本文主要是介绍【JAVA Reference】Cleaner 源码剖析(三),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
我的原则:先会用再说,内部慢慢来。
学以致用,根据场景学源码
文章目录
- 一、架构
- 二、概念
- 三、实战 demo
- 四、源码剖析
- 4.1 sun.misc.Cleaner 类
- 4.2 构造方法
- 4.3 create 方法
- 4.4 add 方法
- 4.5 remove 方法
- 4.6 clean 方法
- 4.7 static变量 dummyQueue
- 4.8 static 变量 first
- 4.9 成员变量 thunk
- 五、番外篇
一、架构
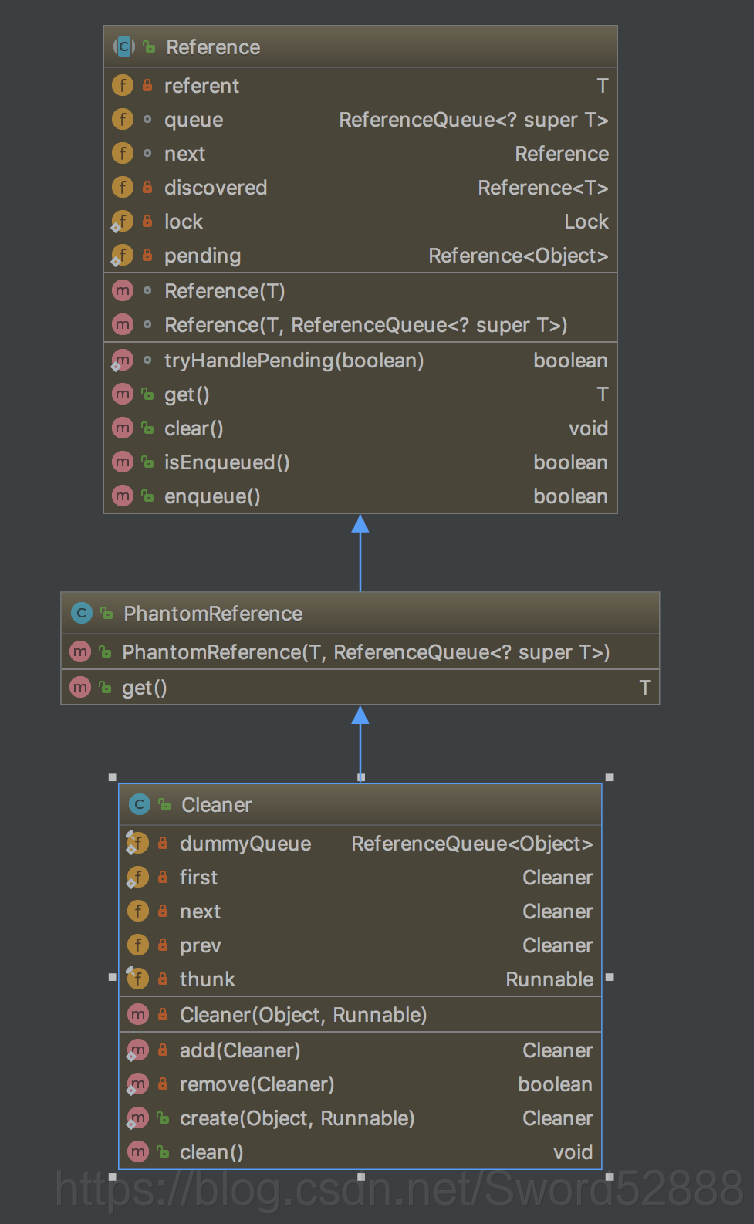
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
二、概念
- sun.misc.Cleaner是JDK内部提供的用来释放非堆内存资源的API。JVM只会帮我们自动释放堆内存资源,但是堆外内存无能为力,该类提供了回调机制,通过这个类能方便的释放系统的其他资源。
- 目的就是在 GC 前,你还可以做点事情。这是你最后的机会
- Cleaner 继承了 PhantomReference,是一个虚幻引用。
三、实战 demo
public class _05_00_TestCleaner {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {int index = 0;while (true) {Thread.sleep(1000);// 提醒 GC 去进行垃圾收集了System.gc();// 该对象不断重新指向其他地方,那么原先指针指向的对象的就属于需要回收的数据DemoObject obj = new DemoObject("demo01");/*增加 obj 的虚引用,定义清理的接口 DoSomethingThread第一个参数:需要监控的堆内存对象第二个参数:程序释放资源前的回调。*/Cleaner.create(obj, new DoSomethingThread("thread_" + index++));}}static class DoSomethingThread implements Runnable {private String name;public DoSomethingThread(String name) {this.name = name;}// do something before gc@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(name + " running DoSomething ...");}}@Data@AllArgsConstructorstatic class DemoObject{private String name;}
}
输出:
thread_0 running DoSomething ...
