本文主要是介绍【Linux】第四十二站:线程局部存储与线程分离,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、线程的局部存储
1.实现多线程
如果我们想创建多线程,我们可以用下面的代码类似去实现
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 10struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);int i = 0;while(i < 10){cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(pthread_self()) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << endl;sleep(1);i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);sleep(1);}for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++){pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);}return 0;
}
运行结果如下图所示
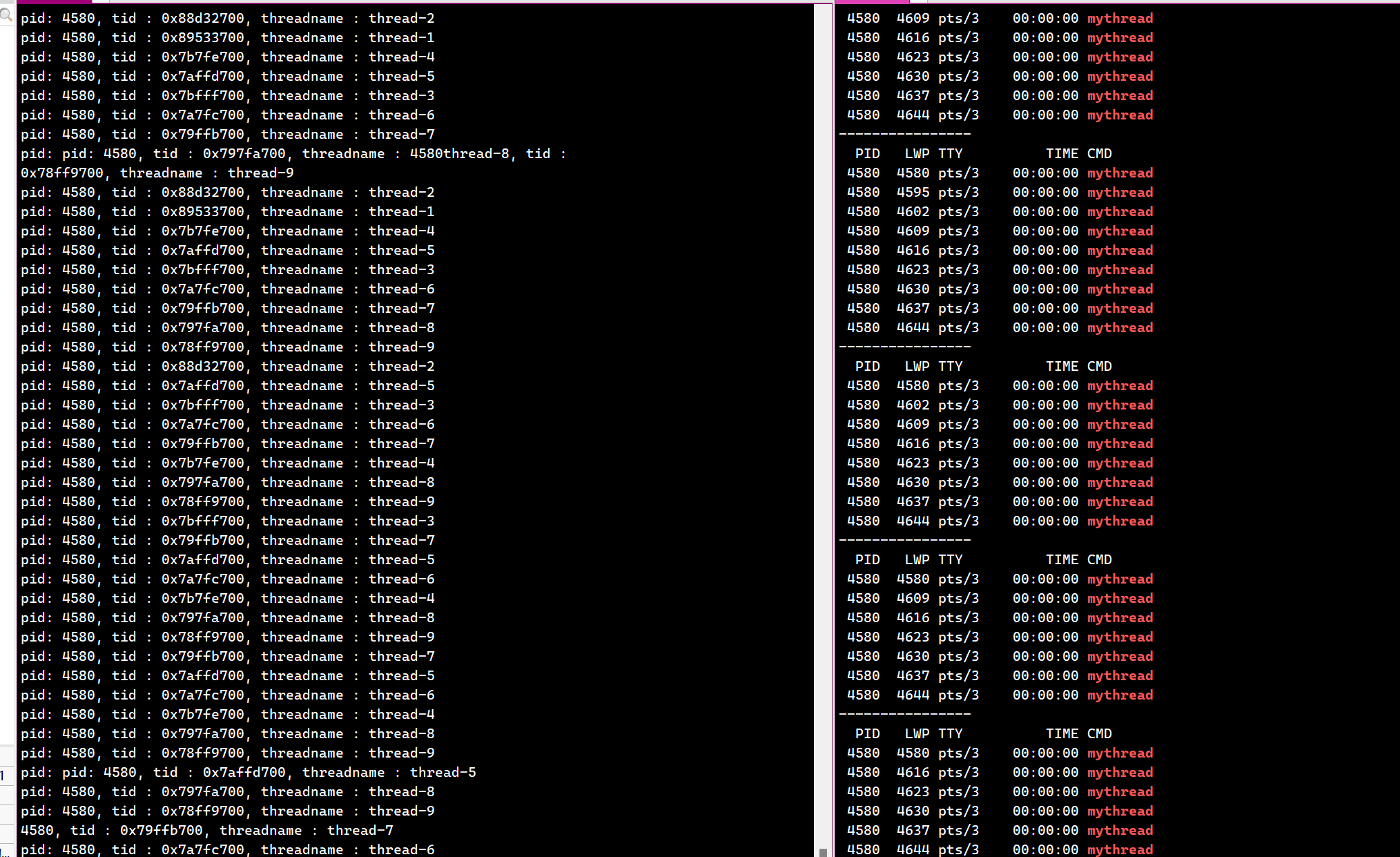
在这里我们就发现了一个问题:
所有的线程,执行的都是这个函数
一旦一个线程修改了数据,其他线程看到这个数据都会被修改
2.线程有独立的栈结构
当代码如下的时候
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 3struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{int test_i = 0;threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);int i = 0;while(i < 10){cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(pthread_self()) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << ", test_i: " << test_i << ", &test_i: " << toHex((pthread_t)&test_i) << endl;sleep(1);i++;test_i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);sleep(1);}for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++){pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);}return 0;
