本文主要是介绍进程间通信,无名管道pipe,有名管道mkfifo,信号的基础概念,signal函数,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
我要成为嵌入式高手之2月28日Linux高编第十一天!!
学习笔记
进程间通信
总共6种通信方法,主要是前五种方式
第一种方式:管道
一、无名管道
只能用于具有亲缘关系的进程间通信
pipe
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
功能:创建一个无名管道
参数:
pipefd[0]:读
pipefd[1]:写
返回值:成功返回0;失败返回-1
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{pid_t pid;int fd[2];int ret;char tmpbuff[4096];ret = pipe(fd);if (ret == -1){perror("fail to pipe");return -1;}pid = fork();if (pid == -1){perror("fail to fork");return -1;}if (pid == 0){strcpy(tmpbuff, "hello world!");write(fd[1], tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));}else if (pid > 0){read(fd[0], tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));//read有等待作用,若文件标识符内没有可读内容,会等待到有可读内容printf("tmpbuff = %s\n", tmpbuff);}close(fd[0]);close(fd[1]);return 0;
} 
无名管道的特性:
1、管道中至少有一个写端:
读取数据时如果有数据直接读取;管道中没有数据,阻塞等待直到有数据写入,然后读出,继续向后执行 。
2、管道中没有写端:
读取数据时,如果管道中有数据直接读取,管道中没有数据不阻塞等待直接向下执行
3、管道中至少有一个读端:
写入数据时,如果管道中没有存满则直接写入,如果管道中存满则阻塞等待,直到有数据读出才继续写入
4、管道中没有读端:
写入数据时,会产生管道破裂的错误,导致程序崩溃
二、有名管道
操作方式:
打开管道文件(open)--->读写(read,write)管道文件--->关闭(close)管道文件
特性:有名管道必须读写两端同时加入才能继续向下执行
1、mkfifo
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
功能:创建一个管道文件
参数:
pathname:管道文件的路径(名字包含在路径里)
mdoe:权限(0777、0664)
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1;
练习:编写两个进程A B, A给B发送一条消息,B收到消息打印后给A回复一条消息
注:在接收函数之前都加入memset
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{int fatob = 0;int fbtoa = 0;char tmpbuff[1024] = {0};mkfifo("/tmp/ATOB", 0777);mkfifo("/tmp/BTOA", 0777);fatob = open("/tmp/ATOB", O_WRONLY);if (fatob == -1){perror("fail to open1");return -1;}fbtoa = open("/tmp/BTOA", O_RDONLY);if (fbtoa == -1){perror("fail to open2");return -1;}while (1){memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));gets(tmpbuff);write(fatob, tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));read(fbtoa, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));printf("RECV: %s\n", tmpbuff);}close(fatob);close(fbtoa);return 0;
}
#include "head.h"int main(void)
{int fatob = 0;int fbtoa = 0;char tmpbuff[1024] = {0};mkfifo("/tmp/ATOB", 0777);mkfifo("/tmp/BTOA", 0777);fatob = open("/tmp/ATOB", O_RDONLY);if (fatob == -1){perror("fail to open1");return -1;}fbtoa = open("/tmp/BTOA", O_WRONLY);if (fbtoa == -1){perror("fail to open2");return -1;}while (1){memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));read(fatob, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));printf("RECV: %s\n", tmpbuff);memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));gets(tmpbuff);write(fbtoa, tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));}close(fatob);close(fbtoa);return 0;
}

进阶难版
#include "head.h"pthread_t tid1;
pthread_t tid2;void *Write(void *arg)
{int fatob = 0;char tmpbuff[1024] = {0};while (1){mkfifo("/tmp/ATOB", 0777);fatob = open("/tmp/ATOB", O_WRONLY);if (fatob == -1){perror("fail to open1");return NULL;}memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));gets(tmpbuff);write(fatob, tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));if (!strcmp(tmpbuff, ".quit")){break;}close(fatob);}pthread_cancel(tid2);return NULL;
}void *Read(void *arg)
{int fbtoa;char tmpbuff[1024] = {0};while (1){mkfifo("/tmp/BTOA", 0777);fbtoa = open("/tmp/BTOA", O_RDONLY);if (fbtoa == -1){perror("fail to open2");return NULL;}memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));read(fbtoa, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));if (!strcmp(tmpbuff, ".quit")){break;}printf("RECV: %s\n", tmpbuff);close(fbtoa);}pthread_cancel(tid1);return NULL;
