本文主要是介绍Android安卓进程保活(三)双进程拉活(Java层),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Android进程保活·双进程拉活(Java层)
Android进程
此文章代码Github有提交https://github.com/NorthernBrain/DoubleService
其它文章
Android安卓进程保活(一)1像素且透明ActivityAndroid安卓进程保活(二)设置前台Service
Android安卓进程保活(三)双进程拉活(Java层)
首先你要知道Android中的进程以及它的优先级,下面来说明它进程
- 前台进程 (Foreground process)
- 可见进程 (Visible process)
- 服务进程 (Service process)
- 后台进程 (Background process)
- 空进程 (Empty process)
下面进行解释:
前台进程(Foreground process):
用户当前操作所必需的进程。如果一个进程满足以下任一条件,即视为前台进程:- 托管用户正在交互的 Activity(已调用 Activity 的 onResume() 方法)
- 托管某个 Service,后者绑定到用户正在交互的 Activity
- 托管正在“前台”运行的 Service(服务已调用 startForeground())
- 托管正执行一个生命周期回调的 Service(onCreate()、onStart() 或 onDestroy())
- 托管正执行其 onReceive() 方法的 BroadcastReceiver
可见进程 (Visible process):
没有任何前台组件、但仍会影响用户在屏幕上所见内容的进程。 如果一个进程满足以下任一条件,即视为可见进程:- 托管不在前台、但仍对用户可见的 Activity(已调用其 onPause() 方法)。例如,如果前台 Activity 启动了一个对话框,允许在其后显示上一 Activity,则有可能会发生这种情况。
- 托管绑定到可见(或前台)Activity 的 Service。
可见进程被视为是极其重要的进程,除非为了维持所有前台进程同时运行而必须终止,否则系统不会终止这些进程。
服务进程 (Service process):
正在运行已使用 startService() 方法启动的服务且不属于上述两个更高类别进程的进程。尽管服务进程与用户所见内容没有直接关联,但是它们通常在执行一些用户关心的操作(例如,在后台播放音乐或从网络下载数据)。因此,除非内存不足以维持所有前台进程和可见进程同时运行,否则系统会让服务进程保持运行状态。后台进程 (Service process):
包含目前对用户不可见的 Activity 的进程(已调用 Activity 的 onStop() 方法)。这些进程对用户体验没有直接影响,系统可能随时终止它们,以回收内存供前台进程、可见进程或服务进程使用。 通常会有很多后台进程在运行,因此它们会保存在 LRU (最近最少使用)列表中,以确保包含用户最近查看的 Activity 的进程最后一个被终止。如果某个 Activity 正确实现了生命周期方法,并保存了其当前状态,则终止其进程不会对用户体验产生明显影响,因为当用户导航回该 Activity 时,Activity 会恢复其所有可见状态。空进程 (Empty process):
不含任何活动应用组件的进程。保留这种进程的的唯一目的是用作缓存,以缩短下次在其中运行组件所需的启动时间。 为使总体系统资源在进程缓存和底层内核缓存之间保持平衡,系统往往会终止这些进程。进程优先级:
首先空进程是最先被回收的,其次便是后台进程,依次往上,前台进程是最后才会被结束。Android进程保活
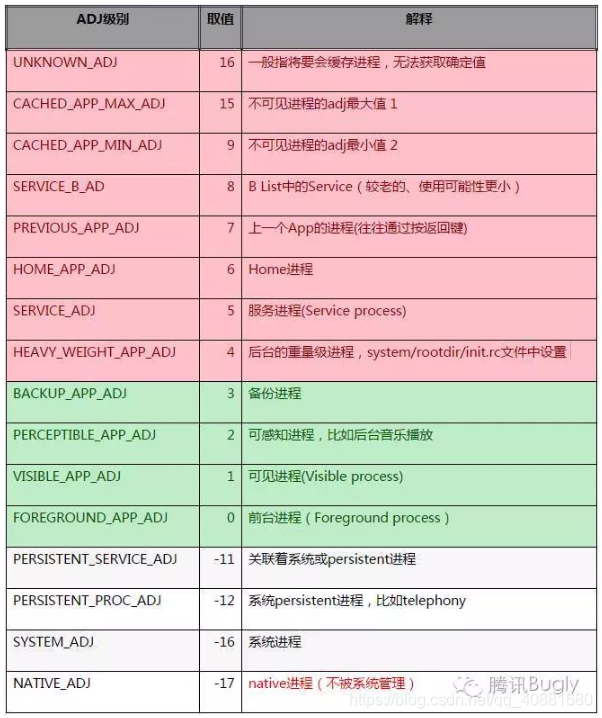
有很多种方法可以实现Android的进程保活,比如通过 1像素且透明Activity提升App进程优先级、 通过设置前台Service提升App进程优先级、 Java层的双进程拉活、 JobScheduler实现、 NDK双进程守护、 使用账户同步拉活、 workmanager实现。下面这幅图,说明的是:
- 红色部分是容易被回收的进程,属于android进程
- 绿色部分是较难被回收的进程,属于android进程
- 其他部分则不是android进程,也不会被系统回收,一般是ROM自带的app和服务才能拥有
本篇文章介绍的是进程第三种方式:
- 双进程拉活(Java层)
双进程拉活(Java层):
当一个进程结束后,立刻调用启动另一个进程,这样实现互相调用,互相启动( 只有在一个进程结束时候才会启动另一个进程)
首先创建LocalService.java继承自Service(android.app.Service):↓
public class LocalService extends Service {@Overridepublic IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {return new LocalBinder();}@Overridepublic int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {/*第一个参数Intent第二个参数ServiceConnection*//*** 第三个参数介绍:* Flag for {@link #bindService}: automatically create the service as long* as the binding exists. Note that while this will create the service,* its {@link android.app.Service#onStartCommand}* method will still only be called due to an* explicit call to {@link #startService}. Even without that, though,* this still provides you with access to the service object while the* service is created.** <p>Note that prior to {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH},* not supplying this flag would also impact how important the system* consider's the target service's process to be. When set, the only way* for it to be raised was by binding from a service in which case it will* only be important when that activity is in the foreground. Now to* achieve this behavior you must explicitly supply the new flag* {@link #BIND_ADJUST_WITH_ACTIVITY}. For compatibility, old applications* that don't specify {@link #BIND_AUTO_CREATE} will automatically have* the flags {@link #BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY} and* {@link #BIND_ADJUST_WITH_ACTIVITY} set for them in order to achieve* the same result.