}
运行结果为:
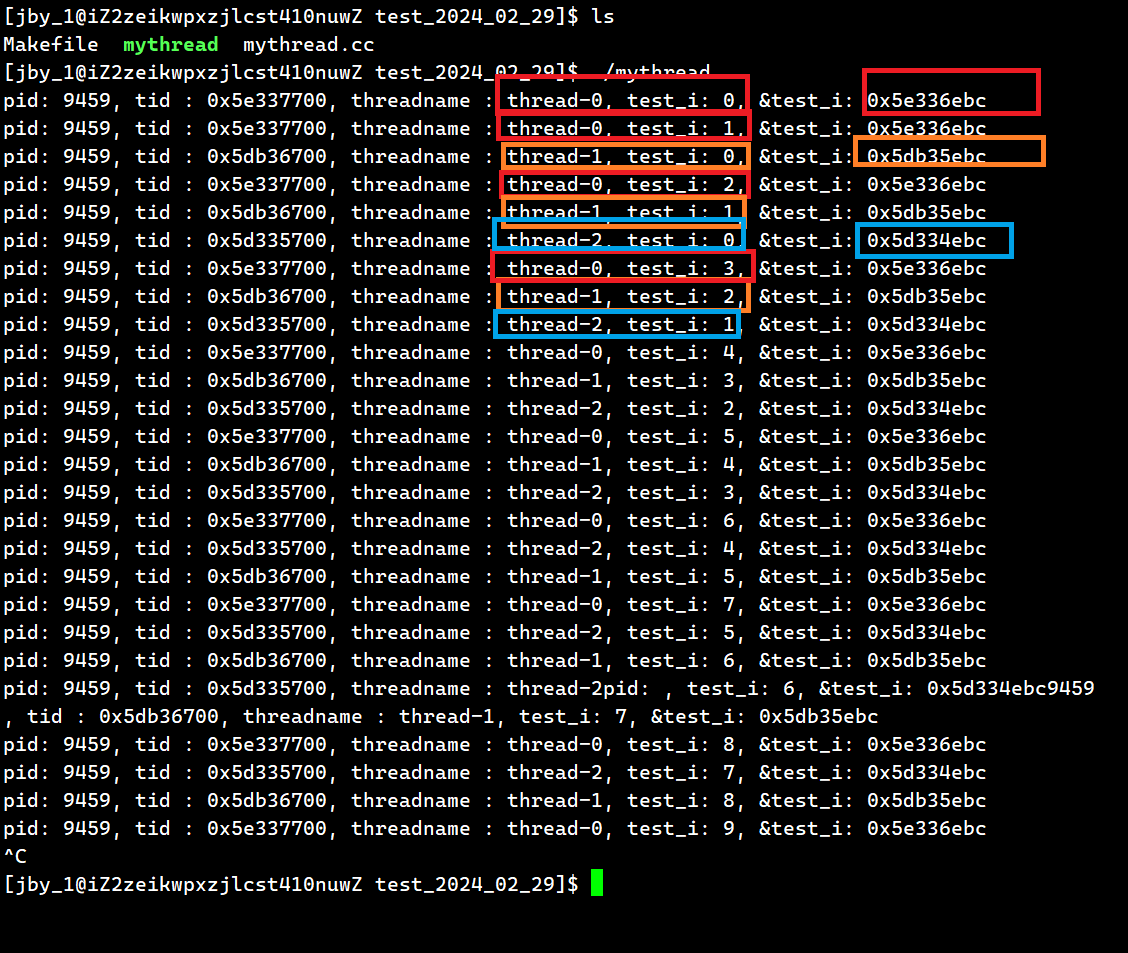
我们可以看到每一个线程的test_i都会独立的增长,并且每个test_i的地址都不一样
这是因为每一个线程都会有自己独立的栈结构。
3.线程之间没有秘密
那么如果我们主线程就想要访问上面线程1的变量,我们可以做到吗?当然可以做到,因为它也在同一个地址空间中。
就比如下面的代码就可以实现主线程访问线程2的变量
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 3int *p = NULL;struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{int test_i = 0;threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);if(td->threadname == "thread-2"){p = &test_i;}int i = 0;while(i < 10){cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(pthread_self()) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << ", test_i: " << test_i << ", &test_i: " << &test_i << endl;sleep(1);i++;test_i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);}sleep(1); //确保复制成功cout << "main thread get a thread local value, val: " << *p << ", &val: " << p << endl; for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++){pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);}return 0;
}
运行结果为:

所以其实在线程和线程当中没有秘密,只不过我们要求每一个线程有自己独立的栈,但是他们还在通一个地址空间中,线程的栈上的数据,也是可以被其他线程看到并且访问的。如果我们一个线程想要访问另一个线程的值,当然可以访问,只不过我们平时禁止这样做。
4.线程的局部存储
