本文主要是介绍SpringMVC 学习(三)之 @RequestMapping 注解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
1 @RequestMapping 注解介绍
2 @RequestMapping 注解的位置
3 @RequestMapping 注解的 value 属性
4 @RequestMapping 注解的 method 属性
5 @RequestMapping 注解的 params 属性(了解)
6 @RequestMapping 注解的 headers 属性(了解)
7 @RequestMapping 注解的 produces 属性(了解)
8 @RequestMapping 注解的 consumes 属性(了解)
9 SpringMVC 支持 ant 风格的路径
10 SpringMVC 支持路径中的占位符(重点)
1 @RequestMapping 注解介绍
@RequestMapping 注解作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系。它主要有六种属性,分别是 value、method、header、params、produces、consumes。这六种属性之间是与的关系,联合使用会使请求地址的映射更加精确。
- value:指定请求路径
- method:指定请求方法
- header:指定请求头信息
- params:指定请求参数
- produces:指定返回的媒体类型
- consumes:指定处理的媒体类型
2 @RequestMapping 注解的位置
@RequestMapping 注解可以放在方法或类的上方,以指定请求的路径和其他相关的信息。
- 放在处理请求的方法上,设置映射请求的请求路径的具体信息
@RequestMapping("/path")
public String handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {// 处理请求的逻辑return "success";
}上述代码中,收到请求路径为 /path 的请求,会调用 handleRequest 方法处理
- 放在控制器类上,设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class MyController {@RequestMapping("/users")public String handleUsersRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {// 处理用户请求的逻辑return "success";}
}上述代码中,/api 是请求路径的初始信息,/users 是请求路径的具体信息,只有收到请求路径为 /api/users 的请求,才会调用 MyController 控制器中的 handleUsersRequest 方法。
3 @RequestMapping 注解的 value 属性
@RequestMapping 注解的 value 属性通过请求地址匹配请求映射,是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求,一般而言,必须设置 value,配合其它属性使映射更精确。
jsp
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test1">请求路径: /login/test1</a><br/>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test2">请求路径: /login/test2</a>控制器
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/login")
public class MyController {@RequestMapping(value = "/test1")public String handler1() {System.out.println("处理器1");return "success";}@RequestMapping(value = {"test2", "/test3"})public String handler2() {System.out.println("处理器2");return "success";}
}4 @RequestMapping 注解的 method 属性
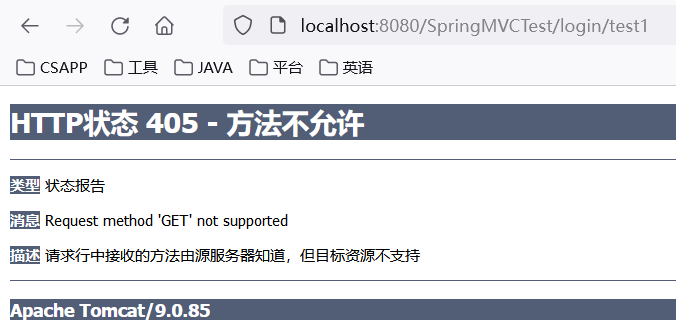
@RequestMapping 注解的 method 属性通过请求的请求方式匹配请求映射,是一个 RequestMethod 类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求。若当前请求的请求地址满足请求映射的 value 属性,但是请求方式不满足 method 属性,则浏览器报错 405:Request method 'POST' not supported。
常用的请求方式有 GET、POST、PUT、DELETE,但是目前的浏览器只支持 GET、POST 请求方法,若要发送 PUT 和 DELETE 请求,则需要通过 Spring 提供的过滤器 HiddenHttpMethodFilter。
对于处理指定请求方式的控制器方法,SpringMVC中提供了@RequestMapping的派生注解
- 处理 GET 请求的映射 --> @GetMapping
- 处理 POST 请求的映射 --> @PostMapping
- 处理 PUT 请求的映射 --> @PutMapping
- 处理 DELETE 请求的映射 --> @DeleteMapping
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test1">请求路径: /login/test1</a><br/>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test2">请求路径: /login/test2</a>@Controller
@RequestMapping("/login")
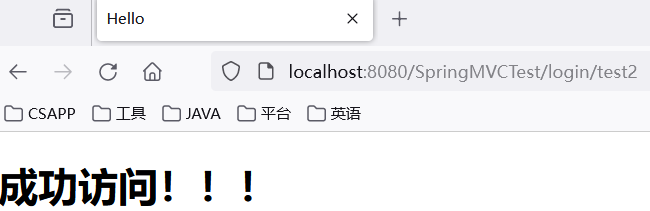
public class MyController {@RequestMapping(value = "/test1", method = {RequestMethod.POST})public String handler1() {System.out.println("处理器1");return "success";}@RequestMapping(value = {"test2", "/test3"}, method = {RequestMethod.GET})public String handler2() {System.out.println("处理器2");return "success";}
}
5 @RequestMapping 注解的 params 属性(了解)
@RequestMapping注解的 params 属性通过请求参数匹配请求映射,是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求参数和请求映射的匹配关系。注意,请求参数不要空格,空格也是一个字符。
- "param":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 param 请求参数
- "!param":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带 param 请求参数
- "param=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 param 请求参数且 param=value
- "param!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 param 请求参数但是 param!=value
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test1?username=西施&password=123">请求路径: /login/test1?username=西施&password=123</a><br/>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test2?username=赵飞燕&password=111">请求路径: /login/test2?username=赵飞燕&password=111</a><br/>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test2?password=111">请求路径: /login/test2?password=111</a>@Controller
@RequestMapping("/login")
