本文主要是介绍RocketMQ源码解析——存储部分(1)消息存储的底层`MappedFile`,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1 关于`MappedByteBuffer`
- 2 关于`MapedFile`
- 2.1 属性分析
- 2.2 文件的生命周期方法
- 2.2.1 创建文件的`init`方法
- 2.2.2 文件的引用`hold`和释放`release`
- 2.2.3 清楚内存映射`cleanUp`和删除文件`destroy`
- 2.3 数据写入和提交方法分析
- 2.3.1 拼接消息的`appendMessage`方法
- 2.3.2 提交消息到缓冲的`commit`方法
- 2.3.3 刷新数据到文件的`flush`方法
- 2.5 读取数据`selectMappedBuffer`
在前面的一篇文章中说了 RocketMQ的文件系统的整体设计,在后面讲道理其在存储设计上面的一些优化。其中用到了内存映射的方式( 将磁盘上的物理文件直接映射到用户态的内存地址中)减少了传统IO将磁盘文件数据在操作系统内核地址空间的缓冲区和用户应用程序地址空间的缓冲区之间来回进行拷贝的性能开销。其实也就是我们说的零拷贝。关于零拷贝网上有很多讲解,后续也可以专门介绍一下零拷贝相关的。
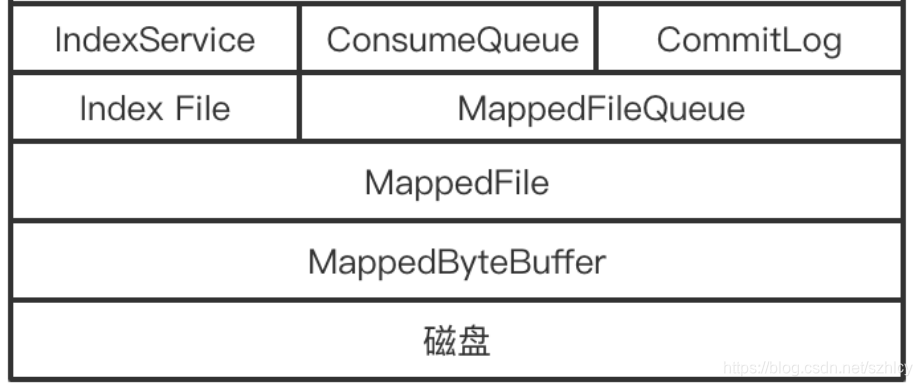
前面也说过RocketMQ的3大文件类型和2个小文件类型。这些文件的读写都是通过
java.nio.MappedByteBuffer类来进行完成的。而在RocketMQ中使用
MapedFile类来进一步的封装的。
MapedFile类提供了顺序写、随机读、内存数据刷盘、内存清理等与文件相关的服务。
1 关于MappedByteBuffer
MappedByteBuffer是jdk1.4版本的Java new IO简称nio中提出的。通过重要的类描述来简单的了解一下
/**
A direct byte buffer whose content is a memory-mapped region of a file.
Mapped byte buffers are created via the FileChannel.map method. This class extends the ByteBuffer class with operations that are specific to memory-mapped file regions.