}int main(void)
{int ret1 = 0;int ret2 = 0;ret1 = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, Write, NULL);if (ret1 != 0){perror("fail to tid1");return -1;}ret2 = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, Read, NULL);if (ret2 != 0){perror("fail to tid2");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);return 0;
}
#include "head.h"pthread_t tid1;
pthread_t tid2;void *Write(void *arg)
{int fbtoa = 0;char tmpbuff[1024] = {0};while (1){mkfifo("/tmp/BTOA", 0777);fbtoa = open("/tmp/BTOA", O_WRONLY);if (fbtoa == -1){perror("fail to open1");return NULL;}memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));gets(tmpbuff);write(fbtoa, tmpbuff, strlen(tmpbuff));if (!strcmp(tmpbuff, ".quit")){break;}close(fbtoa);}pthread_cancel(tid2);return NULL;
}void *Read(void *arg)
{int fatob;char tmpbuff[1024] = {0};while (1){mkfifo("/tmp/ATOB", 0777);fatob = open("/tmp/ATOB", O_RDONLY);if (fatob == -1){perror("fail to open2");return NULL;}memset(tmpbuff, 0, sizeof(tmpbuff));read(fatob, tmpbuff, sizeof(tmpbuff));if (!strcmp(tmpbuff, ".quit")){break;}printf("RECV: %s\n", tmpbuff);close(fatob);}pthread_cancel(tid1);return NULL;
}int main(void)
{int ret1 = 0;int ret2 = 0;ret1 = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, Write, NULL);if (ret1 != 0){perror("fail to tid1");return -1;}ret2 = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, Read, NULL);if (ret2 != 0){perror("fail to tid2");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);return 0;
}
第二种方式:信号
信号用来实现内核层和用户层信息的交互,也可以用来实现进程间通信
一、信号的种类
kill -l来查看
1) SIGHUP(挂起)
2) SIGINT(中断)
3) SIGQUIT(退出)
4) SIGILL
5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT(产生异常)
7) SIGBUS(总线错误)
8) SIGFPE
9) SIGKILL(杀死信号)
10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV(段错误)
12) SIGUSR2
13) SIGPIPE(管道破裂)
14) SIGALRM(定时时间到了)
15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT
17) SIGCHLD(一个子进程结束,给父进程发送的信号)
18) SIGCONT(让进程继续执行)
19) SIGSTOP(让进程挂起)
20) SIGTSTP(让进程挂起)
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO(异步IO) 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7
42) SIGRTMIN+8 43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11
46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13 48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15
50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12 53) SIGRTMAX-11
54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3
62) SIGRTMAX-2 63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX
所有的信号都可以让进程结束
二、信号处理方式
1、缺省:
按照系统默认的方式处理
2、忽略:
不响应信号
3、捕捉:
按照自己设定的方式处理信号
注意:
9号信号(杀死)和19号信号(暂停)不可被忽略和捕捉,即只能按照缺省的方式处理
可键入:
SIGINT:ctrl + c
SIGQUIT:ctrl + \
SIGTSTP:ctrl + z
4、signal
#include <signal.h>
typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);
sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler);
功能:改变信号的处理方式
参数:
signum:信号的编号
handler:信号的处理方式
SIG_IGN 忽略处理
SIG_DFL 缺省处理
函数首地址 捕捉处理
返回值:
成功返回之前处理函数的首地址
失败返回SIG_ERR
练习:
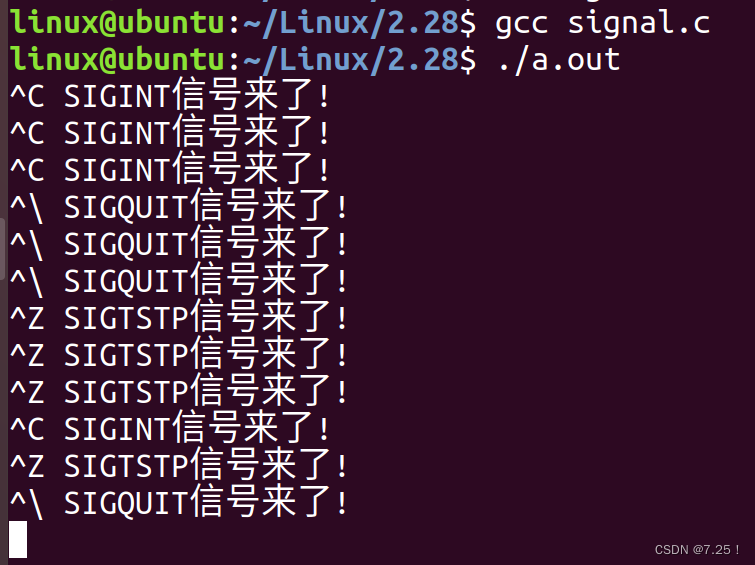
#include "head.h"void handler1(int signo)
{printf(" SIGINT信号来了!\n");return;
}void handler2(int signo)
{printf(" SIGQUIT信号来了!\n");return;
}void handler3(int signo)
{printf(" SIGTSTP信号来了!\n");return;
}int main(void)
{signal(SIGINT, handler1);signal(SIGQUIT, handler2);signal(SIGTSTP, handler3);while (1){}return 0;
}
这篇关于进程间通信,无名管道pipe,有名管道mkfifo,信号的基础概念,signal函数的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






