本文主要是介绍deepxde一些接口理解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
第一个是PDE这个类
Args:geometry: Instance of ``Geometry``.pde: A global PDE or a list of PDEs. ``None`` if no global PDE.bcs: A boundary condition or a list of boundary conditions. Use ``[]`` if noboundary condition.num_domain (int): The number of training points sampled inside the domain.num_boundary (int): The number of training points sampled on the boundary.train_distribution (string): The distribution to sample training points. One ofthe following: "uniform" (equispaced grid), "pseudo" (pseudorandom), "LHS"(Latin hypercube sampling), "Halton" (Halton sequence), "Hammersley"(Hammersley sequence), or "Sobol" (Sobol sequence).anchors: A Numpy array of training points, in addition to the `num_domain` and`num_boundary` sampled points.exclusions: A Numpy array of points to be excluded for training.solution: The reference solution.num_test: The number of points sampled inside the domain for testing PDE loss.The testing points for BCs/ICs are the same set of points used for training.If ``None``, then the training points will be used for testing.auxiliary_var_function: A function that inputs `train_x` or `test_x` and outputsauxiliary variables.Warning:The testing points include points inside the domain and points on the boundary,and they may not have the same density, and thus the entire testing points maynot be uniformly distributed. As a result, if you have a reference solution(`solution`) and would like to compute a metric such