thread_1 running DoSomething ...
thread_2 running DoSomething ...
thread_3 running DoSomething ...
thread_4 running DoSomething ...
thread_5 running DoSomething ...
thread_6 running DoSomething ...
thread_7 running DoSomething ...
thread_8 running DoSomething ...
thread_9 running DoSomething ...
...
结论:
cleaner 类,可以让你在对象被回收前,干点其他事情。临终遗言吧。效果等同于 finalize
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
四、源码剖析
4.1 sun.misc.Cleaner 类
package sun.misc;import java.lang.ref.*;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedAction;
public class Cleanerextends PhantomReference<Object>
{// 静态私有全局变量// 在 ReferenceHandler 线程的处理中, Cleaner 对象是不进入这个队列的,设置的目的,是为了能进 pending private static final ReferenceQueue<Object> dummyQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>();// Doubly-linked list of live cleaners, which prevents the cleaners// themselves from being GC'd before their referents//// 静态私有全局变量,链表的头static private Cleaner first = null;private Cleanernext = null,prev = null;// 往前面插入private static synchronized Cleaner add(Cleaner cl) {if (first != null) {cl.next = first;first.prev = cl;}first = cl;return cl;}// 删除某个节点private static synchronized boolean remove(Cleaner cl) {// If already removed, do nothing// 已经被删除了,就啥事都不用干if (cl.next == cl)return false;// 如果是头节点if (first == cl) {// 如果有后继节点if (cl.next != null)first = cl.next;else // 如果是头节点,又没后继节点,那么 first = nullfirst = cl.prev;}// 如果后继节点不是 nullif (cl.next != null)cl.next.prev = cl.prev;// 如果前驱节点不是 nullif (cl.prev != null)cl.prev.next = cl.next;// next 和 prev 指针都指向自己,这个表示已经是被删掉了// Indicate removal by pointing the cleaner to itselfcl.next = cl;cl.prev = cl;return true;}//实现 Runable 接口的对象,这个对象会在实现的 run 方法里做 gc 前清理资源的操作,它的run方法最终会由 ReferenceHander 线程来调用执行// ReferenceHander 从 pending 队列里面取数据,然后调用 sun.misc.Cleaner#clean 方法,clean 方法会调用 thunk.run() 方法private final Runnable