本文主要是介绍YOLOv9改进策略 | 损失函数篇 | EIoU、SIoU、WIoU、DIoU、FocusIoU等二十余种损失函数,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、本文介绍
这篇文章介绍了YOLOv9的重大改进,特别是在损失函数方面的创新。它不仅包括了多种IoU损失函数的改进和变体,如SIoU、WIoU、GIoU、DIoU、EIOU、CIoU,还融合了“Focus”思想,创造了一系列新的损失函数。这些组合形式的损失函数超过了二十余种,每种都针对特定的目标检测挑战进行优化。文章会详细探讨这些损失函数如何提高YOLOv9在各种检测任务中的性能,包括提升精度、加快收敛速度和增强模型对复杂场景的适应性。本文章主要是为了发最近新出的Inner思想改进的各种EIoU的文章服务,其中我经过实验在绝大多数下的效果都要比本文中提到的各种损失效果要好。

专栏地址:YOLOv9有效涨点专栏-持续复现各种顶会内容-有效涨点-全网改进最全的专栏
目录
一、本文介绍
二、各种损失函数的基本原理
2.1 交集面积和并集面积
2.2 IoU
2.3 SIoU
2.4 WioU
2.5 GIoU
2.6 DIoU
2.7 EIoU
2.8 CIoU
2.9 FocusLoss
三、核心代码
四、添加教程
4.1 步骤一
4.2 步骤二
4.3 步骤三
五、全文总结
二、各种损失函数的基本原理
2.1 交集面积和并集面积
在理解各种损失函数之前我们需要先来理解一下交集面积和并集面积,在数学中我们都学习过集合的概念,这里的交集和并集的概念和数学集合中的含义是一样的。

2.2 IoU
论文地址:IoU Loss for 2D/3D Object Detectio
适用场景:普通的IoU并没有特定的适用场景
概念: 测量预测边界框和真实边界框之间的重叠度(最基本的边界框损失函数,后面的都是居于其进行计算)。
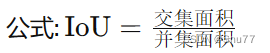
2.3 SIoU
论文地址:SIoU: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:适用于需要高精度边界框对齐的场景,如精细的物体检测和小目标检测。
概念: SIoU损失通过融入角度考虑和规模敏感性,引入了一种更为复杂的边界框回归方法,解决了以往损失函数的局限性,SIoU损失函数包含四个组成部分:角度损失、距离损失、形状损失和第四个未指定的组成部分。通过整合这些方面,从而实现更好的训练速度和预测准确性。

2.4 WioU
论文地址:WIoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism
适用场景:适用于需要动态调整损失焦点的情况,如不均匀分布的目标或不同尺度的目标检测。
概念:引入动态聚焦机制的IoU变体,旨在改善边界框回归损失。
![]()
2.5 GIoU
论文地址:GIoU: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:适合处理有重叠和非重叠区域的复杂场景,如拥挤场景的目标检测。
概念: 在IoU的基础上考虑非重叠区域,以更全面评估边界框

2.6 DIoU
论文地址:DIoU: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:适用于需要快速收敛和精确定位的任务,特别是在边界框定位精度至关重要的场景。
概念:结合边界框中心点之间的距离和重叠区域。

2.7 EIoU
论文地址:EIoU:Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression
适用场景:可用于需要进一步优化边界框对齐和形状相似性的高级场景。
概念:EIoU损失函数的核心思想在于提高边界框回归的准确性和效率。它通过以下几个方面来优化目标检测:
1. 增加中心点距离损失:通过最小化预测框和真实框中心点之间的距离,提高边界框的定位准确性。
2. 考虑尺寸差异:通过惩罚宽度和高度的差异,EIoU确保预测框在形状上更接近真实框。
3. 结合最小封闭框尺寸:将损失函数与包含预测框和真实框的最小封闭框的尺寸相结合,从而使得损失更加敏感于对象的尺寸和位置。
EIoU损失函数在传统IoU基础上增加了这些考量,以期在各种尺度上都能获得更精确的目标定位,尤其是在物体大小和形状变化较大的场景中。
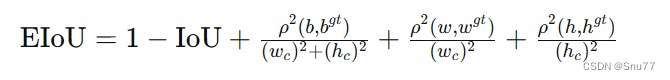
2.8 CIoU
论文地址:CIoU:Enhancing Geometric Factors in Model Learning
适用场景:适合需要综合考虑重叠区域、形状和中心点位置的场景,如复杂背景或多目标跟踪。
概念:综合考虑重叠区域、中心点距离和长宽比。