as.. code-block:: pythonModel.compile(metrics=["l2 relative error"])then the metric may not be very accurate. To better compute a metric, you cansample the points manually, and then use ``Model.predict()`` to predict thesolution on thess points and compute the metric:.. code-block:: pythonx = geom.uniform_points(num, boundary=True)y_true = ...y_pred = model.predict(x)error= dde.metrics.l2_relative_error(y_true, y_pred)Attributes:train_x_all: A Numpy array of points for PDE training. `train_x_all` isunordered, and does not have duplication. If there is PDE, then`train_x_all` is used as the training points of PDE.train_x_bc: A Numpy array of the training points for BCs. `train_x_bc` isconstructed from `train_x_all` at the first step of training, by default itwon't be updated when `train_x_all` changes. To update `train_x_bc`, set itto `None` and call `bc_points`, and then update the loss function by``model.compile()``.num_bcs (list): `num_bcs[i]` is the number of points for `bcs[i]`.train_x: A Numpy array of the points fed into the network for training.`train_x` is ordered from BC points (`train_x_bc`) to PDE points(`train_x_all`), and may have duplicate points.train_aux_vars: Auxiliary variables that associate with `train_x`.test_x: A Numpy array of the points fed into the network for testing, orderedfrom BCs to PDE. The BC points are exactly the same points in `train_x_bc`.test_aux_vars: Auxiliary variables that associate with `test_x`.
翻译
参数:
geometry:“geometry”的实例。
pde:全局pde或pde列表。如果没有全局PDE,则为“None”。