*/
public abstract class MappedByteBuffer extends ByteBuffer{
}
这个类的作用就是,创建一个直接缓冲区而缓冲区的内容是内存中的文件的内容。可以通过直接操作缓冲区的内容,直接操作内存文件的内容。
这个类创建的方式是通过FileChannel.map方式进行创建的。
2 关于MapedFile
MapedFile是与RocketMQ的文件模块中最底层得到对象,提供了对文件记录的一些操作方法。后面就对这个类重要属性和方法进行分析。
2.1 属性分析
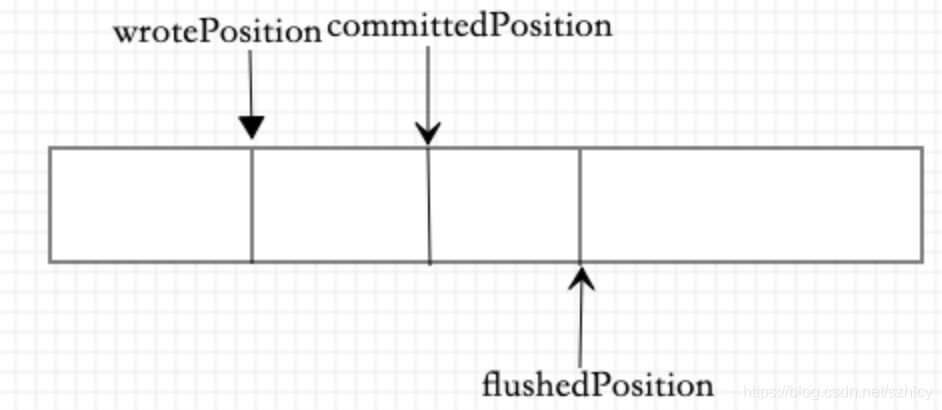
//pageCache的大小public static final int OS_PAGE_SIZE = 1024 * 4;//文件已使用的映射虚拟内存private static final AtomicLong TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY = new AtomicLong(0);//映射额文件个数private static final AtomicInteger TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES = new AtomicInteger(0);//已经写入的位置protected final AtomicInteger wrotePosition = new AtomicInteger(0);// 提交完成位置protected final AtomicInteger committedPosition = new AtomicInteger(0);//刷新完成位置private final AtomicInteger flushedPosition = new AtomicInteger(0);//文件大小protected int fileSize;//创建MappedByteBuffer用的protected FileChannel fileChannel;/*** Message will put to here first, and then reput to FileChannel if writeBuffer is not null.* 消息将首先放在这里,如果writeBuffer不为空,则再放到FileChannel。*/protected ByteBuffer writeBuffer = null;protected TransientStorePool transientStorePool = null;//文件名private String fileName;//文件开始offsetprivate long fileFromOffset;
这里需要额外讲解的是,几个表示位置的参数。wrotePosition,committedPosition,flushedPosition。大概的关系如下wrotePosition<=committedPosition<=flushedPosition<=fileSize
2.2 文件的生命周期方法
2.2.1 创建文件的init方法
init方法在创建MapedFile对象的时候会调用,在其构造器中调用的。主要作用就是创建对应的文件以及获取对应的文件的映射对象。
private void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize) throws IOException {//文件名this.fileName = fileName;//文件大小this.fileSize = fileSize;//创建文件this.file = new File(fileName);//根据文件的名称计算文件其实的偏移量this.fileFromOffset = Long.parseLong(this.file.getName());boolean ok = false;ensureDirOK(this.file.getParent());try {//创建读写类型的fileChannelthis.fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(this.file, "rw").getChannel();//获取写入类型的内存文件映射对象mappedByteBufferthis.mappedByteBuffer = this.fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileSize);//增加已经映射的虚拟内存TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY.addAndGet(fileSize);//已经映射文件数量+1TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES.incrementAndGet();ok = true;} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {log.error("create file channel " + this.fileName + " Failed. ", e);throw e;} catch (IOException e) {log.error("map file " + this.fileName + " Failed. ", e);throw e;} finally {if (!ok && this.fileChannel != null) {this.fileChannel.close();}}}
这里需要说明的一点是,文件名称是文件占用内存偏移量的起始位置,前面说过RocketMQ中消息存储的文件的命名是偏移量来进行命名的。
除了上面的初始化方法之外,还有一种初始化方法,这个方法是在使用临时存储池时,创建MapedFile对象会指定他的writeBuffer属性指向的是堆外内存。
public void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize,final TransientStorePool transientStorePool) throws IOException {init(fileName, fileSize);//从临时存储池中获取bufferthis.writeBuffer = transientStorePool.borrowBuffer();this.transientStorePool = transientStorePool;}
最终调用这个方法的逻辑在AllocateMappedFileService类中。
