本文主要是介绍Android T多屏多显——应用双屏间拖拽移动功能(更新中),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
功能以及显示效果简介
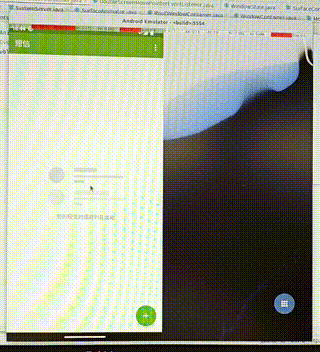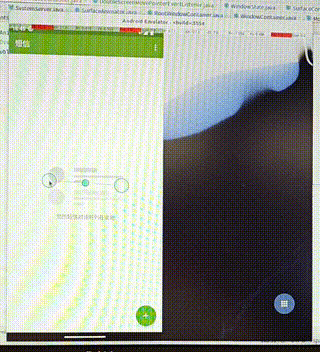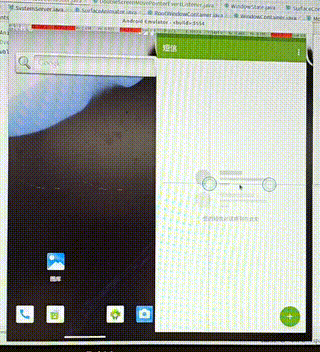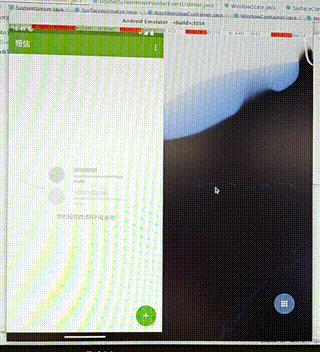
需求:在双屏显示中,把启动的应用从其中一个屏幕中移动到另一个屏幕中。
操作:通过双指按压应用使其移动,如果移动的距离过小,我们就不移动到另一屏幕,否则移动到另一屏。
功能分析
多屏中移动应用至另一屏本质就是Task的移动。
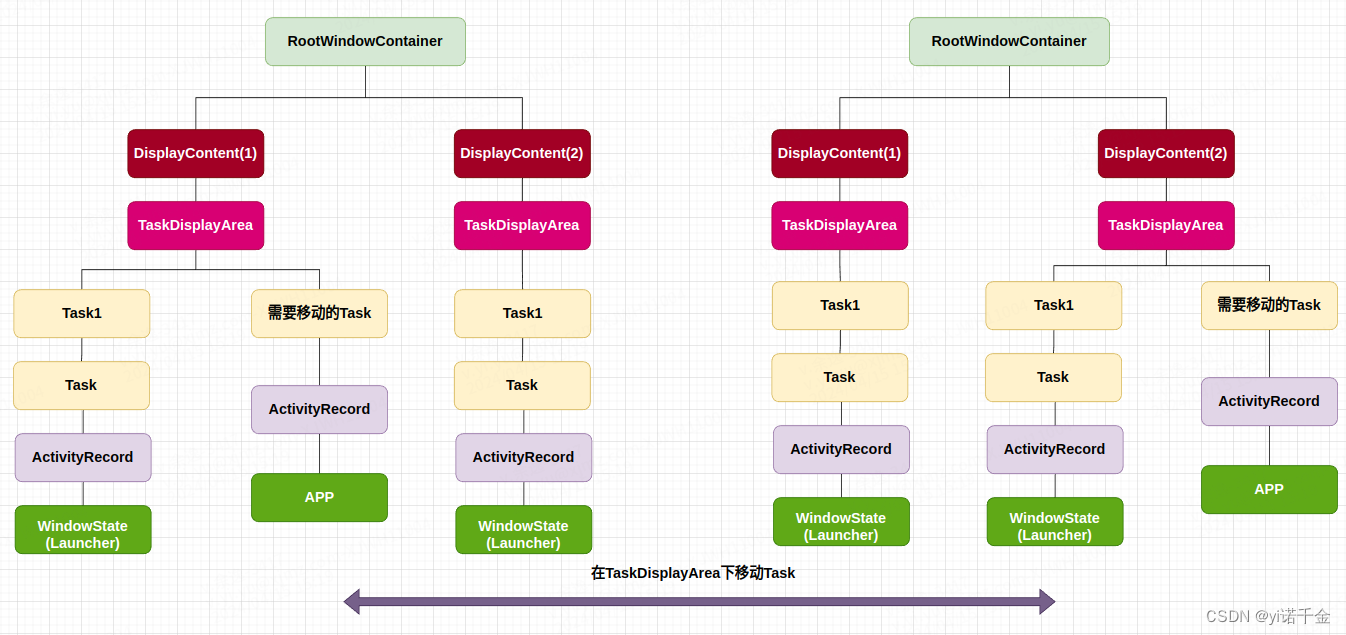
从窗口层级结构的角度来说,就是把Display1中的DefaultTaskDisplayArea上的Task,移动到Display2中的DefaultTaskDisplayArea上。
容器结构简化树状图如下所示:
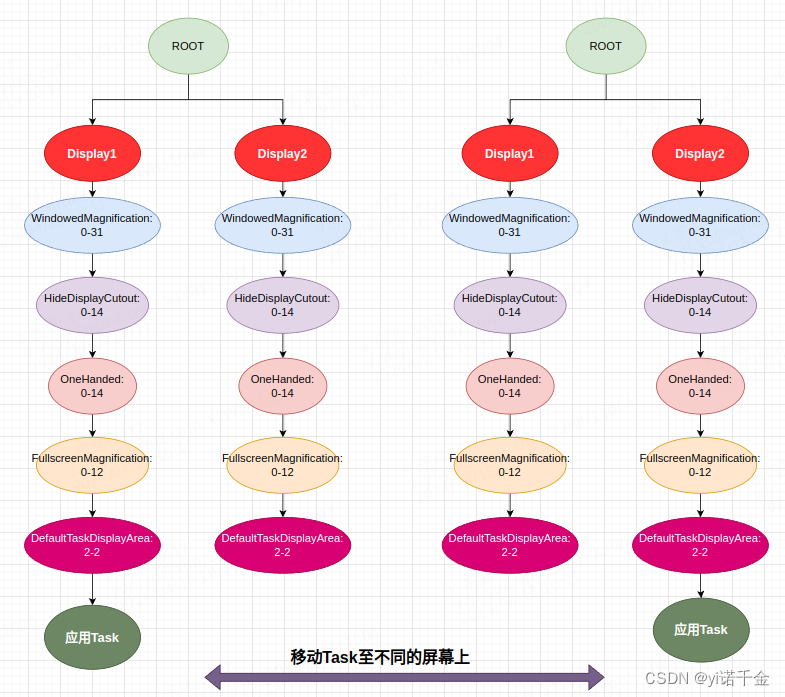
窗口层级结构简化树状图如下所示:
关键代码知识点
移动Task至另一屏幕
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/RootWindowContainer.java
/*** Move root task with all its existing content to specified display.** @param rootTaskId Id of root task to move.* @param displayId Id of display to move root task to.* @param onTop Indicates whether container should be place on top or on bottom.*/void moveRootTaskToDisplay(int rootTaskId, int displayId, boolean onTop) {//根据displayId获取DisplayContentfinal DisplayContent displayContent = getDisplayContentOrCreate(displayId);if (displayContent == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("moveRootTaskToDisplay: Unknown displayId="+ displayId);}//调用moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea方法moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea(rootTaskId, displayContent.getDefaultTaskDisplayArea(),onTop);}入参说明:
rootTaskId需要移动的Task的Id。可以通过Task中getRootTaskId()方法获取。
displayId需要移动到对应屏幕的Display的Id。可以通过DisplayContent中的getDisplayId()方法获取。
onTop移动后的Task是放在容器顶部还是底部。true表示顶部,false表示底部。
代码解释:
这个方法首先通过getDisplayContentOrCreate方法根据displayId获取DisplayContent,然后调用moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea方法进行移动。
其中传递参数displayContent.getDefaultTaskDisplayArea(),表示获取DisplayContent下面的DefaultTaskDisplayArea。
/*** Move root task with all its existing content to specified task display area.** @param rootTaskId Id of root task to move.* @param taskDisplayArea The task display area to move root task to.* @param onTop Indicates whether container should be place on top or on bottom.