*/bindService(new Intent(this,RemoteService.class),connection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);}private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {@Overridepublic void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {//绑定成功}@Overridepublic void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {//当RemoteService所处进程被干掉就重新启动startService(new Intent(LocalService.this,RemoteService.class));bindService(new Intent(LocalService.this,RemoteService.class),connection,Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);}};private class LocalBinder extends Binder {}
}
对LocalService在清单文件中进行注册
<service android:name=".LocalService" />
创建RemoteService.java继承自Service(android.app.Service):↓
public class RemoteService extends Service {public RemoteService() {}@Overridepublic IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {return new RemoteBinder();}@Overridepublic int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {/*第一个参数Intent第二个参数ServiceConnection第三个参数介绍:/*** Flag for {@link #bindService}: automatically create the service as long* as the binding exists. Note that while this will create the service,* its {@link android.app.Service#onStartCommand}* method will still only be called due to an* explicit call to {@link #startService}. Even without that, though,* this still provides you with access to the service object while the* service is created.** <p>Note that prior to {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH},* not supplying this flag would also impact how important the system* consider's the target service's process to be. When set, the only way* for it to be raised was by binding from a service in which case it will* only be important when that activity is in the foreground. Now to* achieve this behavior you must explicitly supply the new flag* {@link #BIND_ADJUST_WITH_ACTIVITY}. For compatibility, old applications* that don't specify {@link #BIND_AUTO_CREATE} will automatically have* the flags {@link #BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY} and* {@link #BIND_ADJUST_WITH_ACTIVITY} set for them in order to achieve* the same result.*/bindService(new Intent(this,RemoteService.class),connection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);}private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {@Overridepublic void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {//绑定成功}@Overridepublic void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {//当RemoteService所处进程被干掉就重新启动startService(new Intent(RemoteService.this,LocalService.class));bindService(new Intent(RemoteService.this,LocalService.class),connection,Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);}};private class RemoteBinder extends Binder{}
}对RemoteService 在清单文件中进行注册,再制定一个进程名字,好区分
<serviceandroid:name=".RemoteService"android:enabled="true"android:exported="true"android:process=":remote" /><!--android:process=":remote"指定进程名-->
最后在MainActivity启动其中一个服务LocalService:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//双进程拉活(Java层)startService(new Intent(this,LocalService.class));}
}
这样就完成了双进程拉活
这篇关于Android安卓进程保活(三)双进程拉活(Java层)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





