本文主要是介绍【STL】list,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
1. list的使用
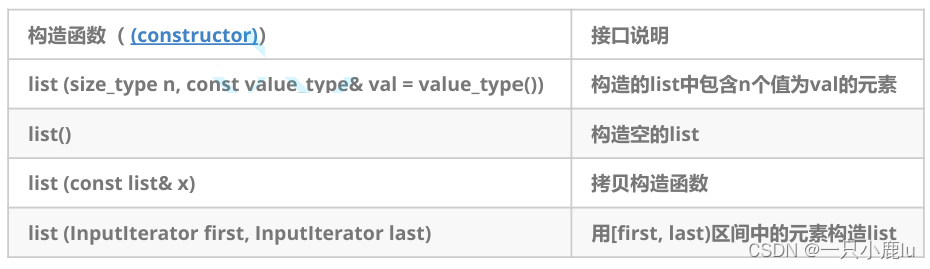
1.1 list的构造
1.2 list iterator的使用
1.3 list capacity
1.4 list element access
1.5 list modifiers
1.6 list的迭代器失效
2. list的模拟实现
3. list与vector的对比
1. list的使用
1.1 list的构造
1.2 list iterator的使用

1. begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动
2. rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动
1.3 list capacity

1.4 list element access

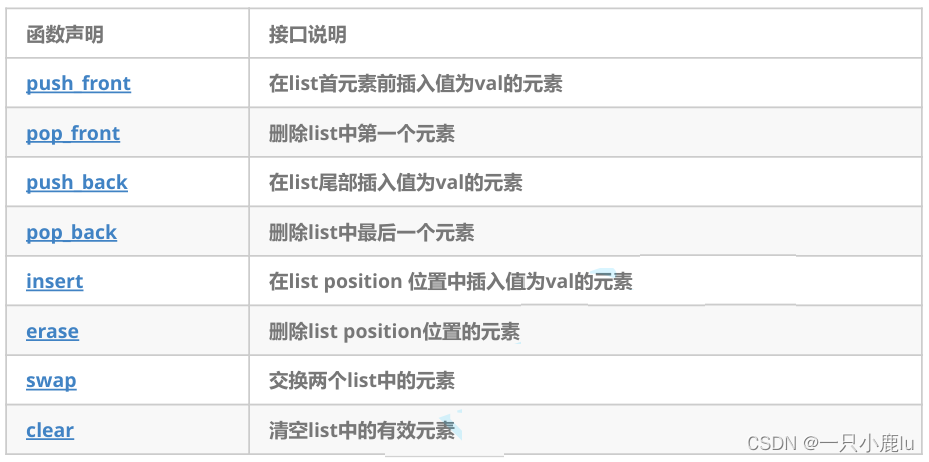
1.5 list modifiers
1.6 list的迭代器失效
迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无效,即该节 点被删除了。因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代 器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
2. list的模拟实现
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>namespace erdong
{template<class T>struct list_node{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;list_node(const T& val = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _val(val){}};// typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;// typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}};/*template<class T>struct __list_const_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;Node* _node;__list_const_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}const T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}__list_const_iterator<T>& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}__list_const_iterator<T> operator++(int){__list_const_iterator<T> tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it){return _node == it._node;}};*/template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;// 这么设计太冗余了,看看库里面如何设计的//typedef __list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;// 这样设计const迭代器是不行的,因为const迭代器期望指向内容不能修改// 这样设计是迭代器本身不能修改// typedef const __list_iterator<T> const_iterator;// const T* ptr1;// T* const ptr2;// 如何设计const迭代器?iterator begin(){//return _head->_next;return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return _head;//return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin() const{//return _head->_next;return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return _head;//return const_iterator(_head);}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_prev = _head;_head->_next = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt)//list(const list& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)//list& operator=(list lt){swap(lt);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}// pos位置之前插入iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;++_size;return newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;--_size;return next;}size_t size(){/*size_t sz = 0;iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){++sz;++it;}return sz;*/return _size;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void Print(const list<int>& lt){list<int>::const_iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){// (*it) += 1;cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}
}3. list与vector的对比

这篇关于【STL】list的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




