nextInt(i + 1);Keyboard.Key keyRandom = objectList.get(index);Keyboard.Key keySrc = objectList.get(i);keyRandom.codes[0] = keySrc.codes[0];keyRandom.label = keySrc.label;// objectList.set(index, objectList.set(i, objectList.get(index)));}} else {Keyboard.Key[] array = (Keyboard.Key[]) objectList.toArray();for (int i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {int index = random.nextInt(i + 1);Keyboard.Key temp = array[i];array[i] = array[index];array[index] = temp;}int i = 0;ListIterator<Keyboard.Key> it = objectList.listIterator();while (it.hasNext()) {Keyboard.Key next = it.next();/*newkeyList.get(i).label = randomResultList.get(i).getLable();newkeyList.get(i).codes[0] = randomResultList.get(i).getCode();*/Keyboard.Key randomKey = array[i++];next.codes = randomKey.codes;next.label = randomKey.label;// it.set(o);//modify value}}}这篇关于[原创]产生多个随机不重复打乱不重复的最优性能代码实现探索的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






