本文主要是介绍LOAM系列——ALOAM配置、安装、问题解决及VLP16测试效果以及关键记录,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
LOAM系列——ALOAM配置、安装、问题解决及VLP16测试效果以及关键记录
- 安装依赖
- 安装
- bag包测试
- 问题解决
- 问题1
- 解决1
- 关键记录
- A-LOAM主要特点
- 残差
- 关键代码
安装依赖
ros
Ceres Solver
PCL
安装
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/A-LOAM.git
cd ../
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
如果你只想编译ALoam功能包,可以在catkin_make后面添加-DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES="aloam_velodyne"命令,如下:
catkin_make -DCATKIN_WHITELIST_PACKAGES="aloam_velodyne"
bag包测试
roslaunch aloam_velodyne aloam_velodyne_VLP_16.launch
rosbag play YOUR_DATASET_FOLDER/nsh_indoor_outdoor.bag
测试截图如下:
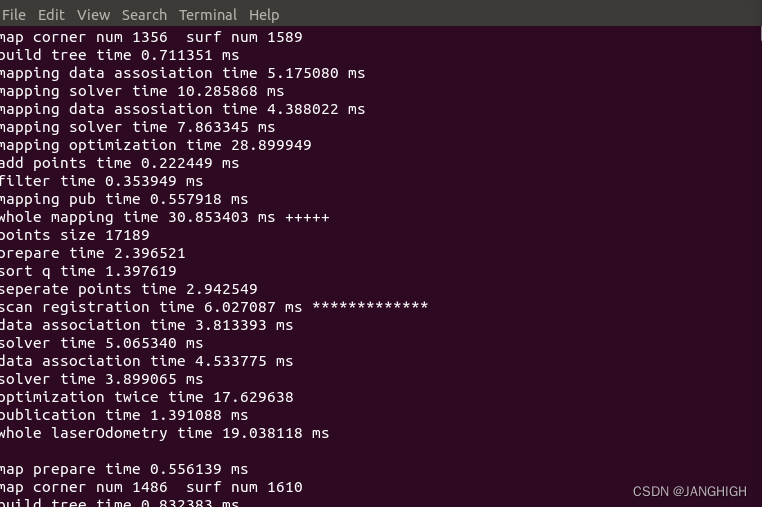
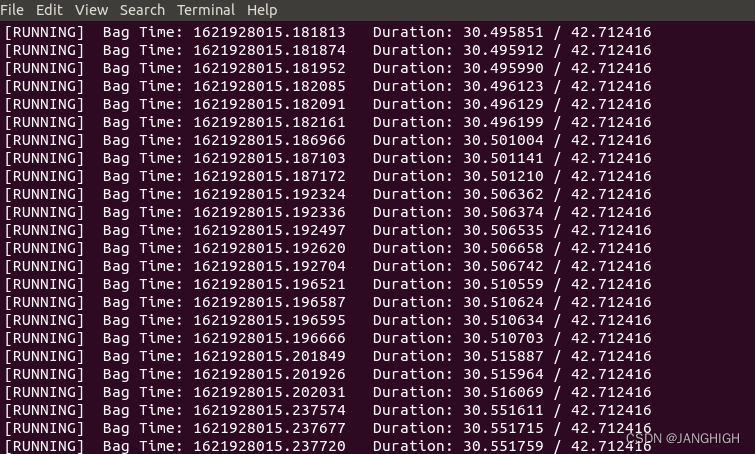