private boolean mmapOperation() {......//如果启用了临时存储池if (messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {try {mappedFile = ServiceLoader.load(MappedFile.class).iterator().next();mappedFile.init(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize(), messageStore.getTransientStorePool());} catch (RuntimeException e) {log.warn("Use default implementation.");mappedFile = new MappedFile(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize(), messageStore.getTransientStorePool());}} else {mappedFile = new MappedFile(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize());}......}
而这里的判断需要满足的是RocketMQ启用了临时存储池(transientStorePoolEnable参数为true,默认为false)并且刷盘模式为异步刷盘并且Broker是Master节点的时候。
2.2.2 文件的引用hold和释放release
在数据提交commit和刷新flush的时候都会跟这两个方法有关系。首先会获取文件的引用,在处理完之后释放。hold和release方法在MappedFile的父类ReferenceResource类中定义的
public synchronized boolean hold() {//是否可用if (this.isAvailable()) {//获取引用的数量,如果大于0说明存在引用,然后增加引用if (this.refCount.getAndIncrement() > 0) {return true;} else {//否则减少this.refCount.getAndDecrement();}}return false;}public void release() {//减少文件的引用long value = this.refCount.decrementAndGet();if (value > 0)return;//如果没有引用了,就可以释放对应的缓冲和内存映射synchronized (this) {this.cleanupOver = this.cleanup(value);}}
2.2.3 清楚内存映射cleanUp和删除文件destroy
public boolean cleanup(final long currentRef) {if (this.isAvailable()) {log.error("this file[REF:" + currentRef + "] " + this.fileName+ " have not shutdown, stop unmapping.");return false;}if (this.isCleanupOver()) {log.error("this file[REF:" + currentRef + "] " + this.fileName+ " have cleanup, do not do it again.");return true;}// 清除映射缓冲区=》clean(this.mappedByteBuffer);
// 减少映射文件所占虚拟内存TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY.addAndGet(this.fileSize * (-1));
// 改变映射文件数量TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES.decrementAndGet();log.info("unmap file[REF:" + currentRef + "] " + this.fileName + " OK");return true;}
//public boolean destroy(final long intervalForcibly) {
// =》删除引用this.shutdown(intervalForcibly);//已经清楚了文件的引用if (this.isCleanupOver()) {try {
// 关闭文件channelthis.fileChannel.close();log.info("close file channel " + this.fileName + " OK");long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 删除文件boolean result = this.file.delete();log.info("delete file[REF:" + this.getRefCount() + "] " + this.fileName+ (result ? " OK, " : " Failed, ") + "W:" + this.getWrotePosition() + " M:"+ this.getFlushedPosition() + ", "+ UtilAll.computeEclipseTimeMilliseconds(beginTime));} catch (Exception e) {log.warn("close file channel " + this.fileName + " Failed. ", e);}return true;} else {log.warn("destroy mapped file[REF:" + this.getRefCount() + "] " + this.fileName+ " Failed. cleanupOver: " + this.cleanupOver);}return false;}
2.3 数据写入和提交方法分析
2.3.1 拼接消息的appendMessage方法
在这个类中存在两种消息的拼接方法一种是供commitlog使用,传入消息内容(putMessage操作),由CommitLog按照规定的格式构造二进制信息并顺序写入ByteBuffer中。
public AppendMessageResult appendMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg, final AppendMessageCallback cb) {return appendMessagesInner(msg, cb);}public AppendMessageResult appendMessages(final MessageExtBatch messageExtBatch, final AppendMessageCallback cb) {return appendMessagesInner(messageExtBatch, cb);}
