本文主要是介绍【 10X summary report】怎么看?详细解读笔记,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
报告内容
在开始正式的分析之前,需要查看在对齐和计数过程中生成的任何总结统计信息。下图是由Cell Ranger工具创建的10X总结报告,在从10X scRNA-seq实验生成计数矩阵时会生成。

The left half of the report describes sequencing and mapping statistics. One thing to note is the “sequencing saturation”, which estimates the proportion of mRNA transcripts that has been sequenced. This is calculated by downsampling the mean number of reads per cell and obtaining the corresponding number of UMIs (nUMI). The relationship between the number of UMIs obtained against the number of reads is then extrapolated to the asymptote, which corresponds to 100% saturation. A low sequencing saturation implies that deeper sequencing will likely recover more UMIs. That said, some preliminary analysis should first be performed to determine if the current number of UMIs recovered is able to answer the biological questions of interest. Also, check that a high percentage of reads are mapped to the genome, which indicates low amounts of contamination.
The top-right portion of the report plots the nUMI captured in each droplet / barcode, with the droplets ordered in decreasing nUMI from left to right. On the left side of the plot, droplets have very high nUMI and are likely to contain cells. As we scan through the droplets towards the right, we eventually encounter a “knee point” where there is a drastic drop in the nUMI. This likely signifies a transition from observing cell-containing droplets to droplets containing cell debris or no cells at all. Droplets that are deemed by Cell Ranger to contain cells are coloured blue here and the algorithm tends to include slightly more cells beyond the plot shoulder. These cells with smaller nUMIs will have to be removed in the quality control step.
From the summary report, there is another important observation: the nUMI does not correspond to the number of reads per cell. Recall that this is because reads with the same UMI originated from a single mRNA molecule and is thus treated as a single UMI count . Thus, the number of counts i.e. nUMI is usually only a fraction (about 1/8 to 1/3) of the number of reads.