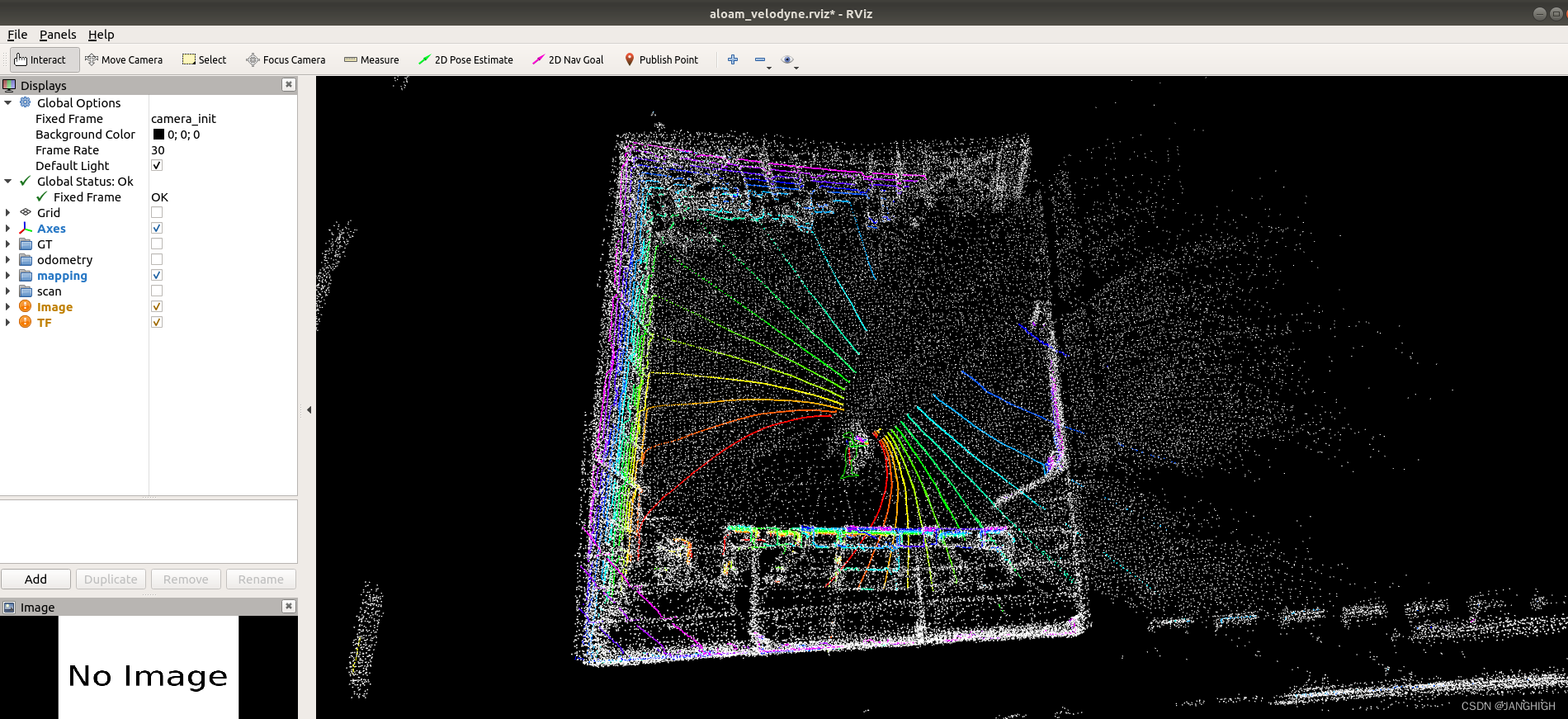
问题解决
问题1
如果运行
roslaunch aloam_velodyne aloam_velodyne_VLP_16.launch
出现如下错误:
[alaserOdometry-3] process has died [pid 23572, exit code 127, cmd xxxxxxx_ws/devel/lib/aloam_velodyne/alaserOdometry __name:=alaserOdometry __log:=xxxxxxx/.ros/log/76115896-bef6-11eb-962f-94e6f7e52acc/alaserOdometry-3.log].
log file:xxxxxxx/.ros/log/76115896-bef6-11eb-962f-94e6f7e52acc/alaserOdometry-3*.log
[alaserMapping-4] process has died [pid 23574, exit code 127, cmd xxxxxxx_ws/devel/lib/aloam_velodyne/alaserMapping __name:=alaserMapping __log:=xxxxxxx/.ros/log/76115896-bef6-11eb-962f-94e6f7e52acc/alaserMapping-4.log].
log file:xxxxxxx/.ros/log/76115896-bef6-11eb-962f-94e6f7e52acc/alaserMapping-4*.log
解决1
卸载glog后,重新运行launch文件,问题解决!
