本文主要是介绍SpringBoot集成Sharding-jdbc水平分表分库,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
SpringBoot集成Sharding-jdbc水平分表分库
- 1.水平分表分库
- 2.参数配置
- 2.application.properties
- 3.代码测试
- 3.1 数据插入
1.水平分表分库
概念在之前写章中:Sharding-JDBC笔记1
2.参数配置
2.application.properties
# Server port
server.port=8080# MyBatis configuration
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mapper/*.xml
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.test.sharding.domain.pojo
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true# Spring Boot application properties
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
spring.application.name=sharding-jdbc-test-02# ShardingSphere configuration
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true# DataSource configuration db1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=db1,db2
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db_1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.password=root# DataSource configuration db2
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db_2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db2.password=root#设置分库策略-以user_id列为数据库的分片键,
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=db$->{user_id % 2 +1}#设置分表策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=db$->{1..2}.t_order_$->{1..2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1}
-
user_id % 2:这部分表示对user_id进行取模运算,模数为2。这样,user_id的值将被分为两类:偶数(结果为0)和奇数(结果为1)。 -
user_id % 2 + 1:这部分是在取模运算的结果上加1。这样,偶数user_id的结果将变为1,奇数user_id的结果将变为2。 -
db$->{...}:这部分是ShardingSphere的语法,用于构建实际的数据库标识。$->{...}中的表达式会计算出一个值,然后这个值会被插入到 db 前缀后面,从而形成一个完整的数据库名称。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=db$->{1..2}.t_order_$->{1..2}