如下所示,代码是多线程访问同一个变量的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 3//int *p = NULL;int g_val = 100;struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{//int test_i = 0;threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);// if(td->threadname == "thread-2")// {// p = &test_i;// }int i = 0;while(i < 10){cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(pthread_self()) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << ", g_val: " << g_val << ", &g_val: " << &g_val << endl; // << ", test_i: " << test_i << ", &test_i: " << &test_i << endl;sleep(1);i++;g_val++;// test_i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);}sleep(1); //确保复制成功// cout << "main thread get a thread local value, val: " << *p << ", &val: " << p << endl; for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++){pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);}return 0;
}
运行结果为:

所以全局变量是被所有的线程看到并同时访问的。
这个g_val就是共享资源。
但是如果一个线程想要一个私有的全局变量呢?
所以我们可以下面这样做:在全局变量之前加上**__thread**
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 3//int *p = NULL;__thread int g_val = 100;struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{//int test_i = 0;threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);// if(td->threadname == "thread-2")// {// p = &test_i;// }int i = 0;while(i < 10){cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(pthread_self()) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << ", g_val: " << g_val << ", &g_val: " << &g_val << endl; // << ", test_i: " << test_i << ", &test_i: " << &test_i << endl;sleep(1);i++;g_val++;// test_i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);}sleep(1); //确保复制成功// cout << "main thread get a thread local value, val: " << *p << ", &val: " << p << endl; for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++){pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);}return 0;
}
运行结果为

这样的对一个变量加上__thread的,我们将这个称作线程的局部存储
而我们前面正好就说了:在线程的tcb中,就有一个线程的局部存储

所以我们可以明显看到,这个变量应该就在动态库中存储着。
这个__thread其实就是编译器编译时候的一个默认选项。
我们也可以直接从前面的两个图中的地址可以看出,没加这个选项的地址比较小(在静态区),加上这个选项地址比较大(处于堆栈之间的共享区)。
注意:这个__thread选项只能定义内置类型,不能用来修饰自定义类型
有了这个选项,对于某些只属于这个线程的变量,我们可以使用这个__thread来进行修饰,让它变为局部存储。这样的好处是可以不用频繁的去调用某些系统调用接口。
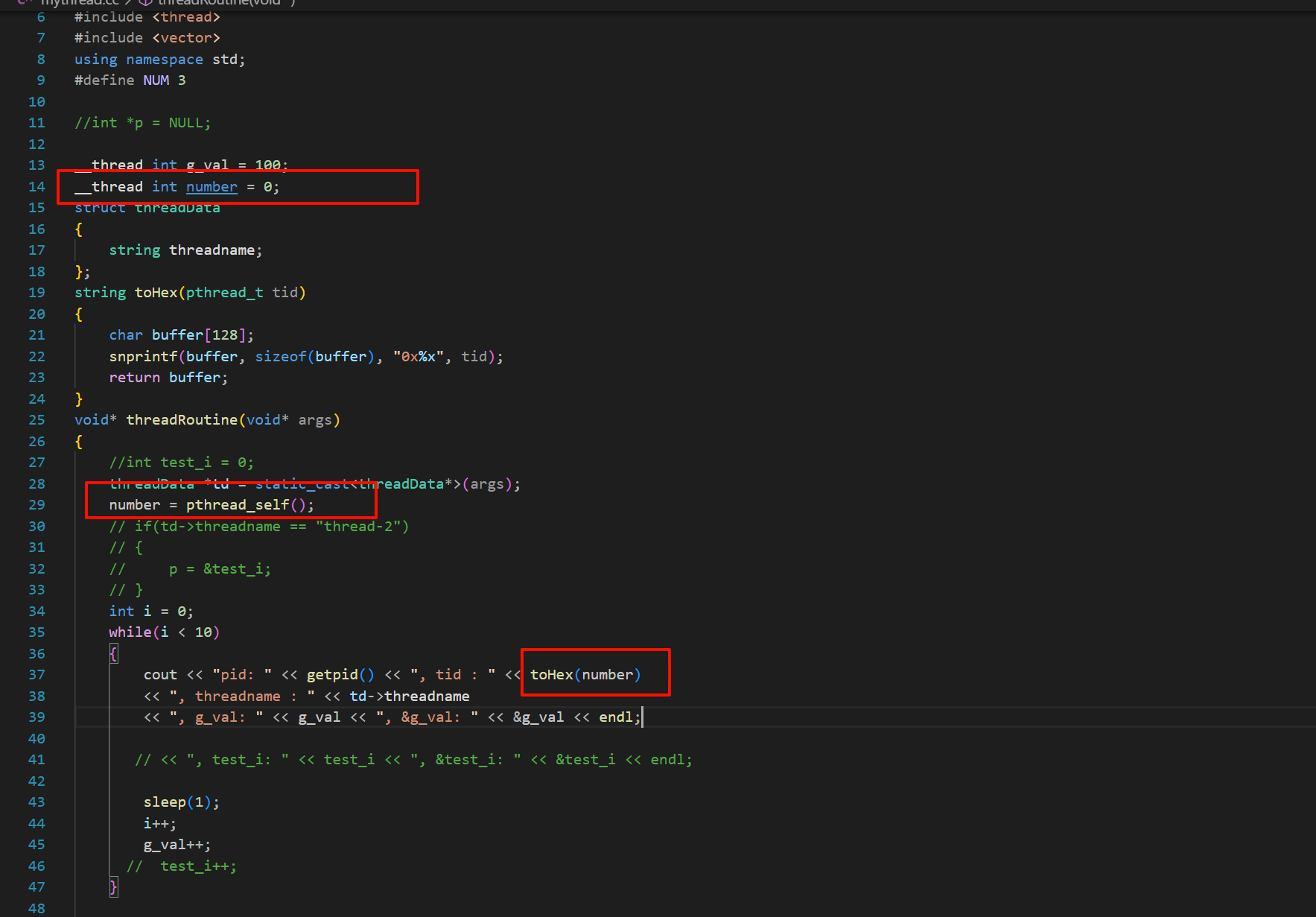
这样就实现了线程级别的全局变量,和其他线程互不干扰。
二、分离线程
- 默认情况下,新创建的线程是joinable的,线程退出后,需要对其进行pthread_join操作,否则无法释放资源,从而造成系统泄漏。
- 如果不关心线程的返回值,join是一种负担,这个时候,我们可以告诉系统,当线程退出时,自动释放线程资源
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
//Compile and link with -pthread.