//public AppendMessageResult appendMessagesInner(final MessageExt messageExt, final AppendMessageCallback cb) {assert messageExt != null;assert cb != null;// 获取当前写的位置int currentPos = this.wrotePosition.get();if (currentPos < this.fileSize) {//这里的writeBuffer,如果在启动的时候配置了启用暂存池,这里的writeBuffer是堆外内存方式。获取byteBufferByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer != null ? writeBuffer.slice() : this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();byteBuffer.position(currentPos);AppendMessageResult result = null;if (messageExt instanceof MessageExtBrokerInner) {
// 消息序列化后组装映射的buffer=》result = cb.doAppend(this.getFileFromOffset(), byteBuffer, this.fileSize - currentPos, (MessageExtBrokerInner) messageExt);} else if (messageExt instanceof MessageExtBatch) {
// 批量消息序列化后组装映射的bufferresult = cb.doAppend(this.getFileFromOffset(), byteBuffer, this.fileSize - currentPos, (MessageExtBatch) messageExt);} else {return new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR);}this.wrotePosition.addAndGet(result.getWroteBytes());this.storeTimestamp = result.getStoreTimestamp();return result;}log.error("MappedFile.appendMessage return null, wrotePosition: {} fileSize: {}", currentPos, this.fileSize);return new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.UNKNOWN_ERROR);}
这里writeBuffer在没有使用暂存池的时候用的是内存映射获取的ByteBuffer对象。另外的一个拼接是直接将二进制信息通过fileChannel拼接到文件中
public boolean appendMessage(final byte[] data) {int currentPos = this.wrotePosition.get();if ((currentPos + data.length) <= this.fileSize) {try {//设置写的起始位置this.fileChannel.position(currentPos);//写入this.fileChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(data));} catch (Throwable e) {log.error("Error occurred when append message to mappedFile.", e);}this.wrotePosition.addAndGet(data.length);return true;}return false;}
2.3.2 提交消息到缓冲的commit方法
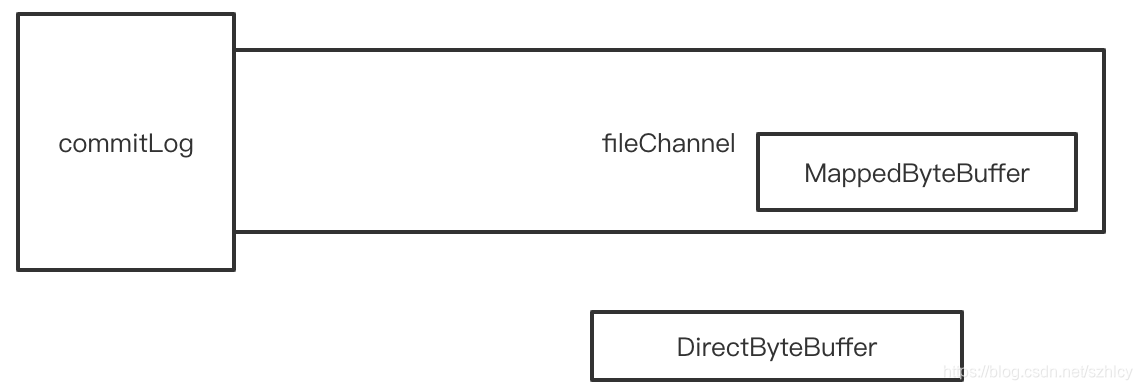
这里的commit方法的作用就是把前面写到缓冲中的数据提交到fileChannel中。这里存在两种情况,一种是使用堆外内存的缓冲,一种是使用内存映射的缓冲。两者的处理方式是不一样的。
public int commit(final int commitLeastPages) {/*** writeBuffer 为 null的情况下,说明没有使用临时存储池,使用的是mappedByteBuffer也就是内存映射的方式,* 直接写到映射区域中的,那么这个时候就不需要写入的fileChannel了。直接返回写入的位置作为已经提交的位置。** writeBuffer 不为 null,说明用的是临时存储池,使用的堆外内存,那么这个时候需要先把信息提交到fileChannel中*/if (writeBuffer == null) {//no need to commit data to file channel, so just regard wrotePosition as committedPosition.return this.wrotePosition.get();}//检查是否需要刷盘if (this.isAbleToCommit(commitLeastPages)) {//检查当前文件是不是有效,就是当前文件还存在引用if (this.hold()) {commit0(commitLeastPages);//引用次数减1this.release();} else {log.warn("in commit, hold failed, commit offset = " + this.committedPosition.get());}}// All dirty data has been committed to FileChannel.if (writeBuffer != null && this.transientStorePool != null && this.fileSize == this.committedPosition.get()) {this.transientStorePool.returnBuffer(writeBuffer);this.writeBuffer = null;}//获取已经刷新的位置return this.committedPosition.get();}