2.9 FocusLoss
论文地址:Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection
适用场景:适用于需要高精度边界框对齐的场景,如精细的物体检测和小目标检测。
Focal Loss由Kaiming He等人在论文《Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection》中提出,旨在解决在训练过程中正负样本数量极度不平衡的问题,尤其是在一些目标检测任务中,背景类别的样本可能远远多于前景类别的样本。
Focal Loss通过修改交叉熵损失,增加一个调整因子,这个因子降低了那些已经被正确分类的样本的损失值,使得模型的训练焦点更多地放在难以分类的样本上。这种方式特别有利于提升小目标或者在复杂背景中容易被忽视的目标的检测性能。简而言之,Focal Loss让模型“关注”(或“专注”)于学习那些对提高整体性能更为关键的样本。
三、核心代码
核心代码的使用方式看章节四!
def xyxy2xywh(x):"""Convert bounding box coordinates from (x1, y1, x2, y2) format to (x, y, width, height) format where (x1, y1) is thetop-left corner and (x2, y2) is the bottom-right corner.Args:x (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The input bounding box coordinates in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.Returns:y (np.ndarray | torch.Tensor): The bounding box coordinates in (x, y, width, height) format."""assert x.shape[-1] == 4, f"input shape last dimension expected 4 but input shape is {x.shape}"y = torch.empty_like(x) if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.empty_like(x) # faster than clone/copyy[..., 0] = (x[..., 0] + x[..., 2]) / 2 # x centery[..., 1] = (x[..., 1] + x[..., 3]) / 2 # y centery[..., 2] = x[..., 2] - x[..., 0] # widthy[..., 3] = x[..., 3] - x[..., 1] # heightreturn ydef bbox_iou(box1, box2, xywh=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, MDPIoU=False,Inner=False, Focaleriou=False, ShapeIoU=False, ratio=0.7, feat_h=640, SIoU=False, EIoU=False,WIoU=False, Focal=False, alpha=1, gamma=0.5,feat_w=640, eps=1e-7, d=0.00, u=0.95, scale=0.0):# Returns Intersection over Union (IoU) of box1(1,4) to box2(n,4)# Get the coordinates of bounding boxesif Inner:if not xywh:box1, box2 = xyxy2xywh(box1), xyxy2xywh(box2)(x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = box1.chunk(4, -1), box2.chunk(4, -1)b1_x1, b1_x2, b1_y1, b1_y2 = x1 - (w1 * ratio) / 2, x1 + (w1 * ratio) / 2, y1 - (h1 * ratio) / 2, y1 + (h1 * ratio) / 2b2_x1, b2_x2, b2_y1, b2_y2 = x2 - (w2 * ratio) / 2, x2 + (w2 * ratio) / 2, y2 - (h2 * ratio) / 2, y2 + (h2 * ratio) / 2# Intersection areainter = (b1_x2.minimum(b2_x2) - b1_x1.maximum(b2_x1)).clamp_(0) * \(b1_y2.minimum(b2_y2) - b1_y1.maximum(b2_y1)).clamp_(0)# Union Areaunion = w1 * h1 * ratio * ratio + w2 * h2 * ratio * ratio - inter + epselse:if xywh: # transform from xywh to xyxy(x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = box1.chunk(4, -1), box2.chunk(4, -1)w1_, h1_, w2_, h2_ = w1 / 2, h1 / 2, w2 / 2, h2 / 2b1_x1, b1_x2, b1_y1, b1_y2 = x1 - w1_, x1 + w1_, y1 - h1_, y1 + h1_b2_x1, b2_x2, b2_y1, b2_y2 = x2 - w2_, x2 + w2_, y2 - h2_, y2 + h2_else: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1.chunk(4, -1)b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2.chunk(4, -1)w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 + epsw2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 + eps# Intersection areainter = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)# Union Areaunion = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + epsself = Noneif scale:self = WIoU_Scale(1 - (inter / union))# IoUiou = inter / unionif Focaleriou:iou = ((iou - d) / (u - d)).clamp(0, 1) # default d=0.00,u=0.95if CIoU or DIoU or GIoU or EIoU or SIoU or WIoU:cw = b1_x2.maximum(b2_x2) - b1_x1.minimum(b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) widthch = b1_y2.maximum(b2_y2) - b1_y1.minimum(b2_y1) # convex heightif CIoU or DIoU or EIoU or SIoU or WIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1c2 = (cw ** 2 + ch ** 2) ** alpha + eps # convex diagonal squaredrho2 = (((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 + (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4) ** alpha # center dist ** 2if CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pytorch/blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * (torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)).pow(2)with torch.no_grad():alpha_ciou = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps))if Focal:return iou - (rho2 / c2 + torch.pow(v * alpha_ciou + eps, alpha)), torch.pow(inter / (union + eps),gamma) # Focal_CIoUelse:return iou - (rho2 / c2 + torch.pow(v * alpha_ciou + eps, alpha)) # CIoUelif EIoU:rho_w2 = ((b2_x2 - b2_x1) - (b1_x2 - b1_x1)) ** 2rho_h2 = ((b2_y2 - b2_y1) - (b1_y2 - b1_y1)) ** 2cw2 = torch.pow(cw ** 2 + eps, alpha)ch2 = torch.pow(ch ** 2 + eps, alpha)if Focal:return iou - (rho2 / c2 + rho_w2 / cw2 + rho_h2 / ch2), torch.pow(inter / (union + eps),gamma) # Focal_EIouelse:return iou - (rho2 / c2 + rho_w2 / cw2 + rho_h2 / ch2) # EIouelif SIoU:# SIoU Loss https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12740.pdfs_cw = (b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) * 0.5 + epss_ch = (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) * 0.5 + epssigma = torch.pow(s_cw ** 2 + s_ch ** 2, 0.5)sin_alpha_1 = torch.abs(s_cw) / sigmasin_alpha_2 = torch.abs(s_ch) / sigmathreshold = pow(2, 0.5) / 2sin_alpha = torch.where(sin_alpha_1 > threshold, sin_alpha_2, sin_alpha_1)angle_cost = torch.cos(torch.arcsin(sin_alpha) * 2 - math.pi / 2)rho_x = (s_cw / cw) ** 2rho_y = (s_ch / ch) ** 2gamma = angle_cost - 2distance_cost = 2 - torch.exp(gamma * rho_x) - torch.exp(gamma * rho_y)omiga_w = torch.abs(w1 - w2) / torch.max(w1, w2)omiga_h = torch.abs(h1 - h2) / torch.max(h1, h2)shape_cost = torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_w), 4) + torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_h), 4)if Focal:return iou - torch.pow(0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost) + eps, alpha), torch.pow(inter / (union + eps), gamma) # Focal_SIouelse:return iou - torch.pow(0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost) + eps, alpha) # SIouelif ShapeIoU:# Shape-Distance #Shape-Distance #Shape-Distance #Shape-Distance #Shape-Distance #Shape-Distance #Shape-Distanceww = 2 * torch.pow(w2, scale) / (torch.pow(w2, scale) + torch.pow(h2, scale))hh = 2 * torch.pow(h2, scale) / (torch.pow(w2, scale) + torch.pow(h2, scale))cw = torch.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex widthch = torch.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex heightc2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squaredcenter_distance_x = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2) / 4center_distance_y = ((b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4center_distance = hh * center_distance_x + ww * center_distance_ydistance = center_distance / c2# Shape-Shape #Shape-Shape #Shape-Shape #Shape-Shape #Shape-Shape #Shape-Shape #Shape-Shape #Shape-Shapeomiga_w = hh * torch.abs(w1 - w2) / torch.max(w1, w2)omiga_h = ww * torch.abs(h1 - h2) / torch.max(h1, h2)shape_cost = torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_w), 4) + torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_h), 4)return iou - distance - 0.5 * shape_costelif WIoU:if Focal:raise RuntimeError("WIoU do not support Focal.")elif scale:return getattr(WIoU_Scale, '_scaled_loss')(self), (1 - iou) * torch.exp((rho2 / c2)), iou # WIoU https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10051else:return iou, torch.exp((rho2 / c2)) # WIoU v1if Focal:return iou - rho2 / c2, torch.pow(inter / (union + eps), gamma) # Focal_DIoUelse:return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoUc_area = cw * ch + eps # convex areaif Focal:return iou - torch.pow((c_area - union) / c_area + eps, alpha), torch.pow(inter / (union + eps),gamma) # Focal_GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdfelse:return iou - torch.pow((c_area - union) / c_area + eps, alpha) # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdfelif MDPIoU:d1 = (b2_x1 - b1_x1) ** 2 + (b2_y1 - b1_y1) ** 2d2 = (b2_x2 - b1_x2) ** 2 + (b2_y2 - b1_y2) ** 2mpdiou_hw_pow = feat_h ** 2 + feat_w ** 2return iou - d1 / mpdiou_hw_pow - d2 / mpdiou_hw_pow # MPDIoUif Focal:return iou, torch.pow(inter / (union + eps), gamma) # Focal_IoUelse:return iou # IoU
四、添加教程
本文代码提到的MPDIoU需要在另一篇文章进行修改一些细节内容,本文的内容以及默认大家修改了我的MPDIoU(不修改会报错)!
另一篇文章的链接:YOLOv9改进策略 | 损失函数篇 | 利用真实边界框损失之MPDIoU助力YOLOv9精度更上一层楼
4.1 步骤一
第一步我们需要先找到如下的文件'utils/metrics.py'(这里以YOLOv9的修改损失函数为例,GELAN的需要修改'utils/loss_tal.py'修改教程一致,本文以YOLOv9的为例)。
我们找到如下图所示的代码!
4.2 步骤二
步骤二我们用章节三中的核心代码完全替换上面4.1红框圈出的整个函数(注意是整个函数红框仅仅是圈出了部分的代码因为代码太多不可能全部圈出来)!
修改完的样子如下图所示!