这个分离接口既可以由主线程来做,也可以由其他新线程来做
我们可以先在join前先分离一下,看看是什么结果
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 3//int *p = NULL;__thread int g_val = 100;
__thread int number = 0;
struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{//int test_i = 0;threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);number = pthread_self();// if(td->threadname == "thread-2")// {// p = &test_i;// }int i = 0;while(i < 10){//cout << "number: " << number << ", pid: " << getpid() << endl;printf("number: 0x%x, pid: %d\n", number, getpid());//cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(number) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << ", g_val: " << g_val << ", &g_val: " << &g_val << endl; // << ", test_i: " << test_i << ", &test_i: " << &test_i << endl;sleep(1);i++;g_val++;// test_i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);}usleep(100000); //确保复制成功// cout << "main thread get a thread local value, val: " << *p << ", &val: " << p << endl; for(auto i : tids){pthread_detach(i);}for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++){int n = pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);printf("n = %d, who = 0x%x, why: %s\n", n , tids[i], strerror(n));}return 0;
}
运行结果为:

可见我们将线程给detach以后,再去join就不会成功了
我们也可以线程自己把自己分离掉
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 3//int *p = NULL;__thread int g_val = 100;
__thread int number = 0;
struct threadData
{string threadname;
};
string toHex(pthread_t tid)
{char buffer[128];snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "0x%x", tid);return buffer;
}
void* threadRoutine(void* args)
{pthread_detach(pthread_self());//int test_i = 0;threadData *td = static_cast<threadData*>(args);number = pthread_self();// if(td->threadname == "thread-2")// {// p = &test_i;// }int i = 0;while(i < 10){//cout << "number: " << number << ", pid: " << getpid() << endl;printf("number: 0x%x, pid: %d\n", number, getpid());//cout << "pid: " << getpid() << ", tid : " << toHex(number) << ", threadname : " << td->threadname << ", g_val: " << g_val << ", &g_val: " << &g_val << endl; // << ", test_i: " << test_i << ", &test_i: " << &test_i << endl;sleep(1);i++;g_val++;// test_i++;}delete td;return nullptr;
}void InitThreadData(threadData* td, int number)
{td->threadname = "thread-" + to_string(number);
}int main()
{vector<pthread_t> tids;for(int i = 0; i < NUM; i++){//注意这种方式不可以,因为都在主线程的栈中定义的变量。一旦for循环每循环一次//td也要随之销毁掉。这里传入的全部都是野指针了。// threadData td;// td.threadname = "";// td.tid = "";pthread_t tid;threadData *td = new threadData;InitThreadData(td, i);pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, threadRoutine, td);tids.push_back(tid);}usleep(100000); //确保复制成功// cout << "main thread get a thread local value, val: " << *p << ", &val: " << p << endl; // for(auto i : tids)// {// pthread_detach(i);// }for(int i = 0; i < tids.size(); i++) {int n = pthread_join(tids[i], nullptr);printf("n = %d, who = 0x%x, why: %s\n", n , tids[i], strerror(n));}return 0;
}
运行结果也是一样的
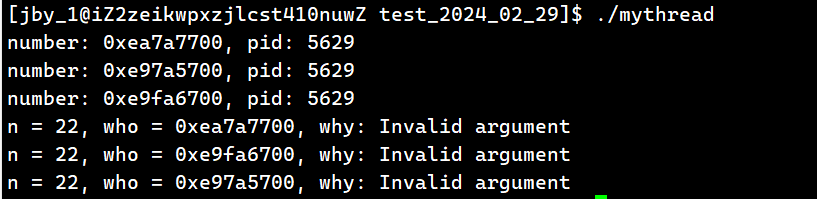
当线程内部的函数结束之后,会自动释放掉线程的资源
我们上面两个例子会发现一个问题,那就是分离线程应该会在线程跑完之后进行回收的。但是为什么还没有跑完就被回收了呢。这是因为我们在下面就有一个join,去等待了线程了。它在等待的发现已经被分离了。就不是阻塞式的等了,立马就出错返回了。出错返回后,这个for循环立刻就跑完了,跑完之后,主线成结束了,所以进程就结束了。所以虽然上面的线程还没有跑完,但是进程已经结束了,这些资源也就被释放了。
这里也告诉我们,即便我们的主线程将线程分离了,不用等待了,但是我们还是要自己去确保主线程是最后退出的,否则会出现一些问题。
所以线程是否被分离其实就是一个属性状态。它一定是要被存储的。所以线程分离其实就是将这个属性进行了修改
这篇关于【Linux】第四十二站:线程局部存储与线程分离的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!