*/void moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea(int rootTaskId, TaskDisplayArea taskDisplayArea,boolean onTop) {//获取Taskfinal Task rootTask = getRootTask(rootTaskId);if (rootTask == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea: Unknown rootTaskId="+ rootTaskId);}final TaskDisplayArea currentTaskDisplayArea = rootTask.getDisplayArea();if (currentTaskDisplayArea == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea: rootTask=" + rootTask+ " is not attached to any task display area.");}if (taskDisplayArea == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("moveRootTaskToTaskDisplayArea: Unknown taskDisplayArea=" + taskDisplayArea);}if (currentTaskDisplayArea == taskDisplayArea) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Trying to move rootTask=" + rootTask+ " to its current taskDisplayArea=" + taskDisplayArea);}//把获取到的task重新挂载到了新display的taskDisplayArearootTask.reparent(taskDisplayArea, onTop);// Resume focusable root task after reparenting to another display area.//窗口或任务reparent之后,恢复焦点,激活相关任务的活动,并更新活动的可见性,以确保窗口管理器和用户界面的状态一致和正确。rootTask.resumeNextFocusAfterReparent();// TODO(multi-display): resize rootTasks properly if moved from split-screen.}
根据前面传递的TaskId获取到Task,在通过rootTask.reparent(taskDisplayArea, onTop);方法,把这个Task重新挂载到了新display的taskDisplayArea上。然后使用rootTask.resumeNextFocusAfterReparent();方法更新窗口焦点显示。
-
rootTask.reparent(taskDisplayArea, onTop);
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.javavoid reparent(TaskDisplayArea newParent, boolean onTop) {if (newParent == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Task can't reparent to null " + this);}if (getParent() == newParent) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Task=" + this + " already child of " + newParent);}//通过调用 canBeLaunchedOnDisplay 方法检查任务是否可以在新父区域所在的显示设备上启动。if (canBeLaunchedOnDisplay(newParent.getDisplayId())) {//实际执行reparent的操作。reparent(newParent, onTop ? POSITION_TOP : POSITION_BOTTOM);//如果Task是一个叶子Task(即没有子Task的Task)if (isLeafTask()) {//调用新父区域的 onLeafTaskMoved 方法来通知新父区域叶子Task已经移动。newParent.onLeafTaskMoved(this, onTop);}} else {Slog.w(TAG, "Task=" + this + " can't reparent to " + newParent);}}其中
reparent(newParent, onTop ? POSITION_TOP : POSITION_BOTTOM);实际执行reparent的操作。这里根据 onTop 的值来决定任务应该被放置在新父区域的顶部还是底部。我们再看看这方法的具体实现。