关键记录
A-LOAM主要特点
1) 去掉了和IMU相关的部分
2) 使用Eigen(四元数)做位姿转换,简化了代码
3) 使用ceres做迭代优化,简化了代码,但降低了效率
代码:https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/A-LOAM
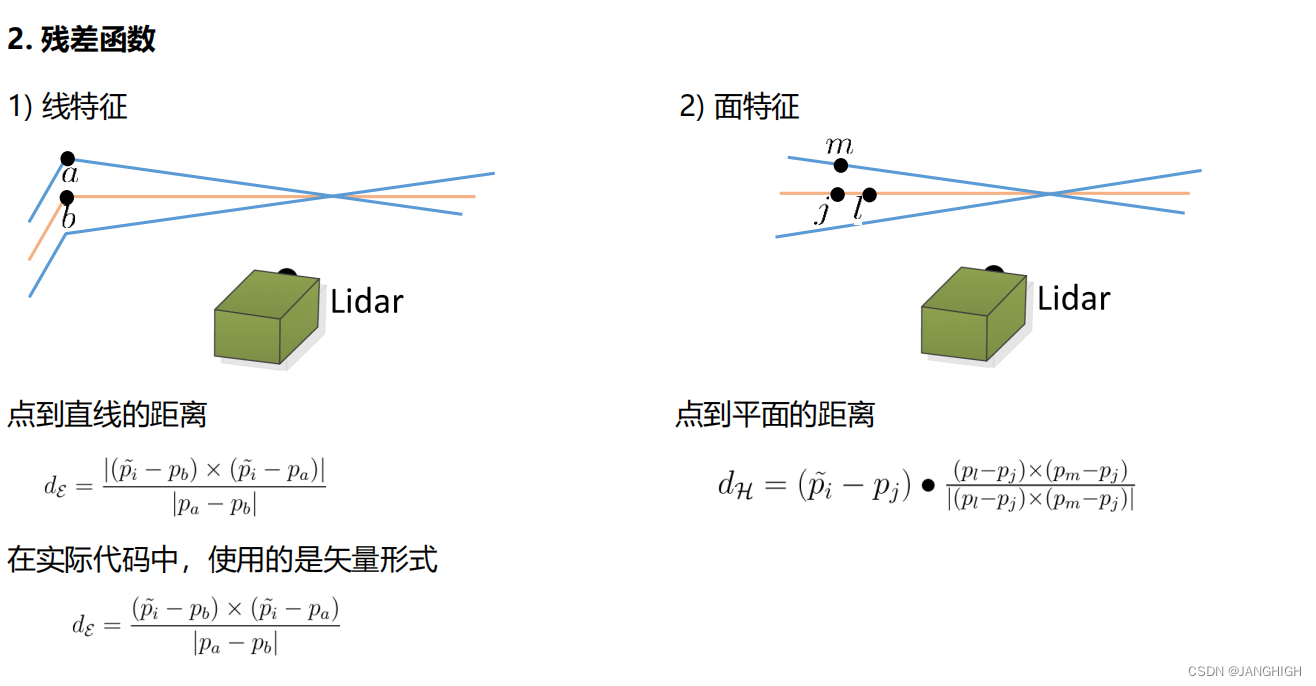
残差
关键代码
// Edgepoints 计算点到直线的距离作为误差函数
struct LidarEdgeFactor
{LidarEdgeFactor(Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a_,Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b_, double s_): curr_point(curr_point_), last_point_a(last_point_a_), last_point_b(last_point_b_), s(s_) {}template <typename T>bool operator()(const T *q, const T *t, T *residual) const // 构建误差函数,点到直线距离,跟论文中一样{Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> cp{T(curr_point.x()), T(curr_point.y()), T(curr_point.z())};Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lpa{T(last_point_a.x()), T(last_point_a.y()), T(last_point_a.z())};Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lpb{T(last_point_b.x()), T(last_point_b.y()), T(last_point_b.z())};//Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_last_curr{q[3], T(s) * q[0], T(s) * q[1], T(s) * q[2]};Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_last_curr{q[3], q[0], q[1], q[2]};Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_identity{T(1), T(0), T(0), T(0)};q_last_curr = q_identity.slerp(T(s), q_last_curr); // 根据s进行插值Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_last_curr{T(s) * t[0], T(s) * t[1], T(s) * t[2]};Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lp;lp = q_last_curr * cp + t_last_curr; Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> nu = (lp - lpa).cross(lp - lpb);Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> de = lpa - lpb;residual[0] = nu.x() / de.norm(); residual[1] = nu.y() / de.norm();residual[2] = nu.z() / de.norm();return true;}static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a_,const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b_, const double s_){// 使用ceres的自动求导return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<LidarEdgeFactor, 3, 4, 3>( //残差维度 第一个参数块维度 第二个参数块维度new LidarEdgeFactor(curr_point_, last_point_a_, last_point_b_, s_)));}Eigen::Vector3d curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b;double s;
};// Planar Points 计算点到平面的距离作为误差函数
struct LidarPlaneFactor
{LidarPlaneFactor(Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, Eigen::Vector3d last_point_j_,Eigen::Vector3d last_point_l_, Eigen::Vector3d last_point_m_, double s_): curr_point(curr_point_), last_point_j(last_point_j_), last_point_l(last_point_l_),last_point_m(last_point_m_), s(s_){ljm_norm = (last_point_j - last_point_l).cross(last_point_j - last_point_m); // 得到平面的单位法向量ljm_norm.normalize();}template <typename T>bool operator()(const T *q, const T *t, T *residual) const{Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> cp{T(curr_point.x()), T(curr_point.y()), T(curr_point.z())};Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lpj{T(last_point_j.x()), T(last_point_j.y()), T(last_point_j.z())};//Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lpl{T(last_point_l.x()), T(last_point_l.y()), T(last_point_l.z())};//Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lpm{T(last_point_m.x()), T(last_point_m.y()), T(last_point_m.z())};Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> ljm{T(ljm_norm.x()), T(ljm_norm.y()), T(ljm_norm.z())};//Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_last_curr{q[3], T(s) * q[0], T(s) * q[1], T(s) * q[2]};Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_last_curr{q[3], q[0], q[1], q[2]};Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_identity{T(1), T(0), T(0), T(0)};q_last_curr = q_identity.slerp(T(s), q_last_curr);Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_last_curr{T(s) * t[0], T(s) * t[1], T(s) * t[2]};Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lp;lp = q_last_curr * cp + t_last_curr; residual[0] = (lp - lpj).dot(ljm); return true;}static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_j_,const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_l_, const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_m_,const double s_){return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<LidarPlaneFactor, 1, 4, 3>( //残差维度 第一个参数块维度 第二个参数块维度new LidarPlaneFactor(curr_point_, last_point_j_, last_point_l_, last_point_m_, s_)));}Eigen::Vector3d curr_point, last_point_j, last_point_l, last_point_m;Eigen::Vector3d ljm_norm;double s;
};
......double para_q[4] = {0, 0, 0, 1}; // ceres用来优化时的数组,四元数
double para_t[3] = {0, 0, 0}; // 平移ceres::LossFunction *loss_function = new ceres::HuberLoss(0.1); // 定义一个0.1阈值的huber核函数,优化时抑制离群点用ceres::LocalParameterization *q_parameterization = new ceres::EigenQuaternionParameterization();
ceres::Problem::Options problem_options;
ceres::Problem problem(problem_options);
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_q, 4, q_parameterization);
problem.AddParameterBlock(para_t, 3);......
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarEdgeFactor::Create(curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b, s);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, para_q, para_t);......
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarPlaneFactor::Create(curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b, last_point_c, s);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, para_q, para_t);......
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;
options.max_num_iterations = 4; // 在非线性优化求解中最多进行几次迭代
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = false;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
注:该处的四元数存储顺序是(x,y,z,w)
关于 problem.AddParameterBlock(para_q, 4, q_parameterization); 的理解见其他博客
这篇关于LOAM系列——ALOAM配置、安装、问题解决及VLP16测试效果以及关键记录的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




