本文主要是介绍政安晨:【Keras机器学习示例演绎】(五)—— 利用视觉变换器进行物体检测,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
导言
导入和设置
准备数据集
实施多层感知器(MLP)
实施补丁创建层
显示输入图像的补丁
实施补丁编码层
构建 ViT 模型
运行实验
评估模型
政安晨的个人主页:政安晨
欢迎 👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏
收录专栏: TensorFlow与Keras机器学习实战
希望政安晨的博客能够对您有所裨益,如有不足之处,欢迎在评论区提出指正!
本文目标:使用视觉变换器进行物体检测的简单 Keras 实现。
导言
Alexey Dosovitskiy 等人撰写的文章 Vision Transformer (ViT) 架构表明,直接应用于图像片段序列的纯变换器可以很好地完成物体检测任务。
在本 Keras 示例中,我们实现了对象检测 ViT,并在 Caltech 101 数据集上对其进行训练,以检测给定图像中的飞机。
导入和设置
import osos.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "jax" # @param ["tensorflow", "jax", "torch"]import numpy as np
import keras
from keras import layers
from keras import ops
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
import scipy.io
import shutil准备数据集
我们使用加州理工学院 101 数据集。
# Path to images and annotations
path_images = "./101_ObjectCategories/airplanes/"
path_annot = "./Annotations/Airplanes_Side_2/"path_to_downloaded_file = keras.utils.get_file(fname="caltech_101_zipped",origin="https://data.caltech.edu/records/mzrjq-6wc02/files/caltech-101.zip",extract=True,archive_format="zip", # downloaded file formatcache_dir="/", # cache and extract in current directory
)
download_base_dir = os.path.dirname(path_to_downloaded_file)# Extracting tar files found inside main zip file
shutil.unpack_archive(os.path.join(download_base_dir, "caltech-101", "101_ObjectCategories.tar.gz"), "."
)
shutil.unpack_archive(os.path.join(download_base_dir, "caltech-101", "Annotations.tar"), "."
)# list of paths to images and annotations
image_paths = [f for f in os.listdir(path_images) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(path_images, f))
]
annot_paths = [f for f in os.listdir(path_annot) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(path_annot, f))
]image_paths.sort()
annot_paths.sort()image_size = 224 # resize input images to this sizeimages, targets = [], []# loop over the annotations and images, preprocess them and store in lists
for i in range(0, len(annot_paths)):# Access bounding box coordinatesannot = scipy.io.loadmat(path_annot + annot_paths[i])["box_coord"][0]top_left_x, top_left_y = annot[2], annot[0]bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y = annot[3], annot[1]image = keras.utils.load_img(path_images + image_paths[i],)(w, h) = image.size[:2]# resize imagesimage = image.resize((image_size, image_size))# convert image to array and append to listimages.append(keras.utils.img_to_array(image))# apply relative scaling to bounding boxes as per given image and append to listtargets.append((float(top_left_x) / w,float(top_left_y) / h,float(bottom_right_x) / w,float(bottom_right_y) / h,))# Convert the list to numpy array, split to train and test dataset