bcs:一个边界条件或一系列边界条件。如果没有,请使用“[]”边界条件。
num_domain (int):在域内采样的训练点的数量。
num_boundary (int):在边界上采样的训练点的数量。
train_distribution (string):样本训练点的分布。之一“uniform”(等距网格)、“pseudo”(伪随机)、“LHS”(拉丁超立方体采样),“Halton”(Halton序列),“Hammersley”(Hammersley序列)或“Sobol”(Sobol序列)。
anchors:一个Numpy数组的训练点,除了' num_domain '和' num_boundary '采样点。
exclusions:一个Numpy数组,用于排除训练点。
solution:精确解
num_test:在域内采样用于测试PDE损耗的点数。
bc / ic的测试点是用于训练的同一组点。如果为“None”,则训练点将用于测试。
auxiliary_var_function:一个输入' train_x '或' test_x '并输出的函数
辅助变量。警告:
测试点包括域内点和边界点;
它们可能没有相同的密度,因此整个测试点可能
不是均匀分布的。因此,如果你有一个参考解
(“解决方案”),并希望计算一个metric,例如
. .python代码:Model.compile(metrics=["l2相对错误"])那么度量可能不是很准确。为了更好地计算度量,您可以
手动采样点,然后使用' ' Model.predict() ' '来预测
解这些点并计算度规:. .python代码:X = geom。uniform_points (num边界= True)
Y_true =…
Y_pred = model.predict(x)
错误= dde.metrics。l2_relative_error (y_true y_pred)属性:
train_x_all: PDE训练点的Numpy数组。“train_x_all”是
无序的,没有复制。如果存在PDE,那么
' train_x_all '作为PDE的训练点。
train_x_bc: bc训练点的Numpy数组。“train_x_bc”是
在训练的第一步由' train_x_all '构造,默认情况下为
当' train_x_all '改变时不会更新。要更新' train_x_bc ',请设置它
到' None '并调用' bc_points ',然后更新损失函数
' ' ' ' model.compile()。
Num_bcs (list): ' Num_bcs [i] '是' bcs[i] '的点数。
train_x:输入网络用于训练的点的Numpy数组。
' train_x '从BC点(' train_x_bc ')到PDE点排序
(' train_x_all '),并且可以有重复的点。
train_aux_vars:与' train_x '相关联的辅助变量。
test_x:输入网络用于测试的点的Numpy数组,有序
从bc到PDE。BC点与' train_x_bc '中的点完全相同。
test_aux_vars:与' test_x '相关的辅助变量。
同时之后要用到add_anchors这一部分的东西
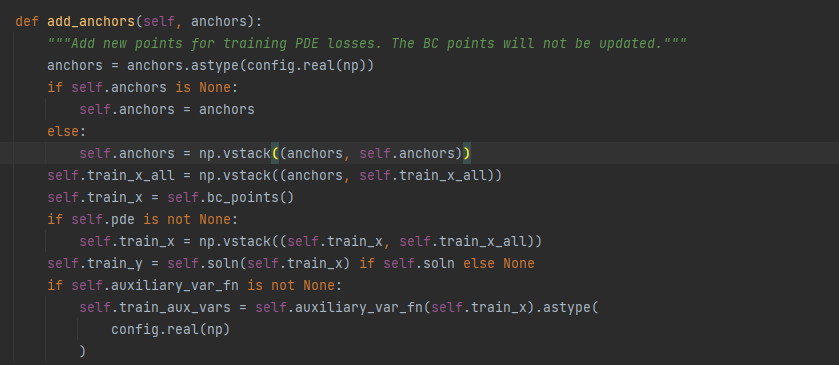 可以看出add_anchors是只会在域内部不断加入数据,但是对于bc的数据是不会改变的
可以看出add_anchors是只会在域内部不断加入数据,但是对于bc的数据是不会改变的
类似的:
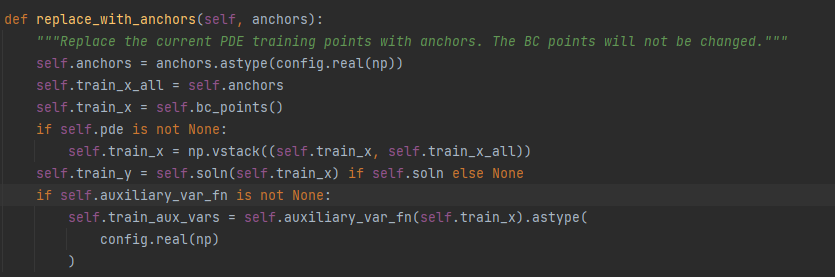 替换也是对于bc的数据不做改变
替换也是对于bc的数据不做改变
 这里看注释应该就是对数据进行了一种变形什么的
这里看注释应该就是对数据进行了一种变形什么的
 ):
):
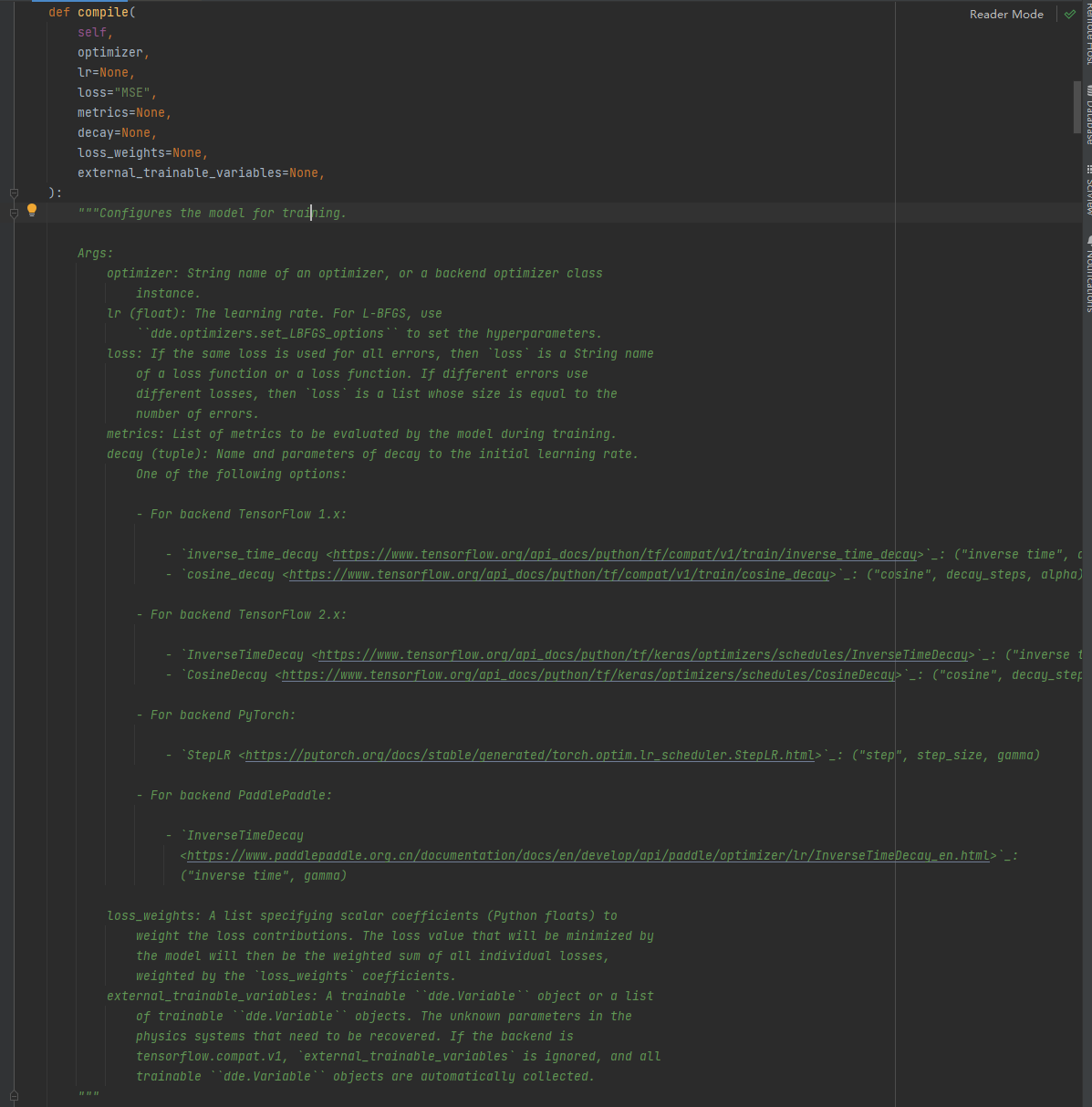
“”"配置训练模型。
参数:
optimizer:优化器或后端优化器类的字符串名称
实例。
lr (float):学习率。对于L-BFGS,使用
“dde.optimizers。set_LBFGS_options ’ ‘设置超参数。
loss:如果所有错误都使用相同的loss,那么’ loss '是一个字符串名称
一个损失函数或者一个损失函数。如果不同的错误使用
不同的损失,那么’损失’就是一个列表,它的大小等于
错误数。
metrics:训练期间模型要评估的指标列表。
衰变(元组):衰变到初始学习率的名称和参数。
以下选项之一:
-后端TensorFlow 1.x:
- ’ inverse_time_decay ’ _: (’ inverse time ', decay_steps, decay_rate)
- ’ cosine_decay ’ _: (’ cos ', decay_steps, alpha)
-后端TensorFlow 2.x:
- ’ InverseTimeDecay ’ _: (’ inverse time ', decay_steps, decay_rate)
- ’ CosineDecay ’ _: (’ cos ', decay_steps, alpha)
-后端PyTorch:
- ’ StepLR ’ _: (“step”, step_size, gamma)
-后端PaddlePaddle:
——“InverseTimeDecay
_:
(“逆时间”,伽马)
loss_weights:指定标量系数(Python浮点数)的列表对损失贡献进行加权。损失值将被最小化然后,模型将是所有个人损失的加权总和,由’ loss_weights ‘系数加权。
external_trainable_variables:一个可训练的dde。变量’ ‘对象或可训练的’ ’ dde列表。变量的对象。物理系统中需要恢复的未知参数。如果后端是tensorflow. pat.v1, ’ external_trainable_variables '将被忽略
可训练的“dde。自动收集变量“”对象。
PDEPointResampler
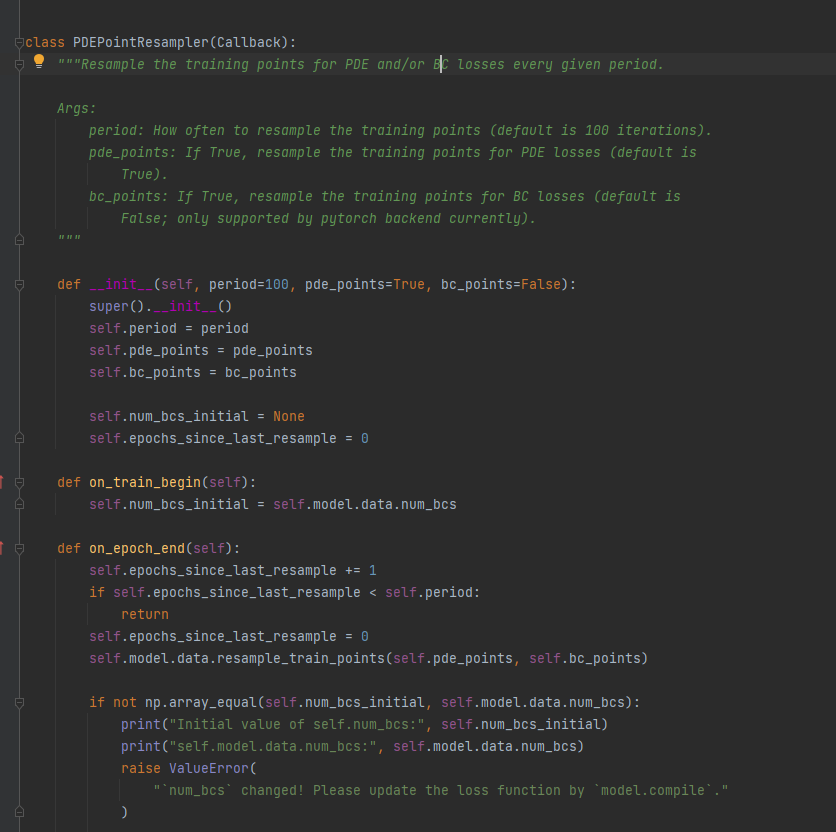 重采样的一个子类
重采样的一个子类
一个是重采样的周期
下面是bc和pde的是否进行重采样
关于deepxde的bc
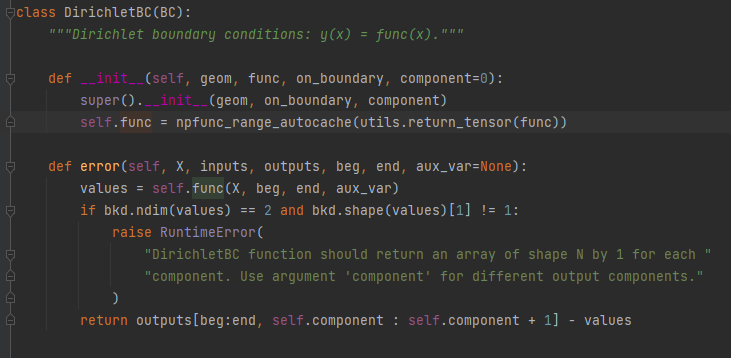
第一类边界条件:
给出未知函数在边界上的数值;
DirichletBC
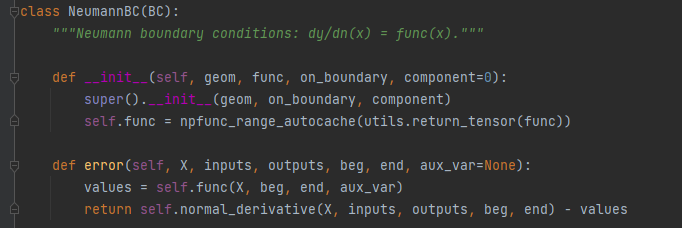
第二类边界条件:
给出未知函数在边界外法线的方向导数
以点的形式表示的边界
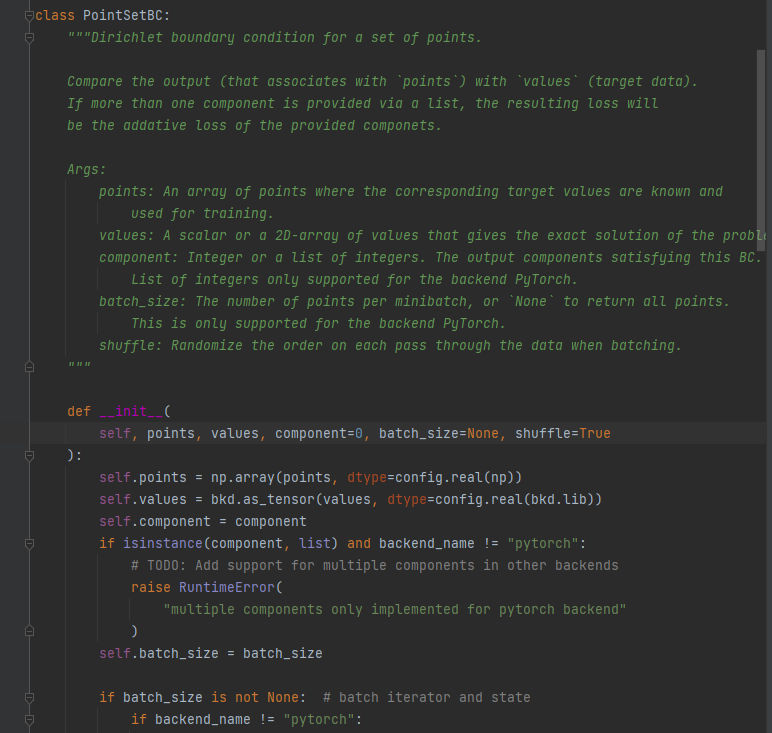
Compare the output (that associates with `points`) with `values` (target data).