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowContainer.javavoid reparent(WindowContainer newParent, int position) {if (newParent == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("reparent: can't reparent to null " + this);}if (newParent == this) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not reparent to itself " + this);}final WindowContainer oldParent = mParent;if (mParent == newParent) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("WC=" + this + " already child of " + mParent);}// Collect before removing child from old parent, because the old parent may be removed if// this is the last child in it.//记录reparent的容器(this)相关信息,这里的this指的是移动的Task,newParent是新的TaskDisplayAreamTransitionController.collectReparentChange(this, newParent);// The display object before reparenting as that might lead to old parent getting removed// from the display if it no longer has any child.//获取之前的DisplayContent和新的DisplayContentfinal DisplayContent prevDc = oldParent.getDisplayContent();final DisplayContent dc = newParent.getDisplayContent();//设置 mReparenting 为 true,表示正在执行reparent操作。//然后从旧父容器中移除当前容器,并将其添加到新父容器的指定位置。//最后,将 mReparenting 设置为 false,表示reparent操作完成。mReparenting = true;oldParent.removeChild(this);newParent.addChild(this, position);mReparenting = false;// Relayout display(s)//标记新父容器对应的显示内容为需要布局。//如果新父容器和旧父容器的显示内容不同,//则触发显示内容改变的通知,并标记旧显示内容也需要布局。//最后,调用layoutAndAssignWindowLayersIfNeeded方法确保显示内容按需进行布局和窗口层级的分配。dc.setLayoutNeeded();if (prevDc != dc) {onDisplayChanged(dc);prevDc.setLayoutNeeded();}getDisplayContent().layoutAndAssignWindowLayersIfNeeded();// Send onParentChanged notification here is we disabled sending it in setParent for// reparenting case.//处理窗口容器在父容器变更时的各种逻辑onParentChanged(newParent, oldParent);//处理窗口容器在不同父容器之间同步迁移的逻辑onSyncReparent(oldParent, newParent);} -
rootTask.resumeNextFocusAfterReparent();
代码路径:frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Task.javavoid resumeNextFocusAfterReparent() {//调整焦点adjustFocusToNextFocusableTask("reparent", true /* allowFocusSelf */,true /* moveDisplayToTop */);//恢复当前焦点任务的顶部活动mRootWindowContainer.resumeFocusedTasksTopActivities();// Update visibility of activities before notifying WM. This way it won't try to resize// windows that are no longer visible.//更新activities的可见性mRootWindowContainer.ensureActivitiesVisible(null /* starting */, 0 /* configChanges */,!PRESERVE_WINDOWS);}
这篇关于Android T多屏多显——应用双屏间拖拽移动功能(更新中)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