(x_train), (y_train) = (np.asarray(images[: int(len(images) * 0.8)]),np.asarray(targets[: int(len(targets) * 0.8)]),
)
(x_test), (y_test) = (np.asarray(images[int(len(images) * 0.8) :]),np.asarray(targets[int(len(targets) * 0.8) :]),
)实施多层感知器(MLP)
我们使用 Keras 示例 "使用视觉转换器进行图像分类 "中的代码作为参考。
def mlp(x, hidden_units, dropout_rate):for units in hidden_units:x = layers.Dense(units, activation=keras.activations.gelu)(x)x = layers.Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)return x实施补丁创建层
class Patches(layers.Layer):def __init__(self, patch_size):super().__init__()self.patch_size = patch_sizedef call(self, images):input_shape = ops.shape(images)batch_size = input_shape[0]height = input_shape[1]width = input_shape[2]channels = input_shape[3]num_patches_h = height // self.patch_sizenum_patches_w = width // self.patch_sizepatches = keras.ops.image.extract_patches(images, size=self.patch_size)patches = ops.reshape(patches,(batch_size,num_patches_h * num_patches_w,self.patch_size * self.patch_size * channels,),)return patchesdef get_config(self):config = super().get_config()config.update({"patch_size": self.patch_size})return config显示输入图像的补丁
patch_size = 32 # Size of the patches to be extracted from the input imagesplt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
plt.imshow(x_train[0].astype("uint8"))
plt.axis("off")patches = Patches(patch_size)(np.expand_dims(x_train[0], axis=0))
print(f"Image size: {image_size} X {image_size}")
print(f"Patch size: {patch_size} X {patch_size}")
print(f"{patches.shape[1]} patches per image \n{patches.shape[-1]} elements per patch")n = int(np.sqrt(patches.shape[1]))
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
for i, patch in enumerate(patches[0]):ax = plt.subplot(n, n, i + 1)patch_img = ops.reshape(patch, (patch_size, patch_size, 3))plt.imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(patch_img).astype("uint8"))plt.axis("off")演绎展示:
Image size: 224 X 224
Patch size: 32 X 32
49 patches per image
3072 elements per patch

实施补丁编码层
PatchEncoder 层通过将补丁投影到大小为 projection_dim 的矢量中,对补丁进行线性变换。它还会在投影向量中添加可学习的位置嵌入。