定义了实际的数据节点。这里表示数据被分布在两个数据库db1和db2中,每个数据库下有两个表,分别是t_order_1和t_order_2。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=order_id
定义了主键生成策略对应的列名,即order_id列。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
指定了主键生成策略的类型为SNOWFLAKE,即使用雪花算法来生成主键。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=order_id
定义了分片键为order_id,即根据order_id的值来决定数据应该存储到哪个表中。
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1}
定义了分片算法表达式。这里表示根据order_id的值取模2后加1的结果来决定数据应该存储到哪个表中。例如,order_id为奇数的数据会被存储到t_order_2表中,而order_id为偶数的数据会被存储到t_order_1表中。
3.代码测试
3.1 数据插入
ShardingMapper.java
@Mapper
public interface ShardingMapper {void insertOrder(@Param("order") Order order);}
插入语句:
<insert id="insertOrder" parameterType="com.test.sharding.domain.pojo.Order">insert into t_order (order_price, user_id, order_status)values (#{order.orderPrice, jdbcType=DECIMAL}, #{order.userId, jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{order.orderStatus, jdbcType=VARCHAR})</insert>
测试语句:
@PostMapping("/insertProduct")public String insertOrder(){Order order = new Order();for(int i = 1 ; i < 10 ; i++){order.setOrderPrice(BigDecimal.valueOf(i*10));order.setUserId(5L);shardingService.insertOrder(order);try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}return "插入成功!";}插入结果:
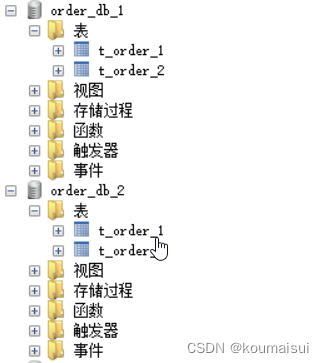
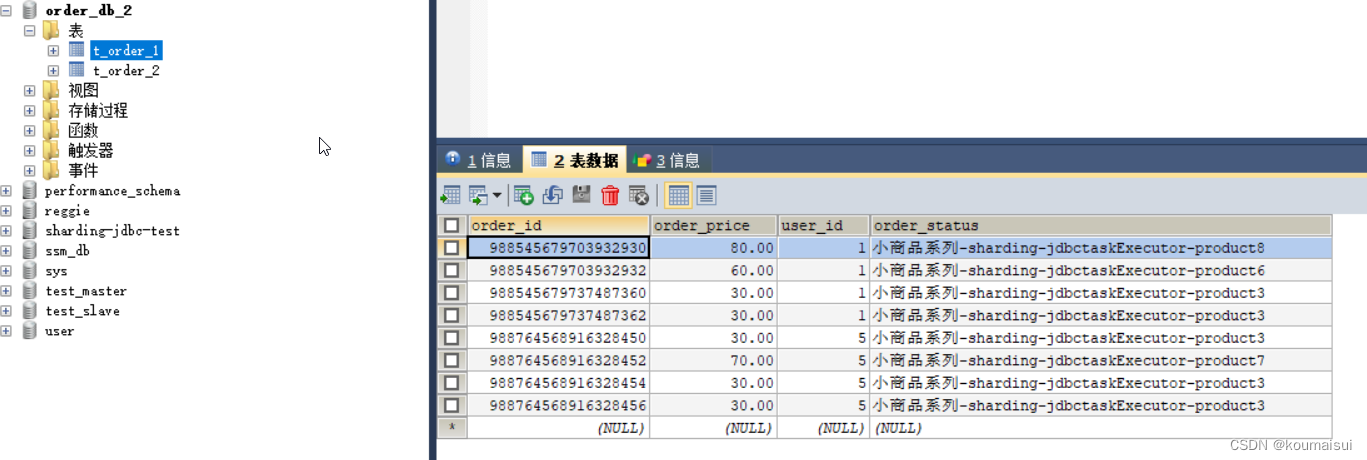
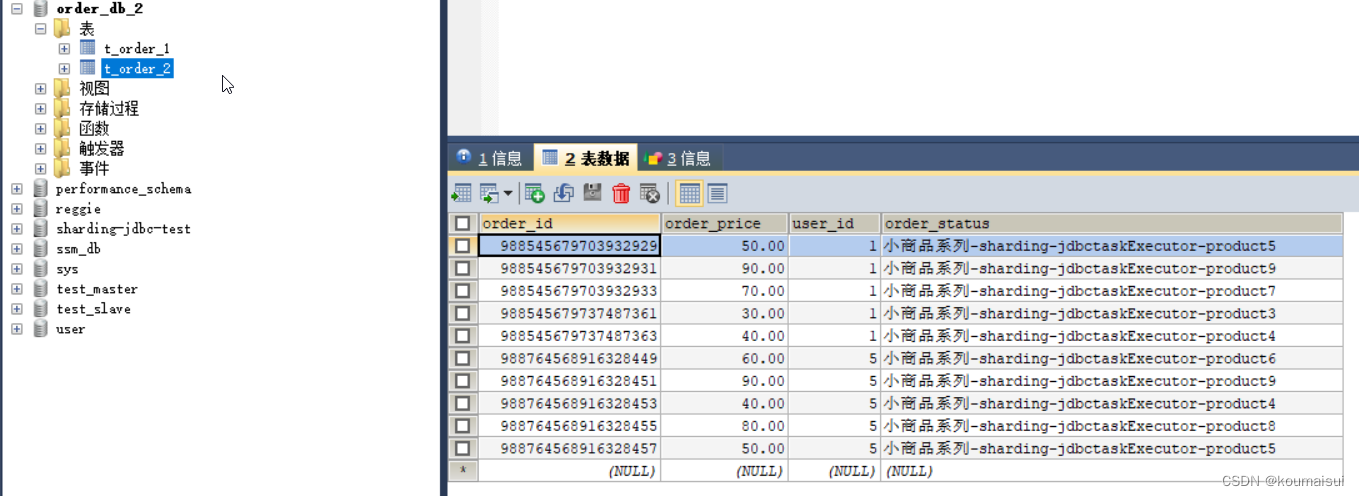
因为user_id设置的是5L所以根据分片算法会将数据插入到order_db_2的数据库中:
这篇关于SpringBoot集成Sharding-jdbc水平分表分库的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