//protected void commit0(final int commitLeastPages) {//获取已经写入的数据的位置int writePos = this.wrotePosition.get();//获取上次提交的位置int lastCommittedPosition = this.committedPosition.get();//如果还有没有提交的数据,则进行写入if (writePos - this.committedPosition.get() > 0) {try {//获取ByteBufferByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer.slice();byteBuffer.position(lastCommittedPosition);byteBuffer.limit(writePos);this.fileChannel.position(lastCommittedPosition);this.fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);this.committedPosition.set(writePos);} catch (Throwable e) {log.error("Error occurred when commit data to FileChannel.", e);}}}
这里需要说明的就是堆外内存和内存映射的区别。使用堆外内存的时候需要先把对应的缓冲中的数据取出来然后保存到fileChannel中,而使用内存映射方式创建的MappedByteBuffer类型的缓冲是直接保存在fileChannel中的。所以不需要做别的处理。类似于下图的关系
2.3.3 刷新数据到文件的flush方法
flush方法比较简单,就是将fileChannel中的数据写入文件中。
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {//检查文件是否有效,也就是有引用,并添加引用if (this.hold()) {//获取写入的位置int value = getReadPosition();try {//We only append data to fileChannel or mappedByteBuffer, never both.//如果writeBuffer不为null,说明用了临时存储池,说明前面已经把信息写入了writeBuffer了,直接刷新到磁盘就可以。//fileChannel的位置不为0,说明已经设置了buffer进去了,直接刷新到磁盘if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {this.fileChannel.force(false);} else {//如果数据在mappedByteBuffer中,则刷新mappedByteBuffer数据到磁盘this.mappedByteBuffer.force();}} catch (Throwable e) {log.error("Error occurred when force data to disk.", e);}//设置已经刷新的值this.flushedPosition.set(value);//释放引用this.release();} else {log.warn("in flush, hold failed, flush offset = " + this.flushedPosition.get());this.flushedPosition.set(getReadPosition());}}return this.getFlushedPosition();}
2.5 读取数据selectMappedBuffer
读取数据的时候,有两种方式。一种是指定位置和读取的长度,一种是读取指定位置后的所有数据。
public SelectMappedBufferResult selectMappedBuffer(int pos, int size) {//获取提交的位置int readPosition = getReadPosition();//如果要读取的信息在已经提交的信息中,就进行读取if ((pos + size) <= readPosition) {//检查文件是否有效if (this.hold()) {//读取数据然后返回ByteBuffer byteBuffer = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();byteBuffer.position(pos);ByteBuffer byteBufferNew = byteBuffer.slice();byteBufferNew.limit(size);return new SelectMappedBufferResult(this.fileFromOffset + pos, byteBufferNew, size, this);} else {log.warn("matched, but hold failed, request pos: " + pos + ", fileFromOffset: "+ this.fileFromOffset);}} else {log.warn("selectMappedBuffer request pos invalid, request pos: " + pos + ", size: " + size+ ", fileFromOffset: " + this.fileFromOffset);}return null;}
//public SelectMappedBufferResult selectMappedBuffer(int pos) {//获取文件读取的位置int readPosition = getReadPosition();if (pos < readPosition && pos >= 0) {if (this.hold()) {//创建新的缓冲区ByteBuffer byteBuffer = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();byteBuffer.position(pos);//获取指定位置到最新提交的位置之间的数据int size = readPosition - pos;ByteBuffer byteBufferNew = byteBuffer.slice();byteBufferNew.limit(size);return new SelectMappedBufferResult(this.fileFromOffset + pos, byteBufferNew, size, this);}}return null;}
下一篇存储部分(2)对MappedFile进一步封装的MappedFileQueue
这篇关于RocketMQ源码解析——存储部分(1)消息存储的底层`MappedFile`的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