class PatchEncoder(layers.Layer):def __init__(self, num_patches, projection_dim):super().__init__()self.num_patches = num_patchesself.projection = layers.Dense(units=projection_dim)self.position_embedding = layers.Embedding(input_dim=num_patches, output_dim=projection_dim)# Override function to avoid error while saving modeldef get_config(self):config = super().get_config().copy()config.update({"input_shape": input_shape,"patch_size": patch_size,"num_patches": num_patches,"projection_dim": projection_dim,"num_heads": num_heads,"transformer_units": transformer_units,"transformer_layers": transformer_layers,"mlp_head_units": mlp_head_units,})return configdef call(self, patch):positions = ops.expand_dims(ops.arange(start=0, stop=self.num_patches, step=1), axis=0)projected_patches = self.projection(patch)encoded = projected_patches + self.position_embedding(positions)return encoded构建 ViT 模型
ViT 模型有多个变换器模块。
多头注意层(MultiHeadAttention)用于自注意,应用于图像补丁序列。编码补丁(跳过连接)和自我注意层的输出被归一化,并输入多层感知器(MLP)。
该模型输出代表物体边界框坐标的四个维度。
def create_vit_object_detector(input_shape,patch_size,num_patches,projection_dim,num_heads,transformer_units,transformer_layers,mlp_head_units,
):inputs = keras.Input(shape=input_shape)# Create patchespatches = Patches(patch_size)(inputs)# Encode patchesencoded_patches = PatchEncoder(num_patches, projection_dim)(patches)# Create multiple layers of the Transformer block.for _ in range(transformer_layers):# Layer normalization 1.x1 = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(encoded_patches)# Create a multi-head attention layer.attention_output = layers.MultiHeadAttention(num_heads=num_heads, key_dim=projection_dim, dropout=0.1)(x1, x1)# Skip connection 1.x2 = layers.Add()([attention_output, encoded_patches])# Layer normalization 2.x3 = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(x2)# MLPx3 = mlp(x3, hidden_units=transformer_units, dropout_rate=0.1)# Skip connection 2.encoded_patches = layers.Add()([x3, x2])# Create a [batch_size, projection_dim] tensor.representation = layers.LayerNormalization(epsilon=1e-6)(encoded_patches)representation = layers.Flatten()(representation)representation = layers.Dropout(0.3)(representation)# Add MLP.features = mlp(representation, hidden_units=mlp_head_units, dropout_rate=0.3)bounding_box = layers.Dense(4)(features) # Final four neurons that output bounding box# return Keras model.return keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=bounding_box)运行实验