4.3 步骤三
我们上面相当于以及在项目内添加了Inner等损失函数,下一部我们教的是大家如何开启Inner的损失函数!
我们需要找到如下的文件'utils/loss_tal_dual.py' 按照图示进行修改!
class BboxLoss(nn.Module):def __init__(self, reg_max, use_dfl=False):super().__init__()self.reg_max = reg_maxself.use_dfl = use_dfldef forward(self, pred_dist, pred_bboxes, anchor_points, target_bboxes, target_scores, target_scores_sum, fg_mask,h=None, w=None):# iou lossbbox_mask = fg_mask.unsqueeze(-1).repeat([1, 1, 4]) # (b, h*w, 4)pred_bboxes_pos = torch.masked_select(pred_bboxes, bbox_mask).view(-1, 4)target_bboxes_pos = torch.masked_select(target_bboxes, bbox_mask).view(-1, 4)bbox_weight = torch.masked_select(target_scores.sum(-1), fg_mask).unsqueeze(-1)weight = target_scores.sum(-1)[fg_mask].unsqueeze(-1)iou = bbox_iou(pred_bboxes_pos, target_bboxes_pos, xywh=False, CIoU=False, Inner=True, Focaleriou=False,MDPIoU=False, ShapeIoU=True, EIoU=False, WIoU=False, DIoU=False, Focal=False, GIoU=False,feat_h=h, feat_w=w, alpha=1, gamma=0.5, eps=1e-7, d=0.00, u=0.95, scale=0.0)if type(iou) is tuple:if len(iou) == 2:# Focus Loss 时返回的是元组类型,进行额外处理loss_iou = ((1.0 - iou[0]) * iou[1].detach() * weight).sum() / target_scores_sumelse:loss_iou = (iou[0] * iou[1] * weight).sum() / target_scores_sumelse:# 正常的损失函数loss_iou = 1.0 - iouloss_iou *= bbox_weightloss_iou = loss_iou.sum() / target_scores_sum# 对应的那个设置为True就开启那个损失函数除了Inner之外其余的都只能单独使用只有Innner可以配合其它损失函数使用# dfl lossif self.use_dfl:dist_mask = fg_mask.unsqueeze(-1).repeat([1, 1, (self.reg_max + 1) * 4])pred_dist_pos = torch.masked_select(pred_dist, dist_mask).view(-1, 4, self.reg_max + 1)target_ltrb = bbox2dist(anchor_points, target_bboxes, self.reg_max)target_ltrb_pos = torch.masked_select(target_ltrb, bbox_mask).view(-1, 4)loss_dfl = self._df_loss(pred_dist_pos, target_ltrb_pos) * bbox_weightloss_dfl = loss_dfl.sum() / target_scores_sumelse:loss_dfl = torch.tensor(0.0).to(pred_dist.device)return loss_iou, loss_dfl, iou对应的那个设置为True就开启那个损失函数除了Inner和Focal之外其余的都只能单独使用只有Inner可以配合其它损失函数使用

到此我们就修改完成了,上面步骤三以及开启了对应的损失函数机制!
五、全文总结
到此本文的正式分享内容就结束了,在这里给大家推荐我的YOLOv9改进有效涨点专栏,本专栏目前为新开的,后期我会根据各种最新的前沿顶会进行论文复现,也会对一些老的改进机制进行补充,如果大家觉得本文帮助到你了,订阅本专栏(目前免费订阅,后期不迷路),关注后续更多的更新~
专栏地址:YOLOv9有效涨点专栏-持续复现各种顶会内容-有效涨点-全网改进最全的专栏

这篇关于YOLOv9改进策略 | 损失函数篇 | EIoU、SIoU、WIoU、DIoU、FocusIoU等二十余种损失函数的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