thunk;//私有的构造方法,说明 Cleaner 对象是无法直接被创建的,参数为被引用的对象和 ReferenceQueue 成员变量// 创建方法为下方的 createprivate Cleaner(Object referent, Runnable thunk) {super(referent, dummyQueue);this.thunk = thunk;}//这个create静态方法提供给我们来实例化Cleaner对象,需要两个参数,被引用的对象与实现了Runnable接口的对象,新创建的Cleaner对象被加入到了 dummyQueue 队列里public static Cleaner create(Object ob, Runnable thunk) {if (thunk == null)return null;return add(new Cleaner(ob, thunk));}/*** Runs this cleaner, if it has not been run before.*/// clean方法先将对象从 dummyQueue 队列remove移除(这样 Cleaner 对象就可以被gc回收掉了),然后调用thunk的run方法后执行清理操作public void clean() {if (!remove(this))return;try {thunk.run();} catch (final Throwable x) {AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {public Void run() {if (System.err != null)new Error("Cleaner terminated abnormally", x).printStackTrace();System.exit(1);return null;}});}}}
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.2 构造方法
private Cleaner(Object referent, Runnable thunk) {super(referent, dummyQueue);this.thunk = thunk;}
私有的构造方法,说明 Cleaner 对象是无法直接被创建的,参数为被引用的对象和 ReferenceQueue 成员变量,真正创建方法为下方的 create。
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.3 create 方法
这个create静态方法提供给我们来实例化Cleaner对象,需要两个参数:
- 被引用的对象
- 实现了Runnable接口的对象,这个用来回调的时候执行内部的 run 方法
新创建的Cleaner对象被加入到了 dummyQueue 队列里。
public static Cleaner create(Object ob, Runnable thunk) {if (thunk == null)return null;return add(new Cleaner(ob, thunk));}
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.4 add 方法
// 往前面插入 ,跟 Reference 类的队列一脉相承
private static synchronized Cleaner add(Cleaner cl) {if (first != null) {cl.next = first;first.prev = cl;}first = cl;return cl;}
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.5 remove 方法