def run_experiment(model, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size, num_epochs):optimizer = keras.optimizers.AdamW(learning_rate=learning_rate, weight_decay=weight_decay)# Compile model.model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=keras.losses.MeanSquaredError())checkpoint_filepath = "vit_object_detector.weights.h5"checkpoint_callback = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_filepath,monitor="val_loss",save_best_only=True,save_weights_only=True,)history = model.fit(x=x_train,y=y_train,batch_size=batch_size,epochs=num_epochs,validation_split=0.1,callbacks=[checkpoint_callback,keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor="val_loss", patience=10),],)return historyinput_shape = (image_size, image_size, 3) # input image shape
learning_rate = 0.001
weight_decay = 0.0001
batch_size = 32
num_epochs = 100
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2
projection_dim = 64
num_heads = 4
# Size of the transformer layers
transformer_units = [projection_dim * 2,projection_dim,
]
transformer_layers = 4
mlp_head_units = [2048, 1024, 512, 64, 32] # Size of the dense layershistory = []
num_patches = (image_size // patch_size) ** 2vit_object_detector = create_vit_object_detector(input_shape,patch_size,num_patches,projection_dim,num_heads,transformer_units,transformer_layers,mlp_head_units,
)# Train model
history = run_experiment(vit_object_detector, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size, num_epochs
)def plot_history(item):plt.plot(history.history[item], label=item)plt.plot(history.history["val_" + item], label="val_" + item)plt.xlabel("Epochs")plt.ylabel(item)plt.title("Train and Validation {} Over Epochs".format(item), fontsize=14)plt.legend()plt.grid()plt.show()plot_history("loss")演绎展示:
Epoch 1/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 9s 109ms/step - loss: 1.2097 - val_loss: 0.3468
Epoch 2/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.4260 - val_loss: 0.3102
Epoch 3/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.3268 - val_loss: 0.2727
Epoch 4/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.2815 - val_loss: 0.2391
Epoch 5/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.2290 - val_loss: 0.1735
Epoch 6/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 24ms/step - loss: 0.1870 - val_loss: 0.1055
Epoch 7/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.1401 - val_loss: 0.0610
Epoch 8/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.1122 - val_loss: 0.0274
Epoch 9/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0924 - val_loss: 0.0296
Epoch 10/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 24ms/step - loss: 0.0765 - val_loss: 0.0139
Epoch 11/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.0597 - val_loss: 0.0111
Epoch 12/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.0540 - val_loss: 0.0101