下图为本人使用CellRanger V5.2.0对语一个单细胞数据跑出的结果
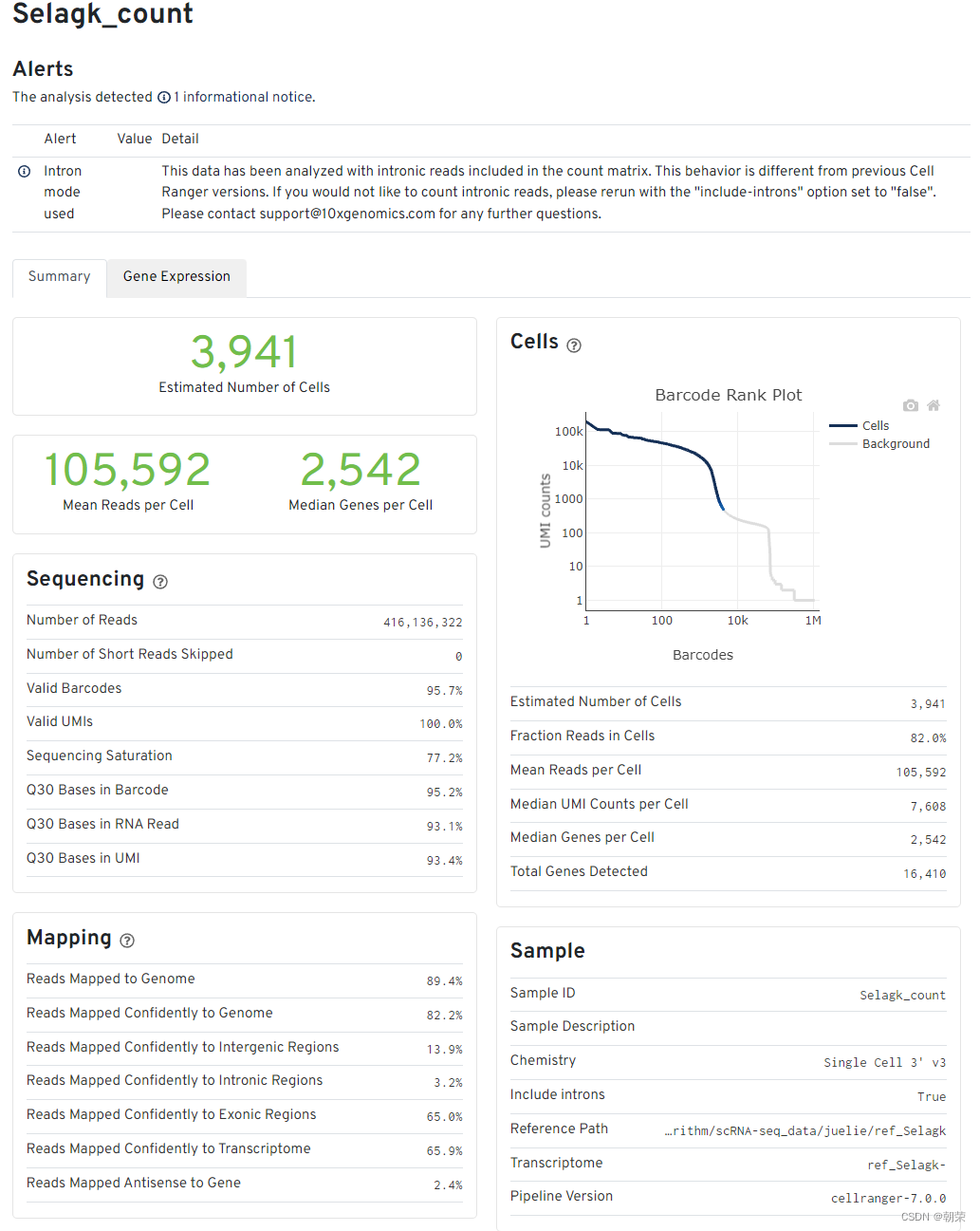
报告解读
细胞和基因数目的评估
- Estimated number of cells - 样本测到的细胞数
- Mean reads per cell - 每个细胞测到的平均reads
- Median genes per cell - 每个细胞基因数的中位数
Sequencing中
Number of reads - 测到的总read数目
Valid barcodes - UMI校正后匹配的UMI数量
Sequencing saturation:测序饱和度。一般60-80%比较合适(阈值范围可以适当调整,但是高于70%或80%左右绝对OK)。如果测到的细胞数多,但是每个细胞里面的平均reads数少,那么饱和度就不高,反之,饱和度高。但也不是越高越好,背后原理是抽样的原理,到达80%左右就可以代表整个样本了。
Q30 bases in barcode - 基于barcode的分数,大于30的比率
Q30 bases in RNA read - 基于RNA read的分数,大于30的比率
Q30 bases in UMI - 基于UMI的分数,大于30的比率
(认为要一般要大于65%,少于这个比例的话,这个页面会报错,)
Mapping结果
- Reads mapped to genome - 比对到选定基因组的reads
- Reands mapped confidently to genome - 仅仅比对到基因组的reads,如果一条reads既可以比对到外显子区又可以比对到非外显子区,那么算比对到了其中一个外显子区
- Reads mapped confidently to intergenic regions - 比对到基因组的基因间区域
- Reads mapped confidently to intronic regions - 比对到内含子区域
- Reads mapped confidently to exonic regions - 比对到外显子区域
- Reads mapped confidently to transcriptome - 比对到转录组的reads,这些读数可以用来UMI的计数
- Reads mapped antisense to gene - 比对到基因的相反的reads
细胞数目评估Cells图
横轴是barcodes,纵轴是UMI数量。通过barcode上的UMI标签分布来评估细胞数目,深蓝色代表细胞,灰色代表背景。
在前期磁珠(bead)与细胞形成油包水的结构过程中,会存在没有把细胞包进去的情况,这时候的油包水结构里面就只有磁珠和一些barcode的序列,而cDNA的碱基序列一般都是barcode碱基序列的10倍以上,就是由此来确定哪些是真实的细胞,哪些是background。
其他指标
- Estimated number of cells - 样本测到的细胞数
- Fraction reads in cells - valid-UMI的质量分数,代表与细胞相关的UMI可靠地比对到基因组,一般要在70%及以上,否则数据质量就不好
- Mean reads per cell - 每个细胞测到的平均reads
- Median genes per cell - 每个细胞的基因数中位数
- Total genes detected - 测到的总基因数,至少有一条UMI
- Median UMI counts per cell - 细胞UMI数量的中间值
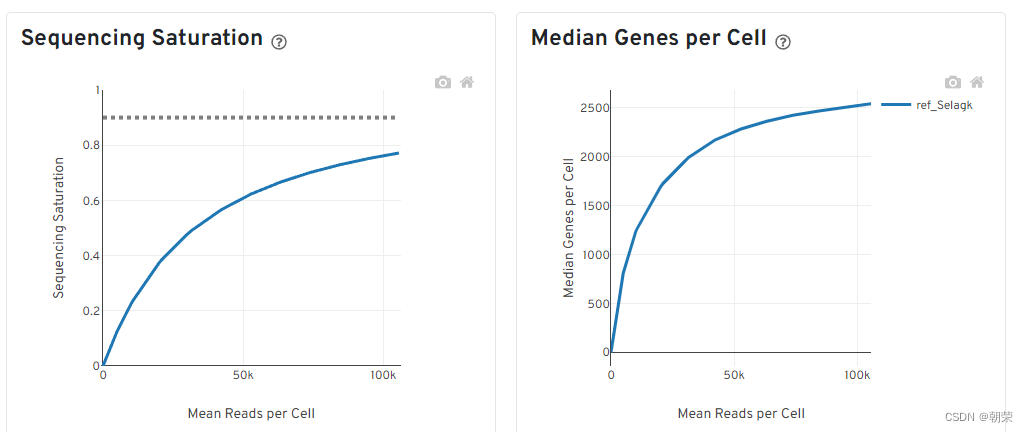
饱和度评估
- 对reads抽样,观察不同抽样条件下检测到的转录本数量占检测到的所有转录本的比例。(如果曲线末端区域平滑,说明测序接近饱和,再增加测序量,覆盖到的转录本数目也不会变化太多。)
- 对reads抽样,观察不同测序数据量情况下检测到的基因数目的分布。(如果曲线末端区域平滑,说明测序接近饱和,再增加测序量,检测到的基因数目也不会变化太多。)
Reference
[1] A Guide to Analyzing Single-cell Datasets, John F. Ouyang, January 2023
这篇关于【 10X summary report】怎么看?详细解读笔记的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