If more than one component is provided via a list, the resulting loss will be the addative loss of the provided componets.Args:points: An array of points where the corresponding target values are known and used for training.values: A scalar or a 2D-array of values that gives the exact solution of the problem.component: Integer or a list of integers. The output components satisfying this BC.List of integers only supported for the backend PyTorch.batch_size: The number of points per minibatch, or `None` to return all points.This is only supported for the backend PyTorch.shuffle: Randomize the order on each pass through the data when batching.
将输出(与“点”相关联)与“值”(目标数据)进行比较。
如果通过列表提供了多个组件,则由此产生的损失将是所提供组件的附加损失。
参数:points:一组点,其中相应的目标值已知并用于训练。values:给出问题精确解的标量或二维值数组。组件:整数或整数列表。满足此 BC 的输出组件。仅后端 PyTorch 支持的整数列表。batch_size:每个小批量的点数,或返回所有点的“无”。这仅支持后端 PyTorch。shuffle:在批处理时随机化每次传递数据的顺序。
几个有用的issues
https://github.com/lululxvi/deepxde/issues/161
是否可以使用 DeepXDE 定义复杂的几何图形?例如,我可以读入一组代表机翼表面的点,而不是使用几何模块吗?
目前DeepXDE不能使用一组点来构建几何体。
1.定义复杂几何体的一种方法是使用CSG。
2.你也可以通过继承基类Geometry来定义你的几何体类。
3.几何体主要是用来生成训练点的。你可以只定义一个像立方体这样的 "假 "几何体,但完全不使用它。具体来说,你设置num_domain=0,num_boundary,并手动构建所有的点,并通过https://deepxde.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/deepxde.data.html#deepxde.data.pde.PDE 中的锚点传递。
https://deepxde.readthedocs.io/en/latest/modules/deepxde.data.html#deepxde.data.pde.PDE
https://github.com/lululxvi/deepxde/issues/64
我们能否在域上的某个特定位置或方向添加训练点,而不是在域上均匀或随机地添加?
例如:
在一个正方形类型的域的情况下。
应该只在直线y=x上取训练点,或者在正方形几何体内部取一个圆型区域。
这篇关于deepxde一些接口理解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