Epoch 13/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 24ms/step - loss: 0.0432 - val_loss: 0.0053
Epoch 14/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 24ms/step - loss: 0.0380 - val_loss: 0.0052
Epoch 15/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.0334 - val_loss: 0.0030
Epoch 16/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 25ms/step - loss: 0.0283 - val_loss: 0.0021
Epoch 17/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 24ms/step - loss: 0.0228 - val_loss: 0.0012
Epoch 18/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0244 - val_loss: 0.0017
Epoch 19/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0195 - val_loss: 0.0016
Epoch 20/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0189 - val_loss: 0.0020
Epoch 21/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0191 - val_loss: 0.0019
Epoch 22/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0174 - val_loss: 0.0016
Epoch 23/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0157 - val_loss: 0.0020
Epoch 24/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0157 - val_loss: 0.0015
Epoch 25/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0139 - val_loss: 0.0023
Epoch 26/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0130 - val_loss: 0.0017
Epoch 27/10018/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0157 - val_loss: 0.0014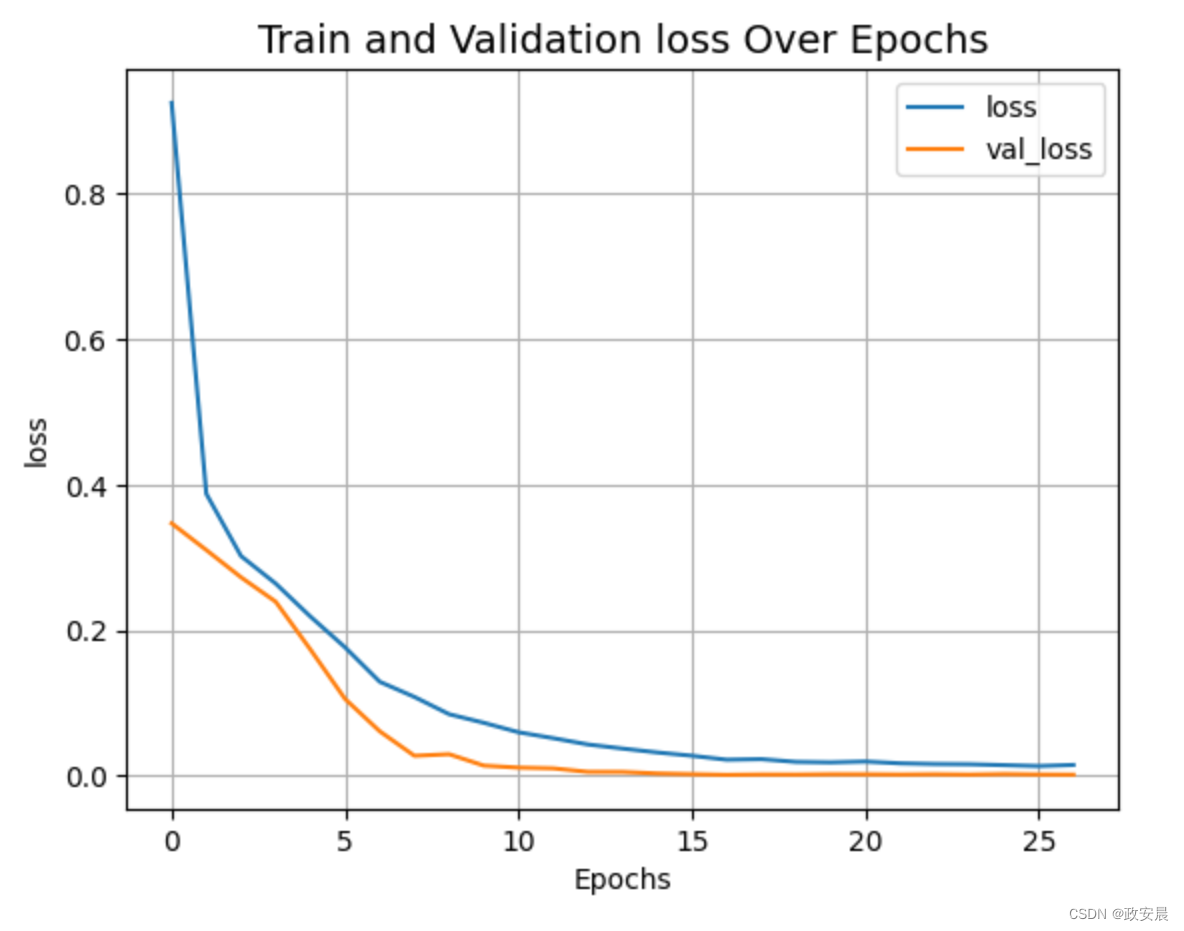
评估模型
import matplotlib.patches as patches# Saves the model in current path
vit_object_detector.save("vit_object_detector.keras")# To calculate IoU (intersection over union, given two bounding boxes)
def bounding_box_intersection_over_union(box_predicted, box_truth):# get (x, y) coordinates of intersection of bounding boxestop_x_intersect = max(box_predicted[0], box_truth[0])top_y_intersect = max(box_predicted[1], box_truth[1])bottom_x_intersect = min(box_predicted[2], box_truth[2])bottom_y_intersect = min(box_predicted[3], box_truth[3])# calculate area of the intersection bb (bounding box)intersection_area = max(0, bottom_x_intersect - top_x_intersect + 1) * max(0, bottom_y_intersect - top_y_intersect + 1)# calculate area of the prediction bb and ground-truth bbbox_predicted_area = (box_predicted[2] - box_predicted[0] + 1) * (box_predicted[3] - box_predicted[1] + 1)box_truth_area = (box_truth[2] - box_truth[0] + 1) * (box_truth[3] - box_truth[1] + 1)# calculate intersection over union by taking intersection# area and dividing it by the sum of predicted bb and ground truth# bb areas subtracted by the interesection area# return ioUreturn intersection_area / float(box_predicted_area + box_truth_area - intersection_area)i, mean_iou = 0, 0# Compare results for 10 images in the test set