public class MyController {@RequestMapping(// 请求路径只能为 /test1value = "/test1",// 请求方法既可以是 GET 方法,也可以是 POST 方法method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST},// 请求路径不能必须包含 username 参数,参数 password 必须为 123params = {"username", "password=123"})public String handler1() {System.out.println("处理器1");return "success";}@RequestMapping(// 请求路径既可以为 /test2,也可以为 /test3value = {"/test2", "/test3"},// 请求方法必须是 GET 方法method = {RequestMethod.GET},// 请求路径中不能包含 username 参数,参数 password 不能为 123params = {"!username", "password!=123"})public String handler2() {System.out.println("处理器2");return "success";}
}测试结果
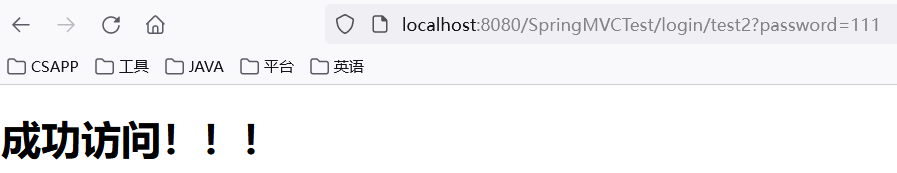
请求路径包含参数 username,且 password 要为 123,则成功访问

请求路径不能包含参数 username,且 password 要为 111,否则,访问失败

6 @RequestMapping 注解的 headers 属性(了解)
@RequestMapping 注解的 headers 属性通过请求头信息匹配请求映射,是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信息和请求映射的匹配关系。和 params 属性用法一致。
- "header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 header 请求头信息
- "!header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带 header 请求头信息
- "header=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 header 请求头信息且 header=value
- "header!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带 header 请求头信息且 header!=value
7 @RequestMapping 注解的 produces 属性(了解)
@RequestMapping 注解的 produces 属性通过返回的媒体类型(即请求头 Accept 中的媒体类型)匹配请求映射,是一个字符串类型的数组。常用的媒体类型有以下几种:
- text/plain:纯文本内容,例如 HTML、XML、CSS 等
- image/jpeg:JPEG 图像
- image/png:PNG 图像
- audio/mpeg:MPEG 音频
- video/mp4:MP4 视频
- application/pdf:PDF 文件
- application/msword:Microsoft Word 文档
- application/vnd.ms-excel:Microsoft Excel 文档
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded:URL 编码的表单数据
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document:OpenXML 格式的 Word 文档
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet:OpenXML 格式的 Excel 文档
注:
- Content-Type: 告诉服务器当前发送的数据是什么格式
- Accept : 用来告诉服务器,客户端能接收哪些格式,最好返回这些格式
8 @RequestMapping 注解的 consumes 属性(了解)
@RequestMapping 注解的 consumes 属性通过处理的媒体类型(即请求头 Content-Type 中的媒体类型,一般而言,POST 方法的请求头有 Content-Type,而 GET 方法的请求头没有 Content-Type)匹配请求映射,是一个字符串类型的数组。
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test1" method="post">用户名: <input type="text" name="username"/> <br>密 码: <input type="password" name="password"/> <br><input type="submit" />
</form>test2">请求路径: /login/test2</a><br/>@Controller
@RequestMapping("/login")
public class MyController {@RequestMapping(// 请求路径只能为 /test1value = "/test1",// 请求路径请求头中的 Context-Type 只能为 application/x-www-form-urlencodedconsumes = {"application/x-www-form-urlencoded"})public String handler1(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {System.out.println("处理器1");System.out.println("Content-Type:" + request.getContentType());return "success";}
}
9 SpringMVC 支持 ant 风格的路径
- ?:表示任意的一个字符
- *:表示任意的 0 ~ n 个字符
- **:表示任意的一层或多层目录,只能是 /**/xxx 的格式
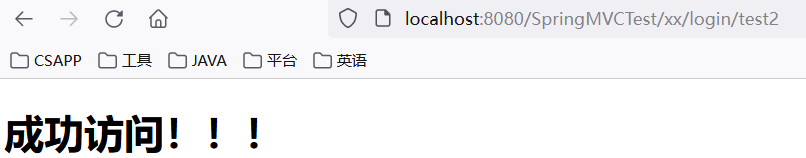
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/xx/login/test1">请求路径: /xx/login/test1</a><br/>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/xx/login/test2">请求路径: /xx/login/test2</a><br/>@Controller
@RequestMapping("/**/login")
public class MyController {@RequestMapping(value = "/?est1")public String handler1() {System.out.println("处理器1");return "success";}@RequestMapping(value = "/te*")public String handler2() {System.out.println("处理器2");return "success";}
}
10 SpringMVC 支持路径中的占位符(重点)
当请求将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping 注解的 value 属性中通过占位符 {xxx} 表示传输的数据,再通过 @PathVariable 注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参。
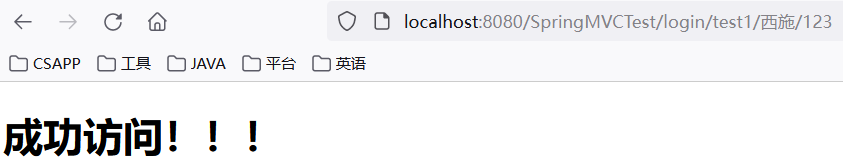
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login/test1/西施/123"> 请求路径: /login/test1/西施/123 </a><br/>@Controller
@RequestMapping("/login")
public class MyController {@RequestMapping(value = "/?est1/{username}/{password}")public String handler1(@PathVariable("username") String username,@PathVariable("password") String password) {System.out.println("处理器1");System.out.println("username:" + username + " password:" + password);return "success";}
}通过请求路径的方式将“西施”和“123”两个值传递给处理器
这篇关于SpringMVC 学习(三)之 @RequestMapping 注解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