// 删除某个节点private static synchronized boolean remove(Cleaner cl) {// If already removed, do nothing// 已经被删除了,就啥事都不用干if (cl.next == cl)return false;// 如果是头节点if (first == cl) {// 如果有后继节点if (cl.next != null)first = cl.next;else // 如果是头节点,又没后继节点,那么 first = nullfirst = cl.prev;}// 如果后继节点不是 nullif (cl.next != null)cl.next.prev = cl.prev;// 如果前驱节点不是 nullif (cl.prev != null)cl.prev.next = cl.next;// next 和 prev 指针都指向自己,这个表示已经是被删掉了// Indicate removal by pointing the cleaner to itselfcl.next = cl;cl.prev = cl;return true;}
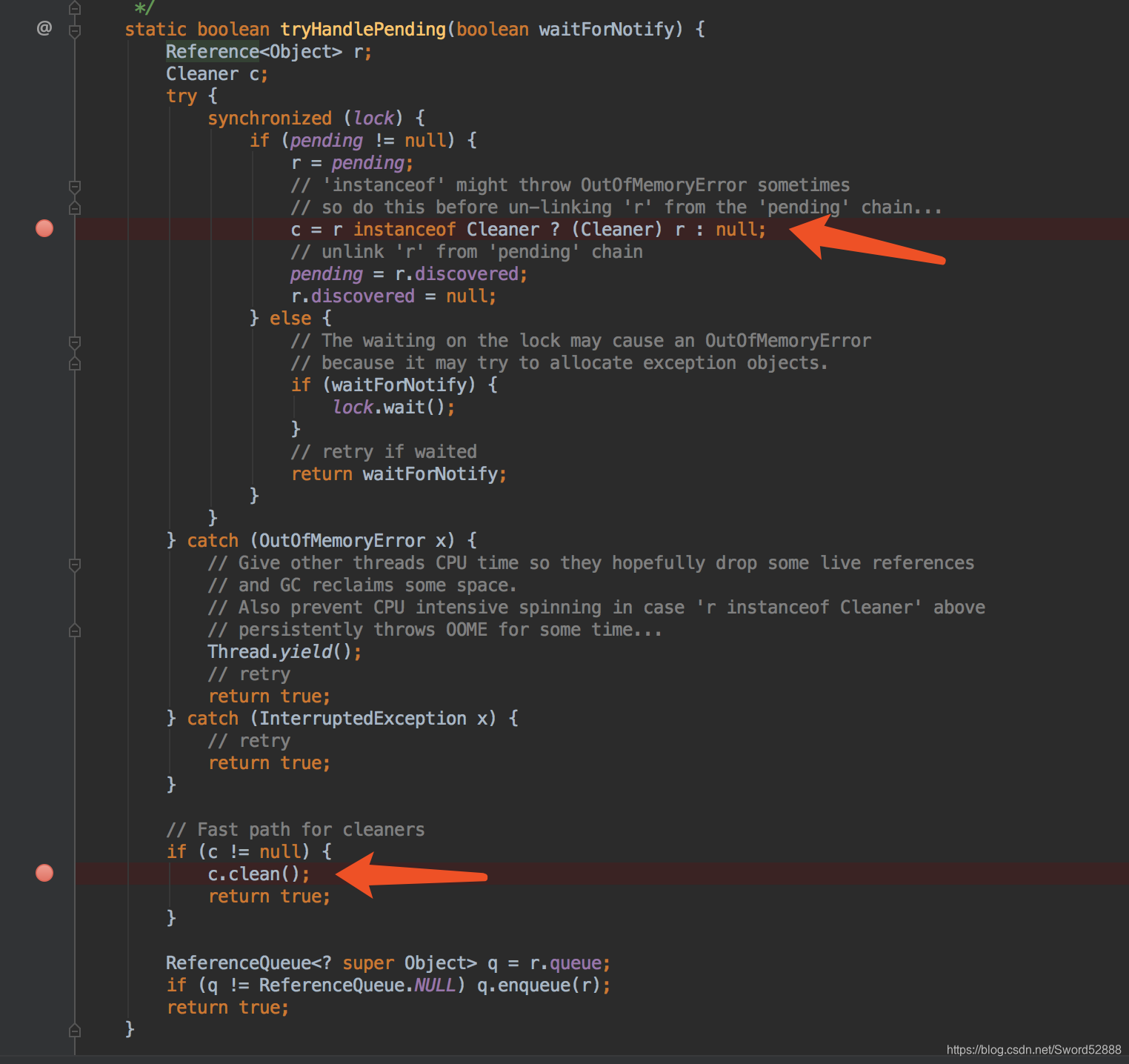
4.6 clean 方法
clean方法先将对象从 dummyQueue 队列remove移除(这样 Cleaner 对象就可以被gc回收掉了),然后调用thunk的run方法后执行清理操作。
// clean方法先将对象从 dummyQueue 队列remove移除(这样 Cleaner 对象就可以被gc回收掉了),然后调用thunk的run方法后执行清理操作public void clean() {if (!remove(this))return;try {thunk.run();} catch (final Throwable x) {AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {public Void run() {if (System.err != null)new Error("Cleaner terminated abnormally", x).printStackTrace();System.exit(1);return null;}});}}
该 clean 方法的调用,直接看上一篇【JAVA Reference】ReferenceQueue 与 Reference 源码剖析(二)
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.7 static变量 dummyQueue
静态私有全局变量
private static final ReferenceQueue<Object> dummyQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
在 ReferenceHandler 线程的处理中, Cleaner 对象是不进入这个队列的,设置的目的,是为了能进 pending
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.8 static 变量 first
// 静态私有全局变量,链表的头,把一堆 cleaner 串起来
private static Cleaner first = null;
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
4.9 成员变量 thunk
private final Runnable thunk;
- 实现 Runable 接口的对象,这个对象会在实现的 run 方法里做 gc 前清理资源的操作,它的run方法最终会由 ReferenceHander 线程来调用执行
- ReferenceHander 从 pending 队列里面取数据,然后调用 sun.misc.Cleaner#clean 方法,clean 方法会调用 thunk.run() 方法
具体看方法=== clean ===
=== 点击查看top目录 ===
五、番外篇
下一章节:【JAVA Reference】Cleaner 对比 finalize 对比 AutoCloseable(四)
上一章节:【JAVA Reference】ReferenceQueue 与 Reference 源码剖析(二)
这篇关于【JAVA Reference】Cleaner 源码剖析(三)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