for input_image in x_test[:10]:fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 15))im = input_image# Display the imageax1.imshow(im.astype("uint8"))ax2.imshow(im.astype("uint8"))input_image = cv2.resize(input_image, (image_size, image_size), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)input_image = np.expand_dims(input_image, axis=0)preds = vit_object_detector.predict(input_image)[0](h, w) = (im).shape[0:2]top_left_x, top_left_y = int(preds[0] * w), int(preds[1] * h)bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y = int(preds[2] * w), int(preds[3] * h)box_predicted = [top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y]# Create the bounding boxrect = patches.Rectangle((top_left_x, top_left_y),bottom_right_x - top_left_x,bottom_right_y - top_left_y,facecolor="none",edgecolor="red",linewidth=1,)# Add the bounding box to the imageax1.add_patch(rect)ax1.set_xlabel("Predicted: "+ str(top_left_x)+ ", "+ str(top_left_y)+ ", "+ str(bottom_right_x)+ ", "+ str(bottom_right_y))top_left_x, top_left_y = int(y_test[i][0] * w), int(y_test[i][1] * h)bottom_right_x, bottom_right_y = int(y_test[i][2] * w), int(y_test[i][3] * h)box_truth = top_left_x, top_left_y, bottom_right_x, bottom_right_ymean_iou += bounding_box_intersection_over_union(box_predicted, box_truth)# Create the bounding boxrect = patches.Rectangle((top_left_x, top_left_y),bottom_right_x - top_left_x,bottom_right_y - top_left_y,facecolor="none",edgecolor="red",linewidth=1,)# Add the bounding box to the imageax2.add_patch(rect)ax2.set_xlabel("Target: "+ str(top_left_x)+ ", "+ str(top_left_y)+ ", "+ str(bottom_right_x)+ ", "+ str(bottom_right_y)+ "\n"+ "IoU"+ str(bounding_box_intersection_over_union(box_predicted, box_truth)))i = i + 1print("mean_iou: " + str(mean_iou / len(x_test[:10])))
plt.show()演绎展示:
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 1s/step1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 2ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 2ms/step 1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 1ms/step
mean_iou: 0.9092338486331416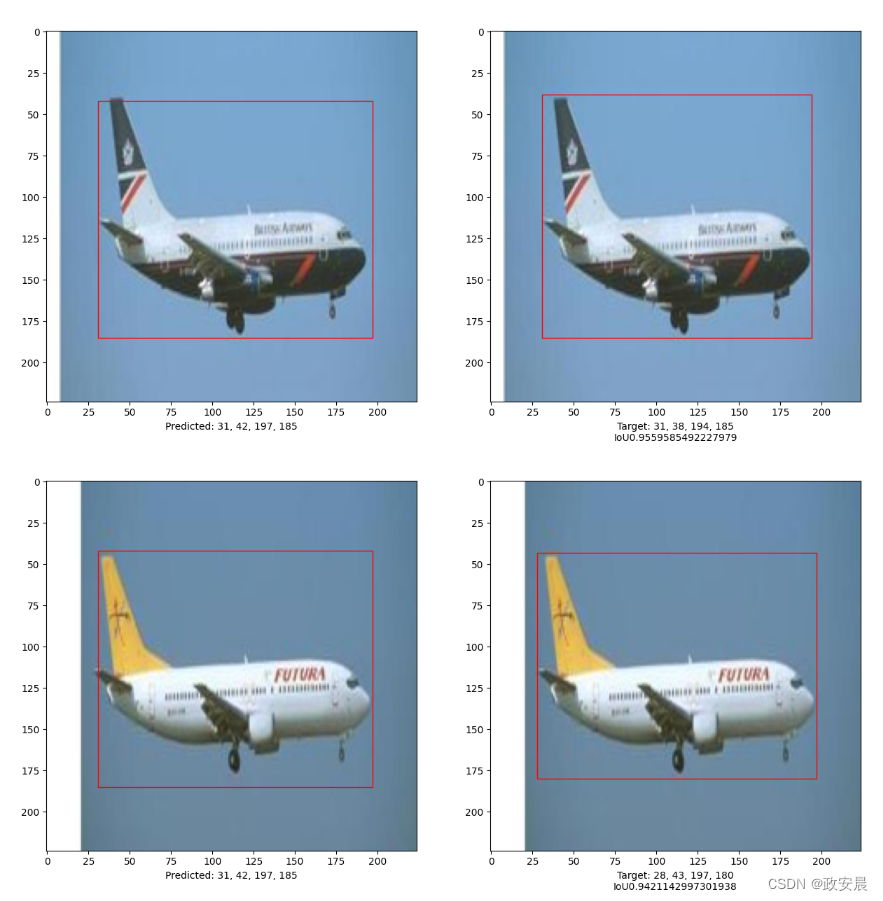
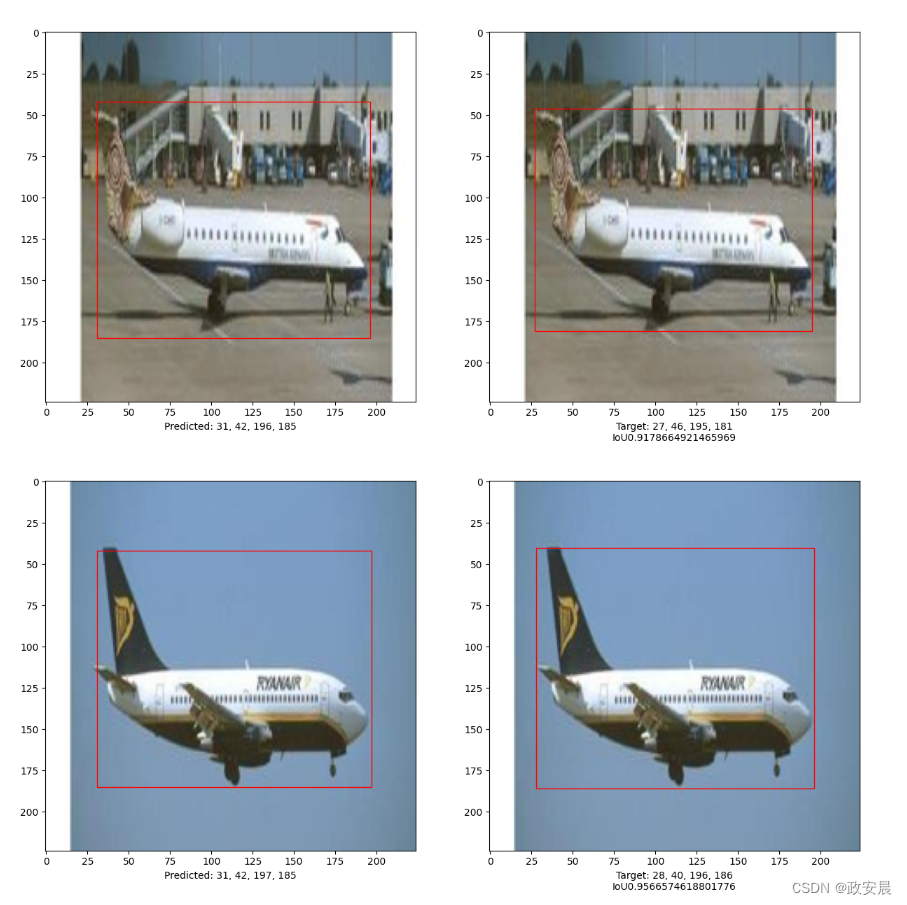



这个例子表明,可以训练一个纯变换器来预测给定图像中物体的边界框,从而将变换器的应用扩展到物体检测任务中。通过调整超参数和预训练,该模型还能得到进一步改进。
这篇关于政安晨:【Keras机器学习示例演绎】(五)—— 利用视觉变换器进行物体检测的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




